Web Filtering
The Web Filtering feature enables the user to provide controlled access to Internet websites by configuring the domain-based or URL-based policies and filters on the device. Domain-based Filtering enables the user to control access to websites/servers at domain level, and URL-based Filtering enables the user to control access to websites at URL level. This section includes the following topics:
Domain-based Filtering
Domain-based filtering allows the user to control access to a domain by permitting or denying access based on the domain-based policies and filters configured on the device. When the client sends a DNS request through the Cisco Cloud Services Router 1000V Series, the DNS traffic is inspected based on the domain-based policies (allowed list/blocked list). Domains that are on the allowed list or blocked list will not be subjected to URL-based filtering even if they are configured. Graylist traffic does not match both allowed list and blocked list, and it is subjected to URL-based filtering if it is configured.
Domain-based Filtering Using Allowed List Filter
To allow the complete domain (cisco.com) without subjecting to any filtering, use the allowed list option . When a user makes a request to access a website using a browser, the browser makes a DNS request to get the IP address of the website. Domain filtering applies the filter on the DNS traffic. If the website’s domain name matches to one of the allowed list patterns, domain filtering adds the website’s address to the allowed list. The browser receives the IP address for the website and sends the HTTP(s) request to the IP address of the website. Domain filtering treats this traffic as allowed traffic. This allowed traffic is not further subjected to URL-based filtering even if it is configured. If the Snort IPS is configured, the traffic will be subjected to Snort IPS .
Domain-based Filtering Using Blocked List Filter
When a user want to block a complete domain (badsite.com), use the blocked list option. Domain filtering applies the filter on the DNS traffic. If the website’s domain name matches to one of the patterns on the blocked list, domain filtering will send the configured blocked server’s IP address in the DNS response to the end user instead of the actual resolved IP address of the website. The browser receives the blocked server’s IP address as the IP address for the website and sends the HTTP(s) request to this IP address. This traffic is not further subjected to URL filtering or Snort IPS even if they are configured.The block server receives the HTTP(s) request and serves a block page to the end user. Also, when the DNS request matches a blocked list, all application traffic to that domain will be blocked.
Domain filtering is applied to all the DNS traffic even if the DNS requests are made in the context of non-HTTP(S) requests such as FTP, telnet, and so on. The blocked listed non-HTTP(S) traffic (FTP, telnet, and so on.) will also be forwarded to the block server. It is block server’s responsibility to serve a block page or deny the request. You can configure an internal or external block server. For configuration steps, see Configure Domain-based Web Filtering with an External Block Server and Configure Domain-based Web Filtering with a Local Block Server.
If the traffic is not part of the allowed list or on the blocked list during domain filtering, it will be subjected to URL filtering and Snort IPS if they are configured.
A user may consider using a combination of domain filtering allowed and blocked pattern lists to design the filters. For example, if a user wants to create an allowed list www\.foo\.combut also wants other domains on a blocked list, such as www\.foo\.abc and www\.foo\.xyz, configure the www\.foo\.com in the allowed list pattern and www\.foo\. in the blocked list pattern.
 Note |
If you are using the www prefix in the allowed or blocked regex pattern, it can create a problem if the Server Name Indicator (SNI) returned in the client message doesn't match. For example, if you want to allow www./foo./com and SNI returns as foo.com only. We recommend not to include the www in the regex match. |
URL-based Filtering
URL-based filtering allows a user to control access to Internet websites by permitting or denying access to specific websites based on the allowed list/blocked list, category, or reputation configuration. For example, when a client sends a HTTP/HTTP(s) request through the Cisco CSR 1000V Cloud Services Router, the HTTP/HTTP(s) traffic is inspected based on the URL filtering policies (Allowed list, Blocked list, Category, and Reputation). If the HTTP/HTTP(s) request matches the blocked list, the HTTP(s) request is blocked either by inline block page response or redirects the URL to a block server. If the HTTP/HTTP(s) request matches the allowed list, the traffic is allowed without further URL filtering inspection.
For HTTPS traffic, the inline block page will not be displayed. URL-based filtering will not decode any encoded URL before performing a lookup.
When there is no allowed list/blocked list configuration on the device, based on the category and reputation of the URL, traffic is allowed or blocked either using a block page or redirect URL for HTTP. For HTTP(s), there is no block page or redirect URL, the flow will be dropped.
The URL database is downloaded from the cloud when the user configures the category/reputation-based URL filtering. The URL category/reputation database has only a few IP address based records and the category/reputation look up occurs only when the host portion of the URL has the domain name. After the full database is downloaded from the cloud, if there are any updates to the existing database, the incremental updates will be automatically downloaded in every 15 minutes. The complete database size is approximately 440 MB and the downloaded database should always synchronize with the cloud. The database will be invalid if the connection to the cloud is lost for more than 24 hours.
If the device does not get the database updates from the cloud, the fail-open option ensures that the traffic designated for URL filtering is not dropped. When you configure the fail-close option, all the traffic destined for URL filtering will be dropped when the cloud connectivity is lost.
 Note |
The web filtering database is periodically updated from the cloud in every 15 minutes. |
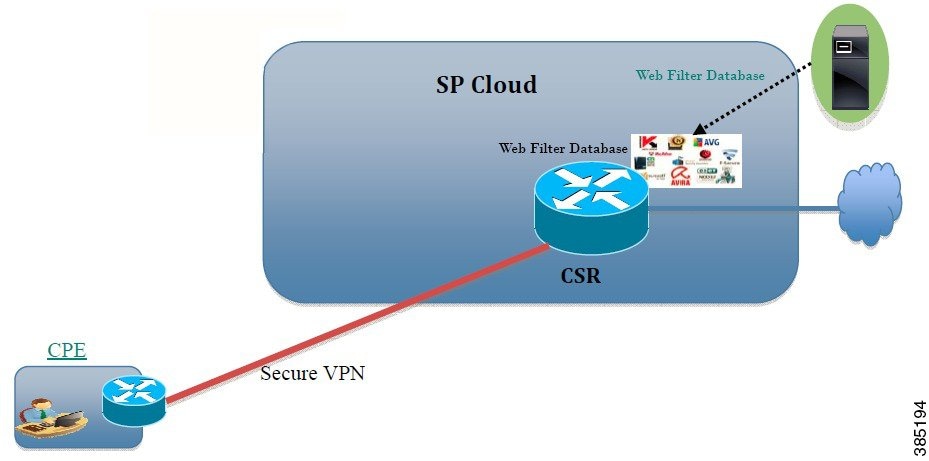
The figure illustrates the Web Filtering topology.
Virtual Service Resource Profiles for URL Filtering
The Cisco ISR 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers support urlf-medium and urlf-high resource profiles along with urlf-low profile. These profiles indicate the CPU and memory resources required to run the virtual service.
|
Platform |
Profile |
Virtual Service Resource Requirements |
Platform Requirements |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
System CPU |
SP Memory |
|||
|
CSR1000v, ISRv |
urlf-low |
25% |
3 GB |
8 GB (RAM) |
|
urlf-medium |
50% |
4 GB |
8 GB (RAM) |
|
|
urlf-high |
75% |
6 GB |
12 GB (RAM) |
|
Cloud-Lookup
The Cloud-Lookup feature operates in single-tenancy mode to retrieve the category and reputation score of URLs that are not available in the local database. The Cloud-Lookup feature is enabled by default.
The Cloud-Lookup feature is an enhancement over the on-box database lookup feature. Earlier, the on-box database lookup feature allowed URLs that are not present in the on-box database and have a reputation score of 0. When Cloud-Lookup is enabled, the URLs that were allowed earlier may be dropped based on the reputation score and the configured block-threshold. In order to allow such URLs, one must add them to an allowed list. Category and reputation scores for different URLs from Cloud-Lookup are explained below.
There are two kinds of URLs:
-
Name based URLs
-
IP based URLs
When the Cloud-Lookup feature is enabled, the category and reputation score of unknown URLs are returned as follows:
Name based URLs
-
Valid URL — corresponding category and reputation score is received.
-
Unknown URL (new URL or unknown to the cloud) — category is 'uncategorized' and reputation score is 40
-
Internal URLs with proper domain name (for example, internal.abc.com) — category and reputation score is based on the base domain name (abc.com from the example above).
-
Completely internal URLs (for example, abc.xyz) — category is 'uncategorized' and reputation score is 40
IP based URLs
-
Public hosted IP — corresponding category and reputation score is received.
-
Private IP like 10.<>, 192.168.<> — category is 'uncategorized' and reputation score is 100
-
Non-hosted/Non-routable IP — category is 'uncategorized' and reputation score is 40
The Cloud-Lookup score is different from the on-box database for these URLs (Unknown/Non-hosted/Non-routable/Internal URLs).
 Note |
The Cloud-Lookup feature is not available in multi-tenancy mode. |
 Feedback
Feedback