Overview of Shadow Traffic Monitoring
From Secure Firewall Version 10.0.0, you can better monitor traffic originating from unsanctioned privacy technologies, referred to as shadow traffic. This type of traffic is specifically designed to evade traditional network monitoring and analysis by advanced firewalls.
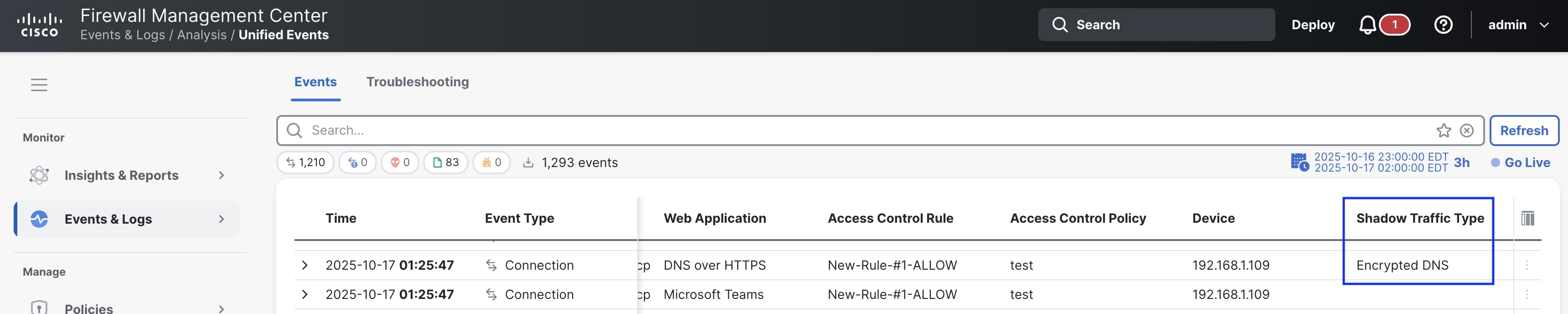
A new dedicated dashboard along with widgets is introduced in the Management Center to track specific shadow traffic flows such as Encrypted DNS, Evasive Private VPN traffic, Multihop Proxy traffic, Domain Fronting, and Fake TLS traffic flows. A new column for shadow traffic has also been added to the Connection Events and Unified Events windows.

The Encrypted Visibility Engine (EVE) and AppID modules detect shadow traffic.
|
Detections by |
Encrypted DNS |
Evasive VPNs |
Multihop Proxy |
Domain Fronting |
Fake TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
EVE |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
AppID |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Detection and monitoring of shadow traffic is enabled by default. If required, you can also disable monitoring of shadow traffic. For more information, see Disable Monitoring of Shadow Traffic.

 Feedback
Feedback