- Preface
- Product Overview
- Basic Router Configuration
- Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring Power Management
- Configuring Security Features
- Configuring Secure Storage
- Configuring Backup Data Lines and Remote Management
- Configuring Ethernet Switches
- Configuring Voice Functionality
- Configuring the Serial Interface
- Configuring Wireless Devices
- Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
- Configuring PPP over ATM with NAT
- Environmental and Power Management
- Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
- Configuring a VPN Using Easy VPN and an IPSec Tunnel
- Configuring Cisco Multimode G.SHDSL EFM/ATM
- Configuring VDSL2 Bonding and Single-Wire Pair
- Configuring Cisco IOx
- Deployment Scenarios
- Troubleshooting Cisco 800 Series Routers
- Cisco IOS Software Basic Skills
- Concepts
- ROM Monitor
- Index
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
The Cisco 819, Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and virtual LANs (VLANs).
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
The Cisco 819, Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and virtual LANs (VLANs). The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable automatic assignment of IP configurations for nodes on these networks.
The figure below shows a typical deployment scenario with two physical LANs connected by the router and two VLANs.
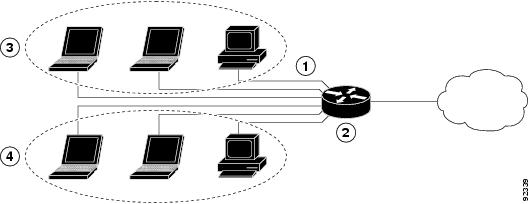
|
1 |
Fast Ethernet LAN (with multiple networked devices) |
|
2 |
Router and DHCP server—Cisco 819, Cisco 860, or Cisco 880 ISR—connected to the Internet |
|
3 |
VLAN 1 |
|
4 |
VLAN 2 |
DHCP
DHCP, which is described in RFC 2131, uses a client/server model for address allocation. As an administrator, you can configure your Cisco 800 series router to act as a DHCP server, providing IP address assignment and other TCP/IP-oriented configuration information to your workstations. DHCP frees you from having to manually assign an IP address to each client.
When you configure a DHCP server, you must configure the server properties, policies, and DHCP options.
 Note | Whenever you change server properties, you must reload the server with the configuration data from the Network Registrar database. |
 Note | Cisco 800 Series Routers do not support DHCP snooping. |
VLANs
The Cisco 819, Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 routers support four Fast Ethernet ports on which you can configure VLANs.
VLANs enable networks to be segmented and formed into logical groups of users, regardless of the user’s physical location or LAN connection.
Configuring DHCP and VLANs
 Note | The procedures in this chapter assume you have already configured basic router features, as well as PPPoE or PPPoA with NAT. If you have not performed these configurations tasks, see the Basic Router Configuration and Configuring a VPN Using Easy VPN and an IPSec Tunnel as appropriate for your router. |
Configuring DHCP
Perform these steps to configure your router for DHCP operation, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
ip
domain
name
name
2.
ip
name-server
server-address1
[server-address2...server-address6]
3.
ip
dhcp
excluded-address
low-address
[high-address]
4.
ip
dhcp
pool
name
5.
network
network-number
[mask
|
prefix-length]
6.
import
all
7.
default-router
address
[address2...address8]
8.
dns-server
address
[address2...address8]
9.
domain-name
domain
10.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Example: DHCP
The following configuration example shows a portion of the configuration file for the DCHP configuration described in this chapter:
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.9.0 ! ip dhcp pool dpool1 import all network 10.10.0.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 10.10.10.10 dns-server 192.168.35.2 domain-name cisco.com ! ip domain name smallbiz.com ip name-server 192.168.11.12
Verifying Your DHCP Configuration
Use the following commands to view your DHCP configuration:
- show ip dhcp import—Displays the optional parameters imported into the DHCP server database.
- show ip dhcp pool—Displays information about the DHCP address pools.
- show ip dhcp server statistics—Displays the DHCP server statistics, such as the number of address pools, bindings, and so forth.
Router# show ip dhcp import Address Pool Name: dpool1 Router# show ip dhcp pool Pool dpool1 : Utilization mark (high/low) : 100 / 0 Subnet size (first/next) : 0 / 0 Total addresses : 254 Leased addresses : 0 Pending event : none 1 subnet is currently in the pool : Current index IP address range Leased addresses 10.10.0.1 10.10.0.1 - 10.10.0.254 0 Router# show ip dhcp server statistics Memory usage 15419 Address pools 1 Database agents 0 Automatic bindings 0 Manual bindings 0 Expired bindings 0 Malformed messages 0 Secure arp entries 0 Message Received BOOTREQUEST 0 DHCPDISCOVER 0 DHCPREQUEST 0 DHCPDECLINE 0 DHCPRELEASE 0 DHCPINFORM 0 Message Sent BOOTREPLY 0 DHCPOFFER 0 DHCPACK 0 DHCPNAK 0 Router#
Configuring VLANs
Perform these steps to configure VLANs on your router, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
vlan
vlan_id
2.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|
Assigning a Switch Port to a VLAN
Perform these steps to assign a switch port to a VLAN, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
interface
switch port
id
2.
switchport
access
vlan
vlan-id
3.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying Your VLAN Configuration
Use the following commands to view your VLAN configuration.
- show—Entered from VLAN database mode. Displays summary configuration information for all configured VLANs.
- show vlan-switch—Entered from privileged EXEC mode. Displays detailed configuration information for all configured VLANs.
Router# vlan database
Router(vlan)# show
VLAN ISL Id: 1
Name: default
Media Type: Ethernet
VLAN 802.10 Id: 100001
State: Operational
MTU: 1500
Translational Bridged VLAN: 1002
Translational Bridged VLAN: 1003
VLAN ISL Id: 2
Name: VLAN0002
Media Type: Ethernet
VLAN 802.10 Id: 100002
State: Operational
MTU: 1500
VLAN ISL Id: 3
Name: red-vlan
Media Type: Ethernet
VLAN 802.10 Id: 100003
State: Operational
MTU: 1500
VLAN ISL Id: 1002
Name: fddi-default
Media Type: FDDI
VLAN 802.10 Id: 101002
State: Operational
MTU: 1500
Bridge Type: SRB
Translational Bridged VLAN: 1
Translational Bridged VLAN: 1003
VLAN ISL Id: 1003
Name: token-ring-default
Media Type: Token Ring
VLAN 802.10 Id: 101003
State: Operational
MTU: 1500
Bridge Type: SRB
Ring Number: 0
Bridge Number: 1
Parent VLAN: 1005
Maximum ARE Hop Count: 7
Maximum STE Hop Count: 7
Backup CRF Mode: Disabled
Translational Bridged VLAN: 1
Translational Bridged VLAN: 1002
VLAN ISL Id: 1004
Name: fddinet-default
Media Type: FDDI Net
VLAN 802.10 Id: 101004
State: Operational
MTU: 1500
Bridge Type: SRB
Bridge Number: 1
STP Type: IBM
VLAN ISL Id: 1005
Name: trnet-default
Media Type: Token Ring Net
VLAN 802.10 Id: 101005
State: Operational
MTU: 1500
Bridge Type: SRB
Bridge Number: 1
STP Type: IBM
Router# show vlan-switch
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0, Fa1, Fa3
2 VLAN0002 active Fa2
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 1002 1003
2 enet 100002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 1 1003
1003 tr 101003 1500 1005 0 - - srb 1 1002
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 1 ibm - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - 1 ibm - 0 0
 Feedback
Feedback