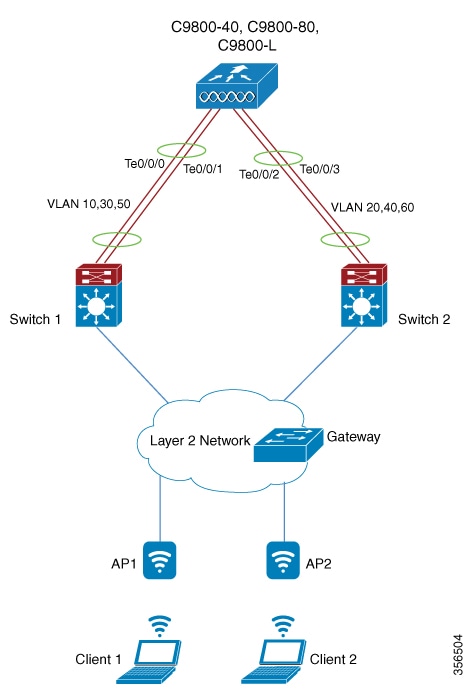
Link aggregation group
A link aggregation group is a port-channeling technology that
-
combines all of a controller’s distribution system ports into a single 802.3ad port channel
-
reduces the number of IP addresses required for port configuration, and
-
dynamically manages port redundancy and load-balances AP transparently to the corresponding user.
LAG simplifies controller configuration by eliminating the need to configure ports for each interface. If any controller port fails, traffic migrates automatically to other functioning ports. As long as at least one controller port is functioning, the system continues to operate. Wireless clients can continue to send and receive data, and APs remain connected to the network.
The wireless management VLAN can be assigned to only one port channel.
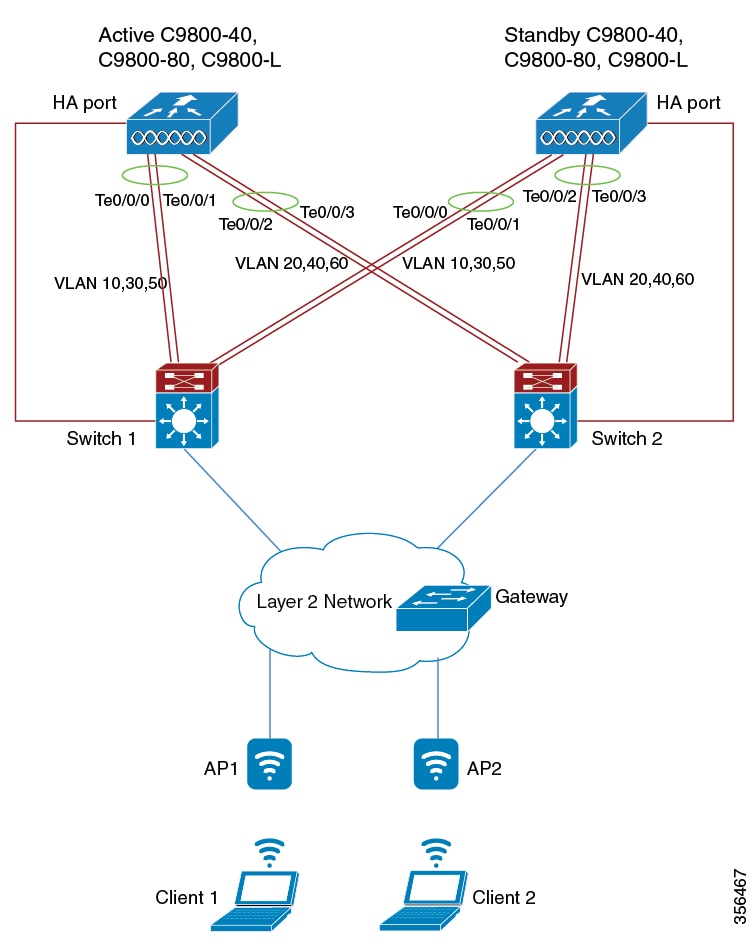
LACP is supported on a standalone controller from the Cisco IOS XE Gibraltar 16.12.x release. LACP is supported on an SSO pair from Cisco IOS XE Amsterdam 17.1.1s and later.
If a dual MAC entry is generated in the switchport MAC table when using ISE licensing enforcement, it may consume two licenses for a single AP. To avoid this issue when only one port is used, choose wired0.
Feature history
This table provides release and related information about the feature explained in this section.
This feature is also available in all the releases subsequent to the one in which they are introduced in, unless noted otherwise.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Link aggregation group |
Cisco IOS XE Amsterdam 17.2.1 |
This feature provides flexibility for connecting the controller to multiple switching infrastructures. Using multi-LAG, you can connect multiple uplinks from the controller to separate uplink switches. |

 Feedback
Feedback