About the Dynamic Attributes Connector
The dynamic attributes connector enables your access control and DNS policy to adapt in real time to the changes in public and private cloud workloads and business-critical software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications. It simplifies policy management by keeping rules up to date without tedious manual updates and policy deployment. Customers require policy rules to be defined based on non-network constructs such as VM name or security group, so that firewall policy is persistent even when the IP address or VLAN changes.
Supported connectors
We currently support:
|
CSDAC version |
AWS |
AWS Security Groups |
AWS Service Tags |
Azure |
Azure Service Tags |
Cisco APIC |
Cisco Cyber Vision |
Cisco Multicl. Defense |
Generic text |
GitHub |
Google Cloud |
Microsoft Office 365 |
Tenable |
vCenter |
Webex |
Zoom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Version 1.1 (on-premises) |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Version 2.0 (on-premises) |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Version 2.2 (on-premises) |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Version 2.3 (on-premises) |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Version 3.0 (on-premises) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Version 3.1 (on-premises) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Cloud-delivered (Cisco Security Cloud Control) |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
Secure Firewall Management Center 7.4.1 |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Secure Firewall Management Center 7.6 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Secure Firewall Management Center 7.7 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Secure Firewall Management Center 10.0.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
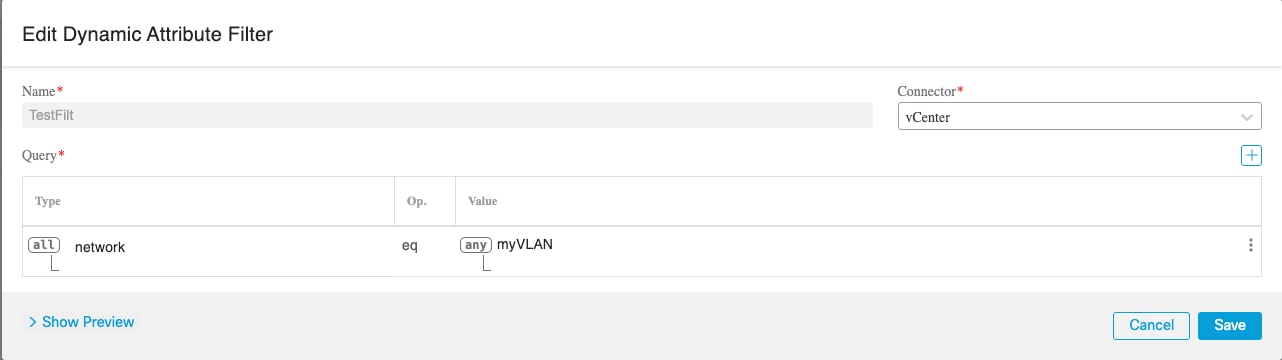
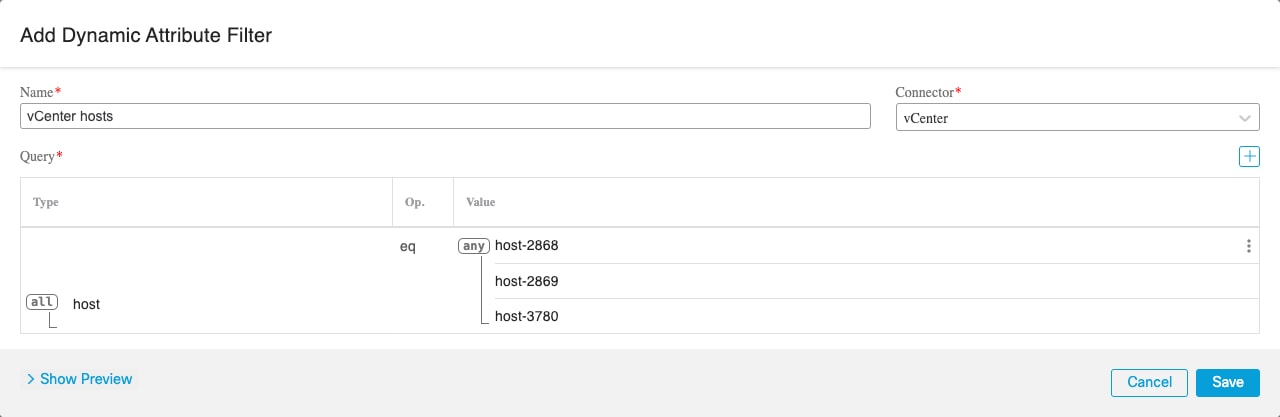
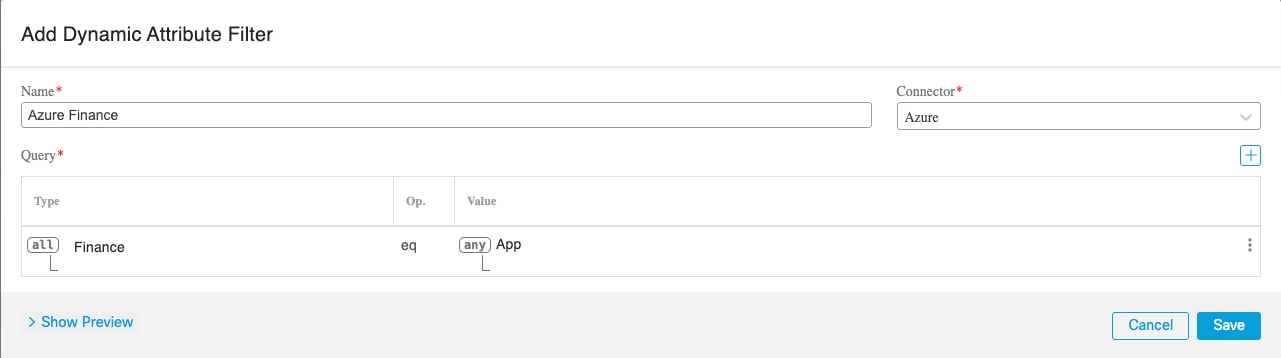
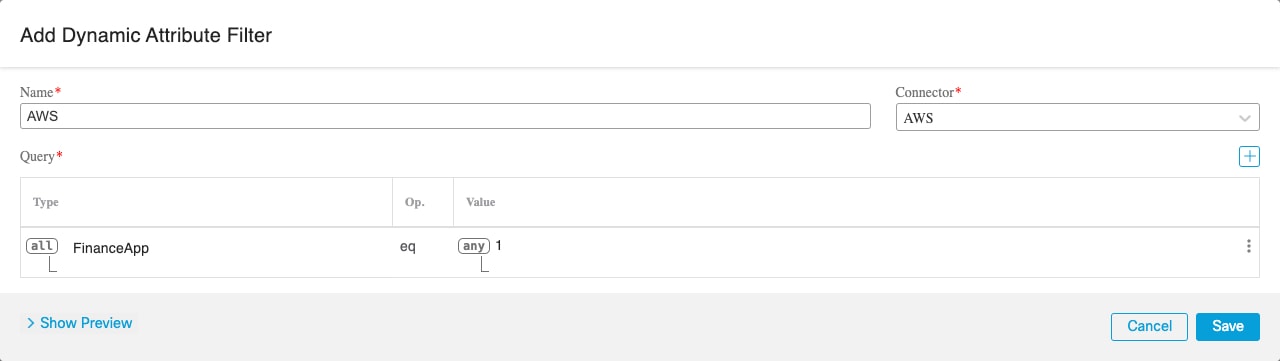
How it works
This topic discusses the architecture of the Dynamic Attributes Connector.
The following figure shows how the system functions at a high level.

-
The system supports certain public cloud providers.
This topic discusses supported connectors (which are the connections to those providers).
-
The dynamic attributes connector is provided with Secure Firewall Management Center.
Related Topics
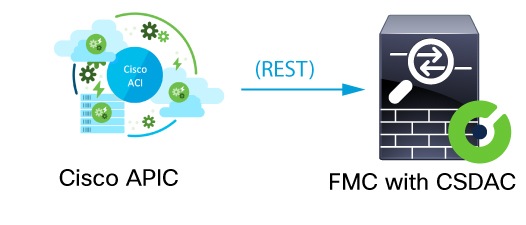
About the Cisco APIC integration with the Secure Firewall Management Center
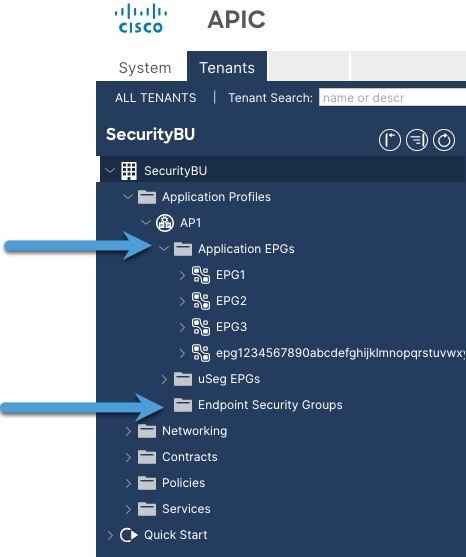
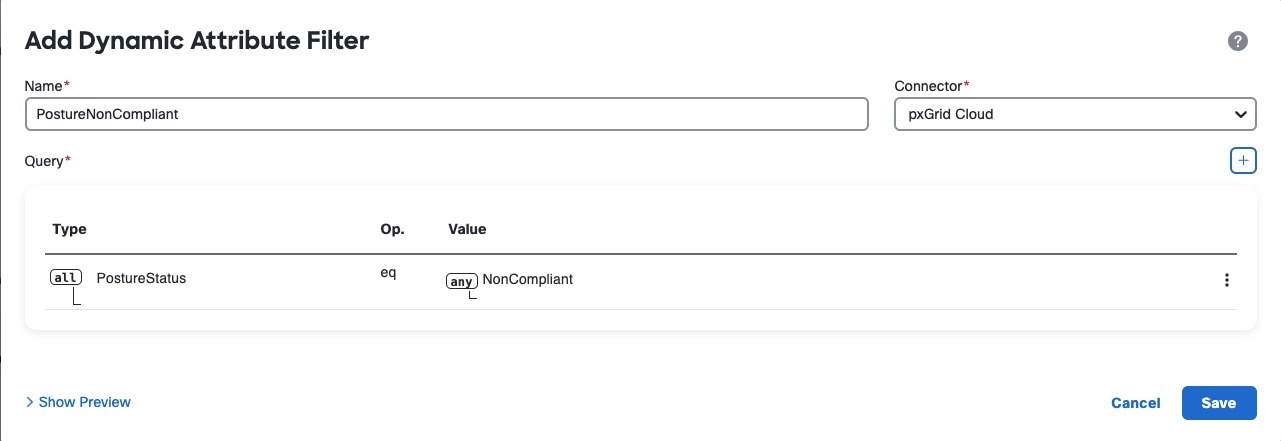
The dynamic attributes connector enables you to send Cisco APIC dynamic endpoint group (EPG) and endpoint security group (ESG) data from Cisco APIC tenants to the Secure Firewall Management Center.
Cisco APIC defines endpoint groups (EPGs) and endpoint security groups (ESGs) that have network object groups. Create a connector in the dynamic attributes connector that pulls that data from Cisco APIC tenants to the Secure Firewall Management Center on which you can use those objects in access control rules.
The following figure shows how the integration works.
Sample configuration
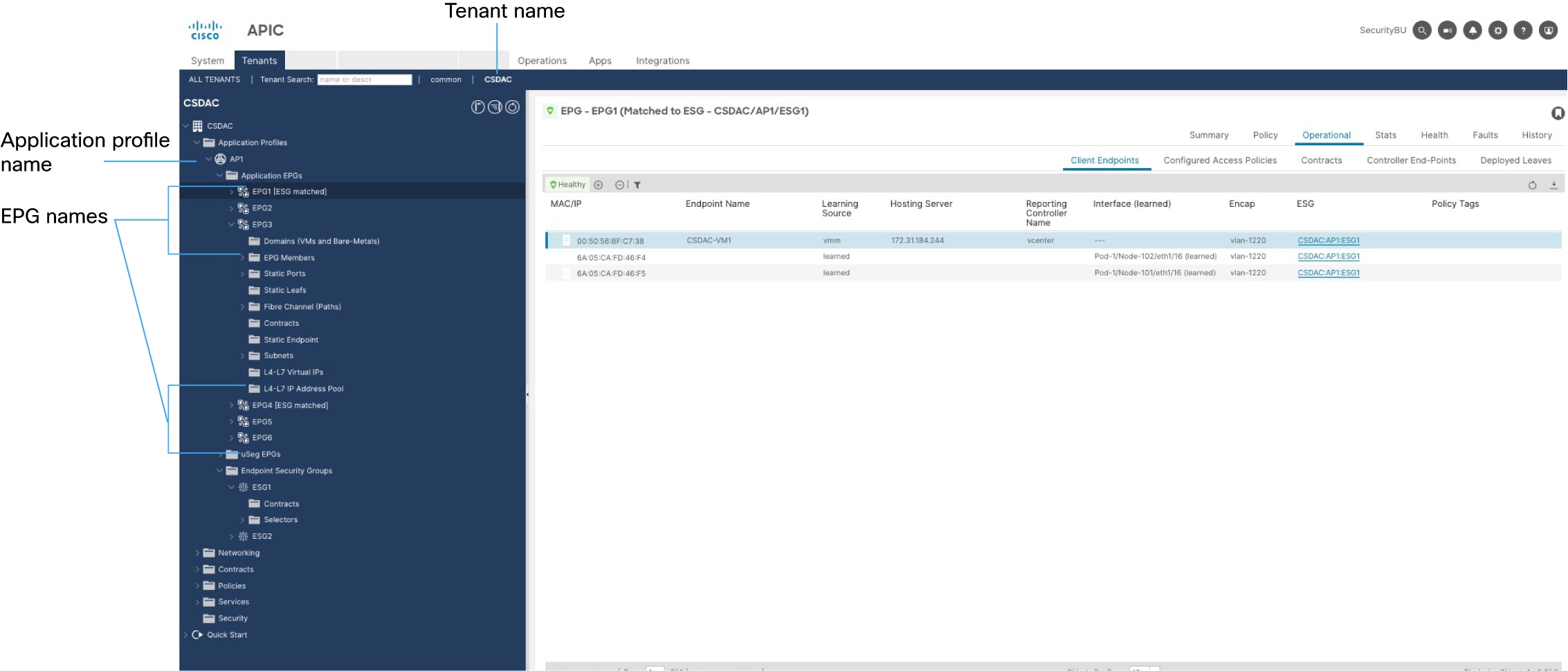
The following sample configuration shows how network object groups are named in the Secure Firewall Management Center based on names in APIC and the APIC connector (not shown).
Network object group names are a concatenation of (in order):
-
Cisco ACI Endpoint Update App Site Prefix value
Cisco APIC tenant name); in this example,
CSDAC. -
Cisco APIC application profile name (in this example,
AP1) -
Cisco APIC EPG name (in this example,
EPG1throughEPG4)

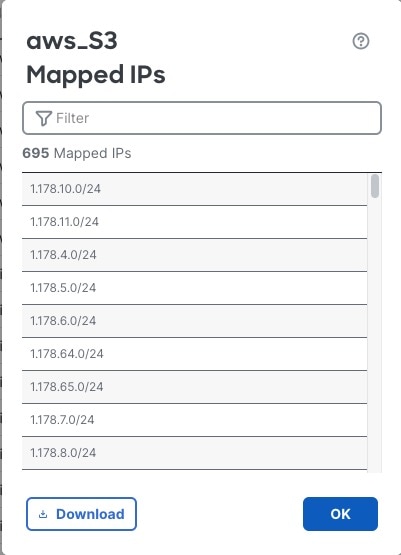
The following figure shows sample Cisco APIC dynamic object names used in an access control rule.
Dynamic objects created by the integration with Cisco APIC have names matching the pattern:
APIC-site-name_tenant-name_application-profile-name_EPG-or-ESG-name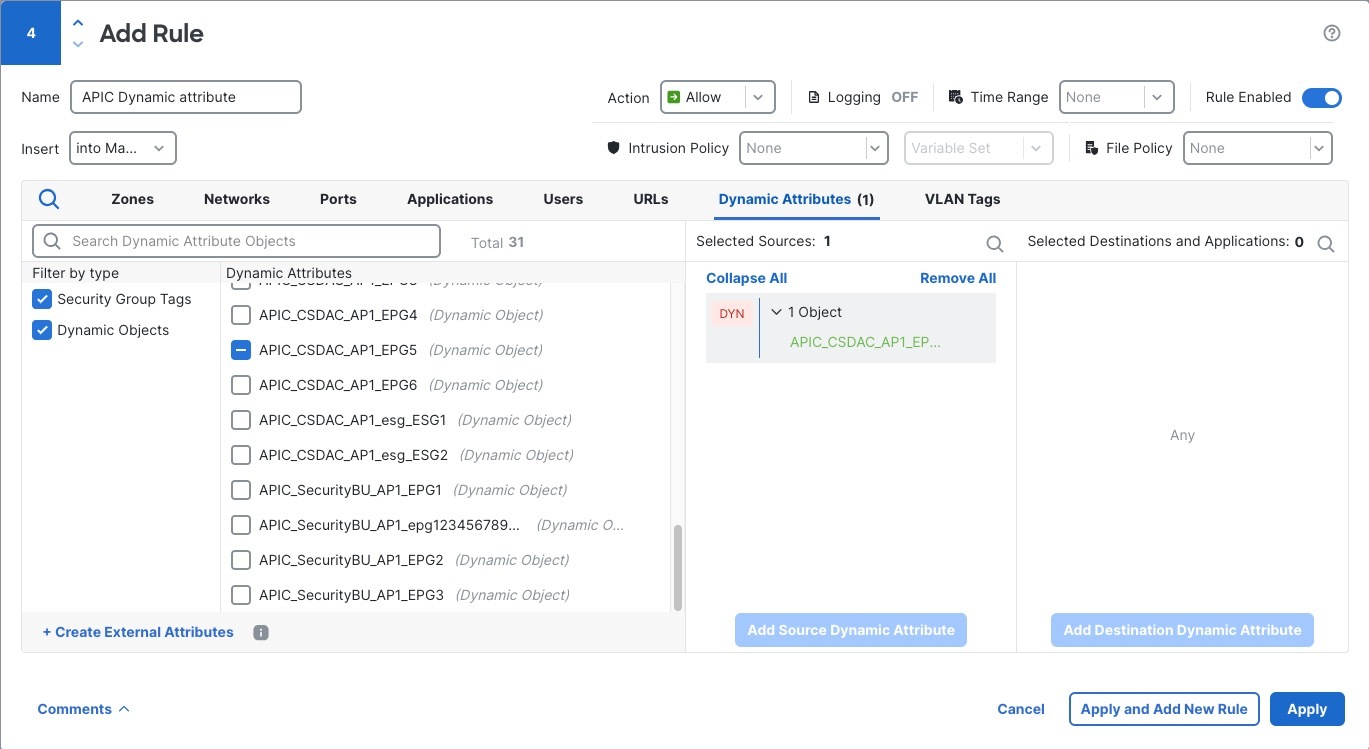
More information
-
For more information about the dynamic attributes connector in the Secure Firewall Management Center, see Secure Firewall Management Center Device Configuration Guide.
History for the dynamic attributes connector
|
Feature |
Minimum Firewall Management Center |
Minimum Firewall Threat Defense |
Details |
|---|---|---|---|
|
DNS rule support for dynamic objects and security group tags. |
10.0.0 |
10.0.0 |
You can configure DNS rules in the DNS policy to use dynamic objects or security group tags (SGT). If you are using these types of objects in access control rules already, you can now extend their use to your DNS policy. We added the Dynamic Attributes tab to the add/edit DNS rule dialog box. |
|
Dynamic firewall |
10.0.0 |
10.0.0 |
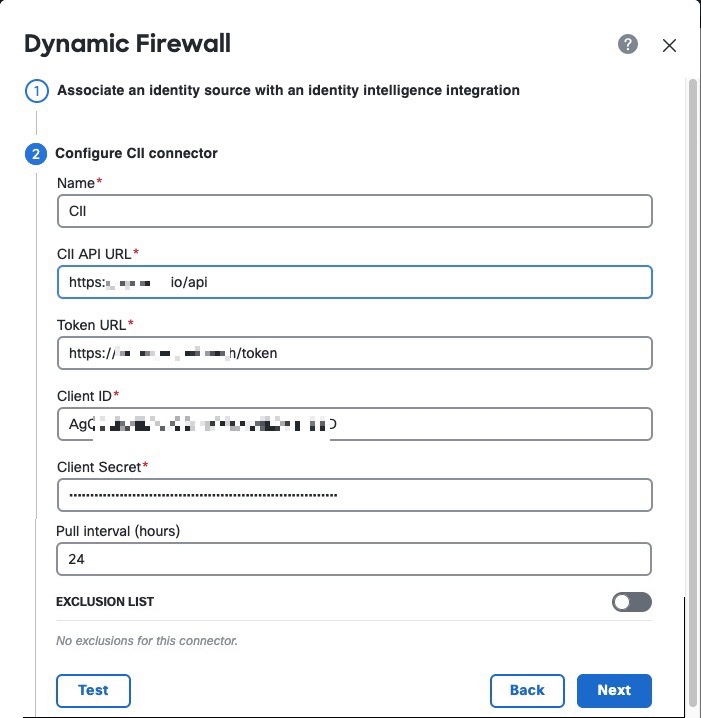
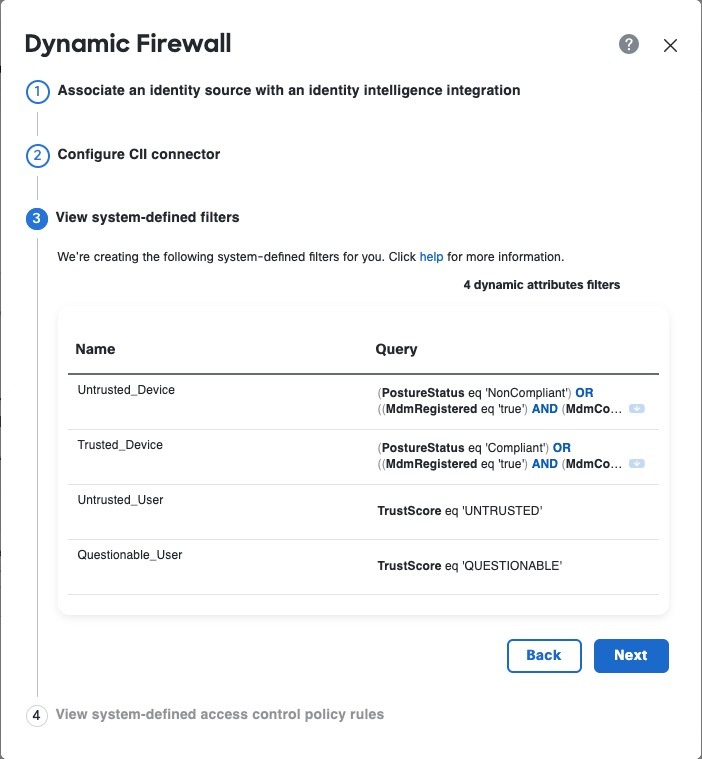
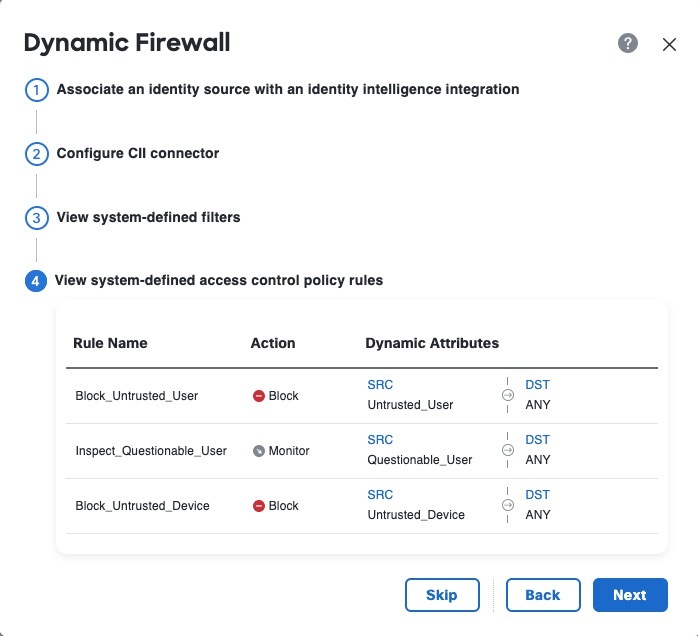
Previously, the Secure Firewall Management CenterSecure Firewall Management Center collected information about users exclusively from the configured identity source, such as Microsoft Active Directory, the passive identity agent, Cisco Identity Services Engine (Cisco ISE), and so on. This information generally included user name, group, and IP address. The dynamic firewall enables you to add user risk scores from Cisco Identity Intelligence to identity source-provided information so you can set policies based on always-current user posture and risk. We enable you to pair user identity with intelligence and use that information in reporting and access control policies. New/modified screens:
|
|
Cisco APIC connector |
10.0.0 |
10.0.0 |
The dynamic attributes connector enables you to send Cisco APIC dynamic endpoint group (EPG) and endpoint security group (ESG) data from Cisco APIC tenants to . New/updated screens: |
|
New connectors |
7.6 |
20241127 |
AWS security groups, AWS service tags, and Cisco Cyber Vision These connectors can send an on-premises Secure Firewall Management Center dynamic objects as can Cisco Security Cloud Control. To receive dynamic objects from an on-premises dynamic attributes connector, version 3.0 of the on-premises dynamic attributes connector is required. |
|
Dynamic Attributes Connector |
7.4.0 |
7.4.0 |
This feature is introduced. The Dynamic Attributes Connector is now included in the Secure Firewall Management Center. You can use the dynamic attributes connector to get IP addresses from cloud-based platforms such as Microsoft Azure in access control rules without having to deploy to managed devices. More information:
New/modified screen: |

 to create a new one.
to create a new one.
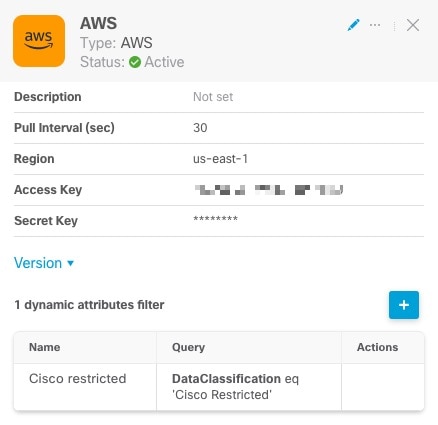
 )
) )
) to close the panel.
to close the panel.
 )
)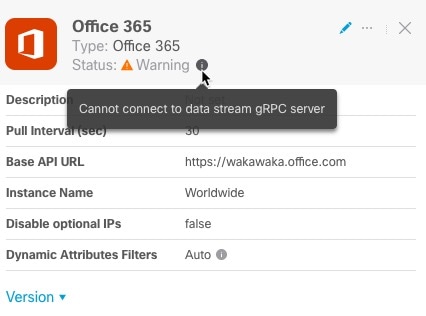
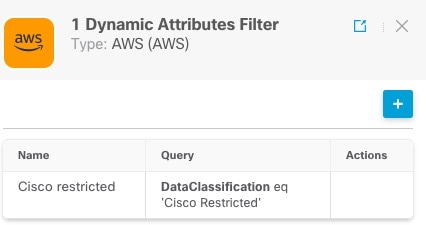
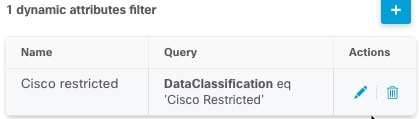
 in the filters column (
in the filters column (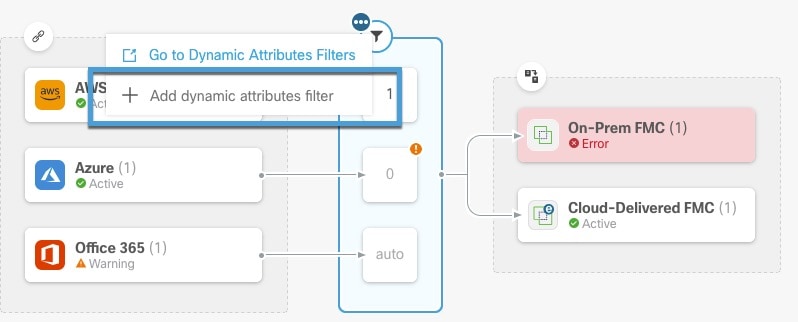
 to add, edit, or delete filters.
to add, edit, or delete filters.
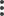 )
)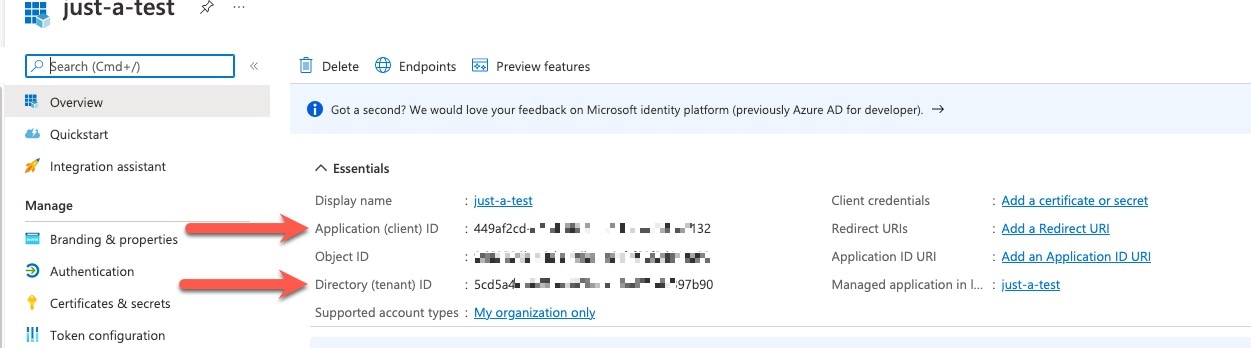
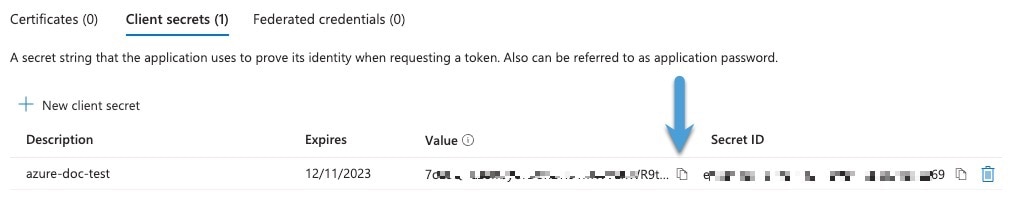


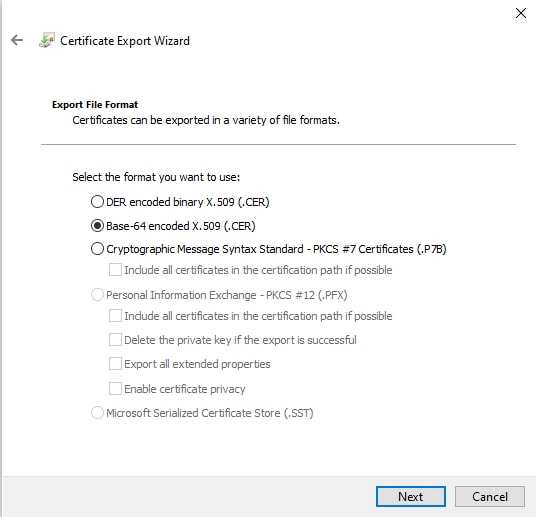
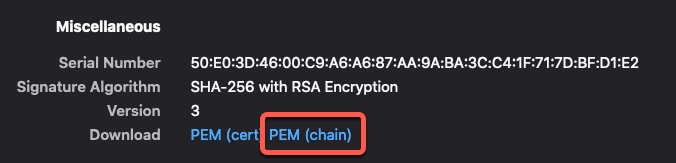
 to copy the token to the clipboard.
to copy the token to the clipboard.
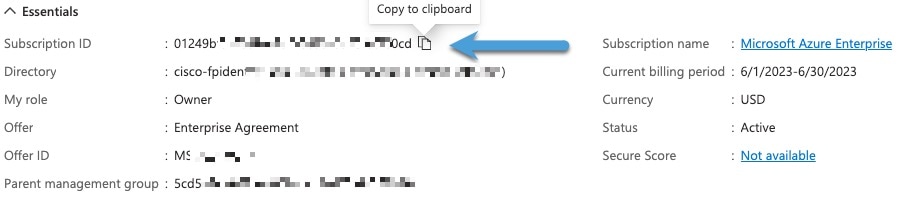
 ).
).




 )
)







 Feedback
Feedback