Overview
Explains a scenario where Direct Internet Access (DIA) with policy-based routing (PBR) improves performance and lowers latency by routing traffic directly to the internet.
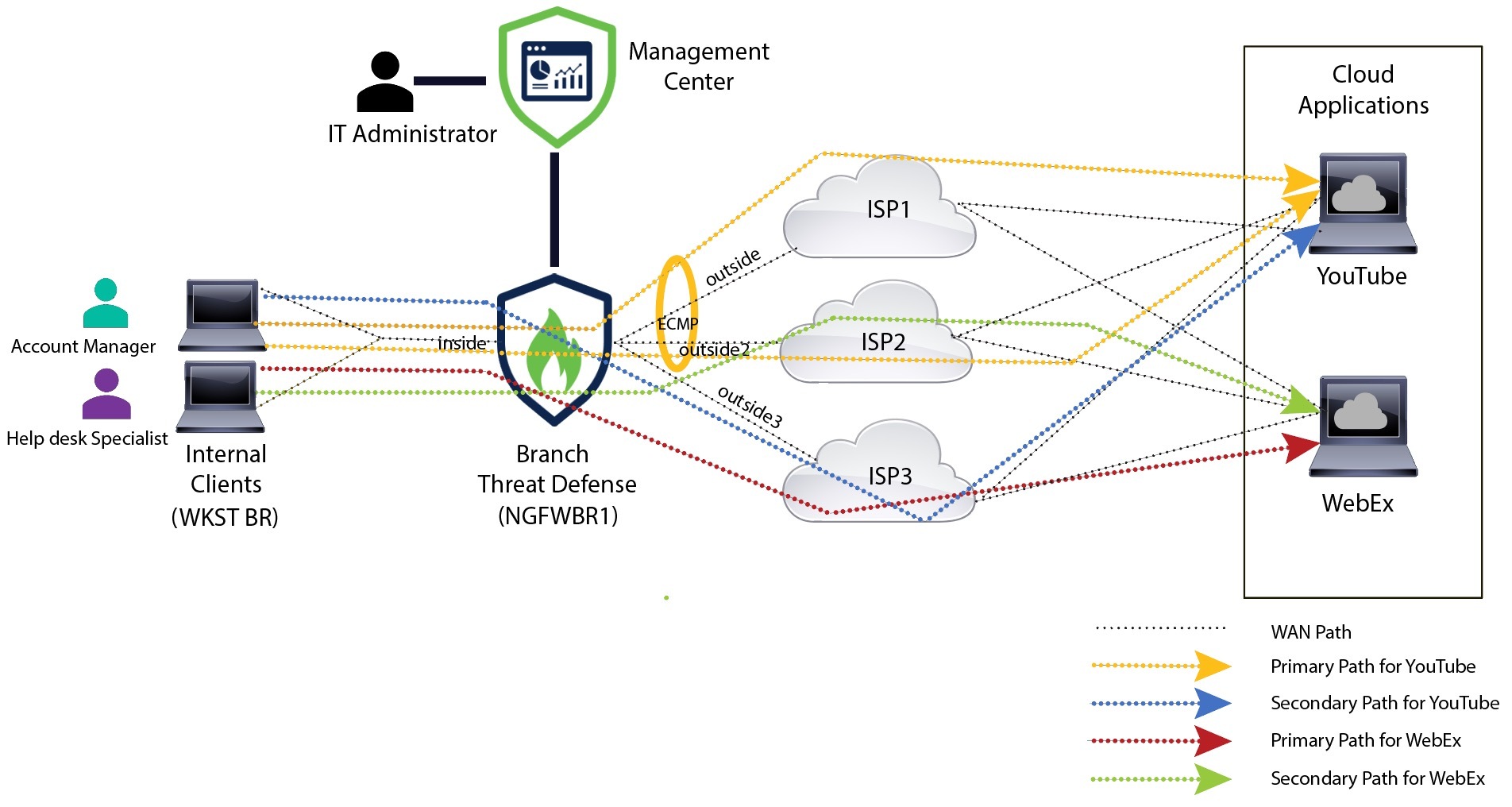
Bob is an account manager and Ann is a help desk specialist. Both work at a branch office of a large corporation. Recently, they have been experiencing latency issues while using web conferencing tools like Webex and streaming platforms like YouTube.
What is at risk?
Network latency and network congestion results in reduced performance and user experience of web conferencing and streaming sessions. This may impact the productivity and efficiency of employees at the branch office, potentially leading to a negative impact on the overall business operations.
How does DIA with PBR solve the problem?
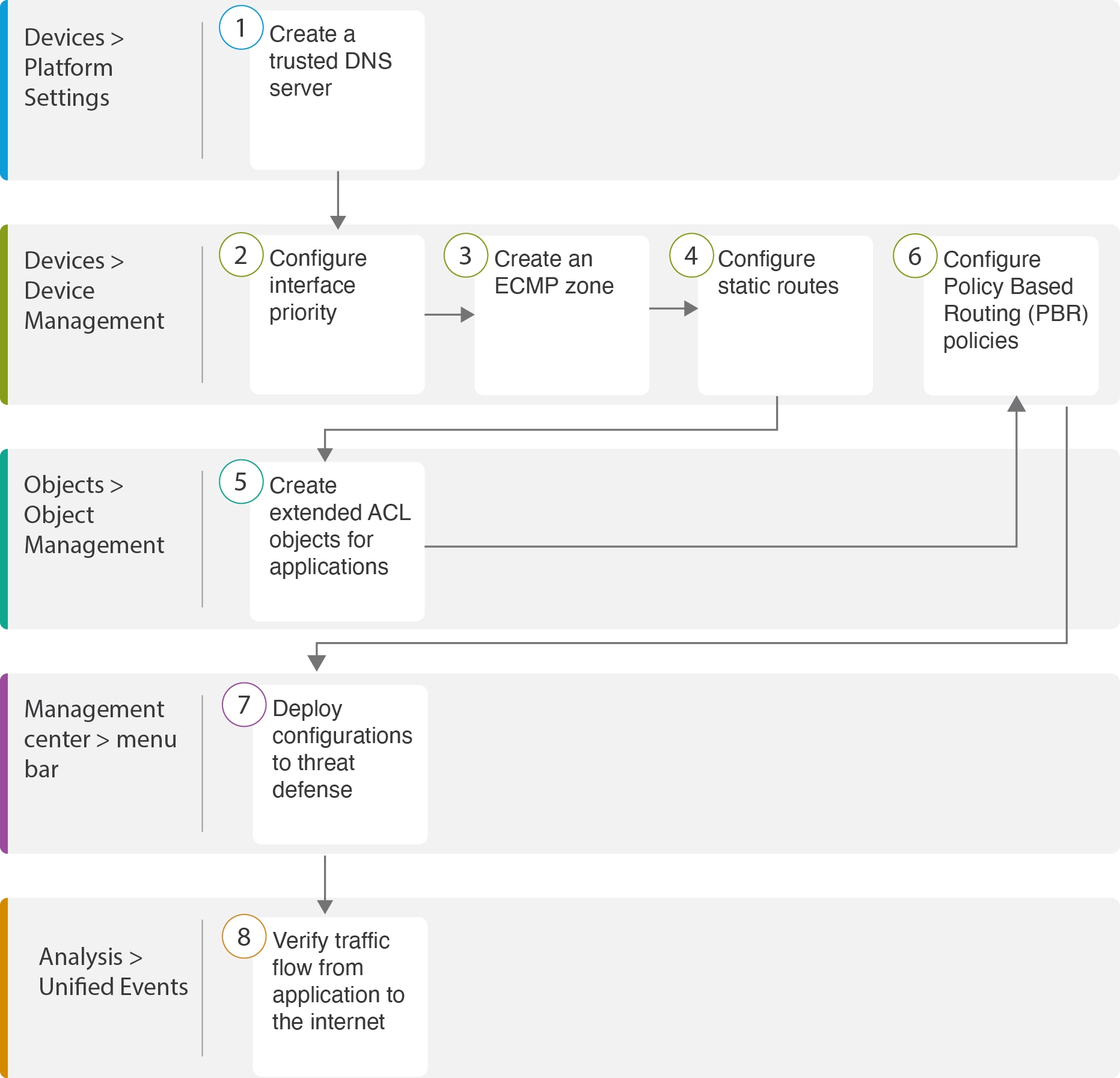
Alice, the IT administrator, used policy based routing in conjunction with DIA to reduce latency in the network.
Direct Internet Access allowed branch offices to access the internet directly, without routing traffic through a central site or data center. This reduced latency by providing a more direct and optimized internet connection for branch users.
Policy based routing separated Webex and YouTube traffic on different egress interfaces. This ensured that the traffic was directed through different paths, reducing the burden on a single interface and improving application performance.