Embedded Collectors in Crosswork Network Controller
Embedded Collectors are included in the single VM deployment of Crosswork Network Controller. The solution collects network data via collector services and transfers it to Cisco Crosswork or external destinations using Kafka or gRPC. It is bundled with Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure and the Element Management Functions application as part of a unified package.
Key attributes:
-
included with the bundled single VM deployment of Crosswork Network Controller
-
collects network data from the network devices using Embedded Collector services
-
transfers data to Crosswork or external systems
-
supports flexible data forwarding using Kafka or gRPC protocols, and
-
enables streamlined integration with the overall Crosswork Network Controller ecosystem.
Access method for the Embedded Collector UI
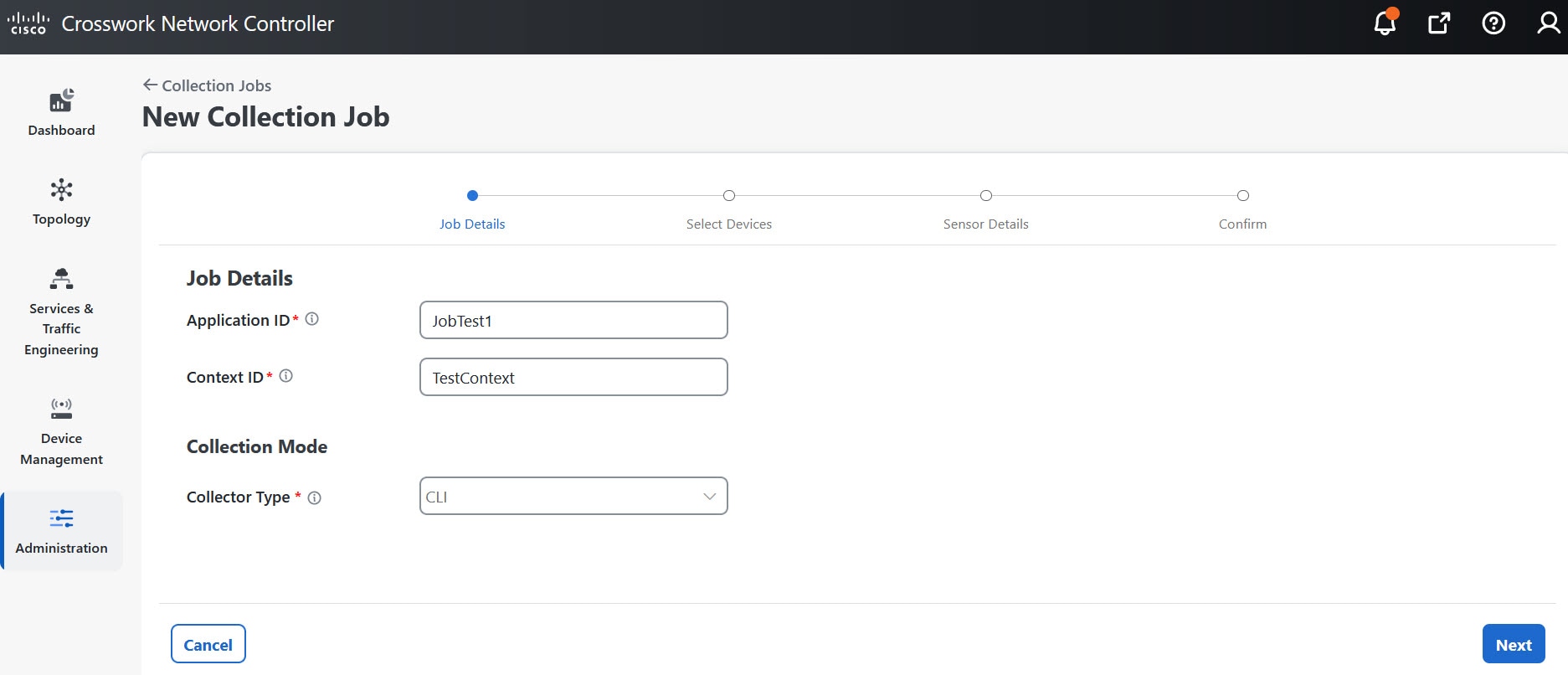
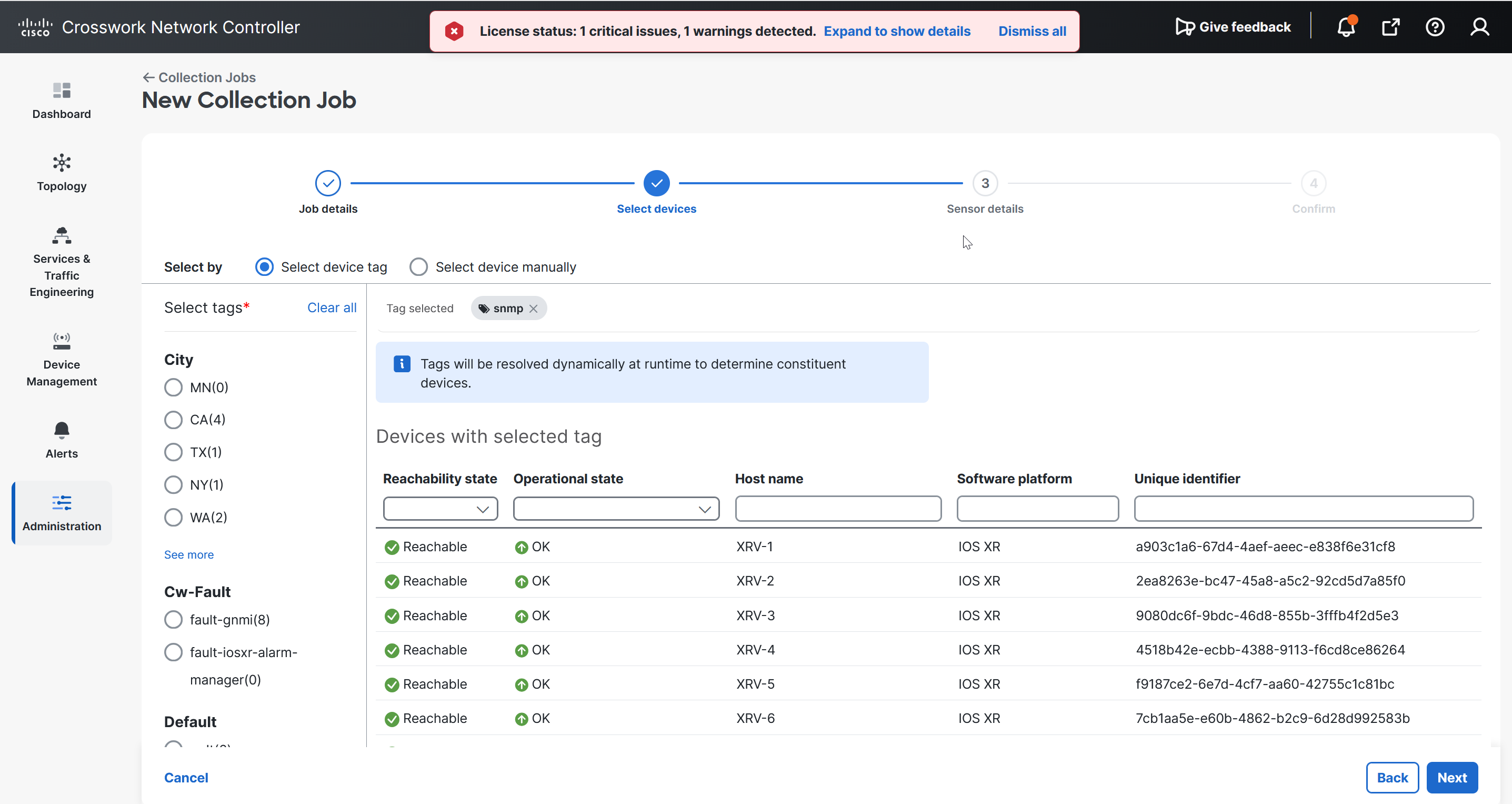
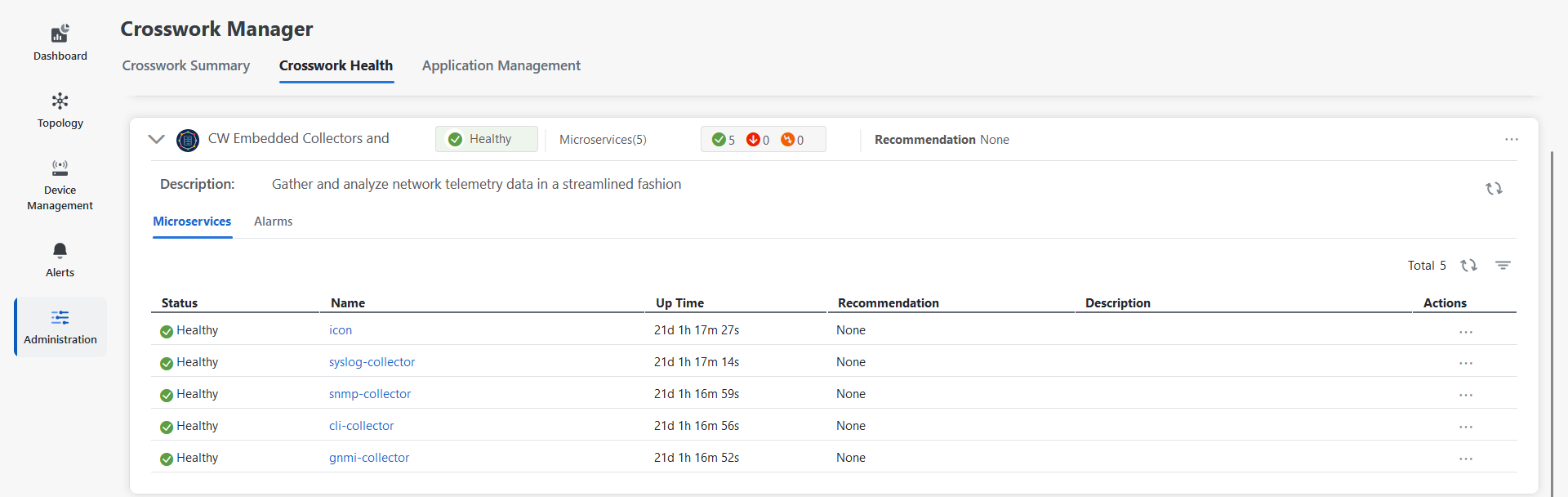
You can access the Embedded Collectors through the management view from the Data Collector(s) Global Settings page in the Crosswork Network Controller UI.
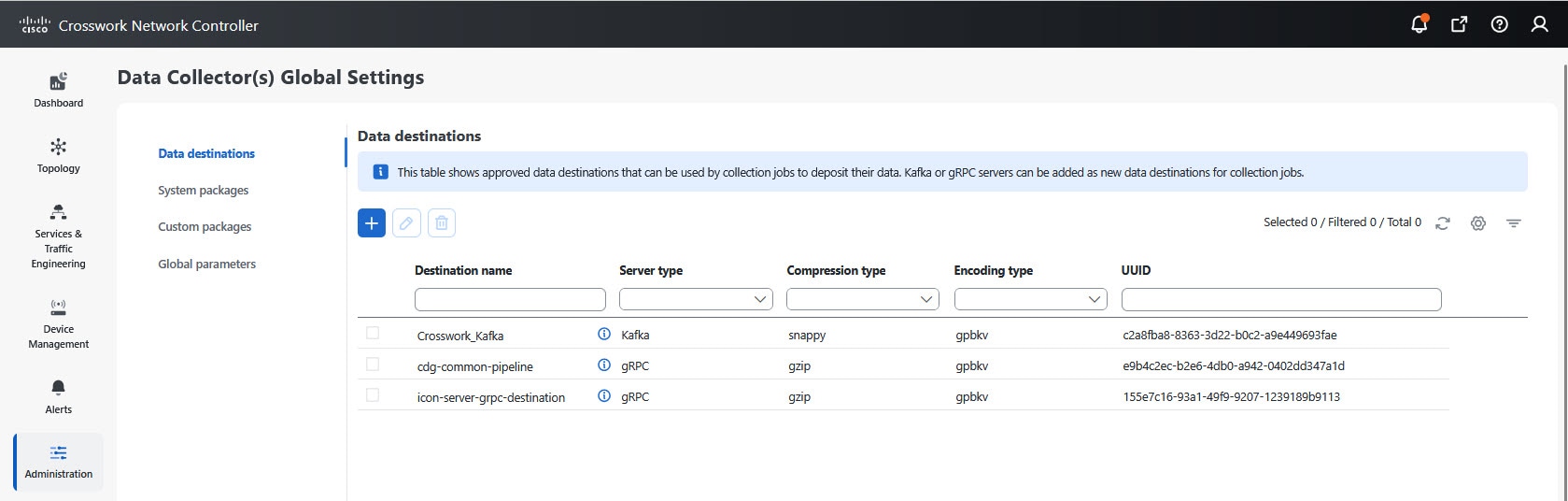
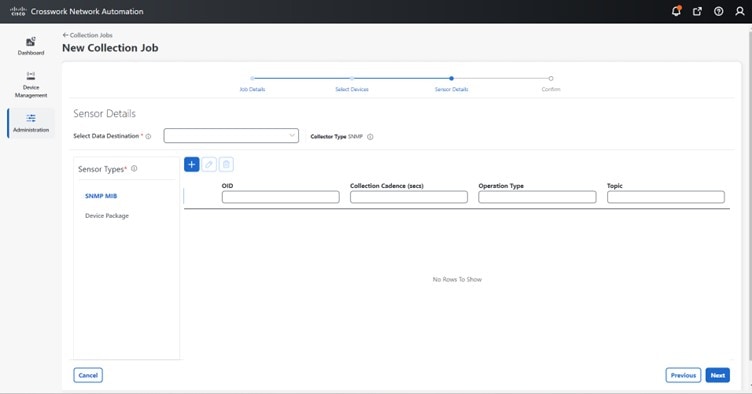
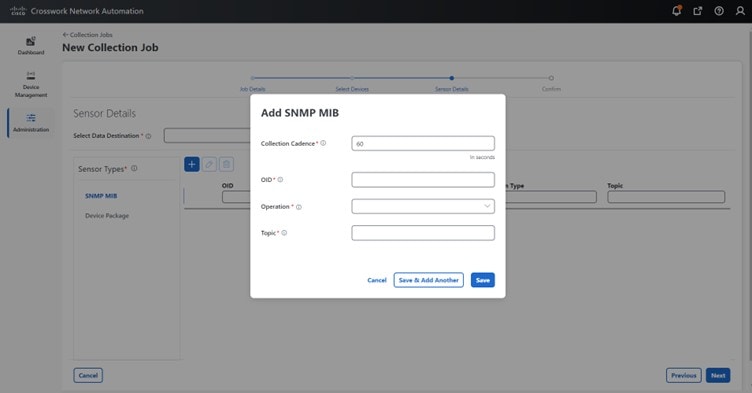
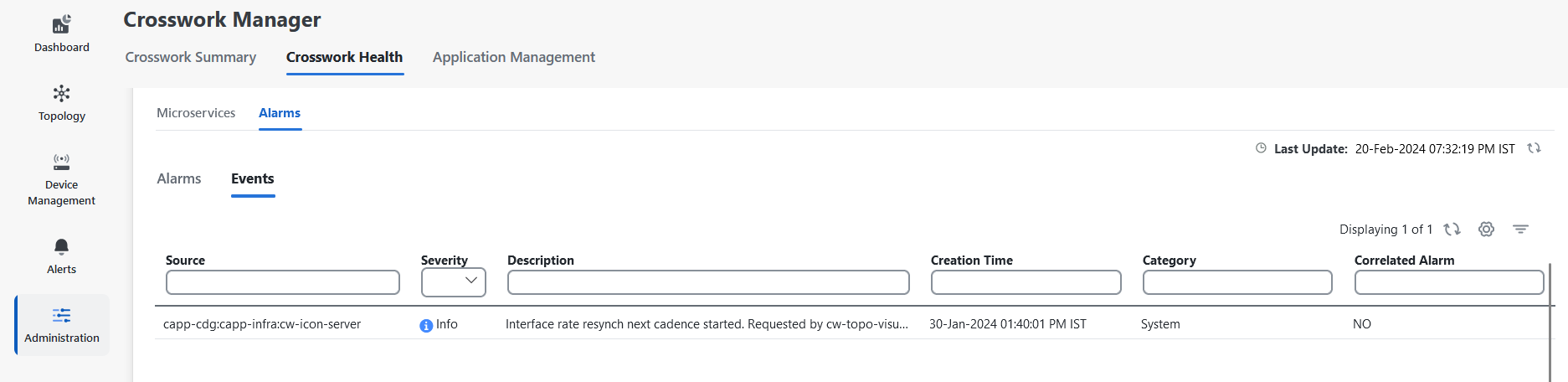
The Data Collector(s) Global Settings page allows you to perform the following administrative operations:
-
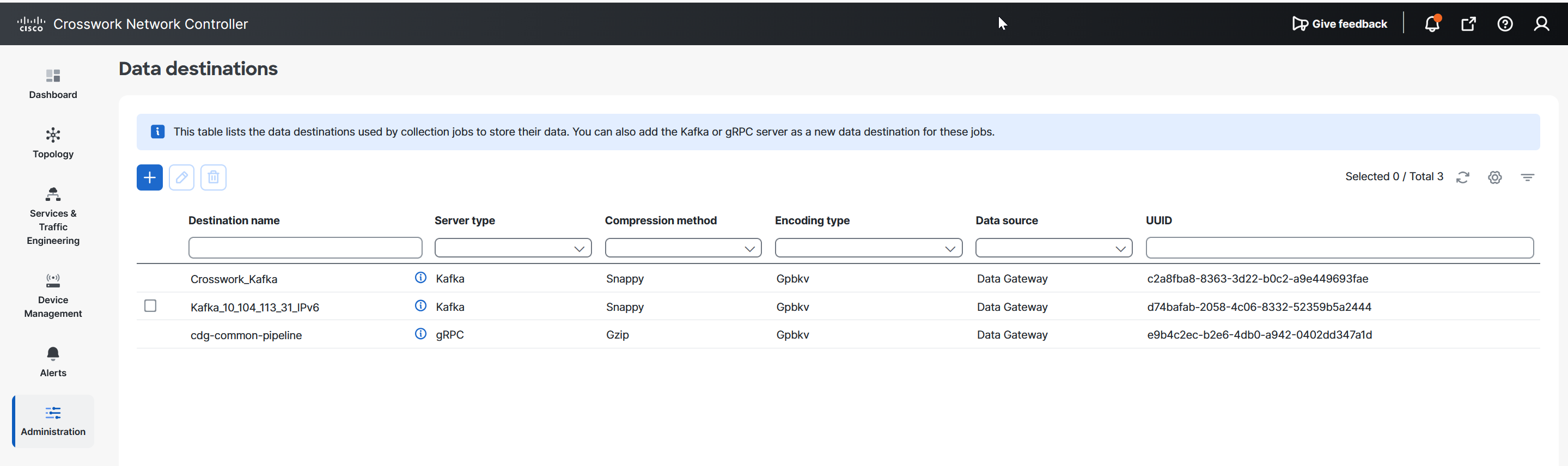
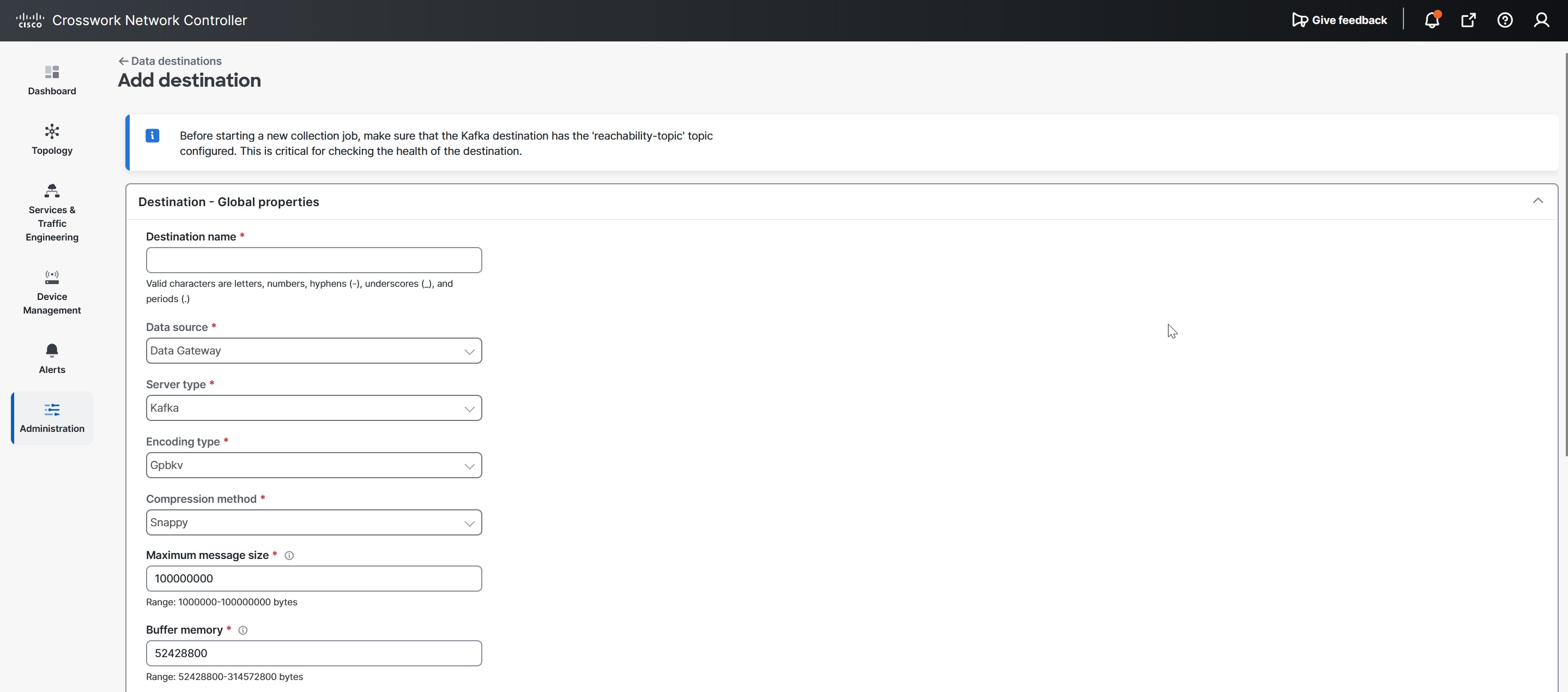
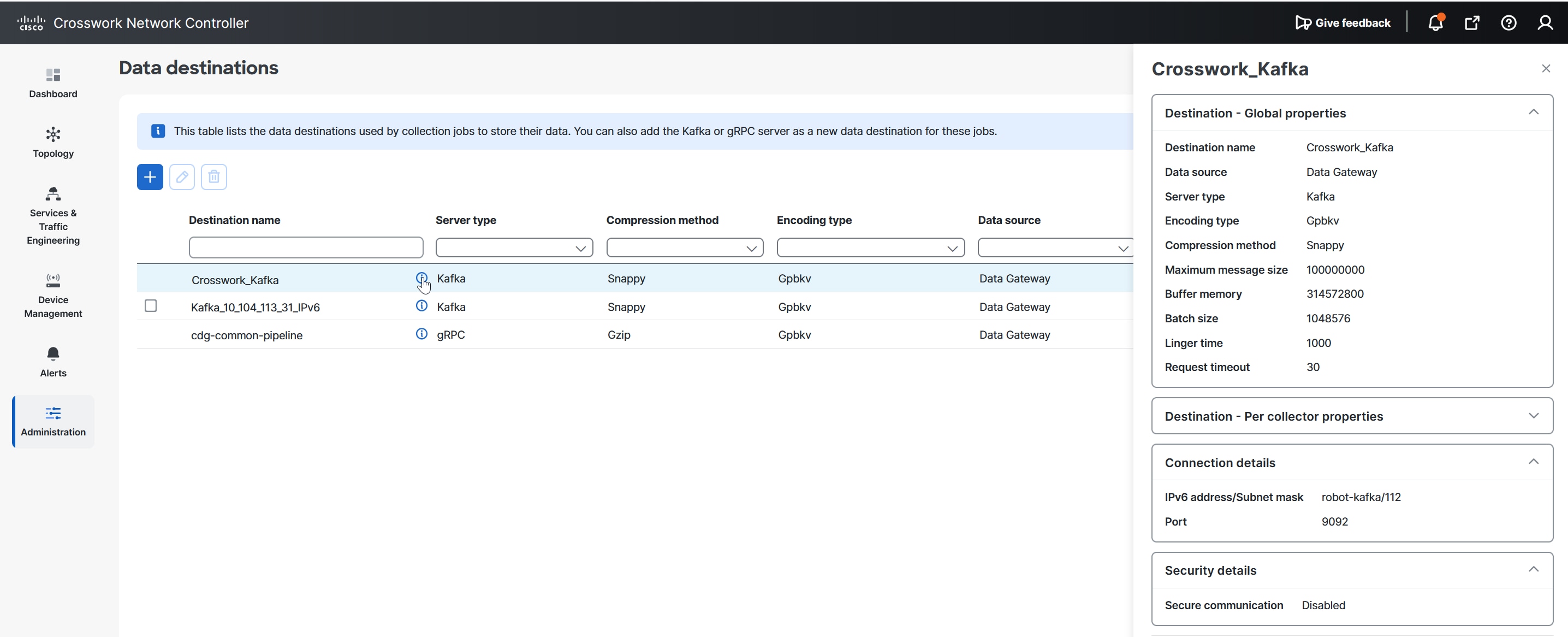
Data destinations: After collecting the telemetry data, the collectors deposit it to an internal or external data destination. By default,
Crosswork_Kafkais an internal data destination. You can define the external destinations using the Cisco Crosswork UI or APIs.To send data to external destinations using collection jobs, you must have an additional license. Make sure that the appropriate license is activated before configuring collection jobs. For the licensing details, see Licensing requirements for external collection jobs.
-
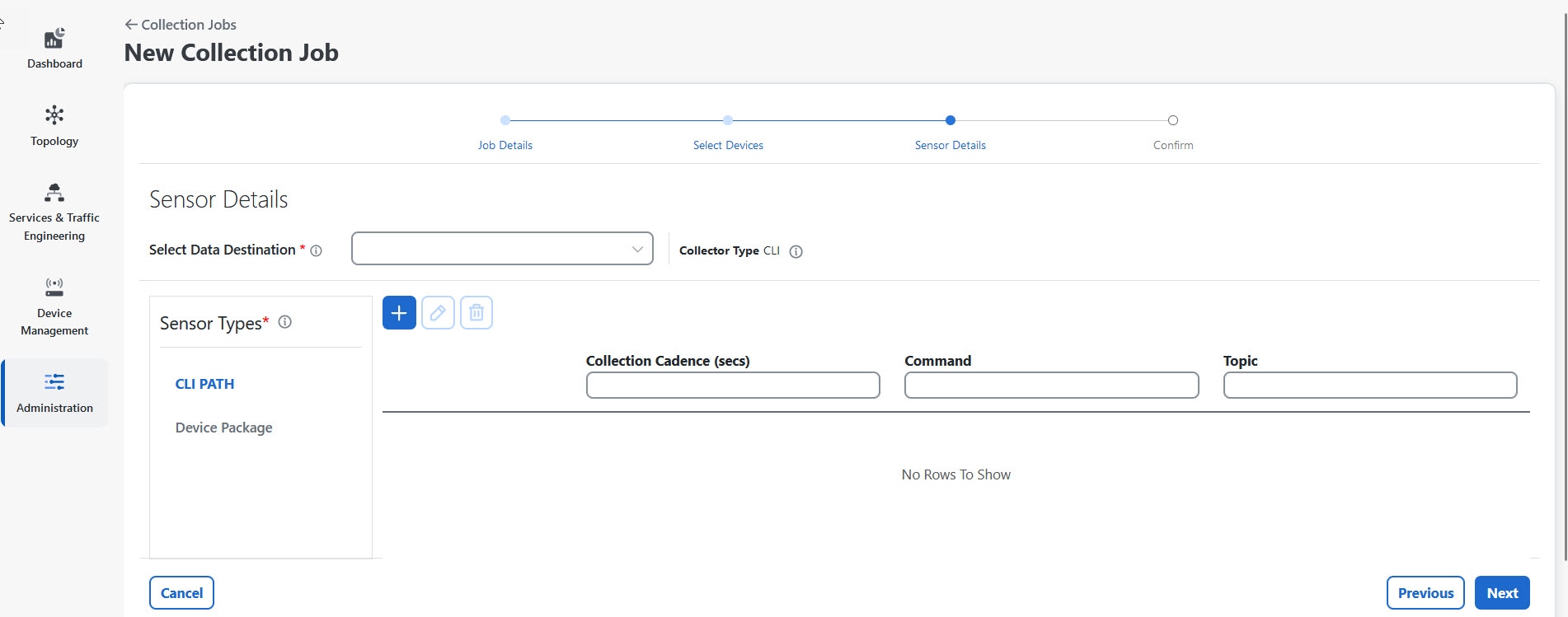
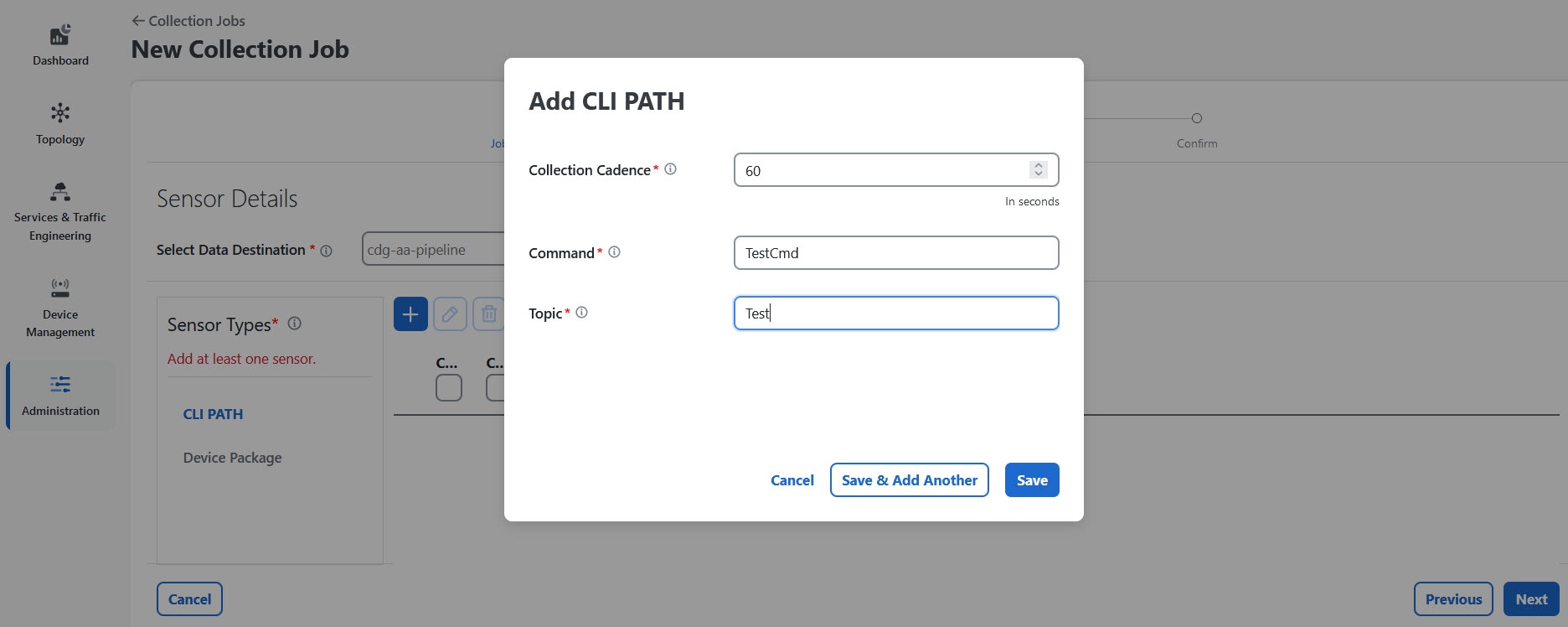
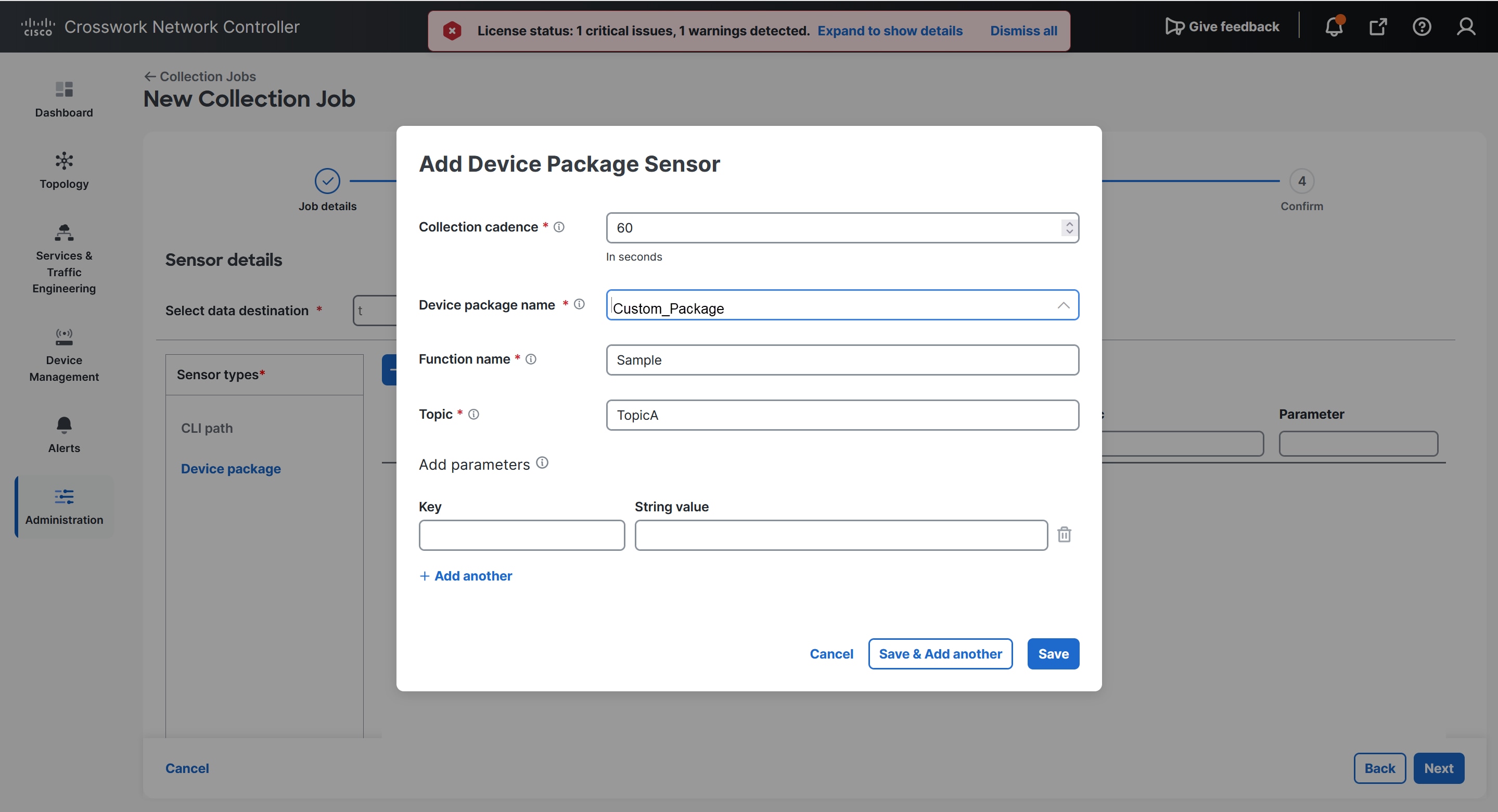
Device packages: By using device packages, the collectors can extend the data collection capabilities for both Cisco applications and third-party devices. The collectors support system and custom packages.
-
System packages: The system device package includes several installation files that are delivered via an application-specific manifest file. Usually, the manifest file is in JSON format.
-
Custom packages: The collectors user interface enables you to configure the port numbers of the collector pods. These port numbers affect the data collection services.
-
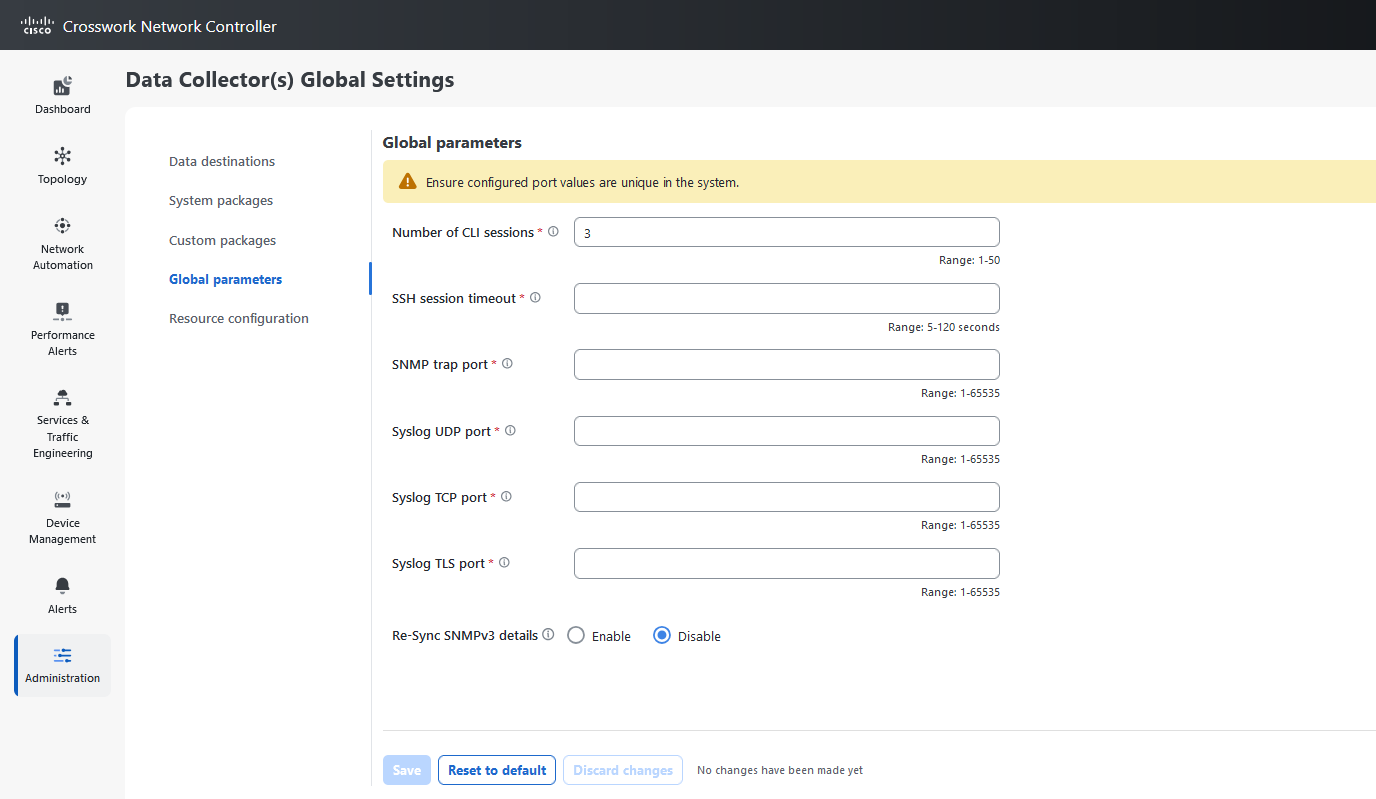
Global parameters: The collectors user interface allows enables you to configure the port numbers of the collector pods, which affect the data collection services. From this window, you can also enable the resync operation that automatically syncs the USM details whenever change occurs.
-

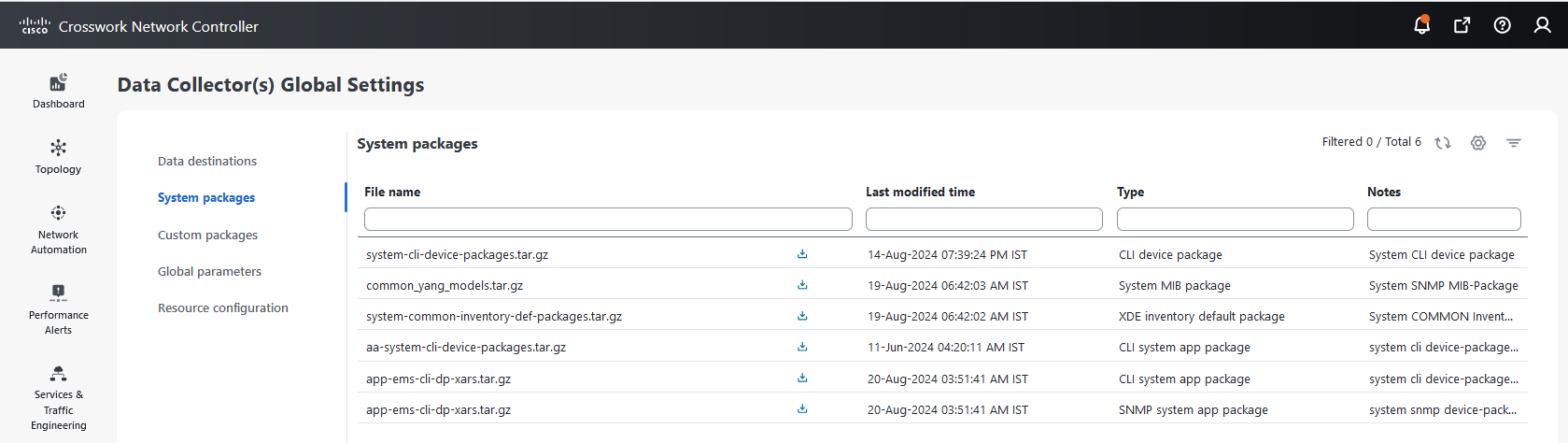
 located next to the package name in the File Name column.
located next to the package name in the File Name column.



 Feedback
Feedback