- Preface
- Product Overview
- Basic Router Configuration
- Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring Power Management
- Configuring Security Features
- Configuring Secure Storage
- Configuring Backup Data Lines and Remote Management
- Configuring Ethernet Switches
- Configuring Voice Functionality
- Configuring the Serial Interface
- Configuring Wireless Devices
- Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
- Configuring PPP over ATM with NAT
- Environmental and Power Management
- Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
- Configuring a VPN Using Easy VPN and an IPSec Tunnel
- Configuring Cisco Multimode G.SHDSL EFM/ATM
- Configuring VDSL2 Bonding and Single-Wire Pair
- Configuring Cisco IOx
- Deployment Scenarios
- Troubleshooting Cisco 800 Series Routers
- Cisco IOS Software Basic Skills
- Concepts
- ROM Monitor
- Index
Configuring PPP over
ATM with NAT
This chapter provides an overview of Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) clients and network address translation (NAT) that can be configured on the Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs).
- Overview
- Configure the Dialer Interface
- Configure the ATM WAN Interface
- Configure DSL Signaling Protocol
- Configure Network Address Translation
- Configuration Example
Overview
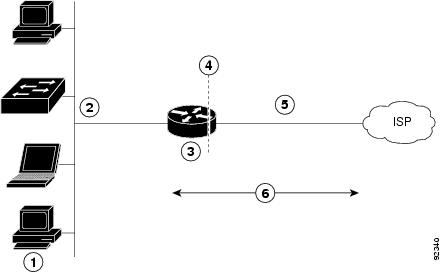
Multiple PCs can be connected to the LAN behind the router. Before traffic from the PCs is sent to the PPPoA session, it can be encrypted, filtered, and so forth. PPP over ATM provides a network solution with simplified address handling and straight user verification like a dial network. Figure 1 shows a typical deployment scenario with a PPPoA client and NAT configured on the Cisco router. This scenario uses a single static IP address for the ATM connection.
|
1 |
Small business with multiple networked devices—desktops, laptop PCs, switches |
|
2 |
Fast Ethernet LAN interface (inside interface for NAT, 192.168.1.1/24) |
|
3 |
PPPoA Client |
|
4 |
Point at which NAT occurs |
|
5 |
ATM WAN interface (outside interface for NAT) |
|
6 |
PPPoA session between the client and a PPPoA server at the ISP |
In this scenario, the small business or remote user on the Fast Ethernet LAN can connect to an Internet service provider (ISP) using the integrated xDSL WAN interface on the Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series ISRs.
The Fast Ethernet interface carries the data packet through the LAN and off-loads it to the PPP connection on the ATM interface. The ATM traffic is encapsulated and sent over the xDSL interface. The dialer interface is used to connect to the ISP.
PPPoA
The PPPoA Client feature on the router provides PPPoA client support on ATM interfaces. A dialer interface must be used for cloning virtual access. Multiple PPPoA client sessions can be configured on an ATM interface, but each session must use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
A PPPoA session is initiated on the client side by the Cisco 860 or Cisco 880 series router.
NAT
NAT (represented as the dashed line at the edge of the Cisco router) signifies two addressing domains and the inside source address. The source list defines how the packet travels through the network.
Configuration Tasks
Perform the following tasks to configure this network scenario:
- Configure the Dialer Interface
- Configure the ATM WAN Interface
- Configure DSL Signaling Protocol
- Configure Network Address Translation
An example showing the results of these configuration tasks is shown in the Configuration Example.
Configure the Dialer Interface
The dialer interface indicates how to handle traffic from the clients, including, for example, default routing information, the encapsulation protocol, and the dialer pool to use. It is also used for cloning virtual access. Multiple PPPoA client sessions can be configured on an ATM interface, but each session must use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
Perform these steps to configure a dialer interface for the ATM interface on the router, starting in global configuration mode.
1.
interface
dialer
dialer-rotary-group-number
2.
ip
address
negotiated
3.
ip
mtu
bytes
4.
encapsulation
encapsulation-type
5.
ppp
authentication {protocol1 [protocol2...]}
6.
dialer
pool
number
7.
dialer-group
group-number
8.
exit
9.
dialer-list
dialer-group
protocol
protocol-name
{permit |
deny |
list
access-list-number |
access-group}
10.
ip
route
prefix
mask {interface-type
interface-number}
DETAILED STEPS
Repeat these steps for any additional dialer interfaces or dialer pools needed.
Configure the ATM WAN Interface
Perform these steps to configure the ATM interface, beginning in global configuration mode.
1. interface type number
2.
pvc
vpi/vci
3.
encapsulation
{aal5auto
|
aal5autoppp
virtual-template
number
[group
group-name]
|
aal5ciscoppp
virtual-template
number
|
aal5mux
protocol
|
aal5nlpid
|
aal5snap}
4.
dialer
pool-member
number
5.
no
shutdown
6.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | interface type
number
Example: Router(config)# interface atm 0 |
Enters interface configuration mode for the ATM interface (labeled ADSLoPOTS or G.SHDSL on the back of your router).
| ||
| Step 2 | pvc
vpi/vci
Example: Router(config-if)# pvc 8/35 |
Creates an ATM PVC for each end node (up to ten) with which the router communicates. Enters ATM virtual circuit configuration mode. When a PVC is defined, AAL5SNAP encapsulation is defined by default. Use the encapsulation command to change this, as shown in Step 3. The VPI and VCI arguments cannot be simultaneously specified as zero; if one is 0, the other cannot be 0. For details about this command and additional parameters that can be set, see the Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking Command Reference. | ||
| Step 3 | encapsulation
{aal5auto
|
aal5autoppp
virtual-template
number
[group
group-name]
|
aal5ciscoppp
virtual-template
number
|
aal5mux
protocol
|
aal5nlpid
|
aal5snap}
Example: Router(config-if-atm-vc)# encapsulation aal5mux ppp dialer |
Specifies the encapsulation type for the PVC and points back to the dialer interface. For details about this command and additional parameters that can be set, see the Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking Command Reference. | ||
| Step 4 | dialer
pool-member
number
Example: Router(config-if-atm-vc)# dialer pool-member 1 |
Specifies the ATM interface as a member of a dialer profile dialing pool. The pool number must be in the range of 1–255. | ||
| Step 5 | no
shutdown
Example: Router(config-if-atm-vc)# no shutdown |
Enables interface and configuration changes just made to the ATM interface. | ||
| Step 6 | exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit Example: Router(config)# |
Exits configuration mode for the ATM interface. |
Configure DSL Signaling Protocol
DSL signaling must be configured on the ATM interface for connection to your ISP. The Cisco 887 and Cisco 867 ISRs support ADSL signaling over POTS and the Cisco 886 ISR supports ADSL signaling over ISDN. The Cisco 888 ISR supports G.SHDSL.
Configuring ADSL
The default configuration for ADSL signaling is shown in Table 1.
|
Attribute |
Description |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Operating mode |
Specifies the operating mode of the digital subscriber line (DSL) for an ATM interface. |
Auto |
|
Loss of margin |
Specifies the number of times a loss of margin may occur. |
— |
|
Training log |
Toggles between enabling the training log and disabling the training log. |
Disabled |
If you wish to change any of these settings, use one of the following commands in global configuration mode.
- dsl operating-mode (from the ATM interface configuration mode)
- dsl lom integer
- dsl enable-training-log
See the Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking Command Reference for details of these commands.
Verifying the Configuration
You can verify that the configuration is set the way you want by using the show dsl interface atm command from privileged EXEC mode.
Router# show dsl interface atm 0
ATM0
Alcatel 20190 chipset information
ATU-R (DS) ATU-C (US)
Modem Status: Showtime (DMTDSL_SHOWTIME)
DSL Mode: ITU G.992.5 (ADSL2+) Annex A
ITU STD NUM: 0x03 0x2
Chip Vendor ID: 'STMI' 'BDCM'
Chip Vendor Specific: 0x0000 0x6193
Chip Vendor Country: 0x0F 0xB5
Modem Vendor ID: 'CSCO' ' '
Modem Vendor Specific: 0x0000 0x0000
Modem Vendor Country: 0xB5 0x00
Serial Number Near:
Serial Number Far:
Modem VerChip ID: C196 (3)
DFE BOM: DFE3.0 Annex A (1)
Capacity Used: 82% 99%
Noise Margin: 12.5 dB 5.5 dB
Output Power: 11.5 dBm 12.0 dBm
Attenuation: 5.5 dB 0.0 dB
FEC ES Errors: 0 0
ES Errors: 1 287
SES Errors: 1 0
LOSES Errors: 1 0
UES Errors: 0 276233
Defect Status: None None
Last Fail Code: None
Watchdog Counter: 0x56
Watchdog Resets: 0
Selftest Result: 0x00
Subfunction: 0x00
Interrupts: 4147 (0 spurious)
PHY Access Err: 0
Activations: 3
LED Status: ON
LED On Time: 100
LED Off Time: 100
Init FW: init_AMR-4.0.015_no_bist.bin
Operation FW: AMR-4.0.015.bin
FW Source: embedded
FW Version: 4.0.15
DS Channel1 DS Channel0 US Channel1 US Channel0
Speed (kbps): 0 19999 0 1192
Cells: 0 0 0 1680867
Reed-Solomon EC: 0 0 0 0
CRC Errors: 0 0 0 326
Header Errors: 0 0 0 131
Total BER: 0E-0 65535E-0
Leakage Average BER: 0E-0 65535E-255
Interleave Delay: 0 36 0 11
ATU-R (DS) ATU-C (US)
Bitswap: enabled enabled
Bitswap success: 0 0
Bitswap failure: 0 0
LOM Monitoring : Disabled
DMT Bits Per Bin
000: 0 0 0 0 F F F F F F F F F F F F
010: 0 0 3 0 F F F F F F F F F F F F
020: F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F
....
DSL: Training log buffer capability is not enabled
Router#
Configure Network Address Translation
Network Address Translation (NAT) translates packets from addresses that match a standard access list, using global addresses allocated by the dialer interface. Packets that enter the router through the inside interface, packets sourced from the router, or both are checked against the access list for possible address translation. You can configure NAT for either static or dynamic address translations.
Perform these steps to configure the outside ATM WAN interface with dynamic NAT, beginning in global configuration mode:
1.
ip
nat
pool
name
start-ip
end-ip {netmask
netmask |
prefix-length
prefix-length}
2.
Do one of the
following:
3. interface type number
4.
ip
nat
{inside
|
outside}
5.
no
shutdown
6.
exit
7. interface type number
8.
ip
nat
{inside
|
outside}
9.
no
shutdown
10.
exit
11.
access-list
access-list-number {deny
|
permit}
source
[source-wildcard]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | ip
nat
pool
name
start-ip
end-ip {netmask
netmask |
prefix-length
prefix-length}
Example: Router(config)# ip nat pool pool1 192.168.1.0 192.168.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 |
Creates pool of global IP addresses for NAT. | ||
| Step 2 | Do one of the following: |
Enables dynamic translation of addresses on the inside interface. The first example shows the addresses permitted by the access list 1 to be translated to one of the addresses specified in the dialer interface 0 . The second example shows the addresses permitted by access list acl1 to be translated to one of the addresses specified in the NAT pool pool1 . | ||
| Step 3 | interface type
number
Example: Router(config)# interface vlan 1 |
Enters configuration mode for the VLAN (on which the Fast Ethernet LAN interfaces [FE0–FE3] reside) to be the inside interface for NAT. | ||
| Step 4 | ip
nat
{inside
|
outside}
Example: Router(config-if)# ip nat inside |
Applies NAT to the Fast Ethernet LAN interface as the inside interface. | ||
| Step 5 | no
shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the configuration changes just made to the Ethernet interface. | ||
| Step 6 | exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit |
Exits configuration mode for the Fast Ethernet interface. | ||
| Step 7 | interface type
number
Example: Router(config)# interface atm 0 |
Enters configuration mode for the ATM WAN interface (ATM0) to be the outside interface for NAT. | ||
| Step 8 | ip
nat
{inside
|
outside}
Example: Router(config-if)# ip nat outside |
Identifies the specified WAN interface as the NAT outside interface. | ||
| Step 9 | no
shutdown
Example: Router(config-if)# no shutdown |
Enables the configuration changes just made to the Ethernet interface. | ||
| Step 10 | exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit |
Exits configuration mode for the ATM interface. | ||
| Step 11 | access-list
access-list-number {deny
|
permit}
source
[source-wildcard]
Example: Router(config)# access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 |
Defines a standard access list permitting addresses that need translation.
|
 Note | If you want to use NAT with a virtual-template interface, you must configure a loopback interface. See Chapter 3, “Basic Router Configuration,” for information on configuring the loopback interface. |
For complete information on NAT commands, see the Cisco NX-OS Release 4.1 documentation set.
Configuration Example
The following configuration example shows a portion of the configuration file for a client in the PPPoA scenario described in this chapter.
The VLAN interface has an IP address of 192.168.1.1 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. NAT is configured for inside and outside.
 Note | Commands marked by “(default)” are generated automatically when you run the show running-config command. |
! interface Vlan1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ip virtual-reassembly (default) ! interface ATM0 no ip address ip nat outside ip virtual-reassembly no atm ilmi-keepalive pvc 8/35 encapsulation aal5mux ppp dialer dialer pool-member 1 ! dsl operating-mode auto ! interface Dialer0 ip address negotiated ip mtu 1492 encapsulation ppp dialer pool 1 dialer-group 1 ppp authentication chap ! ip classless (default) ! ip nat pool pool1 192.168.1.0 192.168.2.0 netmask 0.0.0.255 ip nat inside source list 1 interface Dialer0 overload ! access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit ip route 10.10.25.2 0.255.255.255 dialer 0 !
Verifying Your Configuration with NAT
Use the show ip nat statistics command in privileged EXEC mode to verify the PPPoA client with NAT configuration. You should see verification output similar to the following example:
Router# show ip nat statistics Total active translations: 0 (0 static, 0 dynamic; 0 extended) Outside interfaces: ATM0 Inside interfaces: Vlan1 Hits: 0 Misses: 0 CEF Translated packets: 0, CEF Punted packets: 0 Expired translations: 0 Dynamic mappings: -- Inside Source [Id: 1] access-list 1 interface Dialer0 refcount 0 Queued Packets: 0
 Feedback
Feedback