Overview
Register the firewall with the Firewall Management Center.
Register the firewall with the Firewall Management Center depending on which deployment method you are using.
Secure Firewall 1210/20 Threat Defense Getting Started: Firewall Management Center at a Central Headquarters
Register the firewall with the Firewall Management Center.
Register the firewall with the Firewall Management Center depending on which deployment method you are using.
Zero-Touch Provisioning lets you register devices to the Firewall Management Center by serial number without having to perform any initial setup on the device. The Firewall Management Center integrates with Security Cloud Control for this functionality.
For Firewall Management Center version 7.4, you need to add the device using Security Cloud Control; see the 7.4 guide for more information. The native Firewall Management Center workflow was added in 7.6. Also, for cloud integration in 7.4, see the SecureX Integration page in the Firewall Management Center.
Default Configuration After Registration
When you use zero-touch provisioning, the following interfaces are preconfigured. Note that other settings, such as the DHCP server on inside, access control policy, or security zones, are not configured.
Ethernet 1/1—"outside", IP address from DHCP, IPv6 autoconfiguration
Ethernet 1/2 (or for the 1210// 1220, the VLAN1 interface)— "inside", 192.168.95.1/24
Default route—Obtained through DHCP on the outside interface
Requirements
When you use the outside interface for manager access, it uses DHCP by default. Before you can enable high availability, you need to change the IP address to a static address. Alternatively, you can use the Management interface instead; DHCP is supported on Management with high availability.
If the device does not have a public IP address or FQDN, set a public IP address/FQDN for the Firewall Management Center (for example, if it is behind NAT), so the device can initiate the management connection. See .
DHCP server for either Management or Ethernet 1/1 that provides an IP address and default gateway.
Network access to the OpenDNS public DNS servers. IPv4: 208.67.220.220 and 208.67.222.222; IPv6: 2620:119:35::35. DNS servers obtained from DHCP are never used.
The following names need to be resolved:
| FQDNs |
|---|
| *.cisco.com (many FQDNs) |
| *.defenseorchestrator.com (many FQDNs) |
| *.defenseorchestrator.eu (for the EU, many FQDNs) |
| 0.sourcefire.pool.ntp.org, 1.sourcefire.pool.ntp.org, 2.sourcefire.pool.ntp.org |
| 1.200.159.162.in-addr.arpa |
| 60.19.239.178.in-addr.arpa |
| connected.by.freedominter.net |
| time.cloudflare.com |
| udc.neo4j.org |
| 1. | The first time you add a device using a serial number, integrate the Firewall Management Center with Security Cloud Control.
|
|||||||||||||
| 2. | Obtain your device's serial number. The device includes two serial numbers: the chassis serial number and the PCB (circuit board) serial number. Either serial number should work.
|
|||||||||||||
| 3. | Check your LEDs to make sure the firewall is ready for registration.
|
|||||||||||||
| 4. | Choose . |
|||||||||||||
| 5. | From the Add drop-down menu, choose Device. |
|||||||||||||
| 6. | Click Serial Number, click Basic, and then click Next. 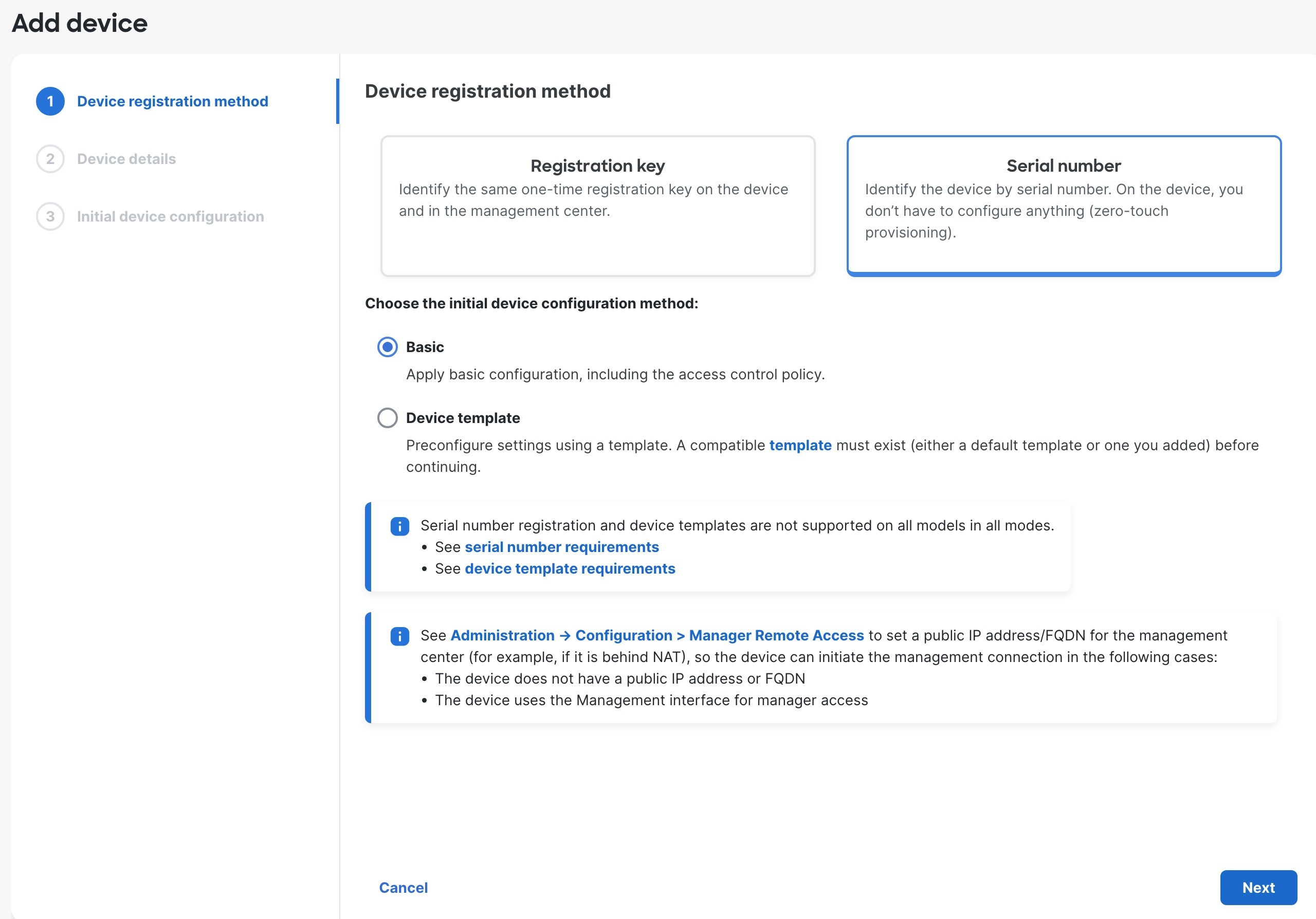
|
|||||||||||||
| 7. | Configure the device details and click Next. 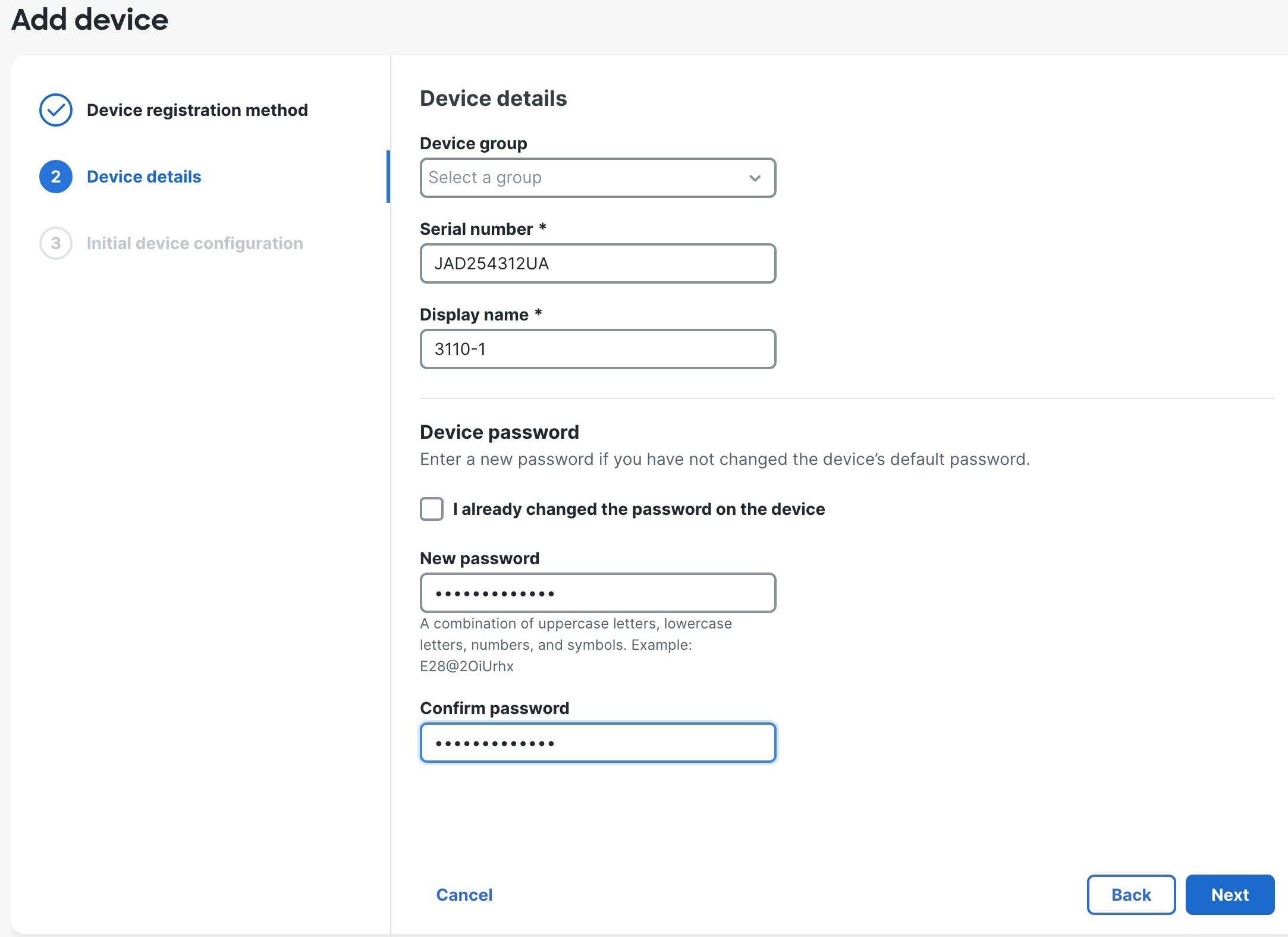
|
|||||||||||||
| 8. | Configure the initial device configuration. 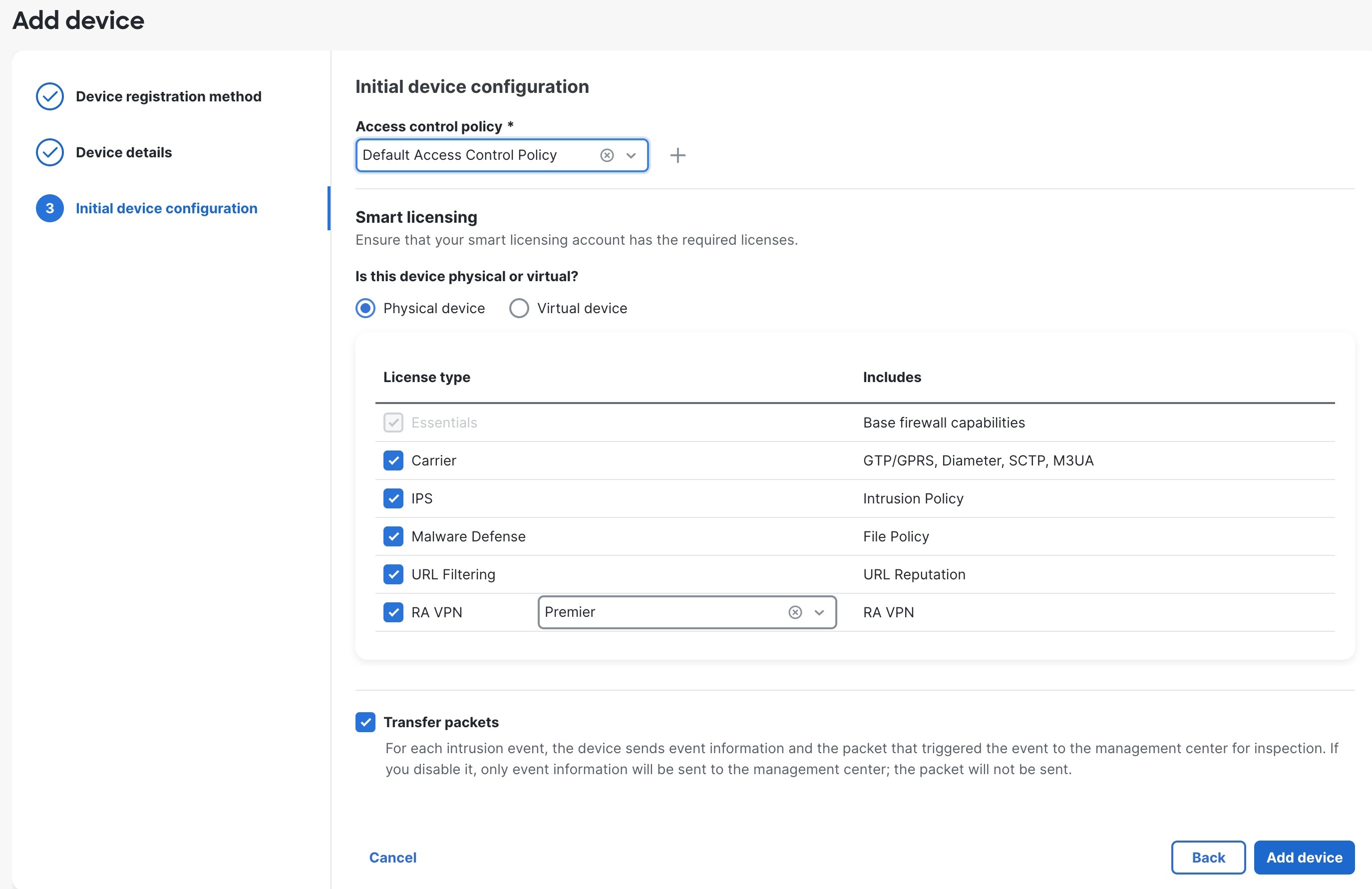
|
|||||||||||||
| 9. | Click Add device. It may take up to two minutes for the Firewall Management Center to verify the device’s heartbeat and establish communication. When using zero-touch provisioning on the outside interface, Security Cloud Control acts as a DDNS provider and does the following:
If you use zero-touch provisioning on the Management interface, DDNS is not supported. The Firewall Management Center must be publicly reachable so the device can initiate the management connection. You can continue to use Security Cloud Control as the DDNS provider, or you can later change the DDNS configuration in the Firewall Management Center to a different method. |
Register the firewall to the Firewall Management Center manually using the device IP address or hostname and a registration key.
| 1. | Log into the Firewall Management Center. |
|
| 2. | Choose . |
|
| 3. | From the Add drop-down menu, choose Device. |
|
| 4. | Click Registration Key, click Basic, and then click Next. 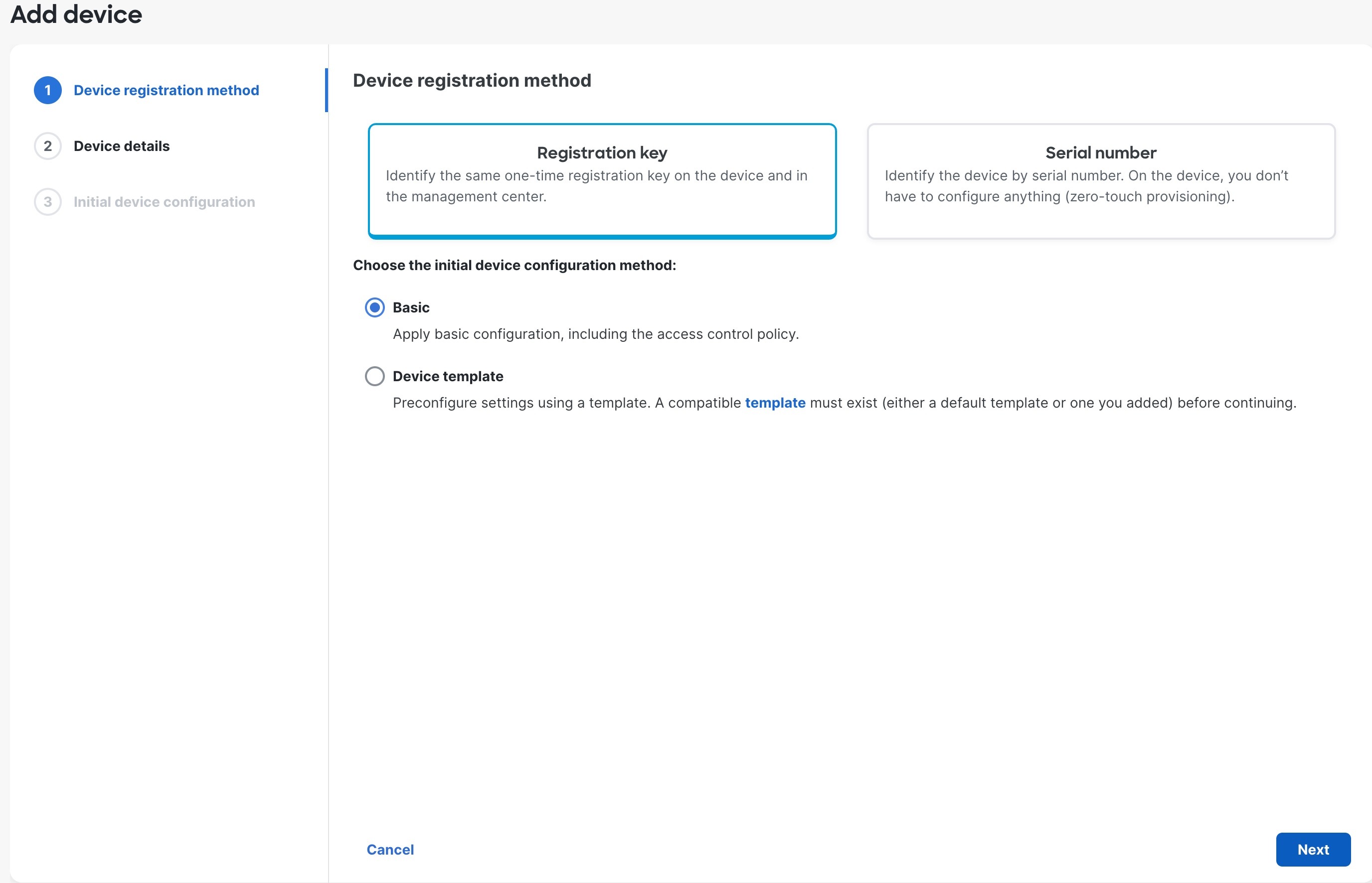
|
|
| 5. | Configure the device details and click Next. 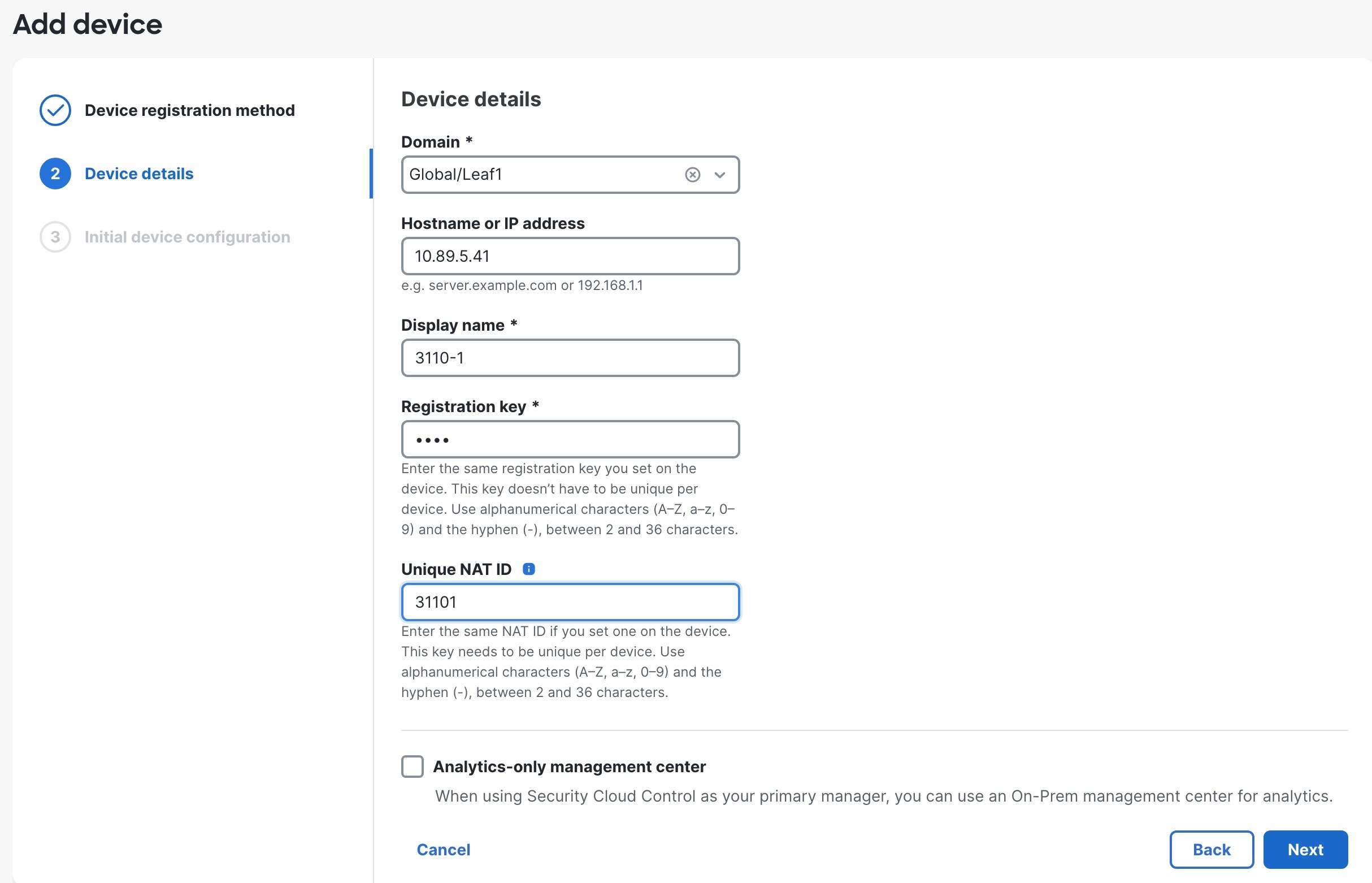
|
|
| 6. | Configure the initial device configuration. 
|
|
| 7. | Click Add device. It may take up to two minutes for the Firewall Management Center to verify the device’s heartbeat and establish communication. If the registration succeeds, the device is added to the list. If it fails, you will see an error message. If the device fails to register, check the following items:
For more troubleshooting information, see https://cisco.com/go/fmc-reg-error. |