- Cisco ASR 901 Router Overview
- Licensing
- First-Time Configuration
- Managing and Monitoring Network Management Features
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Software Upgrade
- Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring Ethernet OAM
- ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring MST on EVC Bridge Domain
- Multiprotocol Label Switching
- Configuring EoMPLS
- Configuring MPLS VPNs
- Configuring MPLS OAM
- Configuring Routing Protocols
- Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
- Configuring T1/E1 Controllers
- Configuring Pseudowire
- Configuring Clocking
- G.8275.1 Telecom Profile
- Cisco IOS IP SLA
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring MLPPP
- Onboard Failure Logging
- Hot Standby Router Protocol and Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
- Configuring Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Configuring Multihop Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
- Bit Error Rate Testing
- Microwave ACM Signaling and EEM Integration
- IPv6 Support on the Cisco ASR 901 Router
- Labeled BGP Support
- BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
- MPLS Traffic Engineering - Fast Reroute Link Protection
- Layer 2 Control Protocol Peering, Forwarding, and Tunneling
- Configuring Inverse Muliplexing over ATM
- IPv6 over MPLS: 6PE and 6VPE
- Storm Control
- Remote Loop-Free Alternate - Fast Reroute
- Digital Optical Monitoring
- IPv4 Multicast
- IPv6 Multicast
- Configuring Switched Port Analyzer
- IP Security
- BCP Support on MLPPP
- ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching
- Configuring NAT for IP Address Conservation
- Auto-IP
- IPv6 Routing: OSPFv3 Authentication Support with IPsec
- Policy-Based Routing
- Generic Routing Encapsulation
- Call Home
- PTP Debugging over GRE Tunnel
- Overview
- MAC Layer 2 Access Control Lists
- Index
- BCP Support on MLPPP
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About BCP Support on MLPPP
- How to Configure BCP Support on MLPPP
- Configuration Examples for BCP Support on MLPPP
- Additional References
- Feature Information for BCP Support on MLPPP
BCP Support on
MLPPP
BCP Support on MLPPP
This feature module describes how to configure Bridge Control Protocol (BCP) Support over Multilink PPP (MLPPP).
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About BCP Support on MLPPP
The BCP, as described in RFC 3518, is responsible for configuring, enabling and disabling the bridge protocol modules on both ends of the point-to-point link. The BCP feature enables forwarding of Ethernet frames over serial networks, and provides a high-speed extension of enterprise LAN backbone traffic through a metropolitan area.
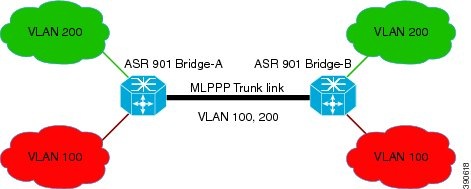
When BCP is supported on MLPPP, it enables transport of Ethernet Layer 2 frames through MLPPP. In the following diagram, Bridge-A is connected to Bridge-B using MLPPP. The MLPPP bundle acts as a trunk link connecting Bridge-A and Bridge-B, transporting multiple VLANs. Using this feature, the hosts in VLAN 100, who are connected to Bridge-A, can talk to the hosts in VLAN 200, who are connected to Bridge-B.
Supported Profiles and Protocols
Quality of Service
The Ethernet Layer 2 traffic is classified on the egress at the Multilink interface based on IP DSCP or VLAN CoS bits. Based on this classification, egress policing (bandwidth percent or priority percent) is achieved. You can also re-mark the QoS field. The following table lists the options available for re-marking.
| IP DSCP | VLAN CoS or PCP Bits |
|---|---|
|
Set IP DSCP (re-mark IP DSCP) |
Set IP DSCP |
|
Set VLAN QoS or Priority Code Point (PCP) Bits |
Set VLAN CoS Bits (re-mark VLAN CoS or PCP Bits) |
|
Bandwidth Percent or Priority Percent |
Bandwidth Percent or Priority Percent |
Bridging and Routing
Both routing and bridging can co-exist on the same MLPPP interface. Routing is achieved on the MLPPP interface by running BCP after configuring an IP address on the SVI.
 Note | Configuring IP address on the SVI of the MLPPP interface does not bring up the IP Control Protocol (IPCP). |
For information on configuring the IP address on the SVI of the MLPPP interface, see the “Enabling Routing on the MLPPP Interface Running BCP” section.
How to Configure BCP Support on MLPPP
- Configuring Multiple EFPs Bridged Through the Same Link
- Enabling Routing on an MLPPP Interface Running BCP
- Configuring Multiple Encapsulated VLANs Bridged Through Different Multilinks
- Configuring QoS for BCP Support on MLPPP
- Verifying BCP Support on MLPPP
Configuring Multiple EFPs Bridged Through the Same Link
To bridge multiple EFPs through the same multilink, you should create two EFPs and add them to the multilink.
To configure an EFP and a multilink, complete the following tasks:
Configuring an EFP
To configure an EFP, complete the following steps:
Adding an EFP to a Multilink
To add an EFP to a multilink, complete the following steps:
Enabling Routing on an MLPPP Interface Running BCP
To enable routing on an MLPPP interface running BCP, complete the following steps:
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Router(config)# interface Multilink 5 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 |
service instance
number
ethernet
Example: Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet |
Configures an EFP (service instance) and enters service instance configuration mode. |
| Step 5 |
encapsulation dot1q
vlan-id
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 60 |
Configures encapsulation type for the service instance. |
| Step 6 |
rewrite
ingress
tag
pop 1
symmetric
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric |
Specifies that encapsulation modification occurs on packets at ingress. |
| Step 7 |
bridge-domain
bridge-id
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 100 |
Configures the bridge domain ID. |
| Step 8 |
exit
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# exit |
Exits service instance configuration mode and enters the interface configuration mode. |
| Step 9 |
interface
type
number
Example: Router(config)# interface VLAN 100 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. |
| Step 10 |
ip adddress
ip-address-primary
ip-address-secondary
Example: Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.8 255.255.255.0 |
Specifies a primary or secondary IP address for an interface. |
Configuring Multiple Encapsulated VLANs Bridged Through Different Multilinks
You should create two encapsulated VLANs and add them to two multilinks for this configuration to work.
To configure multiple encapsulated VLANs bridged through different multilinks, complete the following tasks:
Adding an Encapsulated VLAN to Multilinks
To add an encapsulated VLAN to separate multilinks, complete the following steps:
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Router(config)# interface Multilink 5 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 |
service instance
number
ethernet
Example: Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet |
Configures an EFP (service instance) and enters service instance configuration mode. | ||
| Step 5 |
encapsulation
dot1q
vlan-id
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 60 |
Configures encapsulation type for the service instance. | ||
| Step 6 |
rewrite
ingress
tag
pop 1
symmetric
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric |
Specifies that encapsulation modification occurs on packets at ingress. | ||
| Step 7 |
bridge-domain
bridge-id
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 100 |
Configures the bridge domain ID. | ||
| Step 8 |
exit
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# exit |
Exits service instance configuration mode and enters the interface configuration mode.
|
Configuring QoS for BCP Support on MLPPP
The egress policy at the multilink interface matches the IP DSCP value and VLAN CoS bits. Based on this classification it re-marks these values and performs egress policing (Priority percent or Bandwidth percent).
To configure QoS for BCP Support on MLPPP, complete the following tasks:
 Note | Define a QoS policy, and apply it to the MLPPP interface, and configure a matching policy on the EFP interface. |
Defining a QoS Policy
To define a QoS policy, complete the following steps:
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
class-map
match-any
class-map-name
Example: Router(config)# class-map match-any dscpaf11 |
Creates a class map to be used for matching packets to a specified class and enters QoS class-map configuration mode. |
| Step 4 |
match
ip
dscp
dscp-list
Example: Router(config-cmap)# match ip dscp af11 |
Matches IP DSCP packeting using Assured Forwarding (AF) by entering the binary representation of the DSCP value. |
| Step 5 |
class-map
match-any
class-map-name
Example: Router(config-cmap)# class-map match-any qos-group3 |
Creates a class map to be used for matching packets to a specified class. |
| Step 6 |
match
qos-group
qos-group-value
Example: Router(config-cmap)# match qos-group 3 |
Identifies a specific quality of service (QoS) group value as a match criterion. |
| Step 7 |
policy-map
policy-map-name
Example: Router(config-cmap)# policy-map bcpmlpppqos |
Creates a policy map that can be attached to one or more interfaces. |
| Step 8 |
class
class-name
Example: Router(config-pmap)# class dscpaf11 |
Specifies the name of the class whose policy you want to create or change. Alternatively, is used to specify the default class (commonly known as the class-default class) before you configure its policy. |
| Step 9 |
priority
percent
percentage
Example: Router(config-pmap-c)# priority percent 20 |
Provides priority to a class of traffic belonging to a policy map. |
| Step 10 |
set ip dscp
ip-dscp-value
Example: Router(config-pmap-c)# set ip dscp ef |
Marks a packet by setting the IP DSCP value in the type of service (ToS) byte. |
| Step 11 |
class
class-name
Example: Router(config-pmap-c)# class qos-group3 |
Specifies the name of the class whose policy you want to create or change. Alternatively, is used to specify the default class (commonly known as the class-default class) before you configure its policy. |
| Step 12 |
bandwidth
percent
percentage
Example: Router(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 20 |
Specifies the bandwidth allocated for a class belonging to a policy map. |
| Step 13 |
set qos-group
group-id
Example: Router(config-pmap-c)# set qos-group 4 |
Sets a QoS group identifier (ID) that can be used later to classify packets. |
Applying a QoS Policy on an MLPPP Interface
To apply a QoS policy on an MLPPP interface, complete the following steps:
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Router(config)# interface Multilink 5 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 |
service-policy
output policy-map-name
Example: Router(config-if)# service-policy output bcpmlpppqos |
Attaches a policy map to an input interface, a virtual circuit (VC), an output interface, or a VC that will be used as the service policy for the interface or VC. |
| Step 5 |
service instance
number
ethernet
Example: Router(config-if)# service instance 20 ethernet |
Configures an EFP (service instance) and enters service instance configuration mode. |
| Step 6 |
encapsulation dot1q
vlan-id
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 50 |
Configures encapsulation type for the service instance. |
| Step 7 |
rewrite
ingress
tag
pop 1
symmetric
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric |
Specifies that encapsulation modification occurs on packets at ingress. |
| Step 8 |
bridge-domain
bridge-id
Example: Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 100 |
Configures the bridge domain ID. |
Verifying BCP Support on MLPPP
To display the Multilink PPP bundle information on various interfaces on a router, use the show command, as described in the following example:
Router# show ppp multilink interface multilink 1
Multilink1
Bundle name: ASR1
Remote Endpoint Discriminator: [1] ASR1
Local Endpoint Discriminator: [1] ASR2
Bundle up for 17:06:50, total bandwidth 20480, load 6/255
2 receive classes, 2 transmit classes
Receive buffer limit 123040 bytes per class, frag timeout 1000 ms
Bundle is Distributed
Receive Class 0:
0/0 fragments/bytes in reassembly list
0 lost fragments, 0 reordered
0/0 discarded fragments/bytes, 0 lost received
0xB9026C received sequence
Receive Class 1:
0/0 fragments/bytes in reassembly list
0 lost fragments, 0 reordered
0/0 discarded fragments/bytes, 0 lost received
0x5D2E8F received sequence
Transmit Class 0:
0x5CBA5 sent sequence
Transmit Class 1:
0x146FA1 sent sequence
Distributed MLP. Multilink in Hardware.
Distributed Fragmentation is on. Fragment size: 256.
Bundle status is: active
Member links: 10 active, 0 inactive (max 255, min not set)
Se0/6:0, since 01:36:49, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/2:0, since 01:26:26, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/5:0, since 01:25:18, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/9:0, since 01:25:17, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/1:0, since 01:24:25, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/4:0, since 01:24:20, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/0:0, since 01:24:18, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/7:0, since 01:24:17, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/8:0, since 01:23:09, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Se0/3:0, since 01:23:08, 7680 weight, 256 frag size
Configuration Examples for BCP Support on MLPPP
Example: Multilink with a Single EFP
The following is a sample configuration of a multilink with a single EFP.
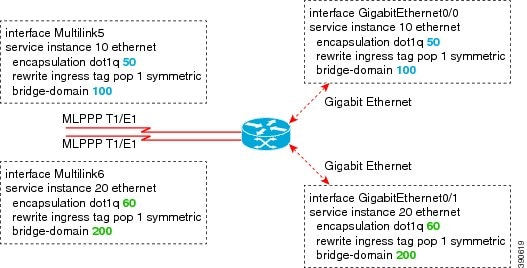
Example: Multilink with Multiple EFPs
The following is a sample configuration of a multilink with multiple EFPs.
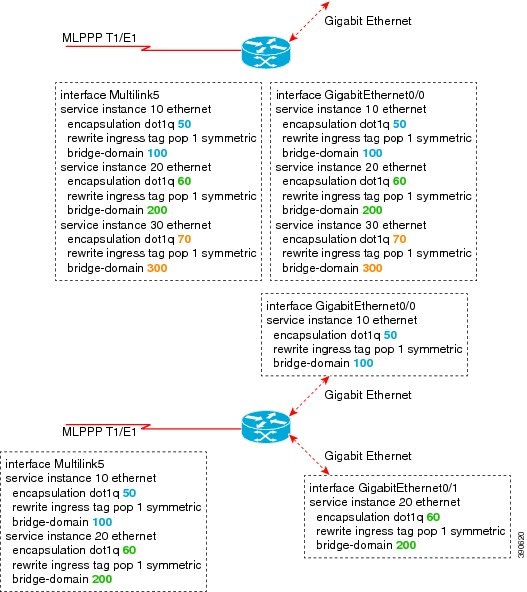
Example: Multilink with QoS
The following is a sample configuration of Multilink with QoS:
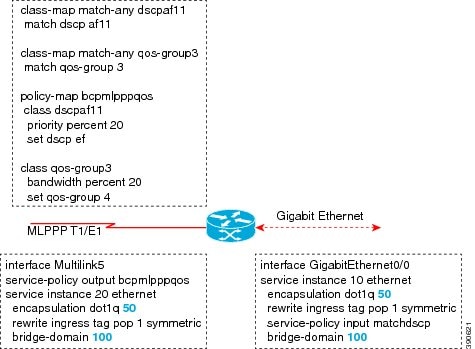
Example: Multilink with Routing on an MLPPP Interface Running BCP
The following is a sample configuration to enable routing on an MLPPP interface running BCP:
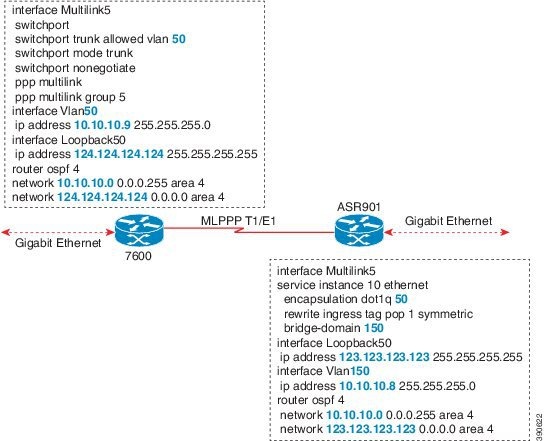
Example: Multilink Between Cisco ASR 901 Series Routers and Cisco C7600 Series Routers
The following is a sample configuration of multilink between a Cisco ASR 901 Series Routers and Cisco C7600 Series Routers:
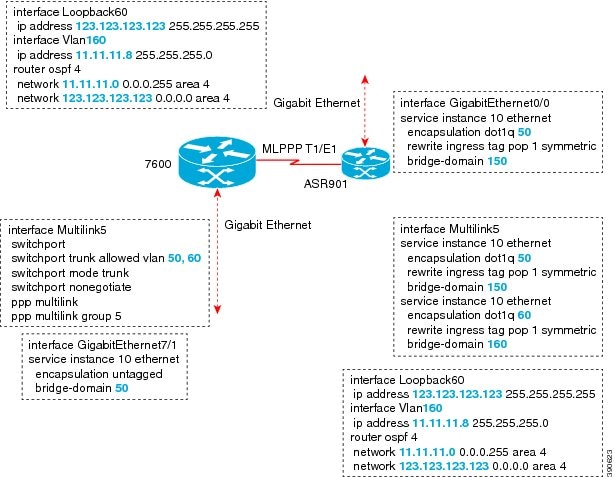
Example: Multilink with Maximum 10 Links
The following is a sample configuration of multilink with maximum 10 links.
Policy Map 1
The following sample configurations show how to configure multilink with maximum 10 links.
class-map match-any qos-group1 match qos-group 1 class-map match-any qos-group2 match qos-group 2 class-map match-any qos-group3 match qos-group 3 class-map match-any qos-group4 match qos-group 4 class-map match-any qos-group5 match qos-group 5 class-map match-any qos-group6 match qos-group 6 class-map match-any qos-group7 match qos-group 7 policy-map bcpmlpppqos class qos-group1 priority percent 20 set qos-group 2 class qos-group2 bandwidth percent 20 set qos-group 3 class qos-group3 bandwidth percent 10 set qos-group 4 class qos-group4 bandwidth percent 5 set qos-group 5 class qos-group5 bandwidth percent 30 set qos-group 6 class qos-group7 bandwidth percent 15 set qos-group 1
Policy Map 2
class-map match-any dscpaf11 match ip dscp af11 class-map match-any dscpaf12 match ip dscp af12 class-map match-any dscpaf21 match ip dscp af21 class-map match-any dscpaf31 match ip dscp af31 class-map match-any dscpcs1 match ip dscp cs1 class-map match-any dscpef match ip dscp ef class-map match-any dscpdefault match ip dscp default policy-map bcpmlpppdscp class dscpaf11 priority percent 20 set ip dscp af12 class dscpaf12 bandwidth percent 20 set ip dscp af13 class dscpaf21 bandwidth percent 10 set ip dscp af22 class dscpaf31 bandwidth percent 5 set ip dscp af32 class dscpcs1 bandwidth percent 30 set ip dscp cs2 class dscpef bandwidth percent 10 set ip dscp cs7 class dscpdefault bandwidth percent 5 set ip dscp cs5
MLPPP-GIG - 1
interface Multilink1
service-policy output bcpmlpppqos
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation untagged
bridge-domain 3000
interface Multilink2
service-policy output bcpmlpppqos
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 50
bridge-domain 2000
service instance 2 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 60
bridge-domain 2001
interface gigabitethernet 0/5
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 50
bridge-domain 2000
service instance 2 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 60
bridge-domain 2001
service instance 3 ethernet
encapsulation untagged
bridge-domain 3000
ADD-MLPPP-GIG - 1
interface Multilink1
service-policy output bcpmlpppqos
service instance 2 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 70
bridge-domain 3001
interface gigabitethernet 0/5
service instance 4 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 70
bridge-domain 3001
MLPPP-GIG-2
interface Multilink1
service-policy output bcpmlpppdscp
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation untagged
bridge-domain 3000
interface Multilink2
service-policy output bcpmlpppdscp
service instance 2 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q any
bridge-domain 3001
interface gigabitethernet 0/5
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation untagged
bridge-domain 3000
service instance 2 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q any
bridge-domain 3001
MLPPP-GIG-3
interface Multilink1
service-policy output bcpmlpppdscp
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation default
bridge-domain 3000
interface gigabitethernet 0/5
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation default
bridge-domain 3000
Sample Configuration of MLPPP Bundled 10 Member Links
interface Multilink1 no ip address load-interval 30 ppp pfc local request ppp pfc remote apply ppp acfc local request ppp acfc remote apply ppp multilink ppp multilink interleave ppp multilink group 1 ppp multilink fragment size 256 ppp multilink multiclass service-policy output bcpmlpppqos service instance 102 ethernet encapsulation dot1q 102 rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric bridge-domain 102 ! interface Serial0/0:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/1:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/2:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/3:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/4:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/5:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/6:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/7:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/8:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1 interface Serial0/9:0 no ip address encapsulation ppp ppp multilink ppp multilink group 1
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to BCP Support on MLPPP feature.
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Cisco ASR 901 Router Commands |
Standards
| Standard | Title |
|---|---|
|
None |
— |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC | Title |
|---|---|
|
RFC 3518 |
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Bridging Control Protocol (BCP) |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Technical Support website contains thousands of pages of searchable technical content, including links to products, technologies, solutions, technical tips, and tools. Registered Cisco.com users can log in from this page to access even more content. |
Feature Information for BCP Support on MLPPP
| Feature Name | Releases | Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
BCP Support on MLPPP |
15.4(2)S |
This feature was introduced on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Routers. The following sections provide information about this feature: |
 Feedback
Feedback