Overview
This topic explains the multi-tier fabric topology in data center networks, highlighting its three-tier structure that enhances connectivity and port usage, and detailing the configuration requirements for Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches to support this architecture.
A multi-tier fabric topology is a data center network design that uses an additional layer of leaf switches, creating a three-tier structure. This design is intended for large data center deployments where it separates aggregation and access network functions onto distinct switch layers, enabling flexible connectivity and port usage through configurable fabric ports.
3-tier Core-Aggregation-Access architectures are common in data center network topologies. As of the Cisco APIC 4.1(1) release, you can create a multi-tier ACI fabric topology that corresponds to the Core-Aggregation-Access architecture, mitigating the need to upgrade costly components such as rack space or cabling. The addition of a tier-2 leaf layer makes this topology possible. The tier-2 leaf layer supports connectivity to hosts or servers on the downlink ports and connectivity to the leaf layer (aggregation) on the uplink ports.
In the multi-tier topology, the leaf switches initially have uplink connectivity to the spine switches and downlink connectivity to the tier-2 leaf switches. To make the entire topology an ACI fabric, all ports on the leaf switches connecting to tier-2 leaf fabric ports must be configured as fabric ports (if not already using the default fabric ports). After APIC discovers the tier-2 leaf switch, you can change the downlink port on the tier-2 leaf to a fabric port and connect to an uplink port on the middle layer leaf.
If you are not using the default fabric ports to connect leaf switches to tier-2 leaf, you must convert the leaf ports from downlink to uplink (leaf switch reload required). For more information about changing port connectivity, see the Access Interfaces chapter of the Cisco APIC Layer 2 Networking Configuration Guide.
This figure shows an example of a multi-tier fabric topology.
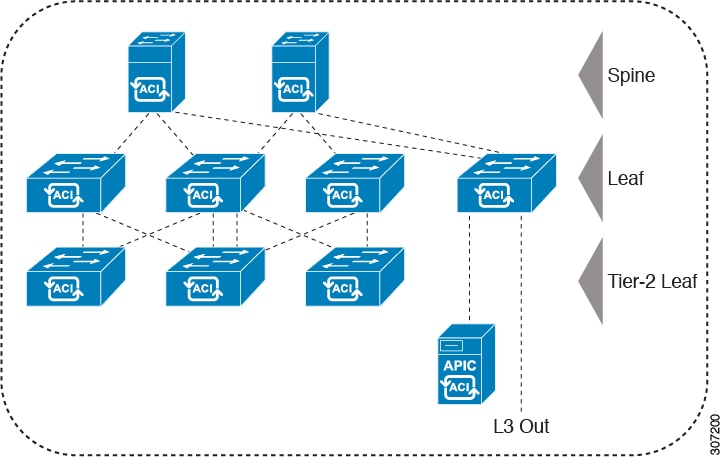
While the topology in the image shows the Cisco APIC and L3Out/EPG connected to the leaf aggregation layer, the tier-2 leaf access layer also supports connectivity to APICs and L3Out/EPGs.
Only Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches with model numbers that end in EX, and later are supported as tier-2 leaf switches and as leaf switches, if there are tier-2 leaf switches attached to them. For more information, see the Supported Switches and Port Speeds for Multi-Tier Archictecture table.
Tier-2 leaf switches attached to remote leaf switches are not supported.
| Switch |
Maximum supported downlink port* (as tier-2 leaf) |
Maximum supported fabric ports (as tier-2 leaf) |
Maximum supported fabric ports (as tier-1 leaf) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nexus 93180YC-EX |
48x1/10/25-Gbps 4x40/100-Gbps |
48 x 10/25-Gbps 6 x 40/100-Gbps |
48 x 10/25-Gbps 6 x 40/100-Gbps |
| Nexus 93108TC-EX |
48x100M/1/10G BASE-T 4x40/100-Gpbs |
6 x 40/100-Gbps |
6 x 40/100-Gbps |
| N9K-9348GC-FXP** |
48 x 100M/1G BASE-T |
4 x 10/25-Gbps 2 x 40/100-Gbps |
4 x 10/25-Gbps 2 x 40/100-Gbps |
| N9K-93180YC-FX |
48 x 1/10/25-Gbps 4x40/100-Gbps |
48 x 10/25-Gbps 6 x 40/100-Gbps |
48 x 10/25-Gbps 6 x 40/100-Gbps |
| N9K-93108TC-FX |
48 x 100M/1/10G BASE-T 4x40/100-Gbps |
6 x 40/100-Gbps |
6 x 40/100-Gbps |
| N9K-93240YC-FX2 |
48x1/10/25-Gbps 10x40/100-Gbps |
48x1/10/25-Gbps 12x40/100-Gbps |
48x10/25-Gbps fiber ports 12x40/100-Gbps |
| N9K-C9336C-FX2 |
34 x 40/100-Gbps |
36 x 40/100-Gbps |
36 x 40/100-Gbps |
| N9K-C93216TC-FX2*** |
96 x 10G BASE-T 10 x 40/100-Gbps |
12 x 40/100-Gbps |
12 x 40/100-Gbps |
| N9K-C93360YC-FX2*** |
96 x 10/25-Gbps 10 x 40/100-Gbps |
52 x 10/25Gbps 12 x 40/100Gbps |
52 x 10/25Gbps 12 x 40/100Gbps |
| N9K-C9364C-GX |
62 x 40/100-Gbps |
62 x 40/100-Gbps |
62 x 40/100-Gbps |
* Last 2 original fabric ports cannot be used as downlink ports.
** If tier-2 leaf does not require much bandwidth, it can be used as tier-1 though it has fewer fiber ports. Copper port cannot be used as a fabric port.
*** Supported beginning with Cisco APIC Release 4.1(2).