Manage Users
As a best practice, administrators should create separate accounts for all users. Prepare a list of the people who will use Cisco Crosswork. Decide on their user names and preliminary passwords, and create user profiles for them. During the creation of a user account, you assign a user role to determine the functionality to which the user will have access. If you will be using user roles other than "admin", create the user roles before you add your users (see Create User Roles).
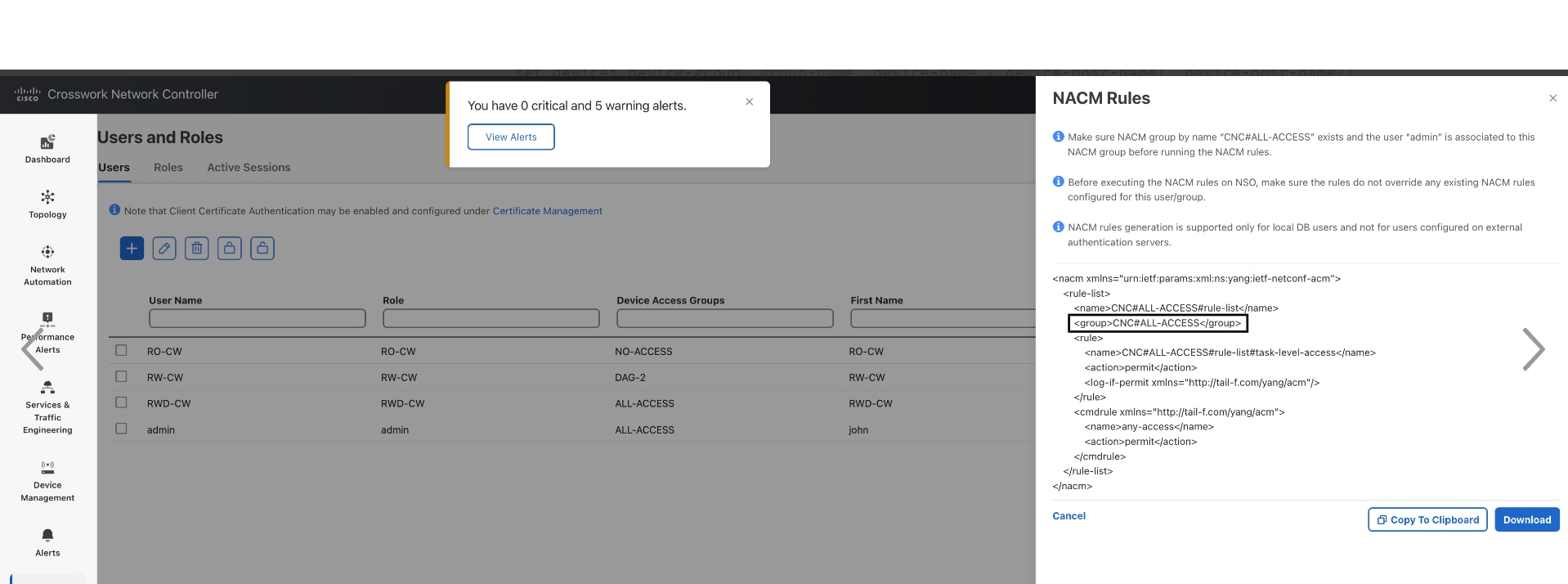
You can optionally view the NETCONF Access Control Model (NACM) rules that let admin members grant access to devices in selected groups and deny access to other devices.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, select tab. From this window, you can add a new user, edit the settings for an existing user, and delete a user. |
|
Step 2 |
To add a new user: |
|
Step 3 |
To edit a user:
|
|
Step 4 |
To delete a user:
|
|
Step 5 |
To view the audit log for a user: |
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) To view NACM rules for a user: |
Administrative Users Created During Installation
During installation, Crosswork creates two special administrative IDs:
-
The virtual machine administrator, with the username cw-admin, and the default password admin. Data center administrators use this ID to log in to and troubleshoot the VM hosting the Crosswork server.
-
The Cisco Crosswork administrator, with the username admin and the default password admin. Product administrators use this ID to log in to and configure the user interface, and to perform special operations, such as creating new user IDs.
The default password for both administrative user IDs must be changed the first time they are used.
User Roles, Functional Categories and Permissions
The Roles window lets users with the appropriate privileges define custom user roles. As with the default admin role, a custom user role consists of:
-
A unique name, such as “Operator” or “admin”.
-
One or more selected, named functional categories, which control whether or not a user with that role has access to the APIs needed to perform specific Cisco Crosswork functions controlled by that API.
-
One or more selected permissions, which control the scope of what a user with that role can do in the functional category.
For a user role to have access to a functional category, that category and its underlying API must show as selected on the Roles page for that role. If the user role shows a functional category as unselected, then users with this role assigned will have no access to that functional area at all.
Some functional categories group multiple APIs under one category name. For example: The “AAA” category controls access to the Password Change, Remote Authentication Servers Integration, and Users and Role Management APIs. With this type of category, you can deny access to some of the APIs by leaving them unselected, while providing access to other APIs under the category by selecting them . For example: If you want to create an “Operator” role who is able to change his own password, but not see or change the settings for your installation’s integration with remote AAA servers, or create new users and roles, you would select the “AAA” category name, but uncheck the “Remote Authentication Server Integration API” and “Users and Role Management API” checkboxes.
For each role with a selected category, the Roles page also lets you define permissions to each underlying functional API:
-
Read permission lets the user see and interact with the objects controlled by that API, but not change or delete them.
-
Write permission lets the user see and change the objects controlled by that API, but not delete them.
-
Delete permission gives the user role delete privileges over the objects controlled by that API. It is useful to remember that delete permission does not override basic limitations set by the Crosswork platform and it applications.
Although you can mix permissions as you wish:
-
If you select an API for user access, you must provide at least “Read” permission to that API.
-
When you select an API for user access, Cisco Crosswork assumes that you want the user to have all permissions on that API, and will select all three permissions for you, automatically.
-
If you uncheck all of the permissions, including “Read”, Cisco Crosswork will assume that you want to deny access to the API, and unselect it for you.
Best Practices:
Cisco recommends that you follow these best practices when creating custom user roles:
-
Restrict Delete permissions in roles for admin users with explicit administrative responsibility for maintenance and management of the Crosswork deployment as a whole.
-
Roles for developers working with all the Cisco Crosswork APIs will need the same permissions as admin users.
-
Apply at least Read and Write permissions in roles for users who are actively engaged in managing the network using Cisco Crosswork.
-
Give read-only access to roles for users who only need to see the data to help their work as system architects or planners.
The following table describes some sample custom user roles you should consider creating:
|
Role |
Description |
Categories/API |
Privileges |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Operator |
Active network manager, triggers Playbooks in response to KPI alerts |
All |
Read, Write |
|
Monitor |
Monitors alerts only |
Health Insights, Inventory, Topology |
Read only |
|
API Integrator |
All |
All |
All |
 Note |
Admin role needs to include permissions for Read, Write, and Delete, while read-write roles need to include both Read and Write permissions. Using Zero Touch Provisioning features requires access to all ZTP APIs. |
Create User Roles
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose tab. The Roles window has a Roles table on the left side and a corresponding Global API Permissions tab on the right side which shows the grouping of user permissions for the selected role. |
|
Step 2 |
On the Roles table, click |
|
Step 3 |
Enter a unique name for the new role. |
|
Step 4 |
To define the user role's privilege settings, select the Global API Permissions tab and perform the following:
|
|
Step 5 |
Click Save to create the new role. To assign the new user role to one or more user IDs, edit the Role setting for the user IDs (see Edit User Roles). |
Clone User Roles
Cloning an existing user role is the same as creating a new user role, except that you need not set privileges for it. If you like, you can let the cloned user role inherit all the privileges of the original user role.
Cloning user roles is a handy way to create and assign many new user roles quickly. Following the steps below, you can clone an existing role multiple times. Defining the cloned user role's privileges is an optional step; you are only required to give the cloned role a new name. If you like, you can assign it a name that indicates the role you want a group of users to perform. You can then edit the user IDs of that group of users to assign them their new role (see Manage Users). Later, you can edit the roles themselves to give users the privileges you want (see Edit User Roles).
 Note |
Some API permissions are predefined in the system admin role and remain unchanged in the cloned role. For example, the system admin role includes the default Read and Write permissions for the Alarms & Events API. These permissions are not configurable for both, original, and cloned admin roles. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose tab. |
|
Step 2 |
Click an existing role. |
|
Step 3 |
Click |
|
Step 4 |
Enter a unique name for the cloned role. |
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Define the role's settings:
|
|
Step 6 |
Click Save to create the newly cloned role. |
Edit User Roles
Users with administrator privileges can quickly change the privileges of any user role other than the default admin role.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose tab. |
|
Step 2 |
Click and select on an existing role from the left side table. The Global API Permissions tab on the right side displays the permission settings for the selected role. |
|
Step 3 |
Define the role's settings:
|
|
Step 4 |
When you are finished, click Save. |
Delete User Roles
Users with administrator privileges can delete any user role that is not the default admin user role or that is not currently assigned to a user ID. If you want to delete a role that is currently assigned to one or more user IDs, you must first edit those user IDs to assign them to a different user role.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose tab. |
|
Step 2 |
Click on the role you want to delete. |
|
Step 3 |
Click |
|
Step 4 |
Click Delete to confirm that you want to delete the user role. |
Global API Permissions
The Roles window lets users with the appropriate privileges define custom user roles.
The following table is an overview of the various Global API Permissions in Cisco Crosswork:
|
Category |
Global API Permissions |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
AAA |
Password Change |
Provides permission to manage passwords. The READ and WRITE permissions are automatically enabled by default. The DELETE permission is not applicable to the password change operation (You cannot delete a password, you can only change it.) |
|
|
Remote Authentication Servers Integration |
Provides permission to manage remote authentication server configurations in Crosswork. You must have READ permission to view/read configuration, and WRITE permission to add/update the configuration of any external authentication server (e.g. LDAP, TACACS) into Crosswork. The Delete permissions are not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
Users and Roles Management |
Provides permission to manage users, roles, sessions, and password policies. Supported operations include "Create new user/role", "Update user/role", "Delete a user/role", "Update task details for a user/role", "Session management (Idle-timeout, max session..)", "update password policy”, “get password tooltip help text”, “get active sessions”, etc. The READ permission allows you to view the content. The WRITE permission allows you to create and update. The DELETE permission allows you to delete a user or role. |
||
|
Know my role - Read only |
Enables the logged in users to understand their permissions, or get new permissions. WRITE and DELETE permissions are not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
User Preferences |
Allows you to manage the dashlets in the homepage. The READ permission allows you to view dashboards, WRITE permission allows your to edit dashboards, DELETE permission allows you to delete dashboards. |
||
|
Administrative Operations |
External Notification Subscription |
Allows you to subscribe or unsubscribe the external kafka notification streaming. The READ permission allows you to view the list of subscriptions. The WRITE and DELETE permissions allows you to edit and delete the subscriptions respectively. |
|
|
RESTCONF Notification Subscription |
Allows you to subscribe or unsubscribe the RESTCONF notification streaming (websocket and connectionless). The READ permission allows you to view the list of subscriptions. The WRITE and DELETE permissions allows you to edit and delete the subscriptions respectively. |
||
|
Device Monitoring |
Device Inventory RESTCONF |
Responsible for the retrieving the inventory information. The READ permission allows you to get all the inventory data such as nodes,termination points, equipments, and modules. The WRITE and DELETE permissions are not applicable for this API as there is no support for configuration-related operations. |
|
|
Performance Monitoring Dashboards |
The READ permission allows displaying any metrics on the Crosswork Network Controller homepage, dashboard window, and deep inventory. The WRITE and DELETE permissions are not applicable for this API. |
||
|
Performance Monitoring Policies |
Allows you to manage monitoring policies. The READ permission allows you to view the monitoring policies. The WRITE permission allows you to create and update monitoring policies. The DELETE permission allows you to delete monitoring policies. |
||
|
Performance Monitoring RESTCONF |
Responsible for the retrieving the device performance metrics. The READ permission allows you to get the metrics information such as CPU, temperature, CRC, and interface utilization. The WRITE and DELETE permissions are not applicable for this API as there is no support for configuration-related operations. |
||
|
Alarms and Events |
Alarm Notification Policies |
The READ permission allows you to read system/network, and device alarm notification policies. The WRITE permission allows you to create system/network, and device alarm notification policies. |
|
|
Alarm Settings |
The READ permission allows you to view alarm settings. The WRITE permission allows you to view and update alarm settings. |
||
|
Alarm Suppression Policies |
The READ permission allows you to view a suppression alarm policy. The WRITE permission allows you to create, update and delete a suppression alarm policy. |
||
|
Alarm & Events |
Allows you to manage alarms. The READ permission allows you to get events/alarms according to request criteria, get the list of Syslog destinations, and get the list of trap destinations. The WRITE permission allows you to set a response for when an alarm is raised, acknowledged, or unacknowledged, create/raise an event, update the event info manifest, and add notes to alarms. The DELETE permission allows you to delete REST destinations, Syslog destinations and trap destinations. |
||
|
Alarm and Events RESTCONF |
Responsible for performing alarms related operations. The READ permission allows you to get all the alarm data (system,network & device). The WRITE permission allows you to acknowledge, unacknowledge, and clear alarms. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
Automated Assurance DSS Instance |
Data Store Service Administrator Settings |
Allows Administrators to view Datastore storage info (READ permission) and run diagnostic tests for external storage (WRITE permission). |
|
|
Data Store Service API |
Allows you to use external storage for longer retention, and to manage external datastore used by Service Assurance for archiving service metrics data. The READ permission allows you to get storage provider information, check storage stats, etc. The WRITE permission allows you to sync the local CW datastore with the external storage and run diagnostics. The DELETE permission allows you to delete an external storage provider. |
||
|
CNC |
CAT FP Deployment Manager APIs |
Allows you to manage function pack upload and deployment. The READ permission enables you to get the list of packages, files, and deployment information. The WRITE permission allows you to upload/deploy/un-deploy a package/function pack/file. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
|
|
CAT Inventory RESTCONF APIs |
North Bound Interface (NBI) RESTCONF interface for the CAT services inventory data (from CAT to external consumers). The READ permission allows you to fetch the services information from CAT. The WRITE permission allows you to invoke operations APIs to retrieve the service information from CAT. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
CAT ISTP REST APIs |
System use only. The READ/WRITE permissions are mandatory for CAT UI/ISTP to function. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
CAT Service Overlay |
Primarily used to investigate issues in the overlay. Only READ permission is applicable. |
||
|
CAT UI |
Mandatory APIs that enable CAT UI to fetch all NSO services and resources. The READ permission allows you to fetch and display all service information. The WRITE permission allows you to commit service assurance information. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
NSO Connector APIs |
Allows you to perform services resync, full-resync, change log-level and return service HA status. The READ permission allows you to check the service status. The WRITE permission is required for all other operations. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
OAM Service APIs |
Not Applicable |
||
|
Change Automation |
Administration APIs |
Provides administrative control to manage job scheduling, manage override credentials, and configuration of user roles for playbook executions. The READ permission allows you to check the status and fetch the information. , while the WRITE permission allows you to make changes. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
|
|
Application APIs |
Allows you to manage the Change Automation tasks (for example, schedule playbook executions, execute playbooks, update playbook jobs, check playbook executions status, check playbook job-set details, list supported YANG modules, etc.) The READ permission allows you to view the applicable information (for example, check the job status, fetch job details, etc.). The WRITE permission is required for playbook job scheduling/execution. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
Playbook APIs |
Allows you to manage playbooks. The READ permission allows you to retrieve playbooks, params, and policy specs. The WRITE permission allows you to import/export, and generate playbooks. The DELETE permission enables you to delete playbooks. |
||
|
Play APIs |
Allows you to manage plays. The READ permission allows you to fetch or view plays, while the WRITE permission allows you to create, update or import a play. The DELETE permission allows you to delete a play. |
||
|
Collection Infra |
Collection APIs |
Permissions for APIs to manage collection jobs. Based on the READ/WRITE/DELETE permissions, you can view collection jobs, create/update new collection jobs (external), or delete existing collection jobs. System collection jobs (data collection setup internally for Crosswork consumption) cannot be modified irrespective of these permissions (permitted for Administrators only), but users with the READ permission will be able to view the details of all collection jobs including system collection jobs. For most users, READ-only permissions would be enough as it enables them to view Collection jobs detail (request and status) and actual data collection status/metrics per device/sensor path level. |
|
|
Data Gateway Manager APIs |
Permissions to perform CRUD operations on Destinations, Data Gateways, Custom Packages, etc. The READ permission allows you to view the data, while the WRITE permission allows you to perform these actions:
|
||
|
Crosswork Optimization Engine |
OPTIMA Analytics |
Allows you to manage analytics in Crosswork Optimization Engine. The READ permission allows you to view/export historical data. The WRITE permission enables you to change the Traffic Engineering Dashboard settings. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
|
|
OPTIMA Analytics Service |
Allows you to manage analytics service in Crosswork Optimization Engine. The READ permission enables you to get LSP events data, LSP utilization, LSP SR-PM metric, Link SR-PM and underutilized LSPs. The WRITE and DELETE permissions are not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
Optima Engine RESTCONF and Optima Engine RESTCONF API for backwards compatibility |
Allows you to customize the RESTCONF API permissions in Crosswork Optimization Engine. The READ permission grants access to perform these actions:
The WRITE permission grants access to perform these actions:
The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
Optimization Engine UI |
Allows you to manage SR policies, RSVP tunnels, LCM, BWoPT, BWoD, Traffic Engineering settings, and Preview policies. The READ permission allows you to view deployed policies, settings, routes, LCM domain config/data, service overlay data, path queries, dashboard metrics, etc. The WRITE permission allows you to configure LCM, BWoD, BWopt, deploy policies, preview Crosswork Optimization Engine-managed policies, etc. The DELETE permission allows you to delete SR policies, RSVP tunnels, remove affinity mapping, and delete LCM domains. |
||
|
Crosswork Optimization Engine v2 |
Optimization Engine RESTCONF API v2 |
Allows you to customize the RESTCONF interface permissions in Crosswork Optimization Engine. The READ permission enables you to fetch L2 and L3 topology details, and Segment Routing Policy details. The WRITE permission allows you to fetch policy routes, provision/modify/delete/preview SR policies, and manage LCM configuration. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
|
|
Data Gateway Global Settings |
Data Gateway Global Parameters API |
There are certain parameters in the data gateway, which can be changed globally across all gateways in a Deployment. The READ permission allows you to view the data, while the WRITE permission is required to reset/update the data. |
|
|
Data Gateway Global Resources Reset API |
Allows you to reset updates done to the Global Parameters. The READ permission allows you to view the data, while the WRITE permission resets the data. |
||
|
Data Gateway Global Resources Update API |
Allows you to update the Global Parameters. The READ permission allows you to view the data, while the WRITE permission updates the data. |
||
|
Data Gateway Troubleshooting |
Data Gateway Reboot API |
Reboots a data gateway. The WRITE permission allows you to reboot the data gateway. |
|
|
Data Gateway Showtech API |
Generates and downloads showtech logs for a data gateway. The READ permission allows you to view showtech, while WRITE permission generates showtech. Write Permission allows u to generate showtech |
||
|
Health Insights |
Health Insights APIs |
Allows you to manage Health Insights KPIs. The READ permission allows you to view all KPIs, KPI profiles, job details, alerts, etc. The WRITE permission allows you to create or update KPIs and KPI profiles, enable/disable KPI profiles, link KPIs to playbooks, etc. The DELETE permission allows you to delete custom KPIs and KPI profiles. |
|
|
Inventory |
Inventory APIs |
Allows you to manage inventory. The READ permission allows you to
The WRITE permission allows you to
The DELETE permission allows you to
|
|
|
Platform |
Platform APIs |
The READ permission allows you to fetch the server status, cluster node information, application health status, collection job status, certificate information, backup and restore job status, etc. The WRITE permission allows you to
The DELETE permission allows you to delete a VM (identified by an ID) and remove applications from the software repository. |
|
|
Grouping APIs |
Grouping management and Topology groups selection tree. The READ permission allows you to view topology UI, while the WRITE permission allows you to create/update groups. The DELETE permission is needed to delete groups from the Grouping Management page.
|
||
|
View APIs |
Views Management in Topology. The READ permission allows you to see views, the WRITE permission allows you to create/update views, and the DELETE permission will enable delete capabilities. |
||
|
Topology |
Geo |
Provides geo service for offline maps. The READ permission allows you to use Geo Map in offline mode, the WRITE allows you to upload Geo Map files, and DELETE permission allows you to delete the map files in settings. |
|
|
Topology |
Allows you to manage topology pages, settings, or any other pages that uses the Topology visualization framework. The READ permission is mandatory for topology visualization. The WRITE permission enables you to update topology settings, and the DELETE permission allows you to delete a topological link if it goes down. |
||
|
Probe Manager |
Probe Manager APIs |
The READ permission allows you to retrieve the status of a probe session for a given service. The WRITE permission allows you to reactivate a probe. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
|
|
Proxy |
Crosswork Proxy APIs |
Permissions to manages Crosswork proxy APIs for NSO Restconf NBI. The READ permission allows all GET request for NSO REST conf NBI, the WRITE permission allows POST/PUT/PATCH operation, and the DELETE permission enables all delete APIs. |
|
|
Software Image Management |
SWIM |
Allows you to upload images to the SWIM repository, distribute them to devices and install them. The READ permission allows you to list all images from the SWIM repository, view image information from a device, and check the details of any SWIM job. The WRITE permission allows you to upload/distribute and perform all install-related operations. The DELETE permission allows you to delete copied images from a device. You require WRITE/DELETE permission to execute software install/uninstall playbooks in Change Automation. |
|
|
Service Health |
Archiver APIs |
The READ permission allows you to
The WRITE/DELETE permissions are not applicable for these APIs. |
|
|
Assurance Graph Manager APIs |
The READ permission allows you to:
The WRITE/DELETE permissions are not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
CAT SH UI |
The READ permission allows you to:
The WRITE/DELETE permissions are not applicable for these API. |
||
|
Config Manager APIs |
The READ permission allows you to:
The WRITE permission allows you to update the maximum number of services supported for Total and Advanced monitoring. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
||
|
Heuristic Package Manager APIs |
Permissions for Heuristic package management and to manage plugins and config profiles for Service Assurance. The READ permission allows you to export heuristic packages, query for heuristic package details (Rules, Profiles, SubServices, Metrics, Plugins), and query for assurance options. The WRITE permission allows you to import heuristic packages and perform all create/update operations. The DELETE permission allows you to perform delete operations (for example, delete the RuleClass, MetricClass, etc.) |
||
|
Metric Scheduler APIs |
Not Applicable |
||
|
Zero Touch Provisioning |
Config Service |
The READ permission allows you to
The WRITE permission allows you to
The DELETE permission allows you to delete config files and scripts uploaded in the ZTP config repository. |
|
|
Image Service |
The READ permission allows you to
The WRITE permission allows you to update relevant metadata associated with specific image files stored in the ZTP image repository. The DELETE permission allows you to delete image files uploaded in the ZTP image repository |
||
|
ZTP Service |
Allows you to manage the ZTP devices and profiles - add/update/delete into Crosswork. The READ permission enables you to fetch ZTP devices, serial number/OVs, profiles, sample data CSV, list ZTP devices, profiles, and export ZTP devices and metadata. The WRITE permission allows you to add ZTP devices, serial numbers/OVs, profiles and add/update the ZTP device's attributes. The DELETE permission allows you to delete ZTP devices, profiles, serial numbers/ownership vouchers. |
||
|
Licensing |
Common Licensing Management Service (CLMS) APIs |
Permissions for APIs to manage license registration in Crosswork. The READ permission enables you to view Smart Licensing settings, registration status, and license usage while the WRITE permission is required to change any Smart Licensing setting such as register, re-register, de-register, renew a license etc. The DELETE permission is not applicable for these APIs. |
|
|
te-manager |
TE Auto Policy Binding Service |
The READ permission allows you to view individual or all TE criteria and policy templates. The WRITE permission allows you to create or update TE criteria, criteria expression, and policy templates, and to associate or disassociate TE criteria with policy templates and vice versa. The DELETE permission allows you to delete TE criteria, criteria expression, and policy templates, and remove any residual data associated with a service. |
Manage Active Sessions
As an administrator, you can monitor and manage the active sessions in the Cisco Crosswork UI, and perform the following actions:
-
Terminate a user session
-
View user audit log
 Attention |
|
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Active Sessions tab displays all the active sessions in the Cisco Crosswork with details such as user name, source IP, login time, and login method.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
To terminate a user session, click the
|
||
|
Step 3 |
To view audit log for a user, click the The Audit Log window is displayed for the selected user name. For more information on the Audit Logs, see View Audit Log. |
Manage WebSocket subscriptions
If you have subscribed to WebSocket subscriptions using JWT based authentication to authenticate and establish your connections, you can view these subscriptions in the Crosswork Network Controller UI. The types of subscriptions that are supported are:
-
Inventory
-
Alarm
-
Service Notification
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click WebSocket subscriptions. It displays details such as Subscription ID, Topic, Subscribed By, Subscription Time and Source IP.
|
||
|
Step 3 |
To delete a subscription, choose the subscription you want to remove and click the Delete icon. |

 Feedback
Feedback