- Preface
- Product Overview
- Configuring the Router for the First Time
- Configuring a Supervisor Engine 720
- Configuring a Route Switch Processor 720
- Configuring NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- ISSU and eFSU on Cisco 7600 Series Routers
- Configuring RPR and RPR+ Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- Configuring Interfaces
- Configuring a Supervisor Engine 32
- Configuring LAN Ports for Layer 2 Switching
- Configuring Flex Links
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring VTP
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring Private VLANs
- Configuring Cisco IP Phone Support
- Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
- Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
- Configuring L2TPv3
- Configuring STP and MST
- Configuring Optional STP Features
- Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring GTP-SLB IPV6 Support
- IP Subscriber Awareness over Ethernet
- Configuring UDE and UDLR
- Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching on the PFC
- Configuring IPv4 Multicast VPN Support
- Configuring Multicast VPN Extranet Support
- Configuring IP Unicast Layer 3 Switching
- Configuring IPv6 Multicast PFC3 and DFC3 Layer 3 Switching
- Configuring IPv4 Multicast Layer 3 Switching
- Configuring MLDv2 Snooping for IPv6 Multicast Traffic
- Configuring IGMP Snooping for IPv4 Multicast Traffic
- Configuring PIM Snooping
- Configuring Network Security
- Understanding Cisco IOS ACL Support
- Configuring VRF aware 6RD Tunnels
- Configuring VLAN ACLs
- Private Hosts (Using PACLs)
- Configuring IPv6 PACL
- IPv6 First-Hop Security Features
- Configuring Online Diagnostics
- Configuring Denial of Service Protection
- Configuring DHCP Snooping
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring Traffic Storm Control
- Unknown Unicast Flood Blocking
- Configuring PFC QoS
- Configuring PFC QoS Statistics Data Export
- Configuring MPLS QoS on the PFC
- Configuring LSM MLDP based MVPN Support
- Configuring IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1ad
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring NetFlow and NDE
- Configuring Local SPAN, RSPAN, and ERSPAN
- Configuring SNMP IfIndex Persistence
- Power Management and Environmental Monitoring
- Configuring Web Cache Services Using WCCP
- Using the Top N Utility
- Using the Layer 2 Traceroute Utility
- Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding and Detection over Switched Virtual Interface
- Configuring Call Home
- Configuring IPv6 Policy Based Routing
- Using the Mini Protocol Analyzer
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Synchronous Ethernet
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring BGP PIC Edge and Core for IP and MPLS
- Configuring VRF aware IPv6 tunnels over IPv4 transport
- ISIS IPv4 Loop Free Alternate Fast Reroute (LFA FRR)
- Multicast Service Reflection
- Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
- Online Diagnostic Tests
- Acronyms
- Cisco IOS Release 15S Software Images
- Index
Configuring VRF aware 6RD Tunnels
This chapter describes how to configure VRF aware 6RD tunnels on Cisco 7600 series routers. Following are the sections:
Understanding VRF aware 6RD Tunnels
Currently the 6RD tunneling feature on c7600 does not support virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) awareness. The forwarding table lookups for IPv6 overlay addresses and IPv4 transport addresses are performed in global routing tables. This feature extends the 6RD tunneling support for IPv6 overlay addresses and IPv4 transport addresses in VRF.
These scenarios explain the VRF aware 6RD tunnel function:
- IPv6 overlay address in VRF and IPv4 transport address in Global routing table (RT).
- IPv6 overlay address in VRF and IPv4 transport address in VRF.
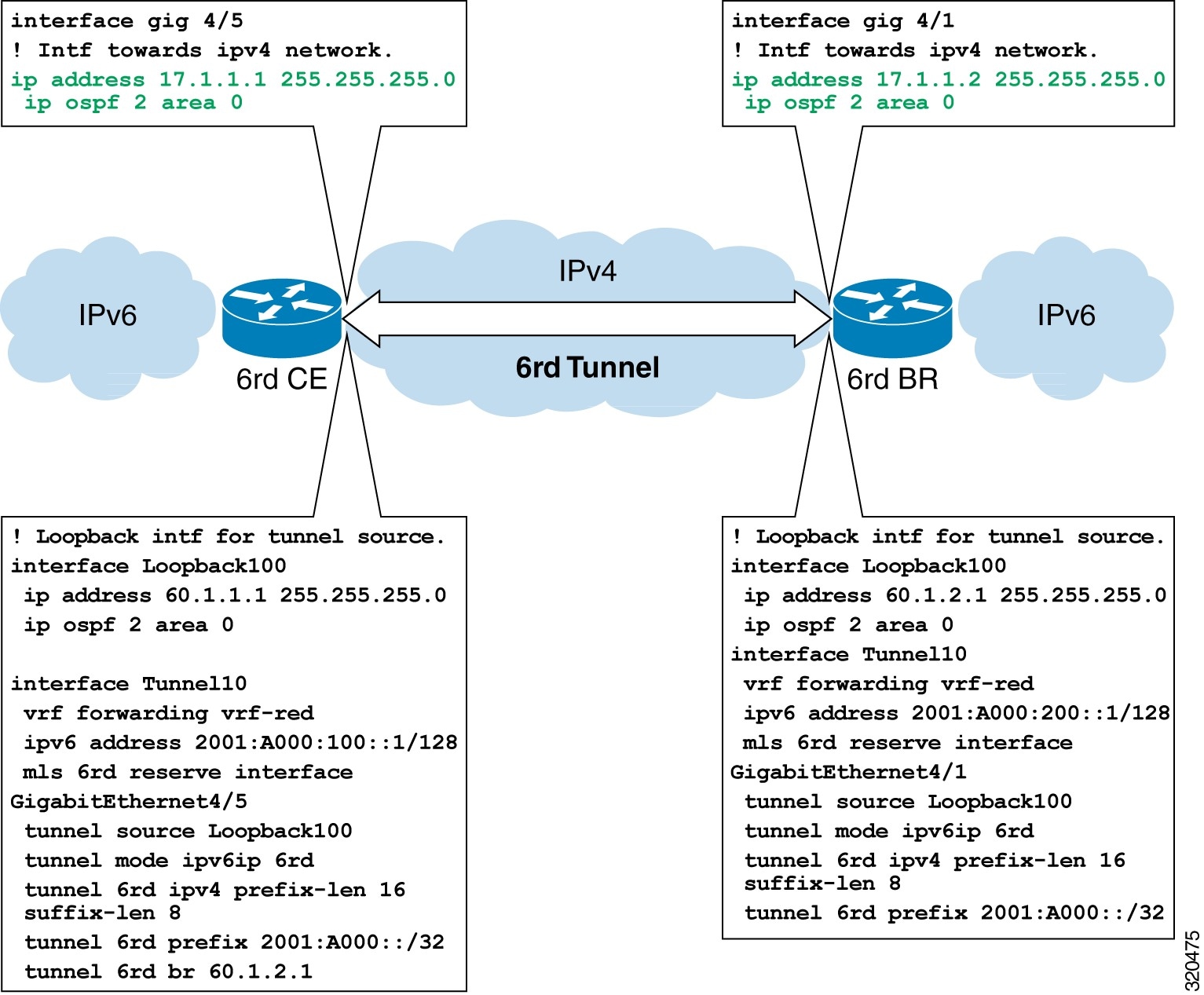
Figure 37-1 Topology for the IPv6 overlay address in VRF, and the IPv4 transport address in GRT.
The VRF Aware IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel should have an ES+ line card towards the tunnel facing side.
Restriction for VRF aware 6RD Tunnels
- Currently the c7600 supports only 256 VRF instances for IPv6.
- The incoming physical interface, and the tunnel interface should have the same VRF instance defined.
- The tunnel transport VRF and the egress physical interface, through which the traffic leaves should have the same VRF instance defined.
- For 6RD customer edge router configuration, the tunnel source and the border relay (BR) address should have the same VRF instance defined as the physical interface, through which the traffic flows.
Configuring VRF aware 6RD Tunnels
For information on VRF aware 6RD tunnels configuration, see:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/7600/install_config/ES40_config_guide/es40_chap13.html#wp1529332
 Feedback
Feedback