Audio Video Bridging
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Introduction to Audio Video Bridging Networks
Information about Audio Video Bridging (AVB)
Audio and video equipment deployments have traditionally been analog single-purpose point-to-point one-way links. Migration to digital transmission also continued to retain the point-to-point one-way links architecture. The dedicated connection model resulted in a mass of cabling in professional and consumer applications, which was hard to manage and operate.
In order to accelerate the adoption to Ethernet based audio/video deployments in an interoperable way IEEE came up with the IEEE Audio Video Bridging standards - IEEE 802.1BA. This defines a mechanism where endpoints and the network will function as a whole to enable high quality A/V streaming across consumer applications to professional audio-video over an Ethernet infrastructure.
 Note |
|
Licenses Supporting AVB
AVB is supported on the following two license levels only:
-
ipbase
-
ipservices
Benefits of AVB
AVB is a standard based mechanism to enable Ethernet based audio-video transmission which has the following benefits:
-
Guaranteed max Latency
-
Synchronized Time
-
Guaranteed Bandwidth
-
Professional Grade
Components of AVB Network
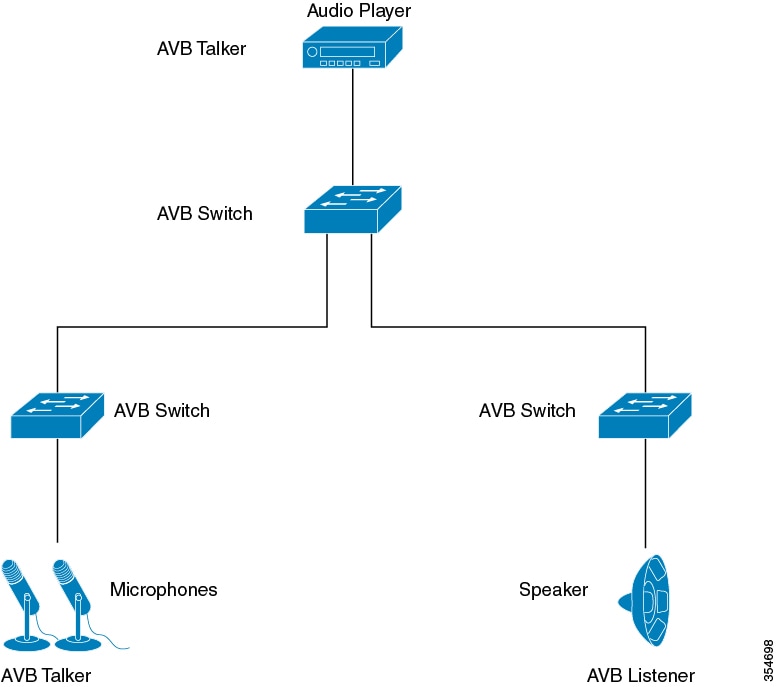
AVB protocols operate only in domains where every device is AVB capable. The AVB network comprises of the AVB talkers, AVB listeners, AVB switches and the grandmaster clock source.
-
AVB Talker - An AVB end station that is the source or producer of a stream, i.e. microphones, video camera, and so on.
-
AVB Listener - An AVB end station that is the destination or consumer of a stream, i.e. speaker, video screen, and so on.
-
AVB Switch - An Ethernet switch that complies with IEEE802.1 AVB standards.
-
AVB stream: A data stream associated with a stream reservation compliant with the Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP).

Note
In some instances, the word “bridge” is used. In this context, it references to a switch.
The IEEE 802.1BA specification requires that an AVB talker must be grandmaster capable. In a typical deployment a network node can also be the grandmaster, provided it can either source or derive timing from a grandmaster capable device and provide the timing to the AVB network using IEEE 802.1AS.
Figure 1 shows a simple illustration of AVB network with different components.
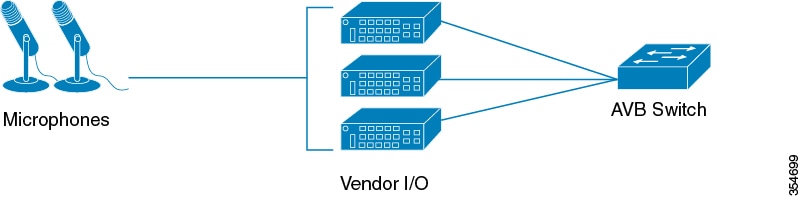
In many instances, the Audio/Video end points (Microphone, Speaker, etc.) are analog devices. AVB end-point vendors introduce Digital Signal Processors (DSP) and I/O devices that provide extensive audio/video processing and aggregate the end-points into an AVB Ethernet interface, as shown in Figure 2.
Supported SKUs for AVB
AVB is supported on the following Catalyst 3850 and Catalyst 3650 SKUs.
-
WS-C3650-24PDM
-
WS-C3650-48FQM
-
WS-C3650-8X24UQ
-
WS-C3650-12X48UQ
-
WS-C3850-12X48U
-
WS-C3850-12XS
-
WS-C3850-16XS
-
WS-C3850-24XS
-
WS-C3850-24XU
-
WS-C3850-32XS
-
WS-C3850-48XS
 Note |
In Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.1, AVB is supported only on the non-mGig interfaces on WS-3850-12X48U. Starting from Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.2, AVB is supported on the mGig interfaces on WS-3850-12X48U and WS-C3850-24XU. |
Information about Generalized Precision Time Protocol (gPTP)
Generalized Precision Time Protocol (gPTP) is an IEEE 802.1AS standard, which provides a mechanism to synchronize clocks of the bridges and end point devices in an AVB network. It defines the mechanism to elect the grandmaster clock (BMCA) among the time-aware bridges and talker and listener. The grandmaster is the root of the timing hierarchy that gets established in the time-aware network and distributes time to nodes below to enable synchronization.
Time synchronization also requires determining the link delay and switch delays in the network nodes. The gptp switch is a IEEE 1588 boundary clock, which also determines the link delay using the peer-to-peer delay mechanism. The delays computed are included in the correction field of the PTP messages and relayed to the end-points. The talker and listener use this gPTP time as a shared clock reference, which is used to relay and recover the media clock. gPTP currently defines only domain 0, which is what the switch supports.
The peer to peer delay mechanism runs on STP blocked ports as well. No other PTP messages are sent over blocked ports.
In a PTP domain, Best Master Clock (BMC) algorithm organizes Clocks and Ports into a hierarchical fashion, which includes clocks and port states:
-
Grandmaster (GM/GMC)
-
Boundary Clock (BC)
-
Master (M)
-
Slave (S)
-
Passive (P)
Information about Multiple Stream Reservation Protocol (MSRP)
Multiple Stream Reservation Protocol (MSRP) provides a mechanism for end stations to reserve network resources that will guarantee the transmission and reception of data streams across a network with the requested QoS. It is one of the core protocols required on an AVB device (talker, listener and switches). It allows talkers to advertise streams across a network of AVB switches and listeners to register for receiving the streams.
MSRP is the key software protocol module for supporting AVB. It enables stream establishment and teardown. It interfaces with gPTP to update the latency information for the streams. It interfaces with the QoS module to setup the hardware resources that would guarantee requested bandwidth for the streams. It also provides the QoS shaping parameters required for the credit based shaper.
 Note |
When AVB is enabled globally the default queuing values will be programmed to 1% bandwidth on the 10G interface. When stream reservation happens via MSRP, the ports will be moved accordingly from the boundary to the core port and the calculated bandwidth will be reserved for the outgoing interfaces for given streams. If a port is enabled with a capture feature like SPAN, RSPAN or Wireshark, there is no MSRP stream reservation. Queuing is programmed with default values of 1% for Class A & Class B of AVB traffic. Hence, all AVB traffic is rate limited to 1% of the bandwidth. |
Functions of MSRP
MSRP performs the following functions:
-
Allows Talkers to advertise Streams and Listeners to discover and register for Streams.
-
Establishes a path through an Ethernet between a Talker and one or more Listeners.
-
Provides guaranteed bandwidth for AVB Streams.
-
Guarantees an upper bound on latency.
-
Discovers and reports the worst case end-to-end latency between the Talker and each of its Listeners.
-
Reports failure reason and location when a path between the Talker and a Listener cannot satisfy bandwidth requirements.
-
Supports multiple classes of traffic with different latency targets.
-
Protects best effort traffic from starvation by limiting AVB traffic.
-
MSRP Talker declarations are not forwarded along the STP blocked ports.
-
MSRP listens to the STP TCN notification to generate MSRP declarations tear /modify / establish streams.
Information about QoS HQoS
AVB networks guarantee bandwidth and minimum bounded latency for the time-sensitive audio and video streams. AVB defines Class A and Class B as the time-sensitive streams, based on the worst-case latency targets of the traffic from talker to listener.
-
SR-Class A: 2ms
-
SR-Class B: 50ms
The sum of the worst-case latency contributions per hop should result in an overall end-to-end latency of 2 ms or less for SR-Class A and 50ms or less for SR-Class B. A typical AVB deployment of 7 hops from talker to listener meets these latency requirements.
The priority code points map the traffic to the specific stream. Frame forwarding behavior is based on this priority. A credit-based shaper is used to shape the transmission of these streams in accordance with the bandwidth that has been reserved on a given outbound queue so that the latency targets are met.
-
Allow a parent class to shape multiple queues in a child policy
-
Apply specific policy map actions on the aggregate traffic
-
Apply class-specific policy map actions
 Note |
You should not modify the PCP in child policy to map with PCP configured in Parent Policy, e.g. SR Class A cos 3 and SR Class B Cos 2. |
Hierarchical Policing
Hierarchical policing is supported on ingress and egress interfaces. Hierarchical QoS separates the SR and Non-SR class related rules into parent and child policies respectively. AVB SR classes are completely controlled by MSRP client and hence, parent policies containing SR class attributes are governed by MSRP. The end user has complete control over child policies which contain Non-SR class attributes and can modify only the child policies.
AVB HQoS child policies are user modifiable and NVGENed to preserve the configuration if user saves the configuration to the startup-config. So, AVB HQoS child policy configurations are retained even after reload.
Information about Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol (MVRP)
Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol (MVRP) is an application based on MRP. MVRP provides a mechanism for dynamic maintenance of the contents of Dynamic VLAN Registration Entries for each vlan ids, and for propagating the information they contain to other Bridges. This information allows MVRP-aware devices to dynamically establish and update their knowledge of the set of vlan ids associated with VLANs that currently have active members, and through which Ports those members can be reached.
MVRP, from an AVB perspective, is mandatory on the talkers and the listeners. Independent of AVB, MVRP is an IEEE 802.1Q requirement on the VLAN-aware switches. However, manual configuration of VLANS on the switches is sufficient for AVB.
 Note |
VTP should be in the disabled mode or transparent mode for MVRP to work. |
Configuring the AVB Network
Configuring AVB
This section describes the various configurations available for AVB.
Enabling AVB on the switch
 Note |
Both, the avb and avb strict commands must be configured to enable AVB. |
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- avb
- avb strict
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
Step 3 |
avb Example: |
Enables AVB on the switch. |
||
|
Step 4 |
avb strict Example: |
Enables AVB on the switch. This command is used in combination with the avb command to enable AVB.
|
||
|
Step 5 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
What to do next
To disable AVB on the switch, use the "no " form of the command.
Configuring AVB on the devices
You can configure the interfaces along the connectivity path for AVB devices as dot1q trunk ports by using the below commands.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- interface interface-id
- switchport mode trunk
- exit
- vlan 2
- avb vlan vlan-id
- avb
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
Step 3 |
interface interface-id Example: |
Defines the interface to be configured as a trunk, and enters interface configuration mode. |
||
|
Step 4 |
switchport mode trunk Example: |
Configures the port as a trunk port. |
||
|
Step 5 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
||
|
Step 6 |
vlan 2 Example: |
Configures VLAN 2 on the switch.
|
||
|
Step 7 |
avb vlan vlan-id Example: |
(Optional) Sets the specified VLAN as the default AVB VLAN on the switch. Use this command when you need to set the default AVB VLAN other than VLAN 2. The range for vlan-id varies from 2 to 4094. |
||
|
Step 8 |
avb Example: |
Configures AVB on the specified interface. |
||
|
Step 9 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
What to do next
To disable AVB on the switch, use the "no " form of the command.
Configuring gPTP
This section describes the various configurations available for gPTP.
Enabling gPTP on a port
When AVB is enabled on the switch, gPTP for AVB also gets enabled.
 Note |
When gPTP is enabled, Flowcontrol is disabled on all ports. |
You can also enable gPTP globally using the command given below:
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- ptp profile dot1as
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
Step 3 |
ptp profile dot1as Example: |
Enables gPTP on the port. |
|
Step 4 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Enabling gPTP on an interface
You can also enable gPTP on an interface using the command given below:
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- interface interface-id
- ptp enable
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. |
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters the global configuration mode. |
|
Step 3 |
interface interface-id Example: |
Defines the interface to be configured as a trunk, and enters interface configuration mode. |
|
Step 4 |
ptp enable Example: |
Enables gPTP on the specified interface. To disable gPTP on the interface, use the no form of this
command as shown below:
|
|
Step 5 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring the values of PTP clocks
When you configure a profile or mode, the priority1 and priority2 values will be initialised with their default values.
The priority1 and priority2 default values for dot1as profile is 246 and 248 respectively. The priority1 and priority2 default values for default profile is 128 and 128 respectively.
You can configure the values of ptp clock priority1 and priority2 using the commands below:
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- ptp priority1
- ptp priority2
- exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
Step 3 |
ptp priority1 Example: |
Configure the values of ptp clock priority1. 0-255 - This is the range for the value of the ptp clock priority. Select a value withing this range.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
ptp priority2 Example: |
Configure the values of ptp clock priority2. 0-255 - This is the range for the value of the ptp clock priority. Select a value withing this range. |
||
|
Step 5 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuring QoS
This section describes the various configurations available for QOS.
Enabling QOS
When AVB is enabled on the switch, QOS for AVB also gets enabled.
Configuring HQoS
This section describes the various configurations available for HQoS.
Enabling HQoS
When AVB is enabled on the switch, HQoS for AVB also gets enabled.
Migrating from Flat Policy Formats to Hierarchical Policy Formats - Guidelines and Restrictions
Follow the below guidelines when migrating from flat policy formats to hierarchical policy formats for AVB:
-
If you upgrade from Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.1 to Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.2, QoS policies that are in startup configuration of the device will fail with errors. Follow the steps below to properly install HQoS policies on your device:
-
Use the no avb command to disable AVB globally.

Note
When you disable AVB, all the policy-maps and class-maps are automatically removed from the configuration. But, the access-lists are not removed automatically. You must remove the access-lists manually. Ensure that all the QoS policy constructs are removed before upgrading to Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.2.
-
Enable AVB using the avb command. When AVB is enabled, HQoS for AVB also gets enabled.
-
-
We do not recommend migrating from a hierarchical policy format supported release to a flat policy format supported release.
-
You can only modify child policies. Parent policies are completely governed by MSRP.
-
show running config command displays only the child policies.
-
Starting from Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.2, show running config interface command will not display any details of the policy attached. You should use show policy-map interface command for displaying all the details of the policy attached.
Hierarchical QoS Policy Formats
This following example shows hierarchical remarking policy at the ingress interface:
policy-map AVB-Input-Child-Policy
class VOIP-DATA-CLASS
set dscp EF
class MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
set dscp AF41
class BULK-DATA-CLASS
set dscp AF11
class TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
set dscp AF21
class SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
set dscp CS1
class SIGNALING-CLASS
set dscp CS3
class class-default
set dscp default
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-AB
class AVB-SR-A-CLASS
set cos 0 (set 0 for boundary & SR class A PCP value for core port)
class AVB-SR-B-CLASS
set cos 0 (set 0 for boundary & SR class B PCP value for core port)
class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-Policy
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-A
class AVB-SR-A-CLASS
set cos 0 (set 0 for boundary & SR class A PCP value for core port)
class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-Policy
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-B
class AVB-SR-B-CLASS
set cos 0 (set 0 for boundary & SR class B PCP value for core port)
class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-Policy
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-None
class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-PolicyThis following example shows hierarchical queuing policy at the egress interface:
policy-map AVB-Output-Child-Policy
class VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 30
queue-buffers ratio 10
class MULTIMEDIA-CONFERENCING-STREAMING-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 15
queue-limit dscp AF41 percent 80
queue-limit dscp AF31 percent 80
queue-limit dscp AF42 percent 90
queue-limit dscp AF32 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 10
class TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 15
queue-limit dscp AF21 percent 80
queue-limit dscp AF22 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 10
class BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 15
queue-limit dscp AF11 percent 80
queue-limit dscp AF12 percent 90
queue-limit dscp CS1 percent 80
queue-buffers ratio 15
class class-default
bandwidth remaining percent 25
queue-buffers ratio 25
policy-map AVB-Output-Policy
class AVB-SR-A-CLASS
priority level 1 (Shaper value based on stream registration)
class AVB-SR-B-CLASS
priority level 2 (Shaper value based on stream registration)
class CONTROL-MGMT-QUEUE
priority level 3 percent 15
class class-default
bandwidth remaining percent 100
queue-buffers ratio 80
service-policy AVB-Output-Child-Policy
Configuring MVRP
This section describes the various configurations available for MVRP.
Enabling MVRP
 Note |
You must change VTP mode to transparent or off , before enabling dynamic vlan creation via MVRP. |
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- mvrp global
- vtp mode { transparent | off}
- mvrp vlan create
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
Step 3 |
mvrp global Example: |
Enters the MVRP Global configuration mode. |
|
Step 4 |
vtp mode { transparent | off} Example:Example: |
Sets the VTP to transparent or off mode. |
|
Step 5 |
mvrp vlan create Example: |
Enables MVRP on the switches. |
Configuring MVRP on the switch interface
You can configure MVRP on the switch interfaces using the below commands
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- interface interface-id
- mvrp registration {fixed | forbidden | normal}
- mvrp timer {join | leave | leave-all | periodic}
- exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
Step 3 |
interface interface-id Example: |
Defines the interface to be configured as a trunk, and enters interface configuration mode. |
|
Step 4 |
mvrp registration {fixed | forbidden | normal} Example: |
Registers MVRP with the MAD instance.
|
|
Step 5 |
mvrp timer {join | leave | leave-all | periodic} Example: |
Configures the MVRP timer.
|
|
Step 6 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
Monitoring the AVB Network
Monitoring AVB
To display the AVB details, use the commands in the following table:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| show avb domain |
Displays the AVB domain. |
| show avb streams |
Displays the AVB stream information. |
Monitoring gPTP
To display the gPTP protocol details, use the commands in the following table:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| show ptp brief |
Displays a brief status of ptp on the interfaces. |
| show ptp clock |
Displays ptp clock information. |
| show ptp parent |
Displays the parent clock information. |
| show ptp port |
Displays the ptp port information. |
| show platform software fed switch active ptp if-id {interface-id} |
Displays details info about ptp status on the port. |
Monitoring MSRP
To display the MSRP details, use the commands in the following table:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| show msrp streams |
Displays MSRP stream information. |
| show msrp streams detailed |
Displays detailed MSRP stream information. |
| show msrp streams brief |
Displays MSRP stream information in brief. |
| show msrp port bandwidth |
Displays MSRP port bandwidth information. |
Monitoring QoS
To display the QOS details, use the commands in the following table:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| show run interface |
Displays the qos policy details and the interface level policy application. |
| show run |
Displays all the policy map details. |
| show policy-map |
Displays the details of the policy map configuration. |
| show policy-map interface (int-id) |
Displays QOS statistics. |
Monitoring HQoS
To display the HQoS details, use the commands in the following table:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| show run |
Displays all the child policy map details. |
| show policy-map |
Displays the details of the policy map configuration. |
| show platform hardware fed switch active qos queue stats interface interface-id |
Displays the QoS statistics for different queue mappings in AVB. |
| show platform hardware fed switch active qos queue config interface interface-id |
Displays the QoS queue configurations. |
| show policy-map interface interface-id [input | output] |
Displays the AVB QoS statistics. Packet counters for ingress and bytes counters for egress are accounted for QoS Statistics. |
Monitoring MVRP
To display the MVRP details, use the commands in the following table:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| show mvrp summary |
Displays MVRP summary information. |
| show mvrp interface |
Displays interface MVRP information. |
Examples of AVB Configurations and Monitoring
Examples for AVB
This example shows how you can view the AVB domain.
Device#show avb domain
AVB Class-A
Priority Code Point : 3
VLAN : 2
Core ports : 1
Boundary ports : 67
AVB Class-B
Priority Code Point : 2
VLAN : 2
Core ports : 1
Boundary ports : 67
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interface State Delay PCP VID Information
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Te1/0/1 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/2 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/3 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/4 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/5 up N/A Port is not asCapable
Te1/0/6 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/7 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/8 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/9 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/10 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/11 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/12 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/13 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/14 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/15 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/16 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/17 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/18 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/19 up N/A Port is not asCapable
Te1/0/20 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/21 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/22 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/23 up N/A Port is not asCapable
Te1/0/24 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/25 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/26 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/27 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/28 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/29 up N/A Port is not asCapable
Te1/0/30 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/31 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/32 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/33 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/34 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/35 up N/A Port is not asCapable
Te1/0/36 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/37 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/38 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/39 up 507ns
Class- A core 3 2
Class- B core 2 2
Te1/0/40 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/41 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/42 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/43 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/44 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/45 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/46 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/47 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/0/48 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/1 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/2 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/3 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/4 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/5 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/6 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/7 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/8 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/9 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/10 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/11 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/12 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/13 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/14 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/15 down N/A Oper state not up
Te1/1/16 down N/A Oper state not up
Fo1/1/1 down N/A Oper state not up
Fo1/1/2 down N/A Oper state not up
Fo1/1/3 down N/A Oper state not up
Fo1/1/4 down N/A Oper state not up
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the AVB stream information.
Device#show avb streams
Stream ID: 0011.0100.0001:1 Incoming Interface: Te1/1/1
Destination : 91E0.F000.FE00
Class : A
Rank : 1
Bandwidth : 6400 Kbit/s
Outgoing Interfaces:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interface State Time of Last Update Information
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Te1/1/1 Ready Tue Apr 26 01:25:40.634
Stream ID: 0011.0100.0002:2 Incoming Interface: Te1/1/1
Destination : 91E0.F000.FE01
Class : A
Rank : 1
Bandwidth : 6400 Kbit/s
Outgoing Interfaces:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interface State Time of Last Update Information
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Te1/1/1 Ready Tue Apr 26 01:25:40.634
Examples for gPTP
This command can be used to see a brief status of ptp on the interfaces.
Device#show ptp brief
Interface Domain PTP State
FortyGigabitEthernet1/1/1 0 FAULTY
FortyGigabitEthernet1/1/2 0 SLAVE
GigabitEthernet1/1/1 0 FAULTY
GigabitEthernet1/1/2 0 FAULTY
GigabitEthernet1/1/3 0 FAULTY
GigabitEthernet1/1/4 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/1 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/2 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 0 MASTER
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/4 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/6 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/7 0 MASTER
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/8 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/9 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/10 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/11 0 MASTER
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/12 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/13 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/14 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/15 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/16 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/17 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/18 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/19 0 MASTER
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/20 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/21 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/22 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/23 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/24 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/2 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/3 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/4 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/5 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/6 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/7 0 FAULTY
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/8 0 FAULTY
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This command can be used to view ptp clock information.
Device#show ptp clock
PTP CLOCK INFO
PTP Device Type: Boundary clock
PTP Device Profile: IEEE 802/1AS Profile
Clock Identity: 0x4:6C:9D:FF:FE:4F:95:0
Clock Domain: 0
Number of PTP ports: 38
PTP Packet priority: 4
Priority1: 128
Priority2: 128
Clock Quality:
Class: 248
Accuracy: Unknown
Offset (log variance): 16640
Offset From Master(ns): 0
Mean Path Delay(ns): 0
Steps Removed: 3
Local clock time: 00:12:13 UTC Jan 1 1970
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This command can be used to view the parent clock information.
Device#show ptp parent
PTP PARENT PROPERTIES
Parent Clock:
Parent Clock Identity: 0xB0:7D:47:FF:FE:9E:B6:80
Parent Port Number: 3
Observed Parent Offset (log variance): 16640
Observed Parent Clock Phase Change Rate: N/A
Grandmaster Clock:
Grandmaster Clock Identity: 0x4:6C:9D:FF:FE:67:3A:80
Grandmaster Clock Quality:
Class: 248
Accuracy: Unknown
Offset (log variance): 16640
Priority1: 0
Priority2: 128
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This command can be used to view the ptp port information.
Device#show ptp port
PTP PORT DATASET: FortyGigabitEthernet1/1/1
Port identity: clock identity: 0x4:6C:9D:FF:FE:4E:3A:80
Port identity: port number: 1
PTP version: 2
Port state: FAULTY
Delay request interval(log mean): 5
Announce receipt time out: 3
Peer mean path delay(ns): 0
Announce interval(log mean): 1
Sync interval(log mean): 0
Delay Mechanism: End to End
Peer delay request interval(log mean): 0
Sync fault limit: 500000000
PTP PORT DATASET: FortyGigabitEthernet1/1/2
Port identity: clock identity: 0x4:6C:9D:FF:FE:4E:3A:80
Port identity: port number: 2
PTP version: 2
Port state: FAULTY
Delay request interval(log mean): 5
Announce receipt time out: 3
Peer mean path delay(ns): 0
Announce interval(log mean): 1
--More—
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This command can be used to view the port information for a particular interface.
Device#show ptp port gi1/0/26
PTP PORT DATASET: GigabitEthernet1/0/26
Port identity: clock identity: 0x4:6C:9D:FF:FE:4E:3A:80
Port identity: port number: 28
PTP version: 2
Port state: MASTER
Delay request interval(log mean): 5
Announce receipt time out: 3
Peer mean path delay(ns): 0
Announce interval(log mean): 1
Sync interval(log mean): 0
Delay Mechanism: Peer to Peer
Peer delay request interval(log mean): 0
Sync fault limit: 500000000
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This command can be used to view the
Device#show platform software fed switch active ptp if-id 0x20
Displaying port data for if_id 20
=======================================
Port Mac Address 04:6C:9D:4E:3A:9A
Port Clock Identity 04:6C:9D:FF:FE:4E:3A:80
Port number 28
PTP Version 2
domain_value 0
dot1as capable: FALSE
sync_recpt_timeout_time_interval 375000000 nanoseconds
sync_interval 125000000 nanoseconds
neighbor_rate_ratio 0.000000
neighbor_prop_delay 0 nanoseconds
compute_neighbor_rate_ratio: TRUE
compute_neighbor_prop_delay: TRUE
port_enabled: TRUE
ptt_port_enabled: TRUE
current_log_pdelay_req_interval 0
pdelay_req_interval 0 nanoseconds
allowed_lost_responses 3
neighbor_prop_delay_threshold 2000 nanoseconds
is_measuring_delay : FALSE
Port state: : MASTER
sync_seq_num 22023
delay_req_seq_num 23857
num sync messages transmitted 0
num sync messages received 0
num followup messages transmitted 0
num followup messages received 0
num pdelay requests transmitted 285695
num pdelay requests received 0
num pdelay responses transmitted 0
num pdelay responses received 0
num pdelay followup responses transmitted 0
num pdelay followup responses received 0
Examples for MSRP
This example shows how you can view the MSRP stream information.
Device#show msrp streams
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Stream ID Talker Listener
Advertise Fail Ready ReadyFail AskFail
R | D R | D R | D R | D R | D
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
yy:yy:yy:yy:yy:yy:0001 1 | 2 0 | 0 1 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0
zz:zz:zz:zz:zz:zz:0002 1 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the detailed MSRP stream information.
Device#show msrp streams detail
Stream ID: 0011.0100.0001:1
Stream Age: 01:57:46 (since Mon Apr 25 23:41:11.413)
Create Time: Mon Apr 25 23:41:11.413
Destination Address: 91E0.F000.FE00
VLAN Identifier: 1
Data Frame Priority: 3 (Class A)
MaxFrameSize: 100
MaxIntervalFrames: 1 frames/125us
Stream Bandwidth: 6400 Kbit/s
Rank: 1
Received Accumulated Latency: 20
Stream Attributes Table:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interface Attr State Direction Type
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Gi1/0/1 Register Talker Advertise
Attribute Age: 01:57:46 (since Mon Apr 25 23:41:11.413)
MRP Applicant: Very Anxious Observer, send None
MRP Registrar: In
Accumulated Latency: 20
----
Te1/1/1 Declare Talker Advertise
Attribute Age: 00:19:52 (since Tue Apr 26 01:19:05.525)
MRP Applicant: Quiet Active, send None
MRP Registrar: In
Accumulated Latency: 20
----
Te1/1/1 Register Listener Ready
Attribute Age: 00:13:17 (since Tue Apr 26 01:25:40.635)
MRP Applicant: Very Anxious Observer, send None
MRP Registrar: In
----
Gi1/0/1 Declare Listener Ready
Attribute Age: 00:13:17 (since Tue Apr 26 01:25:40.649)
MRP Applicant: Quiet Active, send None
MRP Registrar: In
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the MSRP stream information in brief.
Device#show msrp streams brief
Legend: R = Registered, D = Declared.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Stream ID Destination Bandwidth Talkers Listeners Fail
Address (Kbit/s) R | D R | D
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0011.0100.0001:1 91E0.F000.FE00 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0002:2 91E0.F000.FE01 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0003:3 91E0.F000.FE02 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0004:4 91E0.F000.FE03 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0005:5 91E0.F000.FE04 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0006:6 91E0.F000.FE05 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0007:7 91E0.F000.FE06 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0008:8 91E0.F000.FE07 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.0009:9 91E0.F000.FE08 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
0011.0100.000A:10 91E0.F000.FE09 6400 1 | 1 1 | 1 No
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the MSRP port bandwidth information.
Device#show msrp port bandwidth
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ethernet Capacity Assigned Available Reserved
Interface (Kbit/s) A | B A | B A | B
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Te1/0/1 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/2 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/3 1000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/4 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/5 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/6 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/8 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/9 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/10 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/11 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/12 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/13 1000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/14 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/15 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/16 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/17 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/18 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/19 1000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/20 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/21 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/22 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/23 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/0/24 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Gi1/1/1 1000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Gi1/1/2 1000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Gi1/1/3 1000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Gi1/1/4 1000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/1 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/2 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/3 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/4 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/5 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/6 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/7 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Te1/1/8 10000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Fo1/1/1 40000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Fo1/1/2 40000000 75 | 0 75 | 75 0 | 0
Examples for QoS
This example shows how you can view all the policy map details when AVB is NOT enabled.
Device#show run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 12069 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 02:49:13 UTC Wed Jul 27 2016
!
version 16.3
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-recovery
no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname avb2
!
!
vrf definition Mgmt-vrf
!
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6
exit-address-family
!
!
no aaa new-model
facility-alarm critical exceed-action shutdown
switch 1 provision ws-c3850-12x48u
no ptp globalprotocolenable
!
!
!
vtp domain cisco
vtp mode transparent
!
!
crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-2183322626
enrollment selfsigned
subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-2183322626
revocation-check none
rsakeypair TP-self-signed-2183322626
!
!
--More-----
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view all the policy map details when AVB is enabled.
Device(config)#avb
Device#show run
Building configuration...
*Jul 27 02:49:51.780: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Current configuration : 21114 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 02:49:51 UTC Wed Jul 27 2016
!
!
class-map match-any AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
match dscp ef
match cos 5
class-map match-any AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast
description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data
class-map match-any AVB-VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE
match dscp cs4 cs5 ef
match precedence 4 5
match cos 5
class-map match-any AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-STREAMING-QUEUE
match dscp af41 af42 af43
match dscp af31 af32 af33
match cos 4
class-map match-any AVB-BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE
match dscp cs1 af11 af12 af13
match precedence 1
match cos 1
class-map match-any AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE
match dscp af21 af22 af23
class-map match-any AVB-SR-CLASS-B
match cos 2
class-map match-any AVB-SR-CLASS-A
match cos 3
class-map match-any AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-CONTROL-MGMT-QUEUE
match dscp cs2 cs3 cs6 cs7
match precedence 2 3 6 7
match cos 6 7
!
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-B
class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 3
class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 0
class AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
set dscp ef
class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
set dscp af41
class AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af11
class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af21
class AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
set dscp cs1
class AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
set dscp cs3
class class-default
set dscp default
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-A
class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 0
class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 2
class AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
set dscp ef
class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
set dscp af41
class AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af11
class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af21
class AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
set dscp cs1
class AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
set dscp cs3
class class-default
set dscp default
policy-map AVB-Output-Policy-Default
class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
priority level 1 percent 1
class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
priority level 2 percent 1
class AVB-CONTROL-MGMT-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 10
queue-buffers ratio 10
class AVB-VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 30
queue-buffers ratio 10
class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-STREAMING-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 10
queue-limit dscp af41 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af31 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af42 percent 90
queue-limit dscp af32 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 10
class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 10
queue-limit dscp af21 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af22 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 10
class AVB-BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 15
queue-limit dscp af11 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af12 percent 90
queue-limit dscp cs1 percent 80
queue-buffers ratio 15
class class-default
bandwidth remaining percent 25
queue-buffers ratio 25
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-AB
class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 0
class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 0
class AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
set dscp ef
class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
set dscp af41
class AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af11
class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af21
class AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
set dscp cs1
class AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
set dscp cs3
class class-default
set dscp default
policy-map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-None
class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 3
class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 2
class AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
set dscp ef
class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
set dscp af41
class AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af11
class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af21
class AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
set dscp cs1
class AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
set dscp cs3
class class-default
set dscp default
!
!
--More-----
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can check the qos policy details and the interface level policy application.
Device#show run int Gig 1/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 159 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
switchport mode trunk
service-policy input AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-AB
service-policy output AVB-Output-Policy-Default
end
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the qos statistics on the interface where AVB policy is attached.
Device#show policy-map int Gig 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Service-policy input: AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-AB
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-A (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 3
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 0
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-B (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 2
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 0
Class-map: AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp ef (46)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 5
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp ef
Class-map: AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af41
Class-map: AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af11
--More--
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can check the qos policy details and the interface level policy application with Class A traffic.
Device#show run int gig 1/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 158 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
switchport mode trunk
service-policy input AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-B
service-policy output AVB-Output-Policy-Gi1/0/1
end
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the qos statistics on the interface where Class A AVB traffic sent.
Device#show policy-map int Gig 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Service-policy input: AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-B
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-A (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 3
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 3
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-B (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 2
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 0
Class-map: AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp ef (46)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 5
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp ef
Class-map: AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af41
Class-map: AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af11
--More--
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can check the qos policy details and the interface level policy application with Class B traffic.
Device#show run int gig 1/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 158 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
switchport mode trunk
service-policy input AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-A
service-policy output AVB-Output-Policy-Gi1/0/1
end
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the qos statistics on the interface where Class B AVB traffic is sent.
Device#show policy-map int Gig 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Service-policy input: AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-A
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-A (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 3
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 0
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-B (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 2
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 2
Class-map: AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp ef (46)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 5
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp ef
Class-map: AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af41
Class-map: AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af11
--More--
Examples for HQoS
This example shows how you can view all the policy-map configuration details when AVB is enabled.
Device#show policy-map
Policy Map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-B
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 3
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 0
Class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-Policy
Policy Map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-A
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 0
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 2
Class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-Policy
Policy Map AVB-Output-Policy-Default
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
priority level 1 1 (%)
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
priority level 2 1 (%)
Class AVB-CONTROL-MGMT-QUEUE
priority level 3 15 (%)
Class class-default
bandwidth remaining 100 (%)
queue-buffers ratio 70
service-policy AVB-Output-Child-Policy
Policy Map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-AB
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 0
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 0
Class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-Policy
Policy Map AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-None
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-A
set cos 3
Class AVB-SR-CLASS-B
set cos 2
Class class-default
service-policy AVB-Input-Child-Policy
Policy Map AVB-Input-Child-Policy
Class AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
set dscp ef
Class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
set dscp af41
Class AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af11
Class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af21
Class AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
set dscp cs1
Class AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
set dscp cs3
Class class-default
set dscp default
Policy Map AVB-Output-Child-Policy
Class AVB-VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining 30 (%)
queue-buffers ratio 30
Class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-STREAMING-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining 15 (%)
queue-limit dscp af41 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af31 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af42 percent 90
queue-limit dscp af32 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 15
Class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining 15 (%)
queue-limit dscp af21 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af22 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 15
Class AVB-BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining 15 (%)
queue-limit dscp af11 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af12 percent 90
queue-limit dscp cs1 percent 80
queue-buffers ratio 15
Class class-default
bandwidth remaining 25 (%)
queue-buffers ratio 25
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view all the policy-map configuration details when AVB is disabled.
Device#show policy-map
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 2079 bytes
!
policy-map AVB-Input-Child-Policy
class AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
set dscp ef
class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
set dscp af41
class AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af11
class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
set dscp af21
class AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
set dscp cs1
class AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
set dscp cs3
class class-default
set dscp default
policy-map AVB-Output-Child-Policy
class AVB-VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 30
queue-buffers ratio 30
class AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-STREAMING-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 15
queue-limit dscp af41 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af31 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af42 percent 90
queue-limit dscp af32 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 15
class AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 15
queue-limit dscp af21 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af22 percent 90
queue-buffers ratio 15
class AVB-BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE
bandwidth remaining percent 15
queue-limit dscp af11 percent 80
queue-limit dscp af12 percent 90
queue-limit dscp cs1 percent 80
queue-buffers ratio 15
class class-default
bandwidth remaining percent 25
queue-buffers ratio 25
!
end
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view all the class-map configuration details when AVB is enabled.
Device#show class-map
Class Map match-any AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS (id 31)
Match dscp ef (46)
Match cos 5
Class Map match-any AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS (id 33)
Match access-group name AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS-ACL
Class Map match-any AVB-VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE (id 37)
Match dscp cs4 (32) cs5 (40) ef (46)
Match precedence 4 5
Match cos 5
Class Map match-any AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS (id 32)
Match access-group name AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS-ACL
Class Map match-any AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS (id 36)
Match access-group name AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS-ACL
Class Map match-any AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-STREAMING-QUEUE (id 38)
Match dscp af41 (34) af42 (36) af43 (38)
Match dscp af31 (26) af32 (28) af33 (30)
Match cos 4
Class Map match-any AVB-BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE (id 40)
Match dscp cs1 (8) af11 (10) af12 (12) af13 (14)
Match precedence 1
Match cos 1
Class Map match-any AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS (id 34)
Match access-group name AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS-ACL
Class Map match-any AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE (id 39)
Match dscp af21 (18) af22 (20) af23 (22)
Class Map match-any AVB-SR-CLASS-B (id 42)
Match cos 2
Class Map match-any AVB-SR-CLASS-A (id 41)
Match cos 3
Class Map match-any AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS (id 35)
Match access-group name AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS-ACL
Class Map match-any AVB-CONTROL-MGMT-QUEUE (id 43)
Match ip dscp cs2 (16)
Match ip dscp cs3 (24)
Match ip dscp cs6 (48)
Match ip dscp cs7 (56)
Match ip precedence 6
Match ip precedence 7
Match ip precedence 3
Match ip precedence 2
Match cos 6
Match cos 7
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view all the class-map configuration details when AVB is disabled.
Device#show class-map
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 2650 bytes
!
class-map match-any AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS
match dscp ef
match cos 5
class-map match-any AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE
match dscp cs4 cs5 ef
match precedence 4 5
match cos 5
class-map match-any AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-STREAMING-QUEUE
match dscp af41 af42 af43
match dscp af31 af32 af33
match cos 4
class-map match-any AVB-BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE
match dscp cs1 af11 af12 af13
match precedence 1
match cos 1
class-map match-any AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS-ACL
class-map match-any AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE
match dscp af21 af22 af23
class-map match-any AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS
match access-group name AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS-ACL
end
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view all the AVB QoS statistics.
Device#show policy-map interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/15
GigabitEthernet1/0/15
Service-policy input: AVB-Input-Policy-Remark-AB
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-A (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 3
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 0
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-B (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 2
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 0
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
0 packets
Match: any
Service-policy : AVB-Input-Child-Policy
Class-map: AVB-VOIP-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp ef (46)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 5
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
cos 3
Class-map: AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af41
Class-map: AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-BULK-DATA-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af11
Class-map: AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp af21
Class-map: AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-SCAVENGER-DATA-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp cs1
Class-map: AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS (match-any)
0 packets
Match: access-group name AVB-SIGNALING-CLASS-ACL
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
QoS Set
dscp cs3
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
0 packets
Match: any
QoS Set
dscp default
Service-policy output: AVB-Output-Policy-Default
queue stats for all priority classes:
Queueing
priority level 3
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 7595
queue stats for all priority classes:
Queueing
priority level 2
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
queue stats for all priority classes:
Queueing
priority level 1
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-A (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 3
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Priority: 1% (10000 kbps), burst bytes 250000,
Priority Level: 1
Class-map: AVB-SR-CLASS-B (match-any)
0 packets
Match: cos 2
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Priority: 1% (10000 kbps), burst bytes 250000,
Priority Level: 2
Class-map: AVB-CONTROL-MGMT-QUEUE (match-any)
0 packets
Match: ip dscp cs2 (16)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp cs3 (24)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp cs6 (48)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp cs7 (56)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: ip precedence 6
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: ip precedence 7
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: ip precedence 3
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: ip precedence 2
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 6
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 7
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Priority: 15% (150000 kbps), burst bytes 3750000,
Priority Level: 3
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
0 packets
Match: any
Queueing
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
bandwidth remaining 80%
queue-buffers ratio 70
Service-policy : AVB-Output-Child-Policy
Class-map: AVB-VOIP-PRIORITY-QUEUE (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp cs4 (32) cs5 (40) ef (46)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: precedence 4 5
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 5
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Queueing
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
bandwidth remaining 30%
queue-buffers ratio 30
Class-map: AVB-MULTIMEDIA-CONF-STREAMING-QUEUE (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp af41 (34) af42 (36) af43 (38)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: dscp af31 (26) af32 (28) af33 (30)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 4
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Queueing
queue-limit dscp 26 percent 80
queue-limit dscp 28 percent 90
queue-limit dscp 34 percent 80
queue-limit dscp 36 percent 90
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
bandwidth remaining 15%
queue-buffers ratio 15
Class-map: AVB-TRANSACTIONAL-DATA-QUEUE (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp af21 (18) af22 (20) af23 (22)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 0
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Queueing
queue-limit dscp 18 percent 80
queue-limit dscp 20 percent 90
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
bandwidth remaining 15%
queue-buffers ratio 15
Class-map: AVB-BULK-SCAVENGER-DATA-QUEUE (match-any)
0 packets
Match: dscp cs1 (8) af11 (10) af12 (12) af13 (14)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: precedence 1
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Match: cos 1
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute rate 0 bps
Queueing
queue-limit dscp 8 percent 80
queue-limit dscp 10 percent 80
queue-limit dscp 12 percent 90
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
bandwidth remaining 15%
queue-buffers ratio 15
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
0 packets
Match: any
Queueing
(total drops) 0
(bytes output) 0
bandwidth remaining 25%
queue-buffers ratio 25
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following is a sample output from the show platform hardware fed switch active qos queue config interface interface-id command.
Device#show platform hardware fed switch active qos queue config interface t1/0/11
DATA Port:2 GPN:11 AFD:Disabled QoSMap:2 HW Queues: 16 - 23
DrainFast:Disabled PortSoftStart:1 - 3600
----------------------------------------------------------
DTS Hardmax Softmax PortSMin GlblSMin PortStEnd
----- -------- -------- -------- -------- ---------
0 0 9 33 3 33 0 0 0 0 1 4800
1 0 9 33 4 2400 99 99 0 0 1 4800
2 1 6 30 4 2400 90 90 0 0 1 4800
3 1 5 0 4 2400 189 189 63 63 1 4800
4 1 5 0 4 2400 90 90 30 30 1 4800
5 1 5 0 4 2400 90 90 30 30 1 4800
6 1 5 0 4 2400 90 90 30 30 1 4800
7 1 5 0 4 2400 153 153 51 51 1 4800
Priority Shaped/shared weight shaping_step
-------- ------------- ------ ------------
0 1 Shaped 16383 163
1 2 Shaped 16383 163
2 3 Shaped 125 153
3 7 Shared 50 0
4 7 Shared 100 0
5 7 Shared 100 0
6 7 Shared 100 0
7 7 Shared 60 0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following is a sample output from the show platform hardware fed switch active qos queue stats interface interface-id command.
Device#show platform hardware fed switch active qos queue stats interface t1/0/15
DATA Port:8 Enqueue Counters
-------------------------------
Queue Buffers Enqueue-TH0 Enqueue-TH1 Enqueue-TH2
----- ------- ----------- ----------- -----------
0 1 0 0 23788459506
1 0 0 0 30973507838
2 0 0 12616270 13164040
3 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0
7 0 0 0 119616
DATA Port:8 Drop Counters
-------------------------------
Queue Drop-TH0 Drop-TH1 Drop-TH2 SBufDrop QebDrop
----- ----------- ----------- ----------- ----------- -----------
0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0Examples for MVRP
This example shows how you can view the MVRP summary information.
Device#show mvrp summary
MVRP global state : enabled
MVRP VLAN creation : enabled
VLANs created via MVRP : 2,567
MAC learning auto provision : disabled
Learning disabled on VLANs : none
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This example shows how you can view the interface MVRP information.
Device#show mvrp interface
Port Status Registrar State
Te1/0/47 on normal
Te1/1/3 off normal
Port Join Timeout Leave Timeout Leaveall Timeout Periodic
Timeout
Te1/0/47 20 60 1000 100
Te1/1/3 20 60 1000 100
Port Vlans Declared
Te1/0/47 1-2,567,900
Te1/1/3 none
Port Vlans Registered
Te1/0/47 2,567
Te1/1/3 none
Port Vlans Registered and in Spanning Tree Forwarding State
Te1/0/47 2,567
Te1/1/3 none
Feature Information for AVB
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to https://cfnng.cisco.com/. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Releases |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1a |
Support for AVB was enabled on WS-C3650-8X24UQ and WS-C3650-12X48UQ switch models. |
|
Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.2 |
Enhanced to support hierarchical QoS, which provides a two level parent-child policy. Support for AVB was enabled on mGig interfaces of the WS-3850-12X48U and WS-C3850-24XU. |
|
Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.1 |
This feature was introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback