- Preface
- Product Overview
- Basic Router Configuration
- Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring Power Management
- Configuring Security Features
- Configuring Secure Storage
- Configuring Backup Data Lines and Remote Management
- Configuring Ethernet Switches
- Configuring Voice Functionality
- Configuring the Serial Interface
- Configuring Wireless Devices
- Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
- Configuring PPP over ATM with NAT
- Environmental and Power Management
- Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
- Configuring a VPN Using Easy VPN and an IPSec Tunnel
- Configuring Cisco Multimode G.SHDSL EFM/ATM
- Configuring VDSL2 Bonding and Single-Wire Pair
- Configuring Cisco IOx
- Deployment Scenarios
- Troubleshooting Cisco 800 Series Routers
- Cisco IOS Software Basic Skills
- Concepts
- ROM Monitor
- Index
- Basic Router Configuration
- Interface Ports
- Default Configuration
- Information Needed for Configuration
- Configuring Command-Line Access
- Configuring Global Parameters
- Configuring WAN Interfaces
- Configuring a Fast Ethernet WAN Interface
- Configuring the Media Type
- Configuring a Gigabit Ethernet WAN Interface
- Configuring a V.92 Modem Interface
- Configuring a VDSL2 WAN Interface
- Configuring ADSL or VDSL on Cisco 860VAE and 880VA Multimode ISRs
- Overview of Cisco 860VAE, 886VA, and 887VA Multimode ISRs
- ADSL2/2+ Annex M Mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs
- Configuring Seamless Rate Adaption
- Configuring UBR+
- Configuring ADSL Mode
- Configuring VDSL Mode
- Enabling ADSL2/2+ Annex M Mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs
- Enabling Seamless Rate Adaption
- Configuring UBR+
- Configuring the Training Log Using the CLI
- Configuring a G.SHDSL WAN Interface in ATM mode
- Configuring a G.SHDSL WAN Interface in EFM mode
- Configuring the Cellular Wireless WAN Interface
- Configuring Dual SIM for Cellular Networks on Cisco 819 Series ISR
- Configuring Router for Image and Config Recovery Using Push Button for Cisco 819 Series ISR Router
- Configuring WAN Mode on Cisco 860VAE ISRs
Basic Router
Configuration
This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also describes the default configuration on startup.
 Note | Individual router models may not support every feature described in this guide. Features that are not supported by a particular router are indicated whenever possible. |
This chapter includes configuration examples and verification steps, as available.
For complete information on how to access global configuration mode, see the Entering Global Configuration Mode section.
Basic Router Configuration
This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also describes the default configuration on startup.
 Note | Individual router models may not support every feature described in this guide. Features that are not supported by a particular router are indicated whenever possible. |
This chapter includes configuration examples and verification steps, as available.
For complete information on how to access global configuration mode see Entering Global Configuration Mode, page A-5 .
- Interface Ports
- Default Configuration
- Information Needed for Configuration
- Configuring Command-Line Access
- Configuring Global Parameters
- Configuring WAN Interfaces
- Configuring the Fast Ethernet LAN Interfaces
- Configuring the Wireless LAN Interface
- Configuring a Loopback Interface
- Configuring Static Routes
- Configuring Dynamic Routes
Interface Ports
Table 1 lists the interfaces that are supported for Cisco 860, 880 and 890 series routers and their associated port labels on the equipment.
|
Router |
Interface |
Port Label |
|---|---|---|
|
LAN Ports |
||
|
Cisco 860, Cisco 880, and Cisco 890 series |
Fast Ethernet LAN |
LAN, FE0–FE3 |
|
Wireless LAN |
(no label) |
|
|
Cisco 866VAE, 867VAE |
Ethernet LAN |
LAN, FE0-FE3 |
|
Cisco 866VAE-K9, 867VAE-K9 |
Ethernet LAN |
LAN, GE0, FE0-FE3 |
|
WAN Ports |
||
|
Cisco 861, 861W, 881, 881W, 881G, 881GW, 881-V |
Fast Ethernet WAN |
WAN, FE4 |
|
Cisco 867, 867W |
ADSL2oPOTS WAN |
ADSLoPOTS |
|
Cisco 886, 886W, 886G, 886GW |
ADSL2oISDN WAN |
ADSLoPOTS |
|
Cisco 887, 887W |
ADSL2oPOTS WAN |
ADSLoPOTS |
|
Cisco 887V, Cisco887VW, 887VG, 887VGW |
VDSL2oPOTS WAN |
VDSLoPOTS |
|
Cisco 867VA, 887VA, 887VA-M, 887VA-V, 887VA-V-W |
VDSL/ADSLoPOTS WAN |
VDSL/ADSLoPOTS |
|
Cisco 888, 888W |
G.SHDSL WAN |
G.SHDSL |
|
Cisco 891, 892 |
Fast Ethernet WAN |
FE8 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet WAN |
WAN GE 0 |
|
|
Cisco 866VAE, 867VAE |
Gigabit Ethernet WAN |
WAN GE0 |
|
Cisco 866VAE-K9, 867VAE-K9 |
Gigabit Ethernet WAN |
WAN GE1 |
|
Cisco 866VAE, 866VAE-K9 |
VDSL/ADSLoISDN WAN |
VDSL/ADSL OVER ISDN |
|
Cisco 867VAE, 867VAE-K9 |
VDSL/ADSLoPOTS WAN |
VDSL/ADSL OVER POTS |
|
Router |
Interface |
Port Label |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco 819 Series Router |
4-port Fast Ethernet LAN |
LAN, FE0–FE3 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet WAN |
GE WAN 0 |
|
|
Serial |
Serial |
|
|
Mini USB for 3G port Provisioning |
3G RSVD |
|
|
Console/Aux port |
CON/AUX |
|
|
Cisco 812 Series Router |
Gigabit Ethernet WAN |
GE WAN 0 |
|
|
Mini USB for 3G port Provisioning |
3G RSVD |
|
Console/Aux port |
CON/AUX |
Default Configuration
When you first boot up your Cisco router, some basic configuration has already been performed. All of the LAN and WAN interfaces have been created, console and vty ports are configured, and the inside interface for Network Address Translation (NAT) has been assigned. Use the show running-config command to view the initial configuration, as shown in the following example, for a Cisco 881W.
Router# show running-config User Access Verification Password: Router> en Password: Router# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 986 bytes ! version 12.4 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$g4y5$NxDeM.0hON6YA51bcfGvN1 enable password ciscocisco ! no aaa new-model ! ! ! ! no ip routing no ip cef ! ! ! ! ! multilink bundle-name authe ! ! archive log config hidekeys ! ! ! ! ! interface FastEthernet0 ! interface FastEthernet1 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet3 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet4 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 no ip route-cache duplex auto speed auto ! interface Vlan1 no ip address no ip route-cache shutdown ! interface wlan-ap0 description Service Module interface to manage the embedded AP ip unnumbered Vlan1 no cdp enable arp timeout 0 ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 ! ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ! ! ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 no modem enable line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input telnet ssh ! scheduler max-task-time 5000 ! webvpn cef end Router#
Information Needed for Configuration
Gather the following information, depending on your planned network scenario, before configuring your network:
- If you are setting up an Internet connection, gather the following information:
- If you are setting
up a connection to a corporate network, you and the network administrator must
generate and share the following information for the WAN interfaces of the
routers:
- PPP authentication type: CHAP or PAP
- PPP client name to access the router
- PPP password to access the router
- If you are setting
up IP routing:
- Generate the addressing scheme for your IP network.
- Determine the IP routing parameter information, including IP address and ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs). These PVC parameters are typically virtual path identifier (VPI), virtual circuit identifier (VCI), and traffic-shaping parameters.
- Determine the number of PVCs that your service provider has given you, along with their VPIs and VCIs.
- For each PVC, determine the type of AAL5 encapsulation supported. It can be one of the following:
AAL5SNAP—This can be either routed RFC 1483 or bridged RFC 1483. For routed RFC 1483, the service provider must provide you with a static IP address. For bridged RFC 1483, you may use DHCP to obtain your IP address, or you may obtain a static IP address from your service provider.
AAL5MUX PPP—With this type of encapsulation, you need to determine the PPP-related configuration items.
- If you plan to
connect over an ADSL or G.SHDSL line:
- Order the appropriate line from your public telephone service provider.
For ADSL lines—Ensure that the ADSL signaling type is DMT (also known as ANSI T1.413) or DMT Issue 2.
For G.SHDSL lines—Verify that the G.SHDSL line conforms to the ITU G.991.2 standard and supports Annex A (North America) or Annex B (Europe).
- If you are setting
up 3G:
- You must have service availability on the Cisco 819 ISR from a carrier, and you must have network coverage where your router will be physically placed. For a complete list of supported carriers, see the data sheet at Cisco 3G Wireless Connectivity Solutions.
- You must subscribe to a service plan with a wireless service provider and obtain a SIM card.
- You must install the SIM card before configuring the 3G Cisco 819 ISR. For instructions on how to install the SIM card, see Cisco 800 Series see Configuring Cisco EHWIC and 880G for 3.7G (HSPA+)/3.5G (HSPA)
- You must install the required antennas before you configure the 3G for Cisco 819 ISR. See Table 1 for instructions on how to install the antennas:
|
Antenna |
Instructions for Installig Antenna |
|---|---|
|
3G-ANTM1919D |
See Cisco Multiband Swivel-Mount Dipole Antenna (3G-ANTM1919D). |
|
3G-ANTM1916-CM |
See Cisco Multiband Omnidirectional Ceiling Mount Antenna (3G-ANTM1916-CM) |
|
3G-AE015-R (Antenna Extension) |
|
|
3G-AE010-R (Antenna Extension) |
See Cisco Single-Port Antenna Stand for Multiband TNC Male-Terminated Portable Antenna (Cisco 3G-AE015-R). This document applies to both 3G-AE015-R and 3G-AE010-R. The only difference between these two products is the length of the cable. |
|
3G-ANTM-OUT-OM |
See Cisco 3G Omnidirectional Outdoor Antenna (3G-ANTM-OUT-OM). |
|
3G-ANTM-OUT-LP |
See Cisco Multiband Omnidirectional Panel-Mount Antenna (3G-ANTM-OUT-LP). |
|
3G-ACC-OUT-LA |
|
|
4G-ANTM-OM-CM |
See Cisco 4G Indoor Ceiling-Mount Omnidirectional Antenna (4G-ANTM-OM-CM) |
-
- You must check your LEDs for signal reception as described in Table 2-1 .
- You should be familiar with the Cisco IOS software. See the Cisco IOS documentation beginning with Release 12.4(15)T or later for Cisco 3G support .
- To configure your 3G data profile, you will need the username, password, and access point name (APN) from your service provider:
After collecting the appropriate information, perform a full configuration on your router beginning with the tasks in Configuring Command-Line Access.
- If you plan to connect voice equipment, see Cisco IOS Voice Port Configuration Guide .
- If you need to obtain or change software licenses, see Software Activation on Cisco Integrated Services Routers and Cisco Integrated Service Routers G2 .
Configuring Command-Line Access
To configure parameters to control access to the router, perform the following steps, beginning in global configuration mode:
1. line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number
2.
password
password
3.
login
4. exec-timeout minutes [seconds]
5. line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number
6.
password
password
7.
login
8.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Global Parameters
To configure selected global parameters for your router, perform these steps:
1.
configure
terminal
2.
hostname
name
3.
enable
secret
password
4.
no
ip
domain-lookup
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure
terminal
Example: Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode when using the console port. If you are connecting to the router using a remote terminal, use the following: telnet router name or address Login: login id Password: ********* Router> enable |
| Step 2 | hostname
name
Example: Example: Router(config)# hostname Router |
Specifies the name for the router. |
| Step 3 | enable
secret
password
Example: Example: Router(config)# enable secret cr1ny5ho |
Specifies an encrypted password to prevent unauthorized access to the router. |
| Step 4 | no
ip
domain-lookup
Example: Example: Router(config)# no ip domain-lookup |
Disables the router from translating unfamiliar words (typos) into IP addresses. |
Configuring WAN Interfaces
Configure the WAN interface for your router using one of the following as appropriate:
- Configuring a Fast Ethernet WAN Interface
- Configuring the Media Type
- Configuring a Gigabit Ethernet WAN Interface
- Configuring a V.92 Modem Interface
- Configuring a VDSL2 WAN Interface
- Configuring ADSL or VDSL on Cisco 860VAE and 880VA Multimode ISRs
- Overview of Cisco 860VAE, 886VA, and 887VA Multimode ISRs
- ADSL2/2+ Annex M Mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs
- Configuring Seamless Rate Adaption
- Configuring UBR+
- Configuring ADSL Mode
- Configuring VDSL Mode
- Enabling ADSL2/2+ Annex M Mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs
- Enabling Seamless Rate Adaption
- Configuring UBR+
- Configuring the Training Log Using the CLI
- Configuring a G.SHDSL WAN Interface in ATM mode
- Configuring a G.SHDSL WAN Interface in EFM mode
- Configuring the Cellular Wireless WAN Interface
- Configuring Dual SIM for Cellular Networks on Cisco 819 Series ISR
- Configuring Router for Image and Config Recovery Using Push Button for Cisco 819 Series ISR Router
- Configuring WAN Mode on Cisco 860VAE ISRs
Configuring a Fast Ethernet WAN Interface
To configure the Fast Ethernet interface on a Cisco 861 or 881 ISR, perform these steps, beginning in global configuration mode:
1. interface type number
2.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
3.
no
shutdown
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type number
Example: Router(config)# interface fastethernet 4 |
Enters the configuration mode for a Fast Ethernet WAN interface on the router. |
| Step 2 | ip
address
ip-address
mask
Example: Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 |
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the specified Fast Ethernet interface. |
| Step 3 | no
shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the Ethernet interface, changing its state from administratively down to administratively up. |
| Step 4 | exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit |
Exits configuration mode for the Fast Ethernet interface and returns to global configuration mode. |
 Note | Cisco IOS Release 15.1 (3) T introduces the batch command under the interface mode. You may notice a reduced CPU utilization when interface batching is enabled because packets are processed in batches resulting in more efficient cache usage. |
Configuring the Media Type
Before configuring the Gigabit Ethernet interface on the Cisco 892F ISRs, you must first select the media type as either SFP or RJ45.
To configure the media type, perform the following steps, begining in global configuration mode:
1. interface type number
2. media-type {sfp | rj45}
3.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Gigabit Ethernet WAN Interface
To configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) WAN interface on a Cisco 891, 892, or 860VAE ISR, perform these steps, beginning in global configuration mode:
1. interface type number
2.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
3.
no
shutdown
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type number
Example: Router(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1 |
Enters the configuration mode for a Gigabit Ethernet WAN interface on the router. |
| Step 2 | ip
address
ip-address
mask
Example: Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 |
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the specified Gigabit Ethernet interface. |
| Step 3 | no
shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the Ethernet interface, changing its state from administratively down to administratively up. |
| Step 4 | exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit Example: Router(config)# |
Exits configuration mode for the Gigabit Ethernet interface and returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuring a V.92 Modem Interface
The Cisco 891 ISR has a V.92 modem backup interface. To configure this interface, perform these steps, beginning in global configuration mode:
1. interface type number
2.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
3.
encapsulation
ppp
4.
dialer
in-band
5.
dialer
string
dial-string
6.
dialer-group
group-number
7.
async
mode
dedicated
8.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type number
Example: Example: Router(config)# interface async 1 |
Enters the configuration mode for a V.92 WAN interface (serial interface) on the router. |
| Step 2 | ip
address
ip-address
mask
Example: Example: Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 |
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the specified V.92 interface. |
| Step 3 | encapsulation
ppp
Example: Example: Router(config-if)# encapsulation ppp |
Sets the encapsulation method to point-to-point protocol (PPP) for the serial interface. |
| Step 4 | dialer
in-band
Example: Example: Router(config-if)# dialer in-band |
Specifies that dial-on-demand routing (DDR) is supported. |
| Step 5 | dialer
string
dial-string
Example: Example: Router(config-if)# dialer string 102 |
Specifies the string (telephone number) to be used when placing a call from the interface. |
| Step 6 | dialer-group
group-number
Example: Example: Router(config-if)# dialer-group 1 |
Configures the interface to belong to a specific dialing access group. |
| Step 7 | async
mode
dedicated
Example: Example: Router(config-if)# async mode dedicated |
Places the line into dedicated asynchronous mode using Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) or PPP encapsulation. |
| Step 8 | exit
Example: Example: Router(config-if)# exit Example: Router(config)# |
Exits configuration mode for the V.92 interface and returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuring a VDSL2 WAN Interface
The VDSL2 WAN interface is used on the Cisco 887V ISR platforms. Note that the VDSL2 WAN interface uses Ethernet as the Layer 2 transport mechanism.
To configure VDSL2 on the Cisco 887V ISR, perform these steps, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
controller
vdsl
0
2. interface type number
3.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
4.
shutdown
5.
no
shutdown
6.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring ADSL or VDSL on Cisco 860VAE and 880VA Multimode ISRs
This section contains the following topics:
Overview of Cisco 860VAE, 886VA, and 887VA Multimode ISRs
The Cisco customer premise equipment (CPE) Cisco 866VAE, 867VAE, 866VAE-K9, 867VAE-K9, 886VA and 887VA integrated services routers (ISRs) support asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) 1/2/2+ and very high speed digital subscriber line 2 (VDSL2) transmission modes, also called multimode.
 Note | The 866VAE and 886VA support xDSL over ISDN. The 867VAE and 887VA support xDSL over a plain old telephone system (POTS). |
The default CPE operating mode is auto. Auto mode means that the CPE trains up to the mode configured on the digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM), ADSL1/2/2+, or VDSL2.
The following examples assume the DSLAM is configured in either ADSL2+ mode or VDSL2 mode, and the CPE is configured in auto mode.
Figure 1 shows an ATM WAN or Ethernet WAN network topography.
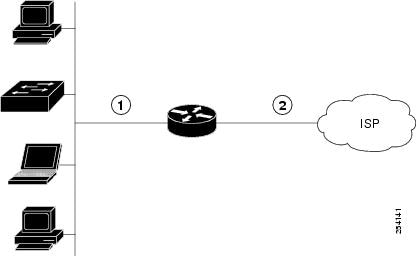
|
1 |
Fast Ethernet LAN interface or Gigabit Ethernet LAN interface |
2 |
ATM WAN interface—ADSL 1/2/2+ mode or Ethernet WAN Interface—VDSL2 mode |
 Note | A DSLAM in Layer 1 mode may be configured for auto mode. A DSLAM in Layer 2 mode must be configured for ATM mode or packet transfer mode (PTM). |
 Note | Cisco 886VA and 887VA allow a maximum of four permanent virtual circuits (PVCs). |
 Note | Cisco 866VAE, Cisco 867VAE, Cisco 866VAE-K9, and Cisco 867VAE-K9 ISRs allow a maximum of two PVCs. |
ADSL2/2+ Annex M Mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs
Annex M is an enhancement of the G.992.3 standard that doubles the upstream bandwidth by "borrowing" 32 additional tones from the downstream frequency range. This feature enables service providers to provision symmetric data rates for ADSL2 and ADSL2+ services with data rates up to 2 Mbps.
Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)T adds support for enabling Annex M data structures on Cisco 887VA platforms and Annex A data structures on Cisco 887VA-M platforms. This features allows both Annex A and Annex M structures to be run on the same platform with a performance tradeoff for the annex that is not optimized for the device. With this feature implementation, the modes supported on Annex A platforms are the same as the modes supported on Annex M platforms (887VA-M and EHWIC-1DSL-VA-M). When digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM) supports Annex M, Annex M mode takes precedence over Annex A mode.
 Note | Cisco 867VAE and 867VAE-K9 require Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M2 or 15.2(2)T or later to use this feature. |
For information on configuring Annex M data structures on Annex A platforms, see the, Enabling ADSL2/2+ Annex M Mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs.
Configuring Seamless Rate Adaption
ADSL connections can be dropped due to a number of reasons, such as crosstalk, changes in noise margin, temperature changes, or interference. ADSL2 addresses these problems by adapting the data rate in real-time. Seamless rate adaptation (SRA) enables the ADSL2 system to change the data rate of the connection during operation without any service interruption or bit errors.
 Note | These features are not currently available on the 866VAE, 867VAE, 866VAE-K9, and 867VAE-K9. |
For information on configuring SRA, see the Enabling Seamless Rate Adaption.
Configuring UBR+
UBR is typically used for data communications applications, such as file transfer and email. UBR is a best effort service and is the lowest class of service in the hierarchy. There are no guarantees to the actual bandwidth allowed. Therefore, UBR virtual circuits (VCs) are susceptible to a large number of cell drops or a high cell transfer delay as cells move from the source to the destination. UBR has no bounds on Cell Delay Variation Tolerance (CDVT) and is only a best effort service.
UBR+ is a special ATM service class developed by Cisco. UBR defines only peak cell rate (PCR); however, UBR+ defines a minimum guaranteed cell rate (MCR) and (on the switch) a cell delay variation tolerance (CDVT).
 Note | On Cisco IOS versions 15.2(1)T and later, UBR+ is compatable with Cisco Multimode 886VA and 887VA routers. |
 Note | These features are not currently available on the 866VAE, 867VAE, 866VAE-K9, and 867VAE-K9. |
For information on configuring UBR+, see the Configuring UBR+.
Configuring ADSL Mode
Configuration tasks
Perform the following tasks to configure ADSL mode:
- Configuring ADSL Auto Mode
- Configuring CPE and Peer for ADSL Mode
- ADSL Configuration Example
- Verifying ADSL Configuration
- Verifying CPE to Peer Connection for ADSL
Configuring ADSL Auto Mode
Perform these steps to configure the DSL controller to auto mode, starting in global configuration mode.
 Note | Configure the DSLAM in ADSL 1/2/2+ mode prior to configuring the router. |
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3. controller vdsl slot
4. operating mode {auto | adsl1 | adsl2 | adsl2+ | vdsl2 | ansi}
5. end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
| ||
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | controller vdsl slot
Example: Example: Router(config)# controller vdsl 0 |
Enters config mode for the VDSL controller. | ||
| Step 4 | operating mode
{auto
|
adsl1
|
adsl2
|
adsl2+
|
vdsl2
|
ansi}
Example: Example: Router(config-controller)# operating mode auto |
Configures the operating mode. The default is auto and is recommended.
| ||
| Step 5 | end
Example: Example: Router(config-controller)# end Example: Router# |
Exits the configuration mode and enters EXEC mode.
|
Configuring CPE and Peer for ADSL Mode
When configuring for ADSL, the ATM main interface or ATM sub-interface must be configured with a PVC and an IP address, perform a no shutdown command on the interface if needed.
Configuring the ATM CPE side
Perform the following steps to configure the ATM CPE side, starting in global configuration mode.
1. interface type number
2. no shutdown
3. interface atm0.1 point-to-point
4. ip address ip-address mask
5.
pvc [name] vpi/vci
6.
protocol protocol {protocol-address [virtual-template] |
inarp} [[no] broadcast | disable-check-subnet | [no] enable-check-subnet]
7. end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type number
Example: Router(config)# interface atm0 |
Enters configuration mode for the ATM WAN interface (ATM0). |
| Step 2 | no shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the configuration changes to the ATM interface. |
| Step 3 | interface atm0.1 point-to-point
Example: Router(config-if)# interface ATM0.1 point-to-point Example: Router(config-subif)# |
Enables ATM0.1 point-to-point interface. |
| Step 4 | ip address ip-address mask
Example: Router(config-subif)# ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 |
Enters IP address and subnet mask. |
| Step 5 | pvc [name] vpi/vci
Example: Router(config-subif)# pvc 13/32 |
Creates or assigns a name to an ATM PVC and enters the ATM virtual circuit configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | protocol protocol {protocol-address [virtual-template] |
inarp} [[no] broadcast | disable-check-subnet | [no] enable-check-subnet]
Example: Router(config-if-atm-vc)# protocol ip 30.0.0.2 broadcast |
Configures a static map for an ATM PVC. |
| Step 7 | end
Example: Router(config-if-atm-vc)# end Router# |
Exits the configuration mode and enters EXEC mode. |
Configuring the ATM Peer side
Perform the following steps to configure the ATM peer side, starting in global configuration mode.
1. interface type number
2. no shutdown
3. interface atm0.1 point-to-point
4. ip address ip-address mask
5.
pvc [name] vpi/vci
6.
protocol protocol {protocol-address [virtual-template] |
inarp} [[no] broadcast | disable-check-subnet | [no] enable-check-subnet]
7. end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type number
Example: Router(config)# interface atm0 |
Enters configuration mode for the ATM WAN interface (ATM0). |
| Step 2 | no shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the configuration changes to the ATM interface. |
| Step 3 | interface atm0.1 point-to-point
Example: Router(config-if)# interface ATM0.1 point-to-point |
Enables the ATM0.1 point-to-point interface. |
| Step 4 | ip address ip-address mask
Example: Router(config-subif)# ip address 30.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 |
Enters IP address and subnet mask. |
| Step 5 | pvc [name] vpi/vci
Example: Router(config-subif)# pvc 13/32 |
Creates or assigns a name to an ATM PVC and enters the ATM virtual circuit configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | protocol protocol {protocol-address [virtual-template] |
inarp} [[no] broadcast | disable-check-subnet | [no] enable-check-subnet]
Example: Router(config-if-atm-vc)# protocol ip 30.0.0.1 broadcast |
Configures a static map for an ATM PVC. |
| Step 7 | end
Example: Router(config-if-atm-vc)# end |
Exits the configuration mode and enters EXEC mode. |
ADSL Configuration Example
The following example shows a typical ADSL2+ configuration set to auto mode. Outputs in bold are critical.
Router# show running Building configuration... Current configuration : 1250 bytes ! ! Last configuration change at 02:07:09 UTC Tue Mar 16 2010 ! version 15.1 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 10 ip source-route ! ! ! ! ip cef no ipv6 cef ! ! ! ! license udi pid CISCO887-V2-K9 sn FHK1313227E license boot module c880-data level advipservices ! ! vtp domain cisco vtp mode transparent ! ! controller VDSL 0 ! vlan 2-4 ! ! ! ! ! interface Ethernet0 no ip address shutdown no fair-queue ! interface BRI0 no ip address encapsulation hdlc shutdown isdn termination multidrop ! interface ATM0 no ip address no atm ilmi-keepalive ! interface ATM0.1 point-to-point ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 pvc 15/32 protocol ip 30.0.0.2 broadcast ! ! interface FastEthernet0 ! interface FastEthernet1 ! interface FastEthernet2 ! interface FastEthernet3 ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ! ! ! ! ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 no modem enable line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login transport input all ! exception data-corruption buffer truncate end
Verifying ADSL Configuration
Verify that the configuration is set properly by using the show controller vdsl 0 command from the privileged EXEC mode. Outputs in bold are critical.
Router# show controller vdsl 0
Controller VDSL 0 is UP
Daemon Status: Up
XTU-R (DS) XTU-C (US)
Chip Vendor ID: 'BDCM' 'BDCM'
Chip Vendor Specific: 0x0000 0x6110
Chip Vendor Country: 0xB500 0xB500
Modem Vendor ID: 'CSCO' 'BDCM'
Modem Vendor Specific: 0x4602 0x6110
Modem Vendor Country: 0xB500 0xB500
Serial Number Near: FHK1313227E 887-V2-K 15.1(20100
Serial Number Far:
Modem Version Near: 15.1(20100426:193435) [changahn
Modem Version Far: 0x6110
Modem Status: TC Sync (Showtime!)
DSL Config Mode: AUTO
Trained Mode: G.992.5 (ADSL2+) Annex A
TC Mode: ATM
Selftest Result: 0x00
DELT configuration: disabled
DELT state: not running
Trellis: ON ON
Line Attenuation: 1.0 dB 1.4 dB
Signal Attenuation: 1.0 dB 0.0 dB
Noise Margin: 6.8 dB 13.6 dB
Attainable Rate: 25036 kbits/s 1253 kbits/s
Actual Power: 13.7 dBm 12.3 dBm
Total FECS: 0 0
Total ES: 0 0
Total SES: 0 0
Total LOSS: 0 0
Total UAS: 0 0
Total LPRS: 0 0
Total LOFS: 0 0
Total LOLS: 0 0
Bit swap: 163 7
Full inits: 32
Failed full inits: 0
Short inits: 0
Failed short inits: 0
Firmware Source File Name (version)
-------- ------ -------------------
VDSL embedded VDSL_LINUX_DEV_01212008 (1)
Modem FW Version: 100426_1053-4.02L.03.A2pv6C030f.d22j
Modem PHY Version: A2pv6C030f.d22j
DS Channel1 DS Channel0 US Channel1 US Channel0
Speed (kbps): 0 24184 0 1047
Previous Speed: 0 24176 0 1047
Total Cells: 0 317070460 0 13723742
User Cells: 0 0 0 0
Reed-Solomon EC: 0 0 0 0
CRC Errors: 0 0 0 0
Header Errors: 0 0 0 0
Interleave (ms): 0.00 0.08 0.00 13.56
Actual INP: 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.80
Training Log : Stopped
Training Log Filename : flash:vdsllog.bin
Verifying CPE to Peer Connection for ADSL
Ping the peer to confirm that CPE to peer configuration is set up correctly.
Router# ping 30.0.0.2 rep 20 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 20, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 30.0.0.2, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (20/20), round-trip min/avg/max = 20/22/28 ms Router#
Configuring VDSL Mode
Configuration tasks
Perform the following tasks to configure VDSL mode:
- Configuring VDSL Auto Mode
- Configuring CPE and Peer for VDSL Mode
- VDSL Configuration Example
- Verifying VDSL Configuration
- Verifying CPE to Peer Connection for VDSL
Configuring VDSL Auto Mode
Perform the following steps to configure the DSL controller to auto mode, starting in global configuration mode.
 Note | Configure the DSLAM in VDSL2 mode prior to configuring the router. |
1. controller vdsl slot
2. operating mode {auto | adsl1 | adsl2 | adsl2+ | vdsl2 | ansi}
3. end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | controller vdsl slot
Example: Router(config)# controller vdsl 0 |
Enters config mode for the VDSL controller. | ||
| Step 2 | operating mode
{auto
|
adsl1
|
adsl2
|
adsl2+
|
vdsl2
|
ansi}
Example: Router(config-controller)# operating mode auto |
Configures the operating mode. The default is auto and is recommended.
| ||
| Step 3 | end
Example: Router(config-controller)# end Router# |
Exits the configuration mode and enters EXEC mode.
|
Configuring CPE and Peer for VDSL Mode
When configuring VDSL, configure the ethernet 0 interface and perform a no shutdown command on the interface if needed. Start in the global configuration mode.
Configuring the VDSL CPE Side
Perform the following steps to configure the VDSL CPE side, starting in the global configuration mode.
1. interface type number
2. ip address ip-address mask
3. no shutdown
4. end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type number
Example: Router(config)# interface ethernet0 |
Enters configuration mode for the Ethernet interface 0. |
| Step 2 | ip address ip-address mask
Example: Router(config-if)# ip address 90.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 |
Enters the IP address and subnet mask. |
| Step 3 | no shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the configuration changes to the ip address and subnet mask. |
| Step 4 | end
Example: Router(config-if)# end |
Exits the configuration mode and enters EXEC mode. |
Configuring the VDSL Peer Side
Perform the following steps to configure the VDSL Peer side, starting in the global configuration mode.
1. interface type number
2. ip address ip-address mask
3. no shutdown
4.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type number
Example: Router(config)# interface ethernet0 |
Enters configuration mode for the Ethernet interface 0. |
| Step 2 | ip address ip-address mask
Example: Router(config-if)# ip address 90.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 |
Configures the IP address and subnet mask. |
| Step 3 | no shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the configuration changes to the IP address and subnet mask. |
| Step 4 | end
Example: Router(config-if)# end |
Exits the configuration mode and enters EXEC mode. |
VDSL Configuration Example
The following example shows a typical output of a VDSL configuration. Outputs in bold are critical.
Router# show running Building configuration... Current configuration : 1250 bytes ! ! Last configuration change at 02:07:09 UTC Tue Mar 16 2010 ! version 15.1 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 10 ip source-route ! ! ! ! ip cef no ipv6 cef ! ! ! ! license udi pid CISCO887-V2-K9 sn FHK1313227E license boot module c880-data level advipservices ! ! vtp domain cisco vtp mode transparent ! ! controller VDSL 0 ! vlan 2-4 ! ! ! ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 no fair-queue ! interface BRI no ip address encapsulation hdlc shutdown isdn termination multidrop ! interface ATM0 no ip address shutdown ! ! interface FastEthernet0 ! interface FastEthernet1 ! interface FastEthernet2 ! interface FastEthernet3 ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ! ! ! ! ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 no modem enable line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login transport input all ! exception data-corruption buffer truncate end
Verifying VDSL Configuration
Verify the configuration is set properly by using the show controller vdsl 0 command from privileged EXEC mode. Outputs in bold are critical.
Router# show controller vdsl 0
Controller VDSL 0 is UP
Daemon Status: Up
XTU-R (DS) XTU-C (US)
Chip Vendor ID: 'BDCM' 'BDCM'
Chip Vendor Specific: 0x0000 0x0000
Chip Vendor Country: 0xB500 0xB500
Modem Vendor ID: 'CSCO' 'BDCM'
Modem Vendor Specific: 0x4602 0x0000
Modem Vendor Country: 0xB500 0xB500
Serial Number Near: FHK1313227E 887-V2-K 15.1(20100
Serial Number Far:
Modem Version Near: 15.1(20100426:193435) [changahn
Modem Version Far: 0x0000
Modem Status: TC Sync (Showtime!)
DSL Config Mode: AUTO
Trained Mode: G.993.2 (VDSL2) Profile 12a
TC Mode: PTM
Selftest Result: 0x00
DELT configuration: disabled
DELT state: not running
Trellis: ON OFF
Line Attenuation: 1.0 dB 0.0 dB
Signal Attenuation: 1.0 dB 0.0 dB
Noise Margin: 12.0 dB 9.5 dB
Attainable Rate: 87908 kbits/s 50891 kbits/s
Actual Power: 13.5 dBm 8.9 dBm
Per Band Status: D1 D2 D3 U0 U1 U2 U3
Line Attenuation(dB): 0.9 2.3 N/A 7.2 2.9 7.0 N/A
Signal Attenuation(dB): 0.9 2.3 N/A N/A 2.3 6.6 N/A
Noise Margin(dB): 14.5 9.3 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Total FECS: 0 0
Total ES: 0 0
Total SES: 0 0
Total LOSS: 0 0
Total UAS: 0 0
Total LPRS: 0 0
Total LOFS: 0 0
Total LOLS: 0 0
Bit swap: 1 0
Full inits: 33
Failed full inits: 0
Short inits: 0
Failed short inits: 0
Firmware Source File Name (version)
-------- ------ -------------------
VDSL embedded VDSL_LINUX_DEV_01212008 (1)
Modem FW Version: 100426_1053-4.02L.03.A2pv6C030f.d22j
Modem PHY Version: A2pv6C030f.d22j
DS Channel1 DS Channel0 US Channel1 US Channel0
Speed (kbps): 0 84999 0 48968
Previous Speed: 0 24184 0 1047
Reed-Solomon EC: 0 0 0 0
CRC Errors: 0 0 0 0
Header Errors: 0 0 0 0
Interleave (ms): 0.00 6.00 0.00 0.00
Actual INP: 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Training Log : Stopped
Training Log Filename : flash:vdsllog.bin
Router#
Verifying CPE to Peer Connection for VDSL
Ping the peer to confirm that CPE to peer configuration is setup correctly.
Router# ping 30.0.0.2 rep 20 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 20, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 30.0.0.2, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (20/20), round-trip min/avg/max = 20/22/28 ms Router#
Enabling ADSL2/2+ Annex M Mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs
 Note | This feature requires Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)T or a later. |
 Note | Cisco 867VAE and 867VAE-K9 require Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M2 or 15.2(2)T or later to use this feature. |
Configuring ADSL2/2+ Annex M mode on Over POTS VDSL2/ADSL Multimode Annex A SKUs.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3. controller vdsl 0
4. operating mode {adsl1 | adsl2 annex a | annex m | adsl2+ annex a | annex m] | ansi | auto| vdsl2}
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | controller vdsl 0 |
Enters configuration mode for the VDSL controller. |
| Step 4 | operating mode
{adsl1
|
adsl2
annex
a |
annex
m
|
adsl2+
annex
a |
annex
m]
|
ansi
|
auto|
vdsl2}
Example: Router(config-controller)# operating mode adsl2+ annex m |
asdl1—Configures operation in ITU G.992.1 Annex A full-rate mode. adsl2—Configures operation in ADSL2 operating mode-ITU G.992.3 Annex A, Annex L, and Annex M. If an Annex operating mode is not chosen, Annex A, Annex L, and Annex M are enabled. The final mode is decided by negotiation with the DSL access multiplexer (DSLAM). adsl2+—Configures operation in ADSL2+ mode-ITU G.992.5 Annex A and AnnexM. If an Annex A operating mode is not chosen, both Annex and Annex M is enabled. The final mode is decided by negotiation with DSLAM. ansi—Configures a router to operate in ANSI full-rate mode-ANSI T1.413. auto—Default setting. Configures the router so that the DSLAM automatically picks the DSL operating mode, in the sequence described in the "Usage Guidelines" section. All supported modes are enabled. vdsl2—Configures operation in ITU G.993.2 mode. annex a, m—(Optional) If the annex option is not specified, both Annex A and Annex M are enabled. The final mode is decided by negotiation with the Digital Synchronous Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM). |
Enabling Seamless Rate Adaption
To enable SRA, perform the following steps.
 Note | SRA mode is disabled by default. |
 Note | SRA requires Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)T or a later release. |
 Note | These features are not currently available on the Cisco 866VAE, 867VAE, 866VAE-K9, or 867VAE-K9. |
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
controller
vdsl
x/y/z
4.
sra
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router# enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | controller
vdsl
x/y/z
Example: Router(config)# controller vdsl 0/0/0 |
Enters controller configuration mode. Use the controller vdsl command in global configuration mode. This command does not have a no form. x—Defines the network module. y—Defines the slot number. z—Defines the port number. |
| Step 4 | sra
Example: router(config-controller)# sra |
Enables SRA mode. Use the no form of the command to disable SRA. |
Example Configuration: Seamless Rate Adaption
The following example enables SRA on a VDSL line:
! ! ! rotuer>enable router# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z router(config)# controller vdsl 0 router(config-controller)# sra router(config-controller)# end router# ! ! !
Configuring UBR+
Perform the following steps to configure UBR+.
 Note | Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)T or a later release is required to run UBR+ on Cisco 886VA, 887VA, and 887VA-M routers. |
 Note | These features are not currently available on the Cisco 866VAE, 867VAE, 866VAE-K9, or 867VAE-K9. |
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3. ubr+ output-pcr output-mcr [input-pcr] [input-mcr]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ubr+
output-pcr output-mcr
[input-pcr]
[input-mcr]
Example: Router(config-if-vc)# ubr+ 10000 3000 9000 1000 |
Configures unspecified bit rate (UBR) quality of service (QoS) and specifies the output peak cell rate and output minimum guaranteed cell rate for an ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC), PVC range, switched virtual circuit (SVC), virtual circuit (VC) class, or VC bundle member. To remove the UBR+ parameters, use the no form of this command. output-pcr—The output peak cell rate (PCR) in kbps. output-mcr—The output minimum guaranteed cell rate in kbps. input-pcr—(Optional for SVCs only) The input PCR in kbps. If this value is omitted, the input-pcr equals the output-pcr. input-mcr—(Optional for SVCs only) The input minimum guaranteed cell rate in kbps. If this value is omitted, the input-mcr equals the output-mcr. |
UBR+ Example
The following example configures UBR+ PVC on a DSL line:
interface atm 0/0 pvc 4/100 ubr+ 2304 2304
The following example specifies the output-pcr argument for an ATM PVC to be 100000 kbps and the output-mcr to be 3000 kbps:
pvc 1/32 ubr+ 100000 3000
The following example specifies the output-pcr, output-mcr, input-pcr, and input-mcr arguments for an ATM SVC to be 10000 kbps, 3000 kbps, 9000 kbps, and 1000 kbps, respectively:
svc lion nsap 47.0091.81.000000.0040.0B0A.2501.ABC1.3333.3333.05 ubr+ 10000 3000 9000 1000
Troubleshooting
There are no new commands for checking traffic on the Cisco 886VA and 887VA. Some helpful commands include the following show commands:
- show interface Ethernet0
- show interface ATM0
- show interface summary
- show controller vdsl 0
- show controller atm0
- show controller vdsl 0 datapath
- show atm pvc
The “Cisco 860, Cisco 880, and Cisco 890 Series Integrated Services Routers Software Configuration Guide, Troubleshooting” section may also be helpful.
Configuring the Training Log Using the CLI
When you initiate the training log capture using the debug vdsl 0 training log on the Cisco 866VAE, Cisco 867VAE, Cisco 866VAE-K9, and Cisco 867VAE-K9 ISRs, the training log file opens. Any messages that are generated are buffered locally and are written to the training log file at 5k bytes per interval. The messages are not written all at one time, as in previous software versions that supported the training log capture feature.
 Note | A maximum log capacity of 8MB (approximately 1 hour of capture) exists on the Cisco 866VAE, Cisco 867VAE, Cisco 866VAE-K9, and Cisco 867VAE-K9 ISRs. Because of this capacity limitation, when the entire log collection exceeds 8MB, the log capture is automatically terminated. |
 Note | Cisco 866VAE, Cisco 867VAE, Cisco 866VAE-K9, and Cisco 867VAE-K9 ISRs do not support the continuous training log autostop feature. |
- Capturing the Training Log
- Halting the Training Log Capture
- Displaying the Training Log Status and File Location
Capturing the Training Log
By default the training log is saved to flash:vdsllog.bin.
To start the training log capture, use the debug vdsl 0 training log command.
Router# debug vdsl 0 training log Router#
The following confirmation is displayed:
Training log generation started for VDSL 0
Halting the Training Log Capture
To stop the training log capture, use the no debug vdsl 0 training log command.
Router# no debug vdsl 0 training log Router#
The following confirmation is displayed:
Training Log file for VDSL written to flash:vdsllog.bin
Displaying the Training Log Status and File Location
To display the training log status and file location, use the show controller vdsl 0 command.
Router# show controller vdsl 0 Router#
The following confirmation is displayed:
Controller VDSL 0 is UP
Daemon Status: NA
XTU-R (DS) XTU-C (US)
Chip Vendor ID: 'BDCM' 'BDCM'
Chip Vendor Specific: 0x0000 0x938C
Chip Vendor Country: 0xB500 0xB500
Modem Vendor ID: 'CSCO' 'BDCM'
Modem Vendor Specific: 0x4602 0x938C
Modem Vendor Country: 0xB500 0xB500
Serial Number Near: GMH1049001M 867VAE-K 15.1(20110
Serial Number Far:
Modem Version Near: 15.1(20110422:230431) [suguraja
Modem Version Far: 0x938C
Modem Status: TC Sync (Showtime!)
DSL Config Mode: AUTO
Trained Mode: G.992.5 (ADSL2+) Annex A
TC Mode: ATM
Selftest Result: 0x00
DELT configuration: disabled
DELT state: not running
Trellis: ON ON
Line Attenuation: 0.0 dB 0.0 dB
Signal Attenuation: 0.0 dB 0.0 dB
Noise Margin: 16.0 dB 14.6 dB
Attainable Rate: 28516 kbits/s 1222 kbits/s
Actual Power: 7.0 dBm 12.4 dBm
Total FECS: 3 0
Total ES: 0 0
Total SES: 0 0
Total LOSS: 0 0
Total UAS: 147 147
Total LPRS: 0 0
Total LOFS: 0 0
Total LOLS: 0 0
Bit swap: 0 0
Full inits: 1
Failed full inits: 0
Short inits: 0
Failed short inits: 0
Firmware Source File Name (version)
-------- ------ -------------------
VDSL embedded (0)
Modem FW Version: 23a
Modem PHY Version: A2pv6C032b.d23a
DS Channel1 DS Channel0 US Channel1 US Channel0
Speed (kbps): 0 24543 0 1020
Previous Speed: 0 0 0 0
Total Cells: 0 87837567 0 3652502
User Cells: 0 0 0 0
Reed-Solomon EC: 0 3 0 0
CRC Errors: 0 0 0 0
Header Errors: 0 0 0 0
Interleave (ms): 0.00 15.00 0.00 3.76
Actual INP: 0.00 57.00 0.00 0.50
Training Log : Stopped
Training Log Filename : flash:vdsllog.bin
Configuring a G.SHDSL WAN Interface in ATM mode
Perform the following steps to configure G.SHDSL on the Cisco 888 ISR perform these steps, beginning in global configuration mode.
1.
controller
dsl
slot/port
2.
mode
atm
3.
line-term
cpe
4.
line-mode
4
wire
standard
5. line-rate {auto | rate}
6.
interface
atm
interface-number
7.
ip-address
ip-address
8.
load-interval
seconds
9. no atm ilmi-keepalive [seconds]
10. pvc [name] vpi/vci
11.
protocol
protocol
protocol-address
broadcast
12. encapsulation [encapsulation-type]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | controller
dsl
slot/port
Example: Router(config)# controller dsl 0 |
Enters controller configuration mode and the controller number. | ||||
| Step 2 | mode
atm
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# mode atm |
Enables ATM encapsulation and creates logical ATM interface 0. | ||||
| Step 3 | line-term
cpe
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# line-term cpe |
Enables CPE. | ||||
| Step 4 | line-mode
4
wire
standard
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# line-mode 4 wire standard |
Enables 4 wire operation. | ||||
| Step 5 | line-rate
{auto |
rate}
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# line-rate 4608 |
Specifies the DSL line rate for the SHDSL port. The range is 192 to 2312 kbps. The default is auto (negotiated between the SHDSL port and the DSLAM).
| ||||
| Step 6 | interface
atm
interface-number
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# interface atm0 |
Enters ATM configuration mode for interface ATM 0. | ||||
| Step 7 | ip-address
ip-address
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# ip-address IP-address |
Assigns an IP address to the DSL ATM interface. | ||||
| Step 8 | load-interval
seconds
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# load-interval 3 |
Assigns a load interval value. | ||||
| Step 9 | no
atm
ilmi-keepalive
[seconds]
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# no atm ilmi-keepalive0 |
Disables Integrated Local Management Interface (ILMI) keepalives. If you enable ILMI keepalives without specifying the number of seconds, the default time interval is 3 seconds. | ||||
| Step 10 | pvc [name]
vpi/vci
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# pvc 0/35 |
Enters atm-virtual-circuit (interface-atm-vc) configuration mode, and configures a new ATM PVC by assigning a name (optional) and VPI/VCI numbers. The default traffic shaping is UBR; the default encapsulation is AAL5+LLC/SNAP. | ||||
| Step 11 | protocol
protocol
protocol-address
broadcast
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# protocol ip 10.10.10.2 broadcast |
Enables IP connectivity and creates a point-to-point IP address for the VC. | ||||
| Step 12 | encapsulation
[encapsulation-type]
Example: Router(config-ctrl)# encapsulation aal5snap |
Configures the ATM adaptation layer (AAL) and encapsulation type.
|
Configuration Example: Configuring a G.SHDSL WAN Interface
The following configuration example shows a 4-wire standard G.SHDSL configuration.
! controller DSL 0 mode atm line-term cpe line-mode 4-wire standard dsl-mode shdsl symmetric annex B line-rate 4608 ! interface BRI0 no ip address encapsulation hdlc shutdown isdn termination multidrop ! ! interface ATM0 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 no atm ilmi-keepalive pvc 0/35 protocol ip 10.10.10.2 broadcast encapsulation aal5snap ! ! interface FastEthernet0 ! interface FastEthernet1 ! interface FastEthernet2 ! interface FastEthernet3 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 2.15.15.26 255.255.255.0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ip route 223.255.254.254 255.255.255.255 Vlan1 no ip http server no ip http secure-server !
Verifying G.SHDSL WAN Interface Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured the router, enter the show running command and look for controller DSL and interface ATM0 parameters.
Router# show running Building configuration... Current configuration : 1298 bytes ! ....... ! controller DSL 0 mode atm line-term cpe line-mode 4-wire standard dsl-mode shdsl symmetric annex B line-rate 4608 ! ! interface ATM0 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 no atm ilmi-keepalive pvc 0/31 protocol ip 10.10.10.5 broadcast encapsulation aal5snap !
Configuring a G.SHDSL WAN Interface in EFM mode
To configure G.SHDSL on the Cisco 888E ISR, perform Configuring Cisco G.SHDSL EFM HWICs in Cisco Routers at:
Configuring the Cellular Wireless WAN Interface
The Cisco 880 series and Cisco 810 series ISRs provide a third generation (3G) wireless interface for use over Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA) networks. The interface is a 34-mm PCMCIA slot for Cisco 880 series.
Its primary application is WAN connectivity as a backup data link for critical data applications. However, the 3G wireless interface can also function as the primary WAN connection for the router.
To configure the 3G cellular wireless interface, follow these guidelines and procedures:
- Prerequisites for Configuring the 3G Wireless Interface
- Restrictions for Configuring the Cellular Wireless Interface
- Data Account Provisioning
- Configuring a Cellular Interface
- Configuring DDR
- Configuring Data Dedicated Transmission Mode (DDTM)
- Examples for Configuring Cellular Wireless Interfaces
Prerequisites for Configuring the 3G Wireless Interface
The following are prerequisites to configuring the 3G wireless interface:
- You must have wireless service from a carrier, and you must have network coverage where your router will be physically placed. For a complete list of supported carriers, see the data sheet at:
- You must subscribe to a service plan with a wireless service provider and obtain a SIM card (GSM modem only) from the service provider.
- You must check your LEDs for signal strength, as described in Table 1.
- You should be familiar with the Cisco IOS software, beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 4.1 or later. For Cisco 3G Wireless support, see the Cisco IOS documentation.
- To configure your GSM data profile, you need the following
information from your service provider:
- Username
- Password
- Access point name (APN)
- To configure your CDMA data profile for manual activation, you need
the following information from your service provider:
- Master Subsidy Lock (MSL) number
- Mobile Directory number (MDN)
- Mobile Station Identifier (MSID)
- Electronic Serial Number (ESN)
|
LED |
LED Color |
Signal Strength |
|---|---|---|
|
P3G RSSI1 |
Amber |
No service available and no RSSI detected |
|
Solid green |
High RSSI (–69 dBm or higher) |
|
|
Fast (16 Hz) blinking green |
Medium RSSI (–89 to –70 dBm) |
|
|
Slow (1 Hz) blinking green |
Low to medium RSSI (–99 to –90 dBm), minimum level for a reliable connection |
|
|
Off |
Low RSSI (less than –100 dBm) |
Restrictions for Configuring the Cellular Wireless Interface
The following restrictions apply to configuring the Cisco 3G wireless interface:
- A data connection can be originated only by the 3G wireless interface. Remote dial-in is not supported.
- Because of the shared nature of wireless communications, the experienced throughput varies depending on the number of active users or the amount of congestion in a given network.
- Cellular networks have higher latency than wired networks. Latency rates depend on the technology and carrier. Latency may be higher when there is network congestion.
- VoIP is not currently supported.
- Any restrictions that are part of the terms of service from your carrier also apply to the Cisco 3G wireless interface.
- Cisco 880G ISR does not support online insertion and removal (OIR) of 3G modems. To replace a modem with another modem of the same type, use the Cisco CLI to enter the shutdown command on the cellular interface before you replace the modems. =
- When a 3G modem is removed, the show interface cellular 0, show run, and show version command outputs still display cellular interface related information. The show interface command displays the following message, all other show commands have empty outputs.
3G Modem not inserted
- You can configure the cellular interface when the 3G modem is removed. However, the configuration is not effective until the 3G modem is inserted. The following message is shown when trying to configure the cellular interface while the modem is absent.
Router(config)# interface cellular 0 Warning: 3G Modem is not inserted Configuration will not be effective until modem is inserted =
- Inserting a different type of modem than was previously removed requires configuration changes and you must reload the system.
Data Account Provisioning
 Note | To provision your modem, you must have an active wireless account with a service provider. A SIM card must be installed in a GSM 3G wireless card. |
To provision your data account, follow these procedures:
- Verifying Signal Strength and Service Availability
- Configuring a GSM Modem Data Profile
- CDMA Modem Activation and Provisioning
Verifying Signal Strength and Service Availability
To verify the signal strength and service availability on your modem, use the following commands in privileged EXEC mode.
 Note | This feature requires Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)T or a later. |
 Note | Cisco 867VAE and 867VAE-K9 require Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M2 or 15.2(2)T or later to use this feature. |
1.
show
cellular
0
network
2. show cellular 0 hardware
3. show cellular 0 connection
4.
show
cellular
0
radio
5.
show
cellular
0
profile
6.
show
cellular
0
security
7.
show
cellular
0
all
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | show
cellular
0
network
Example: Router# show cellular 0 network |
Displays information about the carrier network, cell site, and available service. | ||
| Step 2 | show cellular 0 hardware
Example: Router# show cellular 0 hardware |
Displays the cellular modem hardware information. | ||
| Step 3 | show cellular 0 connection
Example: Router# show cellular 0 connection |
Displays the current active connection state and data statistics. | ||
| Step 4 | show
cellular
0
radio
Example: Router# show cellular 0 radio |
Shows the radio signal strength.
| ||
| Step 5 | show
cellular
0
profile
Example: Router# show cellular 0 profile |
Shows information about the modem data profiles created. | ||
| Step 6 | show
cellular
0
security
Example: Router# show cellular 0 security |
Shows the security information for the modem, such as SIM and modem lock status. | ||
| Step 7 | show
cellular
0
all
Example: Router# show cellular 0 all |
Shows consolidated information about the modem. The profiles that were created, the radio signal strength, the network security, and so on. |
Configuring a GSM Modem Data Profile
To configure or create a new modem data profile, enter the cellular 0 gsm profile create <profile number> <apn> <authentication> <username> <password> command in privileged EXEC mode. See Table 1 for details about the command parameters.
Example
Router# cellular 0 gsm profile create 3 apn.com chap GSM GSMPassword
Table 1 lists the modem data profile parameters.
|
profile number |
Number for the profile that you are creating. You can create up to 16 profiles. |
|
apn |
Access point name. You must get this information from your service provider. |
|
authentication |
Type of authentication, for example, CHAP, PAP. |
|
username |
Username provided by your service provider. |
|
password |
Password provided by your service provider. |
CDMA Modem Activation and Provisioning
Activation procedures may differ, depending upon your carrier. Consult your carrier, and perform one of the following procedures as appropriate:
- Manual activation
- Activation using over the air service provisioning
Table 1 lists the activation and provisioning processes supported by different wireless carriers.
|
Activation and Provisioning Process |
Carrier |
|---|---|
|
Manual Activation using MDN, MSID, MSL |
Sprint |
|
OTASP2 Activation |
Verizon Wireless |
|
IOTA3 for Data Profile refresh |
Sprint |
Manual Activation
 Note | You must have valid mobile directory number (MDN), mobile subsidy lock (MSL), and mobile station identifier (MSID) information from your carrier before you start this procedure. |
To configure a modem profile manually, use the following command, beginning in EXEC mode:
cellular 0 cdma activate manual mdn msid sid nid msl
Besides being activated, the modem data profile is provisioned through the Internet Over the Air (IOTA) process. The IOTA process is initiated automatically when you use the cellular cdma activate manual command.
The following is a sample output from this command:
router# cellular 0 cdma activate manual 1234567890 1234567890 1234 12 12345 NAM 0 will be configured and will become Active Modem will be activated with following Parameters MDN :1234567890; MSID :1234567890; SID :1234; NID 12: Checking Current Activation Status Modem activation status: Not Activated Begin Activation Account activation - Step 1 of 5 Account activation - Step 2 of 5 Account activation - Step 3 of 5 Account activation - Step 4 of 5 Account activation - Step 5 of 5 Secure Commit Result: Succeed Done Configuring - Resetting the modem The activation of the account is Complete Waiting for modem to be ready to start IOTA Beginning IOTA router# *Feb 6 23:29:08.459: IOTA Status Message Received. Event: IOTA Start, Result: SUCCESS *Feb 6 23:29:08.459: Please wait till IOTA END message is received *Feb 6 23:29:08.459: It can take up to 5 minutes *Feb 6 23:29:27.951: OTA State = SPL unlock, Result = Success *Feb 6 23:29:32.319: OTA State = Parameters committed to NVRAM, Result = Success *Feb 6 23:29:40.999: Over the air provisioning complete; Result:Success *Feb 6 23:29:41.679: IOTA Status Message Received. Event: IOTA End, Result: SUCCESS
The IOTA start and end must have “success” as the resulting output. If you receive an error message, you can run IOTA independently by using the cellular cdma activate iota command.
Your carrier may require periodic refreshes of the data profile. Use the following command to refresh the data profile:
cellular cdma activate iota
Activating with Over-the-Air Service Provisioning
To provision and activate your modem using Over-the-Air Service Provisioning (OTASP), use the following command, beginning in EXEC mode.
router # cellular 0 cdma activate otasp phone_number
 Note | You need to obtain the phone number for use with this command from your carrier. The standard OTASP calling number is *22899. |
The following is a sample output from this command:
router# cellular 0 cdma activate otasp *22899 Beginning OTASP activation OTASP number is *22899 steelers_c881G# OTA State = SPL unlock, Result = Success router# OTA State = PRL downloaded, Result = Success OTA State = Profile downloaded, Result = Success OTA State = MDN downloaded, Result = Success OTA State = Parameters committed to NVRAM, Result = Success Over the air provisioning complete; Result:Success
Configuring a Cellular Interface
To configure the cellular interface, enter the following commands, beginning in privileged EXEC mode.
 Note | The PPP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) authentication parameters that you use in this procedure must be the same as the username and password provided by your carrier and configured only under the GSM profile. CDMA does not require a username or password. |
1. configure terminal
2.
interface
cellular
0
3.
encapsulation
ppp
4. ppp chap hostname host
5. ppp chap password 0 password
6.
asynchronous
mode
interactive
7.
ip
address
negotiated
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode from the terminal. |
| Step 2 | interface
cellular
0
Example: Router (config)# interface cellular 0 |
Specifies the cellular interface. |
| Step 3 | encapsulation
ppp
Example: Router (config-if)# encapsulation ppp |
Specifies PPP encapsulation for an interface configured for dedicated asynchronous mode or dial-on-demand routing (DDR). |
| Step 4 | ppp
chap
hostname host
Example: Router (config-if)# ppp chap hostname host@wwan.ccs |
Defines an interface-specific Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) hostname. This must match the username given by the carrier. Applies to GSM only. |
| Step 5 | ppp
chap
password 0 password
Example: Router (config-if)# ppp chap password 0 cisco |
Defines an interface-specific CHAP password. This must match the password given by the carrier. |
| Step 6 | asynchronous
mode
interactive
Example: Router (config-if)# asynchronous mode interactive |
Returns a line from dedicated asynchronous network mode to interactive mode, enabling the slip and ppp commands in privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | ip
address
negotiated
Example: Router (config-if)# ip address negotiated |
Specifies that the IP address for a particular interface is obtained via PPP and IPCP address negotiation. |
 Note | When the cellular interface requires a static IP address, the address may be configured as ip address negotiated. Through IP Control Protocol (IPCP), the network ensures that the correct static IP address is allocated to the device. If a tunnel interface is configured with the ip address unnumbered cellular interface command, the actual static IP address must be configured under the cellular interface, in place of ip address negotiated. For a sample cellular interface configuration, see the Basic Cellular Interface Configuration. |
Configuring DDR
Perform these steps to configure dial-on-demand routing (DDR) for the cellular interface.
1.
configure
terminal
2.
interface
cellular
0
3.
dialer
in-band
4.
dialer
idle-timeout
seconds
5. dialer string string
6. dialer-group number
7.
exit
8. dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name {permit | deny | list access-list-number | access-group}
9. ip access-list access list number permit ip source address
10. line 3
11. script dialer regexp
12.
exit
13. For GSM:
14. interface cellular 0
15. dialer string string
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | interface
cellular
0
Example: Router (config)# interface cellular 0 |
Specifies the cellular interface. |
| Step 3 | dialer
in-band
Example: Router (config-if)# dialer in-band |
Enables DDR and configures the specified serial interface for in-band dialing. |
| Step 4 | dialer
idle-timeout
seconds
Example: Router (config-if)# dialer idle-timeout 30 |
Specifies the duration of idle time, in seconds, after which a line is disconnected. |
| Step 5 | dialer string string
Example: Router (config-if)# dialer string gsm |
Specifies the number or string to dial. Use the name of the chat script here. |
| Step 6 | dialer-group number
Example: Router (config-if)# dialer-group 1 |
Specifies the number of the dialer access group to which a specific interface belongs. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Router (config-if)# exit |
Enters the global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name {permit | deny |
list
access-list-number | access-group}
Example: Router (config)# dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 1 |
Creates a dialer list for traffic of interest and permits access to an entire protocol. |
| Step 9 | ip access-list access list number permit ip source address
Example: Router (config)# ip access list 1 permit any |
Defines traffic of interest. |
| Step 10 | line 3
Example: Router (config-line)# line 3 |
Specifies the line configuration mode. It is always 3. |
| Step 11 | script dialer regexp
Example: Router (config-line)# script-dialer gsm |
Specifies a default modem chat script. |
| Step 12 | exit
Example: Router (config-line)# exit |
Exits line configuration mode. |
| Step 13 | For GSM:
Example: chat-script script name ”” “ATDT*99* profile number#” TIMEOUT timeout value CONNECT Example: For CDMA: Example: chat-script script name "" "ATDT*777* profile number#" TIMEOUT timeout value CONNECT Example: Router (config)# chat-script gsm "" "ATDT*98*2#" TIMEOUT 60 "CONNECT“ |
Configures the line for GSM.
Configures the line for CDMA.
Defines the Attention Dial Tone (ATDT) commands when the dialer is initiated. |
| Step 14 | interface cellular 0
Example: Router (config)# interface cellular 0 |
Specifies the cellular interface. |
| Step 15 | dialer string string
Example: Router (config)# dialer string gsm |
Specifies the dialer script (defined using the chat script command). |
Configuring Data Dedicated Transmission Mode (DDTM)
On CDMA modems, data transmission is disrupted by incoming voice calls if data dedicated transmission mode (DDTM) is disabled. You can enable DDTM mode so the modem ignores incoming voice calls.
To enable DDTM on a CDMA modem, use the cdma ddtm command in configuration mode.
This command is enabled by default. You can disable this feature by using the no cdma ddtm command.
 Note | When DDTM is enabled, only voice calls are blocked for the MC5728v modems. On the AC597E and MC5725 and MC 5727, incoming SMS messages are also blocked. |
Examples for Configuring Cellular Wireless Interfaces
This section provides the following configuration examples:
Basic Cellular Interface Configuration
The following example shows how to configure a gsm cellular interface to be used as a primary WAN connection. It is configured as the default route.
chat-script gsm "" "ATDT*98*2#" TIMEOUT 60 "CONNECT“ ! interface Cellular0 ip address negotiated encapsulation ppp dialer in-band dialer string gsm dialer-group 1 async mode interactive ppp chap hostname cisco@wwan.ccs ppp chap password 0 cisco ppp ipcp dns request ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Cellular0 ! ! access-list 1 permit any dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 1 ! line 3 exec-timeout 0 0 script dialer gsm login modem InOut
The following example shows how to configure a cdma cellular interface to be used as a primary. It is configured as the default route.
chat-script cdma "" "ATDT#777" TIMEOUT 60 "CONNECT“ ! interface Cellular0 ip address negotiated encapsulation ppp dialer in-band dialer string cdma dialer-group 1 async mode interactive ppp chap password 0 cisco ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Cellular0 ! ! access-list 1 permit any dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 1 ! line 3 exec-timeout 0 0 script dialer cdma login modem InOut
Tunnel over Cellular Interface Configuration
The following example shows how to configure the static IP address when a tunnel interface is configured with the ip address unnumbered <cellular interface > command:
interface Tunnel2 ip unnumbered Cellular0 tunnel source Cellular0 tunnel destination 128.107.248.254 interface Cellular0 bandwidth receive 1400000 ip address 23.23.0.1 255.255.0.0 ip nat outside ip virtual-reassembly encapsulation ppp no ip mroute-cache dialer in-band dialer idle-timeout 0 dialer string dial<carrier> dialer-group 1 async mode interactive no ppp lcp fast-start ppp chap hostname <hostname> *** gsm only *** ppp chap password 0 <password> ppp ipcp dns request ! traffic of interest through the tunnel/cellular interface ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Tunnel2
Configuring Dual SIM for Cellular Networks on Cisco 819 Series ISR
The Dual SIM feature implements auto-switch and failover between two cellular networks on a Cisco 819 ISR. This feature is enabled by default with SIM slot 0 being the primary slot and slot 1 being the secondary (failover) slot.
 Note | For instructions on how to configure the Dual SIM feature for 4G LTE cellular networks, see the Cisco 4G LTE Software Installation Guide . |
You can configure the Dual SIM feature using the following commands:
|
Command |
Syntax |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
gsm failovertimer |
gsm failovertimer <1-7>
|
Sets the failover timer in minutes. |
|
gsm sim authenticate |
gsm sim authenticate <0,7> <pin> slot <0-1>
|
Verifies the SIM CHV1 code. |
|
gsm sim max-retry |
gsm sim max-retry <0-65535>
|
Specifies the maximum number of failover retries. The default value is 10. |
|
gsm sim primary slot |
gsm sim primary slot <0-1>
|
Modifies the primary slot assignment. |
|
gsm sim profile |
gsm sim profile <1-16> slot <0-1> |
Configures the SIM profile. |
Note the following:
- For auto-switch and failover to work, configure the SIM profile for slots 0 and 1 using the gsm sim profile command.
- For auto-switch and failover to work, configure the chat script without a specific profile number.
- If no SIM profile is configured, profile #1 is used by default.
- If no GSM failover timer is configured, the default failover timeout is 2 minutes.
- If no GSM SIM primary slot is configured, the default primary SIM is slot 0.
The following example shows you how to set the SIM switchover timeout period to 3 minutes:
router(config-controller)# gsm failovertimer 3
The following example shows you how to authenticate using an unencrypted pin:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim authenticate 0 1234 slot 0
The following example shows you how to set the maximum number of SIM switchover retries to 20:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim max-retry 20
The following example shows you how to set SIM slot 1 as the primary slot:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim primary slot 1
The following example shows you how to configure the SIM card in slot 0 to use profile 10:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim profile 10 slot 0
Perform the following commands to manually switch the SIM:
|
Command |
Syntax |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
cellular GSM SIM |
cellular GSM SIM {lock | unlock}
|
Locks or unlocks the SIM. |
|
gsm sim |
cellular <unit> gsm sim [lock | unlock] <pin>
|
Locks or unlocks the gsm SIM. |
|
gsm sim unblock |
cellular <unit> gsm sim unblock <puk> <newpin>
|
Unblocks the gsm SIM. |
|
gsm sim change-pin |
cellular <unit> gsm sim change-pin <oldpin> <newpin>
|
Changes the PIN of the SIM. |
|
gsm sim activate slot |
cellular <unit> gsm sim activate slot <slot_no>
|
Activates the GSM SIM. |
The following command forces the modem to connect to SIM1:
Router# cellular 0 gsm sim activate slot 1
Configuring Router for Image and Config Recovery Using Push Button for Cisco 819 Series ISR Router
A push button feature is available on the Cisco 819 ISR. The reset button on the front panel of the router enables this feature.
Perform the following steps to use this feature:
1. Unplug power.
2. Press the reset button on the front panel of the router.
3. Power up the sytem while holding down the reset button.
DETAILED STEPS
What to Do Next
Using this button takes effect only during ROMMON initialization. During a warm reboot, pressing this button has no impact on performance. Table 1 shows the high level functionality when the button is pushed during ROMMON initialization.
|
ROMMON Behavior |
IOS Behavior |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Examples of names for default images: c800-universalk9-mz.SPA.default, c-800-universalk9_npe-mz.151T.default, image.default
|
If the configuration named *.cfg is available in nvram storage or flash storage, IOS will perform a backup of the original configuration and will boot up using this configuration.
|
Use the show platform command to display the current bootup mode for the router. The following sections show sample outputs when the button is not pushed and when the button is pushed.
Output When Button Is Not Pushed: Example
router# show platform boot-record Platform Config Boot Record : ============================ Configuration Register at boot time : 0x0 Reset Button Status at Boot Time : Not Pressed Startup-config Backup Status at Boot: No Status Startup-config(backup file)location : No Backup Golden config file at location : No Recovery Detected Config Recovery Status : No Status
Output When Button Is Pushed: Example
router# show platform boot-record
Platform Config Boot Record :
============================
Configuration Register at boot time : 0x0
Reset Button Status at Boot Time : Pressed
Startup-config Backup Status at Boot: Ok
Startup-config(backup file)location : flash:/startup.backup.19000716-225840-UTC
Golden config file at location : flash:/golden.cfg
Config Recovery Status : Ok
Push Button in WLAN AP
When the push button on the front panel is pressed, WLAN AP will perform both image and configuration recovery.
To perform image recovery, WLAN will go into the boot loader so that the user can download the image from the bootloader prompt.
To perform configuration recovery, WLAN AP will overwrite the contents of flash:/config.txt with the contents of flash:/cpconfig-ap802.cfg file if available in flash drive. Otherwise, flash:/config.txt will be deleted.
Configuring WAN Mode on Cisco 860VAE ISRs
The Cisco 866VAE, Cisco 867VAE, Cisco 866VAE-K9, and Cisco 867VAE-K9 routers can be configured to use either a GE interface or a DSL interface as a WAN link. DSL is the default WAN interface when the Cisco 866VAE, Cisco 867VAE, Cisco 866VAE-K9, and Cisco 867VAE-K9 routers boot.
After the router boots up, the desired WAN interface can be selected using the wan mode command. When WAN mode is configured as Ethernet, both ATM0 and Ethernet0 interfaces will be forced into shutdown state. Entering the no shutdown command on either of the DSL interfaces will be rejected with a message WAN interface is Ethernet . Similarly, when the WAN mode is DSL, the GE WAN interface will be put in shutdown state and the no shutdown command will be rejected with the message WAN interface is DSL .
 Note | The routers do not support enabling both GE and DSL interfaces simultaneously. |
Use the wan mode dsl | ethernet command to switch from DSL to Ethernet interfaces or vice versa.
This section contains the following information:
Enabling WAN Mode
Perform the following steps to select and enable WAN mode.
1.
enable
2.
show
running-configuration
3.
wan
mode
{dsl
|
ethernet}
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | show
running-configuration
Example: Router# show running-configuration |
Displays the default entries on boot up.
|
| Step 3 | wan
mode
{dsl
|
ethernet}
Example: Router(config)# wan mode dsl |
Selects the desired WAN mode.
|
| Step 4 | exit
Example: Router(config)# exit Example: Router# |
Exits configuration mode and returns to it would take the router back to privileged EXEC mode. |
Displaying WAN Mode Configuration
Use the show running-config command to view the initial configuration, as shown in the following example for a Cisco 866VAE router.
 Note | Your Cisco router displays the WAN mode during the boot sequence after the initial configuration is complete. |
Router#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1195 bytes ! ! Last configuration change at 13:27:25 UTC Wed Feb 24 2010 version 15.2 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezone service timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! enable password lab ! no aaa new-model wan mode ethernet no ipv6 cef ! ! ! ! ! ip cef ! crypto pki token default removal timeout 0 ! ! ! ! ! ! controller VDSL 0 shutdown ! ! ! ! ! interface ATM0 no ip address shutdown no atm ilmi-keepalive ! interface ATM0.1 point-to-point ip address 202.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 pvc 0/202 ! ! interface Ethernet0 no ip address shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0 no ip address ! interface FastEthernet1 no ip address ! interface FastEthernet2 no ip address ! interface FastEthernet3 no ip address ! interface GigabitEthernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ! ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 no modem enable line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 60000 1000 ! end Router#
Configuring the Fast Ethernet LAN Interfaces
The Fast Ethernet LAN interfaces on your router are automatically configured as part of the default VLAN and are not configured with individual addresses. Access is provided through the VLAN. You can also assign the interfaces to other VLANs. For more information about creating VLANs, see Configuring Ethernet Switches
Configuring the Wireless LAN Interface
The Cisco 860, Cisco 880, and Cisco 890 series wireless routers have an integrated 802.11n module for wireless LAN connectivity. The router can then act as an access point in the local infrastructure. For more information about configuring a wireless connection, see Chapter 11, “Basic Wireless Device Configuration.”
Configuring a Loopback Interface
The loopback interface acts as a placeholder for the static IP address and provides default routing information.
Perform these steps to configure a loopback interface, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
interface
loopback
number
2.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
3.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface
loopback
number
Example: Router(config)# interface Loopback 0 |
Enters configuration mode for the loopback interface. number—number of the loopback interface. |
| Step 2 | ip
address
ip-address
mask
Example: Router(config-if)# ip address 10.108.1.1 255.255.255.0 |
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the loopback interface. |
| Step 3 | exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit Example: Router(config)# |
Exits configuration mode for the loopback interface and returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuration Example: Configuring a Loopback Interface
The loopback interface in this sample configuration is used to support Network Address Translation (NAT) on the virtual-template interface. This configuration example shows the loopback interface configured on the Fast Ethernet interface with an IP address of 200.200.100.1/24, which acts as a static IP address. The loopback interface points back to virtual-template1, which has a negotiated IP address.
! interface loopback 0 ip address 200.200.100.1 255.255.255.0 (static IP address) ip nat outside ! interface Virtual-Template1 ip unnumbered loopback0 no ip directed-broadcast ip nat outside !
Verifying Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured the loopback interface, enter the show interface loopback command. You should see verification output similar to the following example.
Router# show interface loopback 0
Loopback 0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Loopback
Internet address is 200.200.100.1/24
MTU 1514 bytes, BW 8000000 Kbit, DLY 5000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation LOOPBACK, loopback not set
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/0, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Another way to verify the loopback interface is to ping it:
Router# ping 200.200.100.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 200.200.100.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
Configuring Static Routes
Static routes provide fixed routing paths through the network. They are manually configured on the router. If the network topology changes, the static route must be updated with a new route. Static routes are private routes unless they are redistributed by a routing protocol.
Follow these steps to configure static routes, beginning in global configuration mode.
1.
ip
route
prefix
mask {ip-address |
interface-type
interface-number
[ip-address]}
2.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | ip
route
prefix
mask {ip-address |
interface-type
interface-number
[ip-address]}
Example: Router(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.0.0 10.10.10.2 |
Specifies the static route for the IP packets. For details about this command and about additional parameters that can be set, see the Cisco IOS IP Routing Protocols Command Reference . |
| Step 2 | end
Example: Router(config)# end |
Exits router configuration mode, and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
For general information on static routing, see the “Concepts” section on page B-1
Example
In the following configuration example, the static route sends out all IP packets with a destination IP address of 192.168.1.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 on the Fast Ethernet interface to another device with an IP address of 10.10.10.2. Specifically, the packets are sent to the configured PVC.
You do not need to enter the command marked “(default).” This command appears automatically in the configuration file generated when you use the show running-config command.
! ip classless (default) ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2!
Verifying Static Routing Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured static routing, enter the show ip route command and look for static routes signified by the “S.”
You should see verification output similar to the following:
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0
Configuring Dynamic Routes
In dynamic routing, the network protocol adjusts the path automatically, based on network traffic or topology. Changes in dynamic routes are shared with other routers in the network.
The Cisco routers can use IP routing protocols, such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), to learn routes dynamically. You can configure either of these routing protocols on your router.
Configuring Routing Information Protocol
To configure the RIP routing protocol on the router, perform these steps, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
configure
terminal
2.
router
rip
3. version {1 | 2}
4.
network
ip-address
5.
no
auto-summary
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | router
rip
Example: Router(config)# router rip |
Enters router configuration mode, and enables RIP on the router. |
| Step 3 | version {1 |
2}
Example: Router(config-router)# version 2 |
Specifies use of RIP version 1 or 2. |
| Step 4 | network
ip-address
Example: Router(config-router)# network 192.168.1.1 |
Specifies a list of networks on which RIP is to be applied, using the address of the network of each directly connected network. |
| Step 5 | no
auto-summary
Example: Router(config-router)# no auto-summary |
Disables automatic summarization of subnet routes into network-level routes. This allows subprefix routing information to pass across classfull network boundaries. |
| Step 6 | end
Example: Router(config-router)# end |
Exits router configuration mode, and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
For general information on RIP, see the “RIP” section on page B-3
Example Configuration: Configuring Dynamic Routing Protocol
The following configuration example shows RIP version 2 enabled in IP network 10.0.0.0 and 192.168.1.0.
To see this configuration, use the show running-config command from privileged EXEC mode.
! Router# show running-config router rip version 2 network 10.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 no auto-summary !
Verifying RIP Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured RIP, enter the show ip route command and look for RIP routes signified by “R.” You should see a verification output like the following example.
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
R 3.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 2.2.2.1, 00:00:02, Ethernet0/0
Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
To configure Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), perform these steps, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
router
eigrp
as-number
2.
network
ip-address
3.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | router
eigrp
as-number
Example: Example: Router(config)# router eigrp 109 |
Enters router configuration mode and enables EIGRP on the router. The autonomous-system number identifies the route to other EIGRP routers and is used to tag the EIGRP information. |
| Step 2 | network
ip-address
Example: Example: Router(config)# network 192.145.1.0 Example: Router(config)# network 10.10.12.115 |
Specifies a list of networks on which EIGRP is to be applied, using the IP address of the network of directly connected networks. |
| Step 3 | end
Example: Example: Router(config-router)# end Example: Router# |
Exits router configuration mode and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
For general information on EIGRP concepts, see the “Enhanced IGRP” section on page B-3
Example Configuration: EIGRP
The following configuration example shows the EIGRP routing protocol enabled in IP networks 192.145.1.0 and 10.10.12.115. The EIGRP autonomous system number is 109.
To see this configuration, use the show running-config command, beginning in privileged EXEC mode.
! router eigrp 109 network 192.145.1.0 network 10.10.12.115 !
Verifying EIGRP Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured IP EIGRP, enter the show ip route command and look for EIGRP routes indicated by “D.” You should see verification output similar to the following:
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
D 3.0.0.0/8 [90/409600] via 2.2.2.1, 00:00:02, Ethernet0/0
 Feedback
Feedback