Overview
Perform initial configuration using the Firewall Device Manager or the CLI.
For manual provisioning, perfom initial configuration of the firewall using the Secure Firewall Device Manager or using the CLI.
Secure Firewall 1210/20 Threat Defense Getting Started: Firewall Management Center at a Central Headquarters
Perform initial configuration using the Firewall Device Manager or the CLI.
For manual provisioning, perfom initial configuration of the firewall using the Secure Firewall Device Manager or using the CLI.
Using this method, after you register the firewall, the following interfaces will be preconfigured in addition to the Management interface:
Ethernet 1/1—outside, IP address from DHCP, IPv6 autoconfiguration
VLAN1— inside, 192.168.95.1/24
Default route—Obtained through DHCP on the outside interface
Additional interfaces—Any interface configuration from the Firewall Device Manager is preserved.
Other settings, such as the DHCP server on inside, access control policy, or security zones, are not preserved.
| 1. | Connect your computer to the inside interface (Ethernet 1/2 through 1/8 or for the Secure Firewall 1220, 1/2 through 1/10). |
|
| 2. | Log into the Firewall Device Manager.
|
|
| 3. | Use the setup wizard. 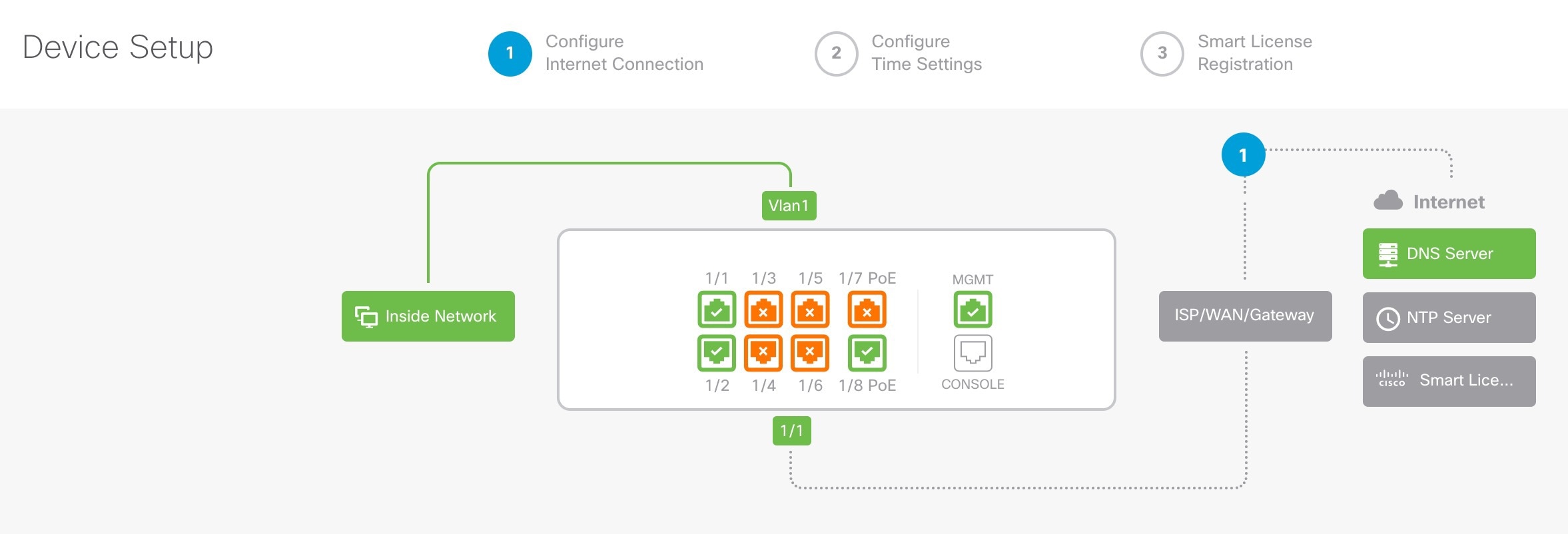
|
|
| 4. | If you want to configure additional interfaces, choose Device, and then click the link in the Interfaces summary. |
|
| 5. | Register with the Firewall Management CenterSecurity Cloud Control by choosing and clicking Proceed Configure the Management Center/SCC/Details.
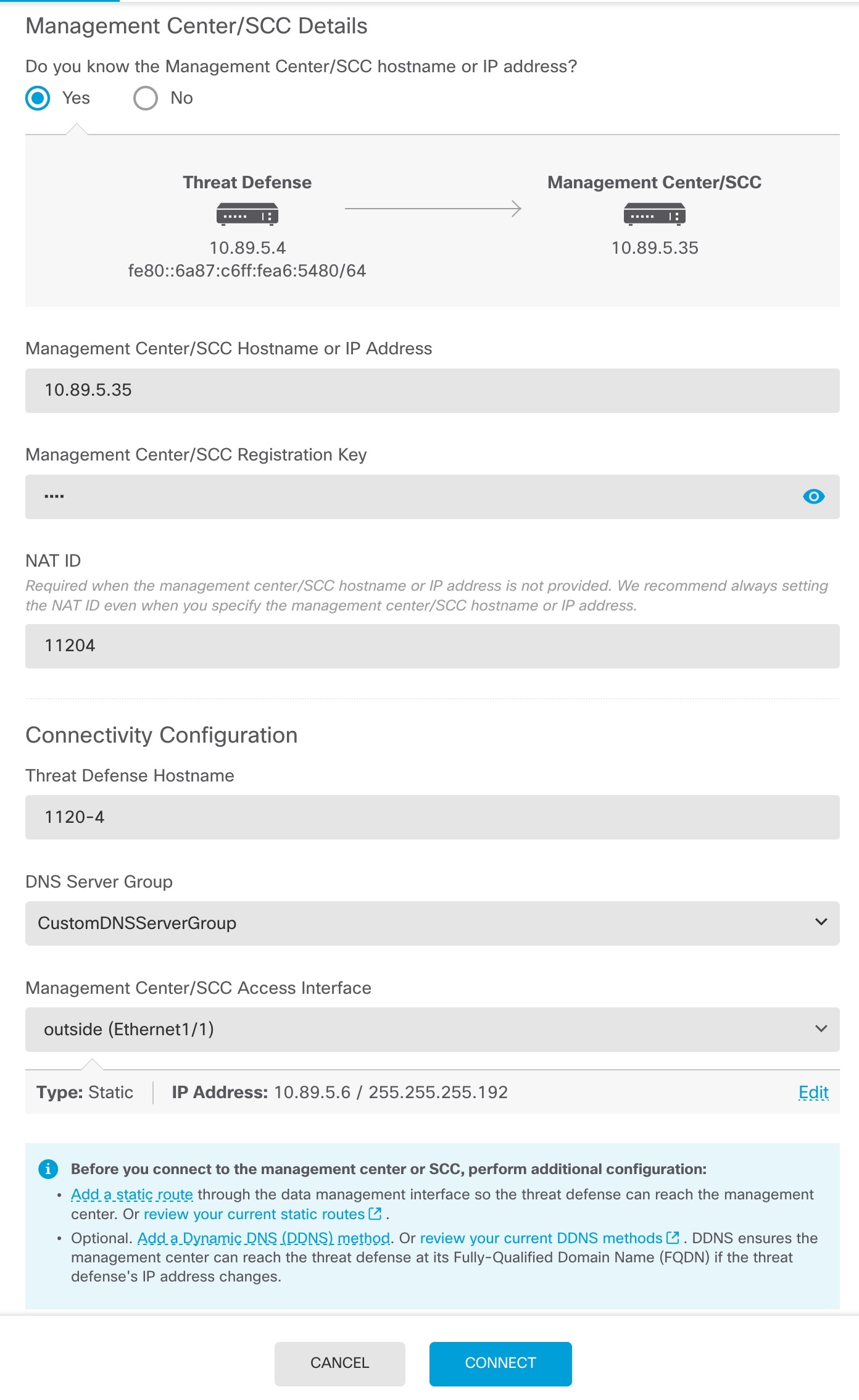
|
|
| 6. | Configure the Connectivity Configuration. |
|
| 7. | (Optional) Click Add a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) method. DDNS ensures the Firewall Management Center can reach the Firewall Threat Defense at its FQDN if the Firewall Threat Defense's IP address changes. |
|
| 8. | Click Connect. The Registration Status dialog box shows the current status of the Firewall Management CenterSecurity Cloud Control registration. 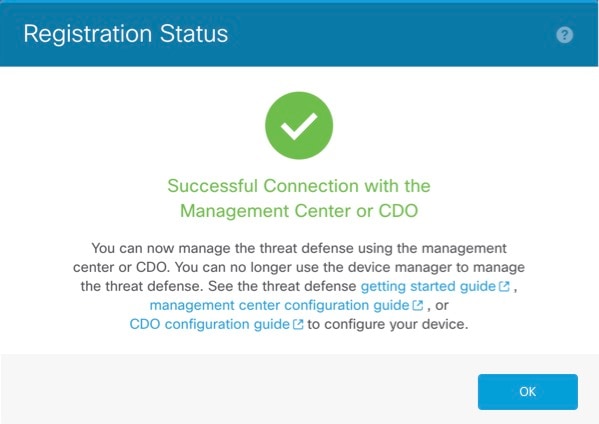
|
|
| 9. | After the Saving Management Center/SCC Registration Settings step on the status screen, go to the Firewall Management CenterSecurity Cloud Control and add the firewall. See Add a firewall using manual provisioning. |
Set the dedicated Management IP address, gateway, and other basic networking settings using the CLI setup script.
| 1. | Connect to the console port and access the Firewall Threat Defense CLI. See Access the Firewall Threat Defense CLI. |
|
| 2. | Complete the CLI setup script for the Management interface settings.
Guidance: Enter y for at least one of these types of addresses. Although you do not plan to use the Management interface, you must set an IP address, for example, a private address. Guidance: Choose manual. DHCP is not supported when using the outside interface for manager access. Make sure this interface is on a different subnet from the manager access interface to prevent routing issues. Guidance: Set the gateway to be data-interfaces. This setting forwards management traffic over the backplane so it can be routed through the outside interface. Guidance: Set the Management interface DNS servers. These will probably match the outside interface DNS servers you set later, since they are both accessed from the outside interface. Guidance: Enter no to use the Firewall Management Center. Guidance: Enter routed. Outside manager access is only supported in routed firewall mode. |
|
| 3. | Configure the outside interface for manager access. configure network management-data-interface After you press Enter, you are prompted to configure basic network settings for the outside interface. Manual IP Address Guidance: To retain the outside DNS servers after registration, you need to re-configure the DNS Platform Settings in the Firewall Management Center. IP Address from DHCP |
|
| 4. | Identify the Firewall Management Center. configure manager add {hostname | IPv4_address | IPv6_address | DONTRESOLVE} reg_key nat_id
Example: |
|
| 5. | Shut down the Firewall Threat Defense so you can send the device to the remote branch office. It's important that you shut down your system properly. Simply unplugging the power or pressing the power switch can cause serious file system damage. Remember that there are many processes running in the background all the time, and unplugging or shutting off the power does not allow the graceful shutdown of your system.
|