Overview
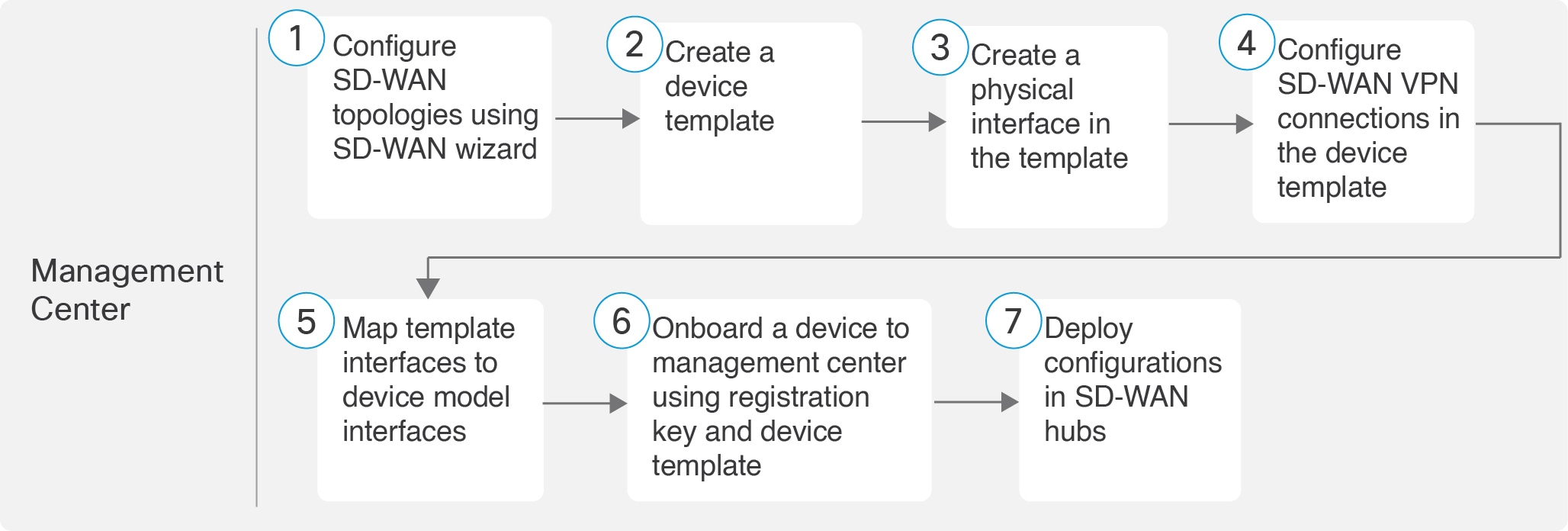
Illustrates the end-to-end workflow to configure a dual ISP SD‑WAN branch office using registration keys and device templates in Firewall Management Center (FMC).
The following flowchart illustrates the workflow for setting up an SD-WAN branch office with dual ISPs using registration key and device templates.
| Step |
Task |
More Information |
|---|---|---|
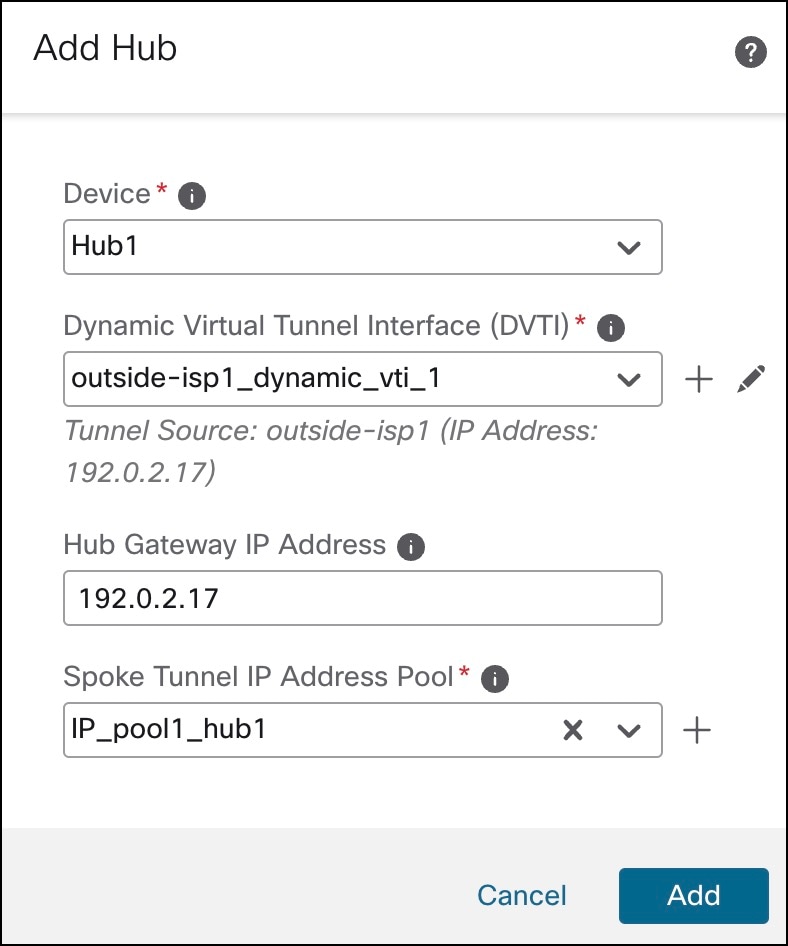
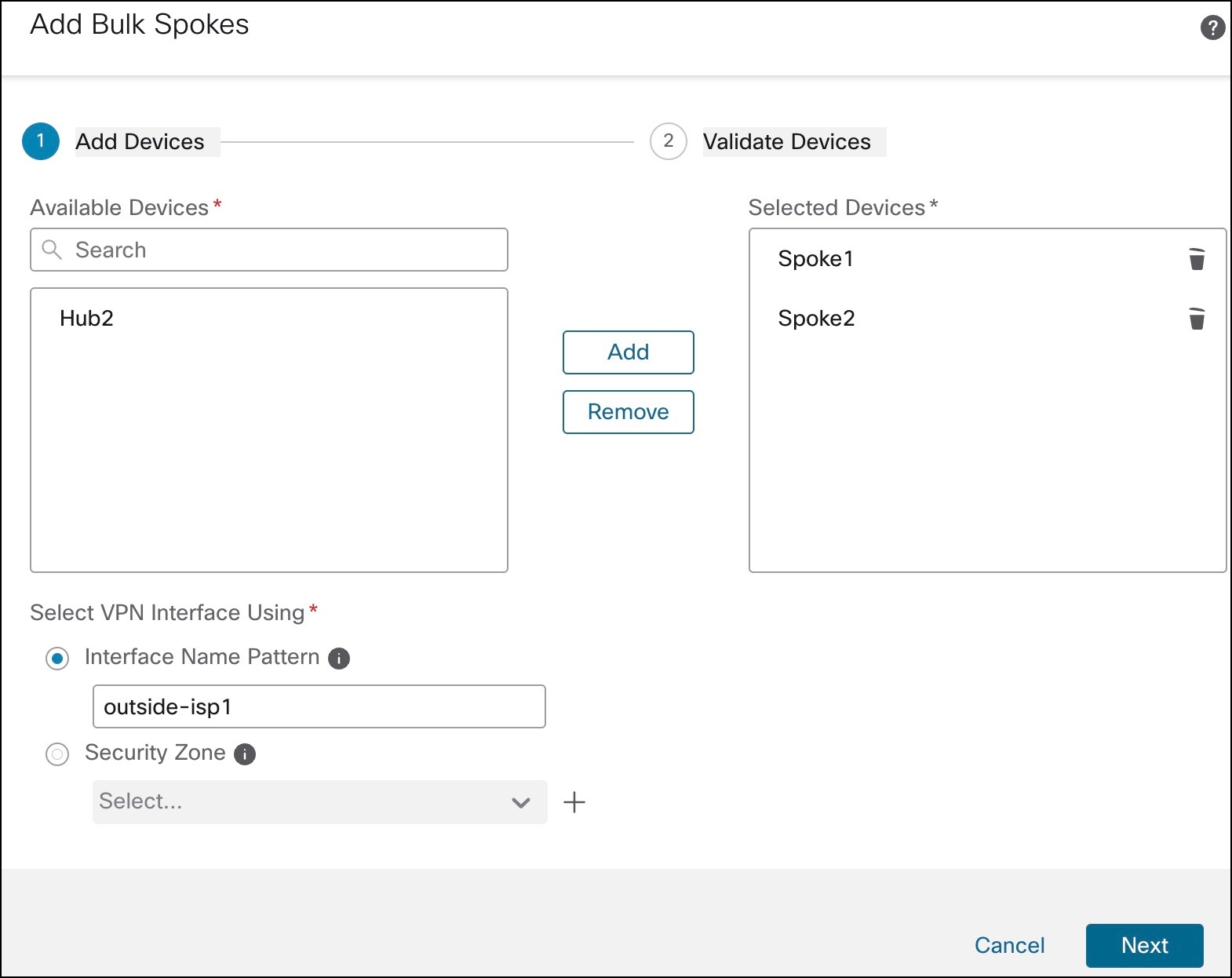
| Configure SD-WAN topologies using SD-WAN wizard |
||
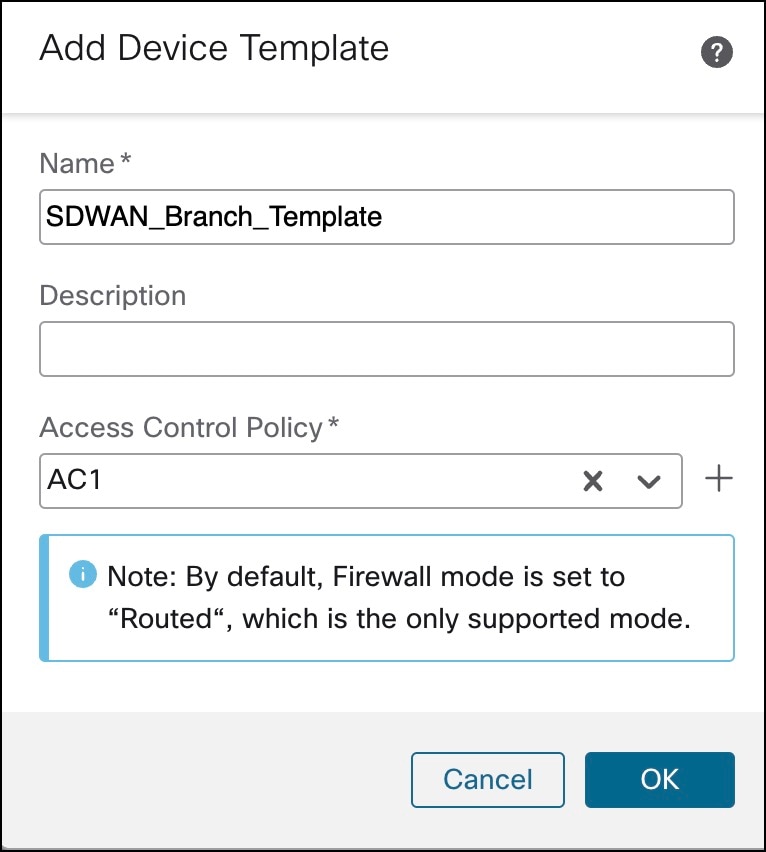
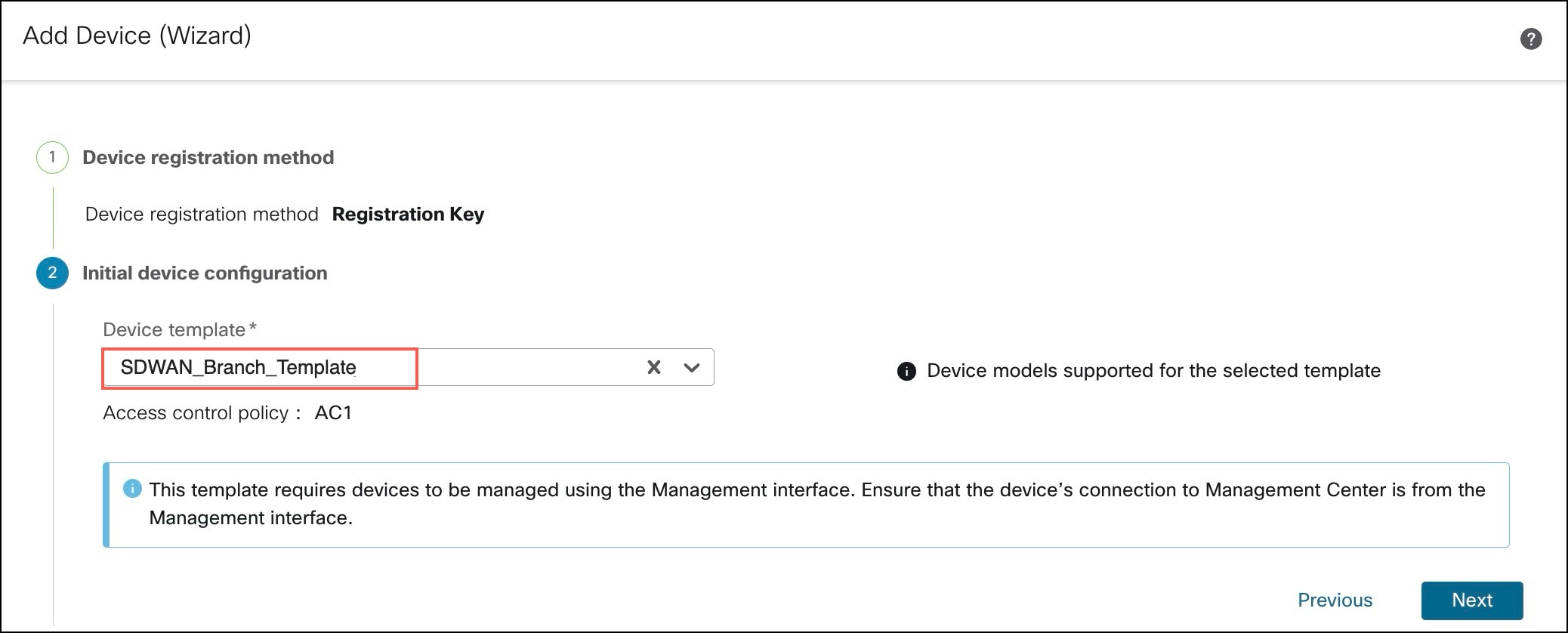
| Create a device template |
||
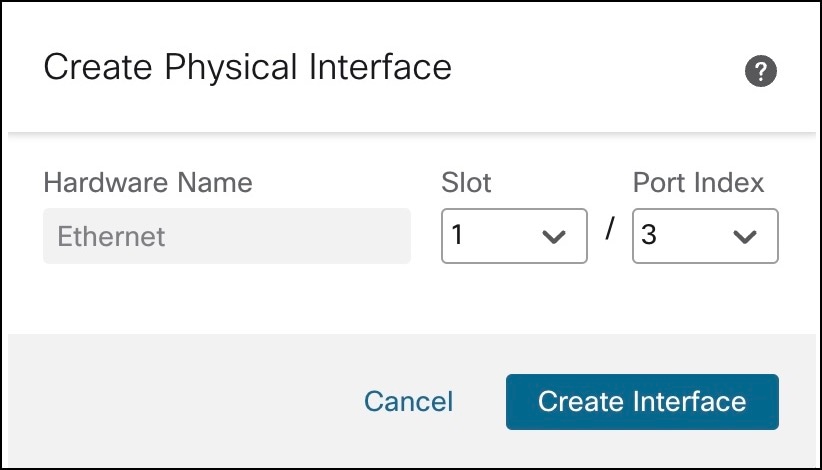
| Create a physical interface in the template. |
||
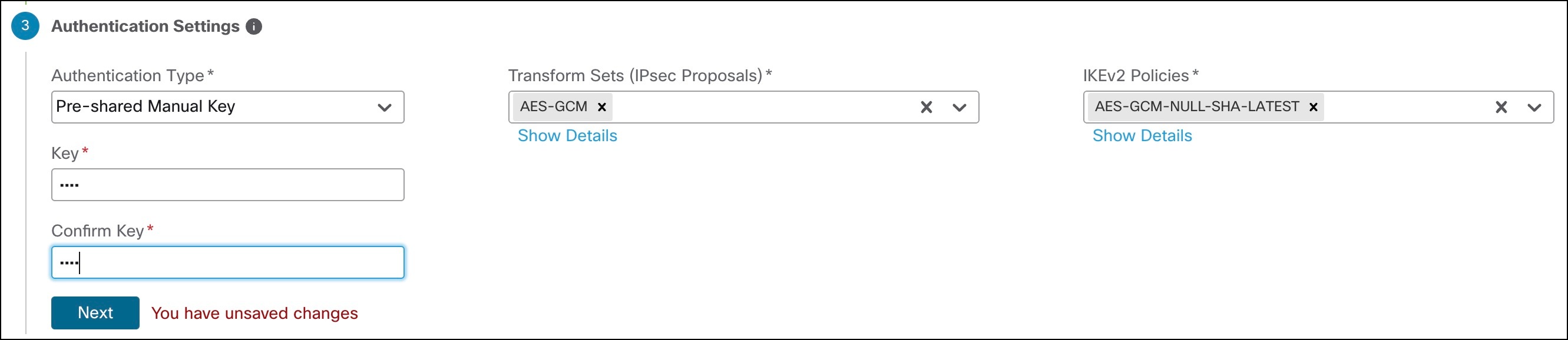
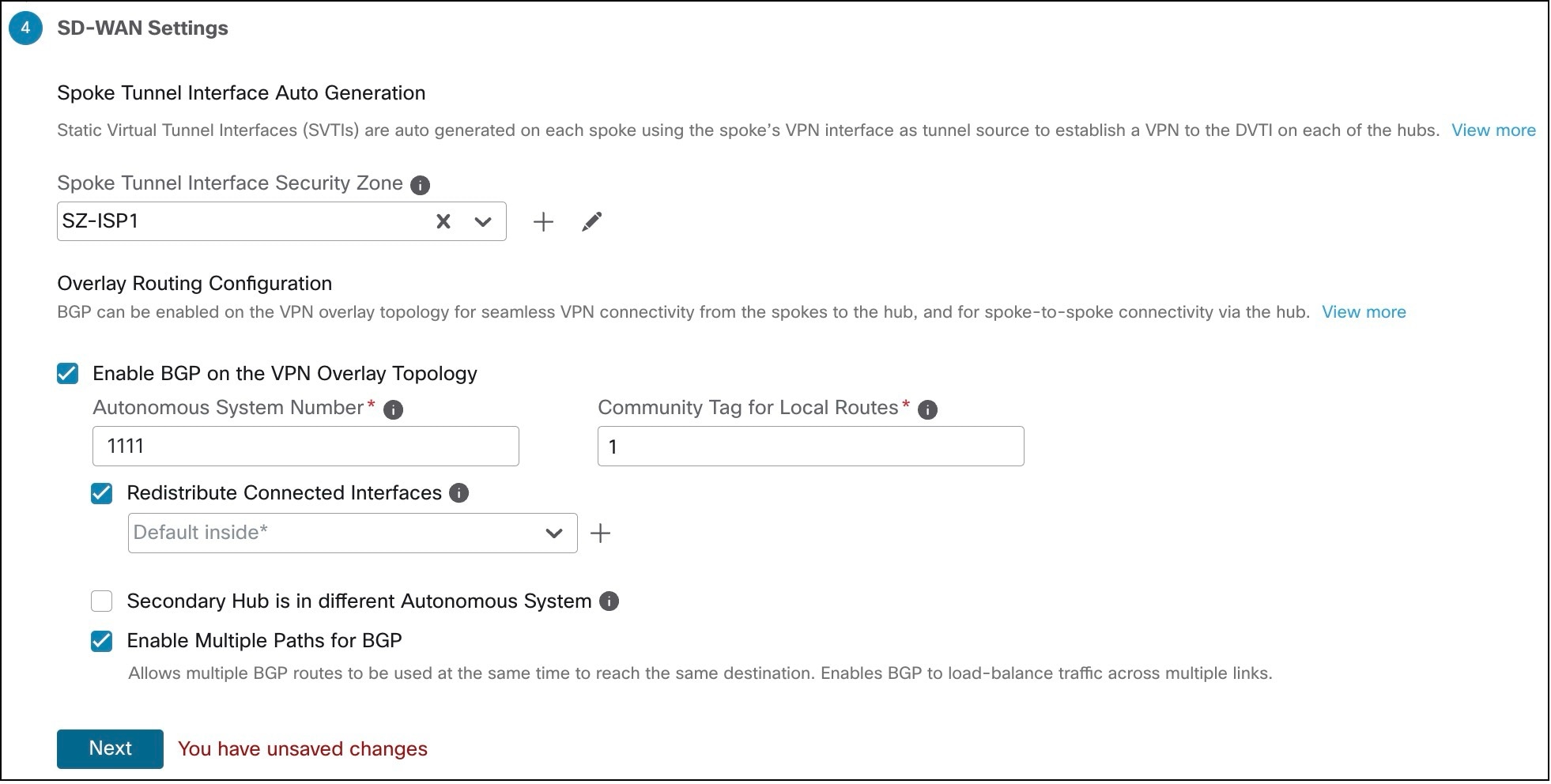
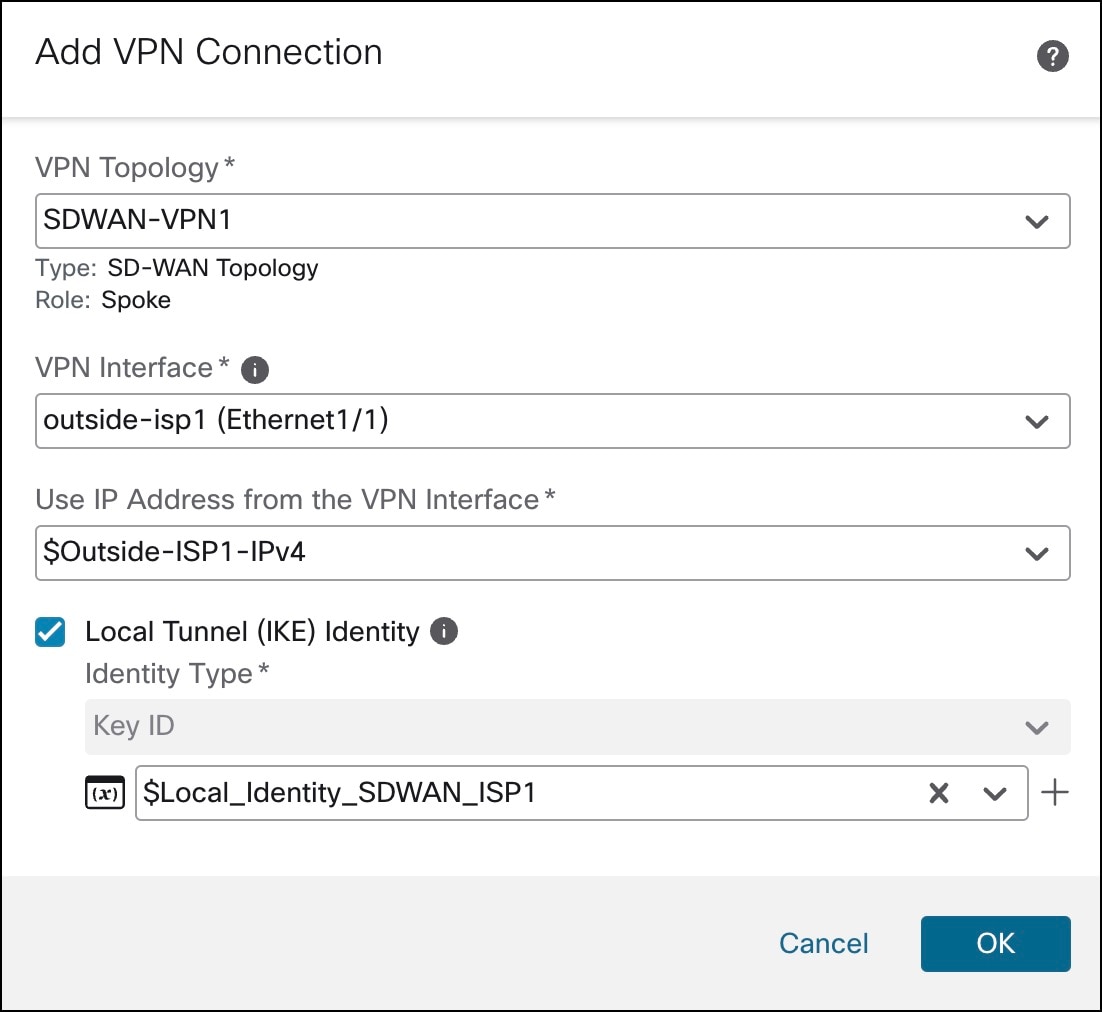
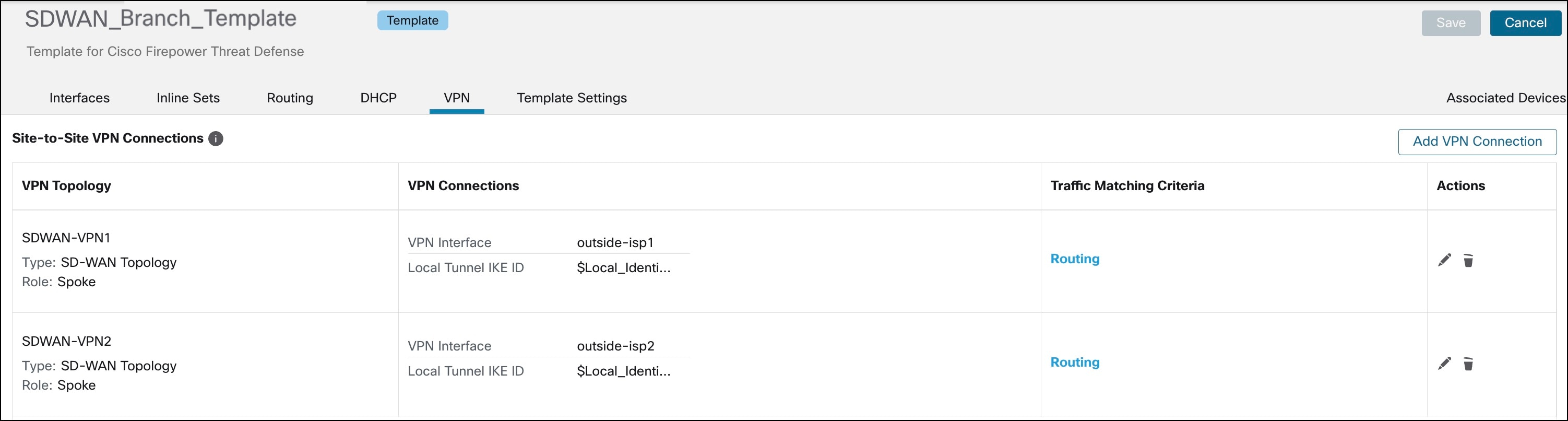
| Configure SD-WAN VPN connections in the device template. |
||
|
|
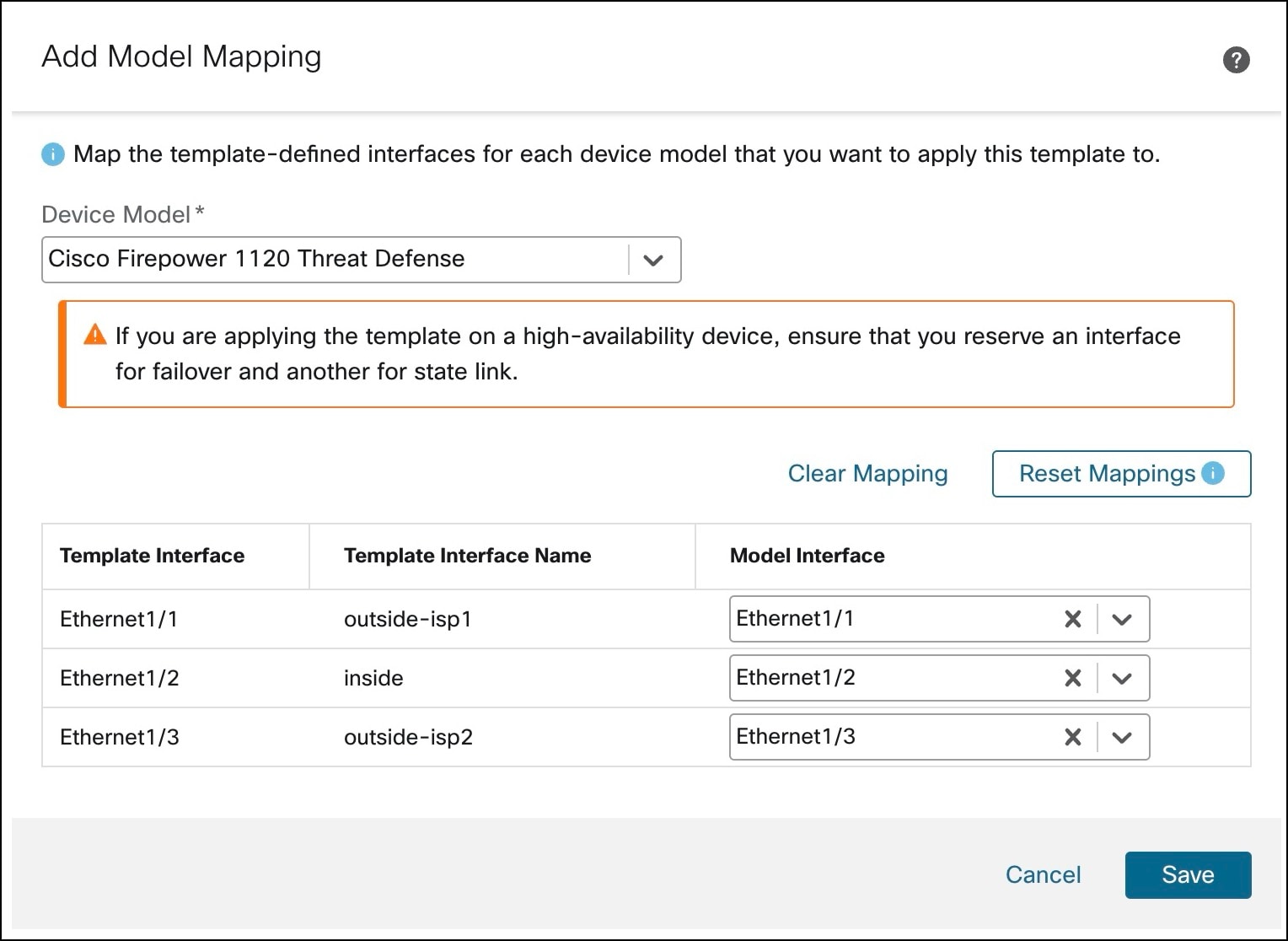
Map template interfaces to device model interfaces. |
|
|
|
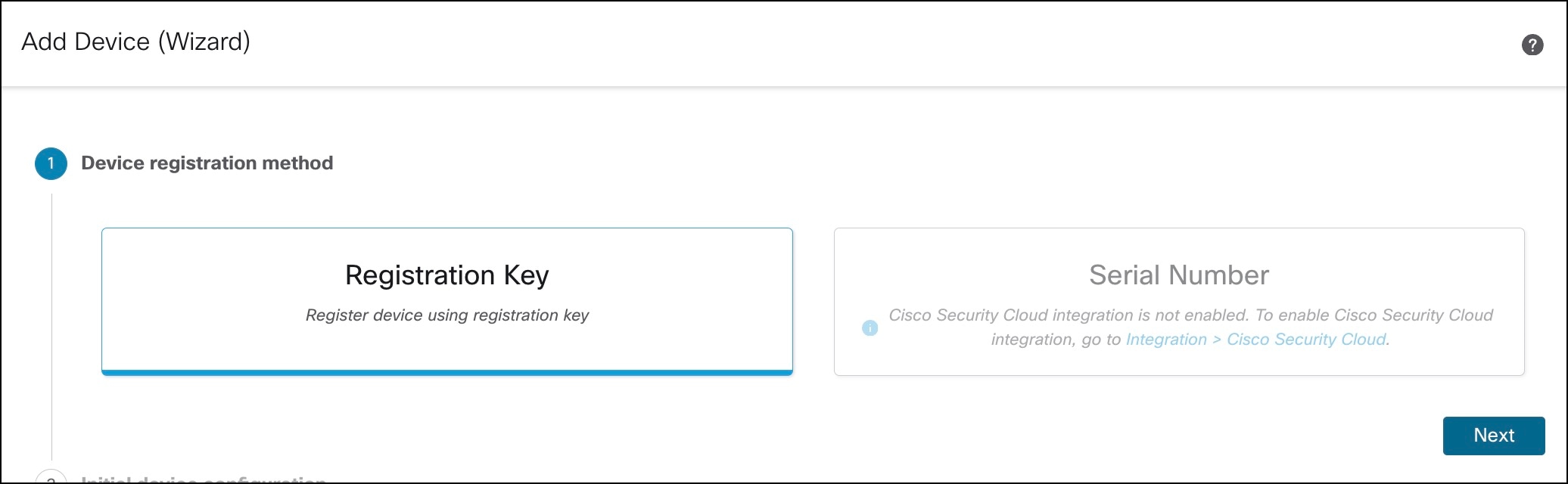
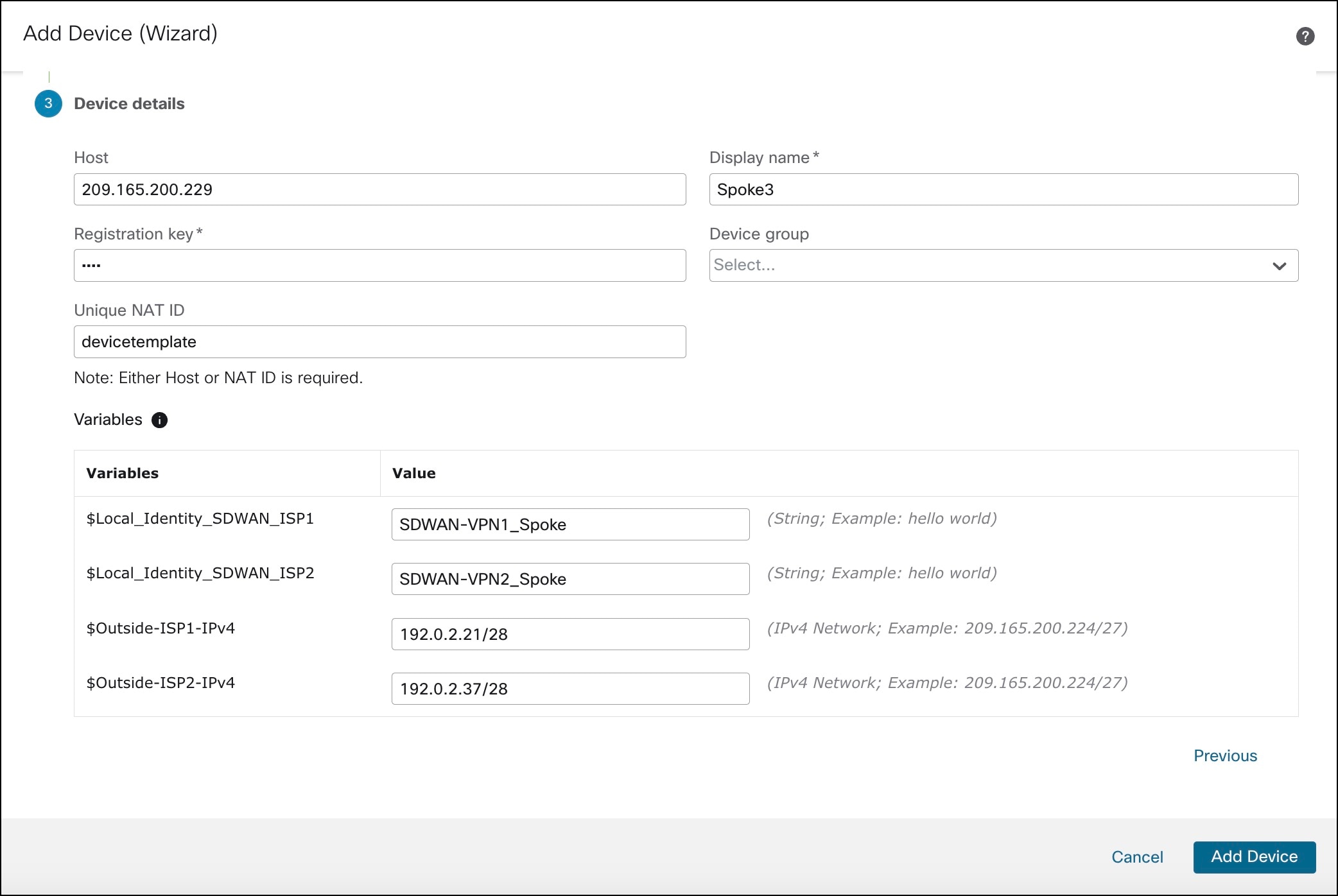
Onboard a device to management center using registration key and device template. |
Onboard a Device to Management Center Using a Registration Key and Device Template |
|
|
Deploy configurations in SD-WAN hubs. |
- |