Certificates
A certificate is an electronic document that:
-
identifies an individual, a server, a company, or entity
-
associates the entity with a unique public key, and
-
is digitally signed by an issuer (Certificate Authority or self-signed) to enable secure communication.
When a certificate is created with a public key, a matching private key is also generated. In TLS, the public key is used to encrypt data being sent to the entity and the private key is used to decrypt.
In a TLS exchange, a hierarchy of certificates is used to verify the validity of the certificate's issuer. This hierarchy is called a trust-chain and consists of 3 types of entities: a root CA certificate (self-signed), possibly multiple levels of intermediate CA certificates, and a server (or client) certificate (end-entity). The intermediate certificates act as a “link of trust” linking the server certificates to the CA’s root certificate and providing additional layers of security. The root certificate's private key signs and issues the next certificate in the chain. Subsequently, the private key for each certificate in the trust chain signs and issues the following certificate, continuing until the end entity certificate is signed. The end-entity certificate is the last certificate in the chain. It is used as a client or server certificate. For more details about these protocols, see X.509 Certificates and HTTPS.
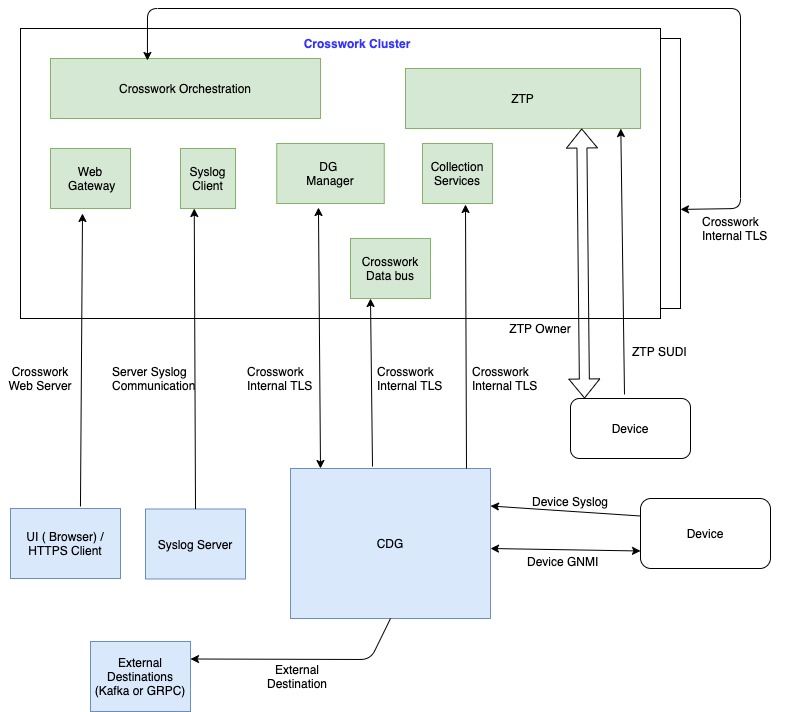
How are certificates used in Crosswork Network Controller?
Communication between Crosswork Network Controller applications and devices as well as between various Crosswork Network Controller components are secured using the TLS protocol. TLS uses X.509 certificates to securely authenticate devices and encrypt data to ensure its integrity from source to destination. Crosswork Network Controller uses both generated certificates and certificates uploaded by clients . Uploaded certificates can be purchased from Certificate authorities (CA) or created as self-signed certificates. For example, the Crosswork Network Controller VM-hosted web server and the client browser-based user interface communicate with each other using Crosswork Network Controller generated X.509 certificates exchanged over TLS.
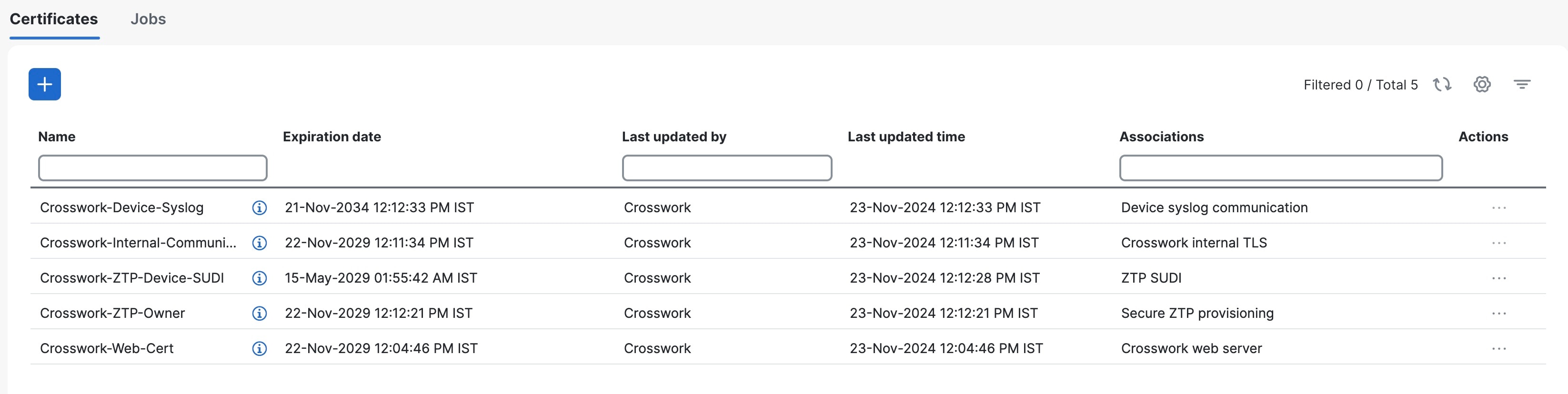
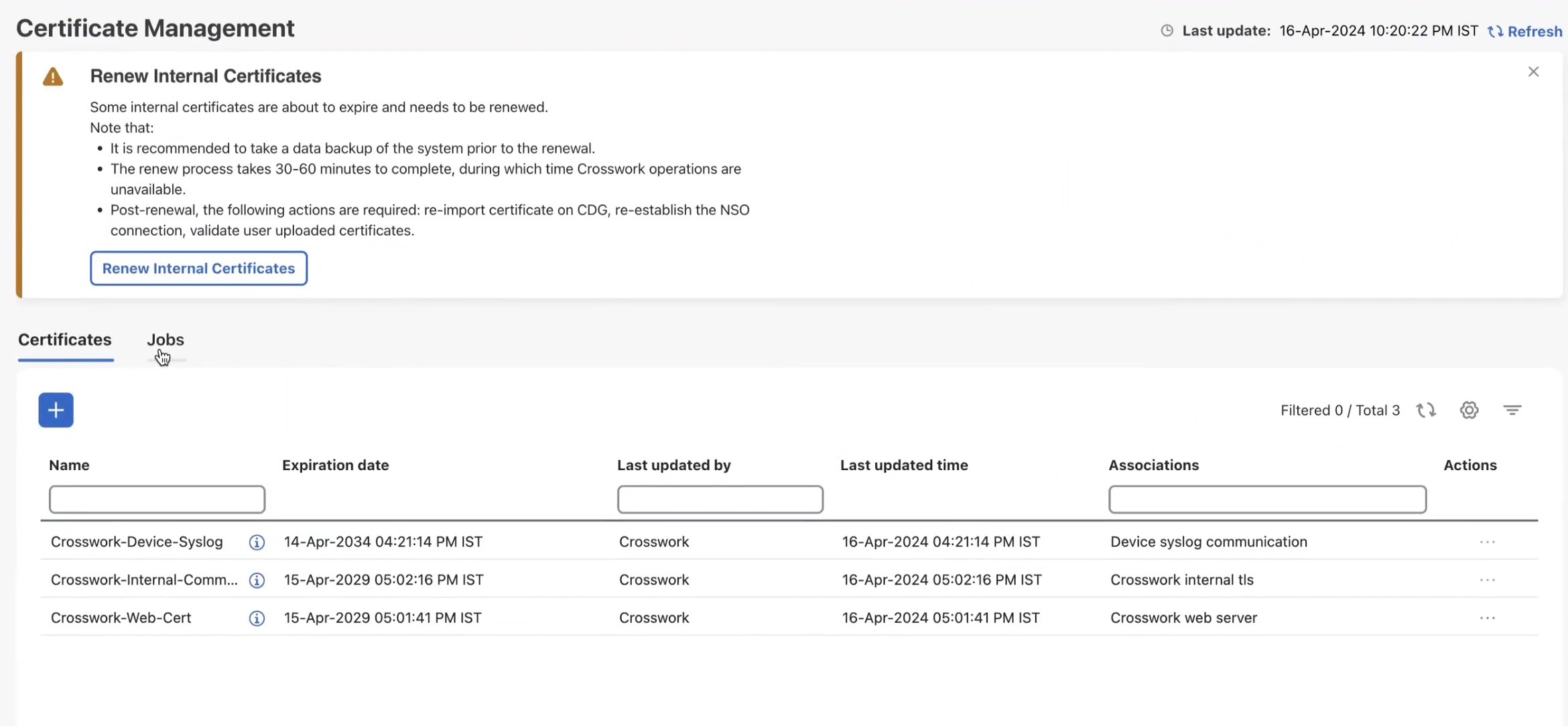
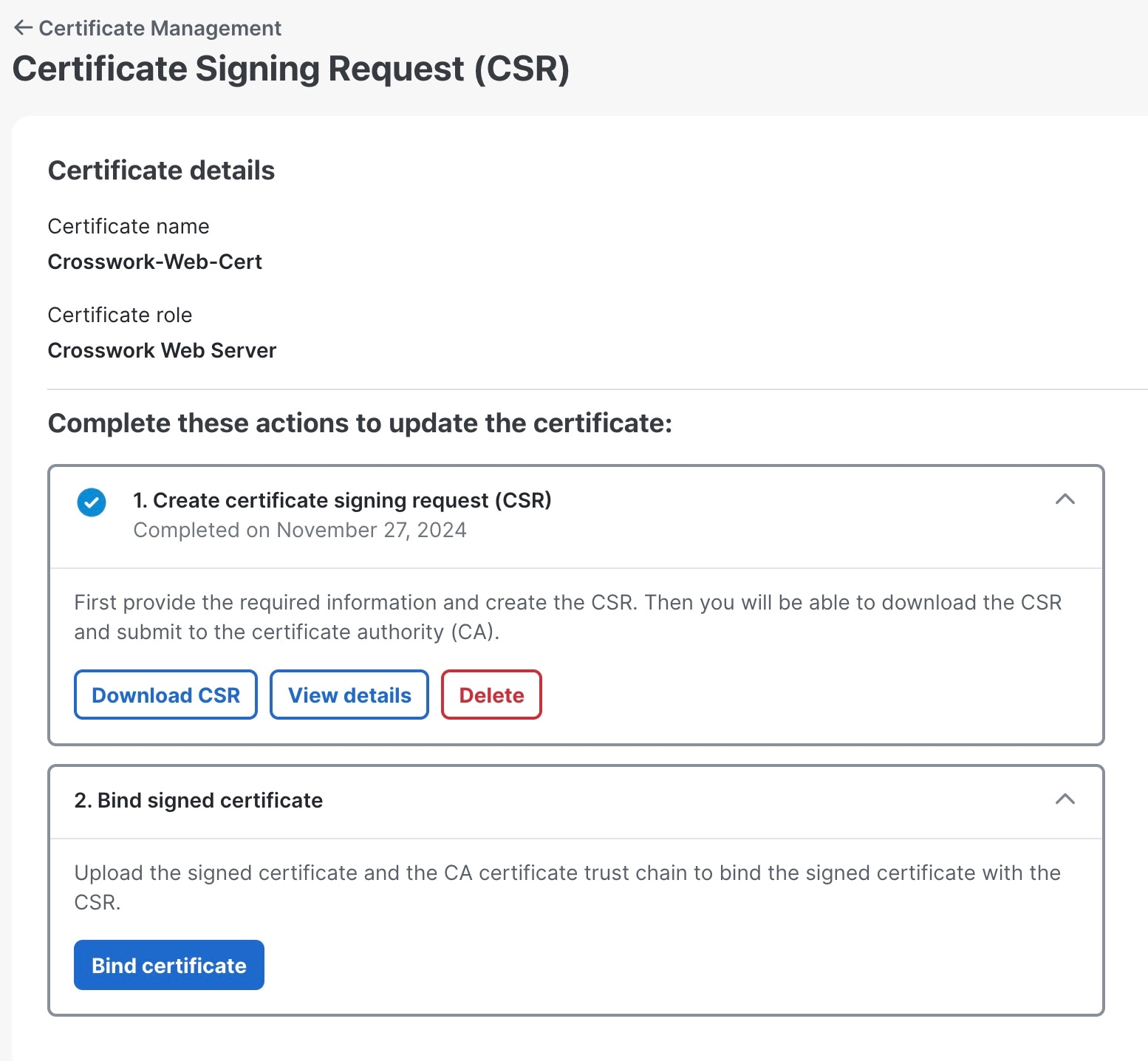
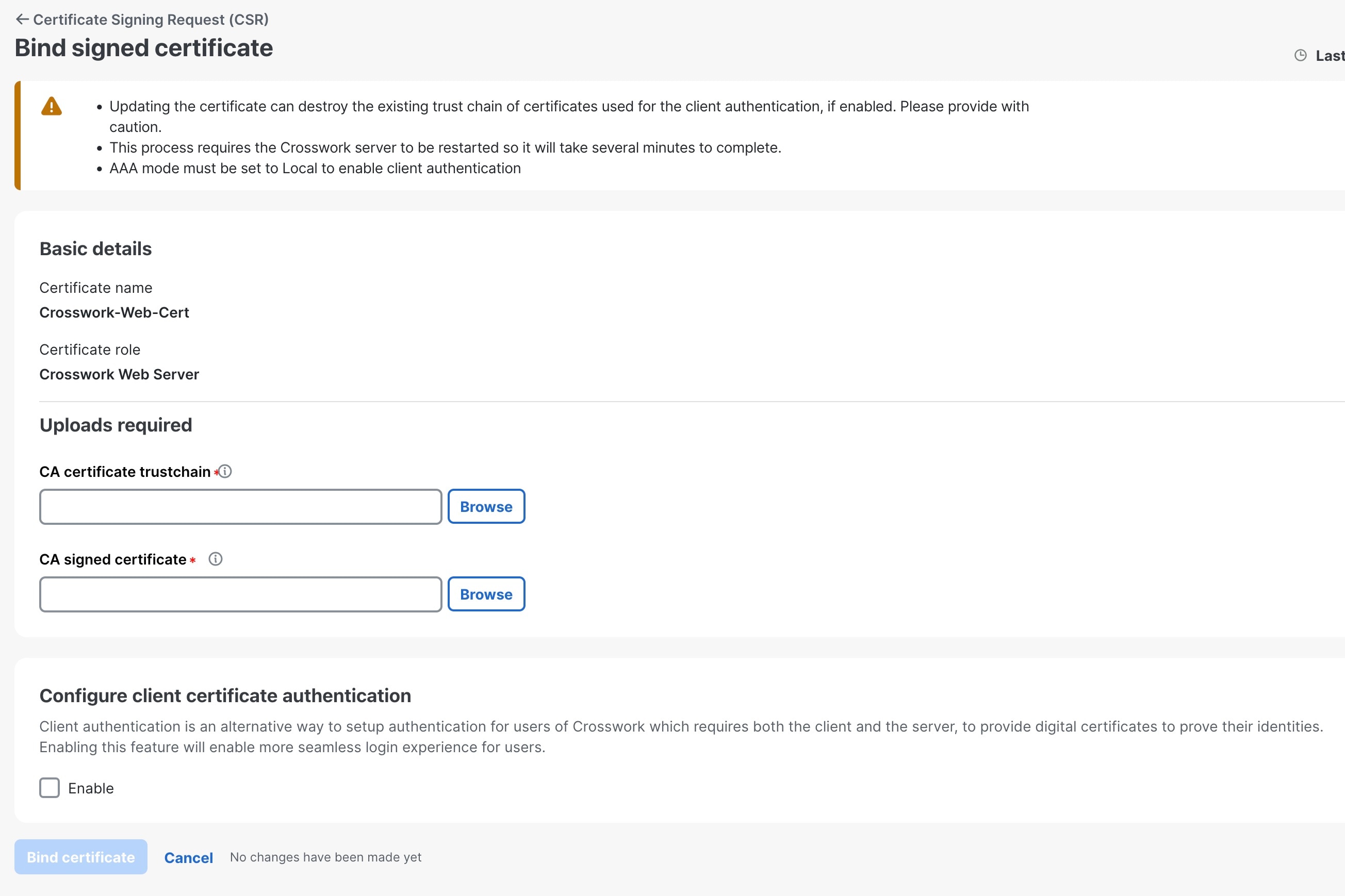
The Certificate Management window ( ) allows you to view, upload, and modify certificates. The following figure displays the default certificates provided by Crosswork Network Controller.

 Feedback
Feedback