- Preface
- Product Overview
- Basic Router Configuration
- Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring Power Management
- Configuring Security Features
- Configuring Secure Storage
- Configuring Backup Data Lines and Remote Management
- Configuring Ethernet Switches
- Configuring Voice Functionality
- Configuring the Serial Interface
- Configuring Wireless Devices
- Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
- Configuring PPP over ATM with NAT
- Environmental and Power Management
- Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
- Configuring a VPN Using Easy VPN and an IPSec Tunnel
- Configuring Cisco Multimode G.SHDSL EFM/ATM
- Configuring VDSL2 Bonding and Single-Wire Pair
- Configuring Cisco IOx
- Deployment Scenarios
- Troubleshooting Cisco 800 Series Routers
- Cisco IOS Software Basic Skills
- Concepts
- ROM Monitor
- Index
Cisco 800 Series Integrated Services Routers Software Configuration Guide
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- July 24, 2014
Chapter: Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Configuring Ethernet
CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
This chapter provides procedures for configuring the network interface device functionality, Ethernet data plane loopback, IEEE connectivity fault management, and Y.1731 performance monitoring.
For configuring EVC Bridge Domain (BD) and the features it supports, see Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain.
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Configuring a Network Interface Device on the L3 Interface
- Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
- CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
- Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
Configuring a Network Interface Device on the L3 Interface
Configuring a Network Interface Device (NID) enables support for the NID functionality on the router without including a NID hardware in the network. This feature combines the Customer-Premises Equipment (CPE) and the NID functionality into a physical device. The following are the advantages of configuring the NID functionality:
- Eliminates a physical device.
- Supports both the managed CPE feature set and the NID requirements.
 Note | This feature is supported only if you have purchased the advipservices licensing module. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html . |
Configuring the NID
The following steps describe how to configure the NID:
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
4.
port-tagging
5.
encapsulation
dot1q
vlan-id
6.
set
cos
cos-value
7.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router>enable |
Enables the privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password when prompted. |
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router#configure terminal |
Enters the global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
Example: Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 |
Specifies an interface and enters the interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | port-tagging
Example: Router(config-if)#port-tagging |
Inserts the VLAN ID into a packet header to identify which Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) the packet belongs to. |
| Step 5 | encapsulation
dot1q
vlan-id
Example: Router(config-if-port-tagging)#encapsulation dot1q 10 |
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q (dot1q), and specifies the VLAN identifier. |
| Step 6 | set
cos
cos-value
Example: Router(config-if-port-tagging)#set cos 6 |
Sets the Layer 2 class of service (CoS) value to an outgoing packet end. |
| Step 7 | end
Example: Router(config-if-port-tagging)#end |
Exits the interface configuration mode. |
Configuration Example
This configuration example shows how to configure the NID:
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 Router(config-if)#port-tagging Router(config-if-port-tagging)#encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-if-port-tagging)#set cos 6 Router(config-if-port-tagging)#end
Verifying the NID Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the port tagging sessions:
- show run int
- ping
Use the show run int command to display the port tagging sessions:
Router#show run int gi0/2 Building configuration... Current configuration : 10585 bytes ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 no ip address duplex auto speed auto port-tagging encapsulation dot1q 10 set cos 6 exit end ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2.1101 encapsulation dot1Q 100 ip address 132.1.101.4 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2.1102 encapsulation dot1Q 100 ip address 132.1.102.4 255.255.255.0 !
Use the ping command to verify the connectivity with port tagging configured:
Router#ping 132.1.101.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 132.1.101.3, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms router#
Troubleshooting the NID Configuration
Table 1 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot the issues pertaining to the NID functionality.
The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information about these commands.
 Caution | Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff. |
 Note | Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console command. |
|
debug Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
debug ethernet nid configuration |
Enables debugging of configuration-related issues. |
|
debug ethernet nid packet egress |
Enables debugging of packet processing (VLAN tag push) on the egress side. |
|
debug ethernet nid packet ingress |
Enables debugging of packet processing (VLAN tag pop) on the ingress side. |
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
The Ethernet Data Plane Loopback feature provides a means for remotely testing the throughput of an Ethernet port. You can verify the maximum rate of frame transmission with no frame loss.
 Note | This feature is supported only if you have purchased the advipservices licensing module. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html . |
 Note | Internal Ethernet data plane loopback is not supported. |
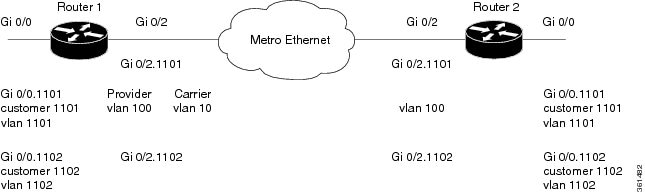
Figure 4-1 represents a sample topology to configure Ethernet data plane loopback.
- Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
- Configuring External Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
- Configuration Examples for Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
- Verifying the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
- Troubleshooting the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Follow the guidelines and take note of the restrictions listed here when configuring Ethernet data plane loopback on a Layer 3 interface:
- Only external loopback (packets coming from the wire side) on the L3 dot1q subinterface and (untagged) main interface are supported.
- To perform a MAC swap, the destination address and source address must be swapped for the packets that are looped back. If the destination address is broadcast or multicast, the MAC address is used as the source address for the packets that are looped back.
- Loopback operations are supported at line rate.
- Untagged frames are not supported on a subinterface. However, the frames for dot1q and qinq are supported on a subinterface.
- dot1ad is not supported on the main interface. However, untagged frames are supported on the main interface.
- Single VLAN is supported as a filtering option for a subinterface, but VLAN list and VLAN range are not supported.
- Only MAC address is supported as a filtering option for the main interface.
- For the filtering option, the destination MAC cannot be combined with inner VLAN or outer VLAN.
- There is no support for L3 and L4 loopback. Source and destination IP address or source and destination ports will not be swapped.
- Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) packets are transparent to the data plane loopback configuration and cannot be looped back.
- Packets coming from the other side of the wire where loopback is configured and having the same destination MAC address are dropped.
- The broadcast and multicast IP addresses of the broadcast and multicast IP frames that are received cannot be used as the source IP address of the frame when it is sent back to the initiator. In such a case, the IP address of the subinterface is used as the source IP address of the frame when it is sent back to the initiator.
Configuring External Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Configuring external Ethernet data plane loopback is permitted on a Layer 3 main interface and subinterfaces.
The following steps show how to configure external Ethernet data plane loopback on a subinterface using single and double tagging. (The procedure to configure external Ethernet data plane loopback on the main interface is similar to this procedure.)
- encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
- encapsulation dot1q vlan-id second-dot1q inner vlan-id
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port.sub-port
4.
Do one of the following:
5.
ethernet
loopback
permit
external
6.
end
7.
ethernet
loopback
start
local
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port.sub-port
external
timeout
none
8.
ethernet
loopback
stop
local
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port.sub-port
id
session-id
9.
show
ethernet
loopback
active
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
This example shows how to configure Ethernet data plane loopback using single tagging:
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 Router(config-subif)#ethernet loopback permit external Router(config-subif)#end
This example shows how to configure Ethernet data plane loopback using double tagging:
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 second-dot1q 1101 Router(config-subif)#ethernet loopback permit external Router(config-subif)#end
This example shows how to start an Ethernet data plane loopback:
Router#ethernet loopback start local interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 external timeout none This is an intrusive loopback and the packets matched with the service will not be able to pass through. Continue? (yes/[no]): Enter yes to continue.
This example shows how to stop an Ethernet data plane loopback:
Router#ethernet loopback stop local interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 id 1 Router#*Oct 21 10:16:17.887: %E_DLB-6-DATAPLANE_LOOPBACK_STOP: Ethernet Dataplane Loopback Stop on interface GigabitEthernet0/2 with session id 1 Router#show ethernet loopback active Total Active Session(s): 0 Total Internal Session(s): 0 Total External Session(s): 0
Verifying the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the Ethernet data plane loopback configuration:
- show ethernet loopback permitted
- show ethernet loopback active
Use the show ethernet loopback permitted command to view the loopback capabilities per interface:
Router#show ethernet loopback permitted -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Interface SrvcInst Direction Dot1q/Dot1ad(s) Second-Dot1q(s) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Gi0/2.1101 N/A External 100 1101
Use the show ethernet loopback active command to display the summary of the active loopback sessions on a subinterface:
Router#show ethernet loopback active Loopback Session ID : 1 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/2.1101 Service Instance : N/A Direction : External Time out(sec) : none Status : on Start time : *10:17:46.930 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013 Time left : N/A Dot1q/Dot1ad(s) : 100 Second-dot1q(s) : 1101 Source Mac Address : Any Destination Mac Address : Any Ether Type : Any Class of service : Any Llc-oui : Any Total Active Session(s): 1 Total Internal Session(s): 0 Total External Session(s): 1
Use the show ethernet loopback active command to display the summary of the active loopback sessions on the main interface:
Router#show ethernet loopback permitted Loopback Session ID : 1 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/2 Service Instance : N/A Direction : External Time out(sec) : none Status : on Start time : *10:14:23.507 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013 Time left : N/A Dot1q/Dot1ad(s) : 1-100 Second-dot1q(s) : 1-1101 Source Mac Address : Any Destination Mac Address : Any Ether Type : Any Class of service : Any Llc-oui : Any Total Active Session(s): 1 Total Internal Session(s): 0 Total External Session(s): 1
Troubleshooting the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
Table 1 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot issues pertaining to the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback feature. The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information about these commands.
 Caution | Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff. |
 Note | Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console command. |
|
debug Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
debug elb-pal-pd all |
Displays all the debugging information about the Ethernet data plane loopback configuration. |
|
debug elb-pal-pd error |
Displays debugging information about Ethernet data plane loopback configuration errors. |
|
debug elb-pal-pd event |
Displays debugging information about Ethernet data plane loopback configuration changes. |
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
IEEE Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) is an end-to-end per-service Ethernet-layer Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) protocol. CFM includes proactive connectivity monitoring, fault verification, and fault isolation for large Ethernet metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and WANs.
 Note | This feature is supported only if you have purchased the advipservices licensing module. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html . |
- Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet CFM
- Configuring Ethernet CFM (Port MEP)
- Configuring Ethernet CFM (Single-Tagged Packets)
- Configuring Ethernet CFM (Double-Tagged Packets)
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet CFM
- A specific domain must be configured. If it is not, an error message is displayed.
- Multiple domains (different domain names) having the same maintenance level can be configured. However, associating a single domain name with multiple maintenance levels is not permitted.
Configuring Ethernet CFM (Port MEP)
Complete these steps to configure and enable Ethernet CFM on a port Maintenance End Point (MEP):
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ethernet
cfm
ieee
4.
ethernet
cfm
global
5.
ethernet
cfm
domain
domain-name
level
value
6.
service
service-name
port
7.
continuity-check
interval
value
8.
end
9.
configure
terminal
10.
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
11.
ethernet
cfm
mep
domain
domain-name
mpid
mpid-value
service
service-name
12.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router>enable |
Enables the privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password when prompted. | ||
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router#configure terminal |
Enters the global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | ethernet
cfm
ieee
Example: Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee |
Enables the IEEE version of CFM. | ||
| Step 4 | ethernet
cfm
global
Example: Router(config)#ethernet cfm global |
Enables CFM processing globally on the router. | ||
| Step 5 | ethernet
cfm
domain
domain-name
level
value
Example: Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm domain carrier level 2 |
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level, and enters the Ethernet CFM configuration mode. level can be any value from 0 to 7. | ||
| Step 6 | service
service-name
port
Example: Router(config-ecfm)#service carrier port |
Creates a service on the interface and sets the config-ecfm-srv submode. | ||
| Step 7 | continuity-check
interval
value
Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check interval 100m |
Enables sending continuity check messages at the set interval. | ||
| Step 8 | end
Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)#end |
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 9 | configure
terminal
Example: Router#configure terminal |
Enters the global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 10 | interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
Example: Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 |
Specifies an interface and enters the interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 11 | ethernet
cfm
mep
domain
domain-name
mpid
mpid-value
service
service-name
Example: Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain carrier mpid 44 service carrier |
Sets a port to a maintenance domain and defines it as an MEP.
| ||
| Step 12 | end
Example: Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#end |
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuration Example for Ethernet CFM (Port MEP)
This example shows how to configure Ethernet CFM on a port MEP:
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee Router(config)#ethernet cfm global Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm domain carrier level 2 Router(config-ecfm)#service carrier port Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check interval 100m Router(config-ecfm-srv)#end Router#configure terminal Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain carrier mpid 44 service carrier Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#end
Verifying the Ethernet CFM Configuration on a Port MEP
Use the following commands to verify Ethernet CFM configured on a port MEP:
- show ethernet cfm domain
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
- ping ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name cos value
- traceroute ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name
- show ethernet cfm error configuration
Use the show ethernet cfm domain command to view details about CFM maintenance domains:
Router#show ethernet cfm domain carrier Domain Name: carrier Level: 2 Total Services: 1 Services: Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name Port none Dwn Y 100ms Disabled Disabled 100 Static carrier Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command to view the MEPs that are configured locally on a router. The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command:
Router#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
Local MEPs:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name Lvl MacAddress Type CC
Ofld Domain Id Dir Port Id
MA Name SrvcInst Source
EVC name
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
44 carrier 2 5657.a844.04fa Port Y
No carrier Down Gi0/2 none
carrier N/A Static
N/A
Total Local MEPs: 1
Local MIPs: None
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to display information about remote maintenance point domains or levels. In the following example, carrier, Provider, and customer are the maintenance point domains that are configured:
On router 1:
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
43 carrier 5657.a86c.fa92 Up N/A
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier Port none N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
33 Provider 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
5 Provider Gi0/2.100
- Provider Vlan 100 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 34 Domain: Provider MA: Provider
3101 customer 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S,C 100,1101 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 4101 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
3102 customer 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1102
- customer1102 S,C 100,1102 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 4102 Domain: customer MA: customer1102
Total Remote MEPs: 4
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to view the details of a remote maintenance point domain:
On router 1:
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote domain carrier service carrier
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
43 carrier 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier S,C 100,1101 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Total Remote MEPs: 1
On router 2:
Router2#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote domain carrier service carrier
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
44 carrier 5657.g945.04fa Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier S,C 100,1101 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 43 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Use the ping command to verify if Loopback Messages (LBM) and Loopback Replies (LBR) are successfully sent and received between the routers:
Router1#ping ethernet mpid 44 domain carrier service carrier cos 5
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5 Ethernet CFM loopback messages to 5657.a86c.fa92, timeout is 5 seconds:!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
Router1#
Use the traceroute command to send the Ethernet CFM traceroute messages:
Router#traceroute ethernet mpid 44 domain carrier service carrier
Type escape sequence to abort. TTL 64. Linktrace Timeout is 5 seconds
Tracing the route to 5657.a86c.fa92 on Domain carrier, Level 2, service carrier
Traceroute sent via Gi0/2
B = Intermediary Bridge
! = Target Destination
* = Per hop Timeout
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC Ingress Ingr Action Relay Action
Hops Host Forwarded Egress Egr Action Previous Hop
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! 1 5657.a86c.fa92 Gi0/2 IngOk RlyHit:MEP
Not Forwarded 5657.g945.04fa
Router#
Configuring Ethernet CFM (Single-Tagged Packets)
Complete these steps to configure and enable Ethernet CFM for single-tagged packets:
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ethernet
cfm
ieee
4.
ethernet
cfm
global
5.
ethernet
cfm
domain
domain-name
level
value
6.
service
service-name
vlan
vlan-id
direction
down
7.
continuity-check
8.
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
9.
ethernet
cfm
mep
domain
domain-name
mpid
mpid-value
service
service-name
10.
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port.subinterface
11.
encapsulation
dot1q
vlan-id
12.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router>enable |
Enables the privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password when prompted. | ||
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router#configure terminal |
Enters the global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | ethernet
cfm
ieee
Example: Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee |
Enables the IEEE version of CFM. | ||
| Step 4 | ethernet
cfm
global
Example: Router(config)#ethernet cfm global |
Enables CFM processing globally on the router. | ||
| Step 5 | ethernet
cfm
domain
domain-name
level
value
Example: Router(config)#ethernet cfm domain customer level 7 |
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level, and enters the Ethernet CFM configuration mode. level can be any value from 0 to 7. | ||
| Step 6 | service
service-name
vlan
vlan-id
direction
down
Example: Router(config-ecfm)#service customer1101 vlan 100 direction down |
Enters the CFM service configuration mode. vlan—Specifies the VLAN. | ||
| Step 7 | continuity-check
Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check |
Enables sending continuity check messages. | ||
| Step 8 | interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 |
Specifies an interface and enters the interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 9 | ethernet
cfm
mep
domain
domain-name
mpid
mpid-value
service
service-name
Example: Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain customer mpid 100 service customer1101 |
Sets a port to a maintenance domain and defines it as an MEP.
| ||
| Step 10 | interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port.subinterface
Example: Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1 |
Specifies a subinterface and enters the subinterface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 11 | encapsulation
dot1q
vlan-id
Example: Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 |
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q (dot1q), and specifies the VLAN identifier. | ||
| Step 12 | end
Example: Router(config-subif)#end |
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuration Example for Ethernet CFM (Single-Tagged Packets)
This example shows how to configure Ethernet CFM for single-tagged packets:
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee Router(config)#ethernet cfm global Router(config)#ethernet cfm domain customer level 7 Router(config-ecfm)#service customer1101 vlan 100 direction down Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain customer mpid 100 service customer1101 Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 Router(config-subif)#end
Verifying the Ethernet CFM Configuration for Single-Tagged Packets
Use the following commands to verify Ethernet CFM configured for single-tagged packets:
- show ethernet cfm domain
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
- show ethernet cfm error configuration
Use the show ethernet cfm domain command to display the maintenance point domains configured in the network. In the following example, the customer, enterprise, and carrier maintenance point domains are configured.
Router#show ethernet cfm domain Domain Name: customer Level: 7 Total Services: 1 Services: Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name Vlan 100 Dwn Y 10s Disabled Disabled 100 Static customer1101 Domain Name: enterprise Level: 6 Total Services: 1 Services: Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name Vlan 110 Dwn Y 10s Disabled Disabled 100 Static custservice Domain Name: carrier Level: 2 Total Services: 1 Services: Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name Vlan 200 Dwn Y 10s Disabled Disabled 100 Static carrier Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command to view the local MEPs. The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command:
Router#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name Lvl MacAddress Type CC
Ofld Domain Id Dir Port Id
MA Name SrvcInst Source
EVC name
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 customer 7 70ca.9b4d.a400 Vlan Y
No customer Down Gi0/2 100
customer1101 N/A Static
N/A
400 enterprise 6 70ca.9b4d.a400 Vlan I
No enterprise Down Gi0/1 110
custservice N/A Static
N/A
44 carrier 2 70ca.9b4d.a400 Vlan N
No carrier Down Gi0/2 200
carrier N/A Static
N/A
Total Local MEPs: 3
Local MIPs: None
Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to display information about remote maintenance point domains or levels.
The following example displays the continuity check messages exchanged between remote MEPs:
On router 1:
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain Ingress
RDI MA Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
110 customer 70ca.9b4d.a400 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2
- customer1101 Vlan 100 N/A
N/A 12s
MPID: 100 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
410 enterprise 70ca.9b4d.a400 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1
- custservice Vlan 110 N/A
N/A 12s
MPID: 400 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
43 carrier 70ca.9b4d.a400 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier Vlan 200 N/A
N/A 12s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Total Remote MEPs: 3
Router1#
On router 2:
Router2#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain Ingress
RDI MA Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 customer 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2
- customer1101 Vlan 100 N/A
N/A 2s
MPID: 110 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
400 enterprise 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1
- custservice Vlan 110 N/A
N/A 2s
MPID: 410 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
44 carrier 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier Vlan 200 N/A
N/A 2s
MPID: 43 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Total Remote MEPs: 3
Router2#
Use the show ethernet cfm error configuration command to view Ethernet CFM configuration errors (if any). The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm error configuration command:
Router#show ethernet cfm error configuration -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- CFM Interface Type Id Level Error type -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Gi0/2 S,C 100 5 CFMLeak
Configuring Ethernet CFM (Double-Tagged Packets)
Complete these steps to configure and enable Ethernet CFM for double-tagged packets:
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ethernet
cfm
ieee
4.
ethernet
cfm
global
5.
ethernet
cfm
domain
domain-name
level
0
to
7
6.
service
service-name
vlan
vlan-id
inner-vlan
inner
vlan-id
direction
down
7.
continuity-check
8.
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
9.
ethernet
cfm
mep
domain
domain-name
mpid
mpid-value
service
service-name
10.
interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port.subinterface
11.
encapsulation
dot1q
vlan-id
second-dot1q
inner
vlan-id
12.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
Example: Router>enable |
Enables the privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password when prompted. | ||
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Router#configure terminal |
Enters the global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | ethernet
cfm
ieee
Example: Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee |
Enables the IEEE version of CFM. | ||
| Step 4 | ethernet
cfm
global
Example: Router(config)#ethernet cfm global |
Enables CFM processing globally on the router. | ||
| Step 5 | ethernet
cfm
domain
domain-name
level
0
to
7
Example: Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm domain customer level 7 |
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level, and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. level can be any value from 0 to 7. | ||
| Step 6 | service
service-name
vlan
vlan-id
inner-vlan
inner
vlan-id
direction
down
Example: Router(config-ecfm)#service customer1101 vlan 100 inner-vlan 30 direction down |
Enters the CFM service configuration mode. The following are the parameters:
| ||
| Step 7 | continuity-check
Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check |
Enables sending continuity check messages. | ||
| Step 8 | interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port
Example: Router(config-ecfm-srv)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 |
Specifies an interface and enters the interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 9 | ethernet
cfm
mep
domain
domain-name
mpid
mpid-value
service
service-name
Example: Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain customer mpid 100 service customer1101 |
Sets a port to a maintenance domain and defines it as an MEP.
MPID—Specifies the maintenance endpoint identifier. | ||
| Step 10 | interface
gigabitethernet
slot/port.subinterface
Example: Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 |
Specifies a subinterface and enters the subinterface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 11 | encapsulation
dot1q
vlan-id
second-dot1q
inner
vlan-id
Example: Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 second-dot1q 30 |
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q (dot1q), and specifies the VLAN identifier. Use the second-dot1q keyword and the inner vlan-id argument to specify the VLAN tag. | ||
| Step 12 | end
Example: Router(config-subif)#end |
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuration Example for Ethernet CFM (Double-Tagged Packets)
This example shows how to configure Ethernet CFM for double-tagged packets:
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee Router(config)#ethernet cfm global Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm domain customer level 7 Router(config-ecfm)#service customer1101 vlan 100 inner-vlan 30 direction down Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check Router(config-ecfm-srv)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2 Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain customer mpid 100 service customer1101 Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 second-dot1q 30 Router(config-subif)#end
Verififying the Ethernet CFM Configuration for Double-Tagged Packets
Use the following commands to verify Ethernet CFM configured for double-tagged packets:
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
- ping ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name cos value
- traceroute ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name
- show ethernet cfm error configuration
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command to view the local MEPs. The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command:
Router#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 customer 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S, C 100, 30 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 100 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to display the remote maintenance point domains. In the following example, customer, carrier, and enterprise are the maintenance point domains that are configured:
On router 1:
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
110 customer 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S, C 100, 30 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 100 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
43 carrier 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2.2
- carrier S, C 50, 20 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
410 enterprise 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1.1
- custservice S, C 200, 70 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 400 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
Router1#
On router 2:
Router2#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 customer 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S, C 100, 30 N/A
N/A 40s
MPID: 110 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
44 carrier 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2.2
- carrier S, C 50, 20 N/A
N/A 40s
MPID: 43 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
400 enterprise 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1.1
- custservice S, C 200, 70 N/A
N/A 40s
MPID: 410 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
Router2#
Use the ping command to verify if Ethernet CFM loopback messages are successfully sent and received between the routers:
Router#ping ethernet mpid 100 domain customer service customer1101 cos 5
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5 Ethernet CFM loopback messages to 8843.e154.6f01, timeout is 5 seconds:!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
Router#
Use the traceroute
command to send the Ethernet CFM traceroute messages:
Router#traceroute ethernet mpid 100 domain customer service customer1101
Type escape sequence to abort. TTL 64. Linktrace Timeout is 5 seconds
Tracing the route to 8843.e154.6f01 on Domain customer, Level 7, service customer1101, vlan 100 inner-vlan 30
Traceroute sent via Gi0/2.1101
B = Intermediary Bridge
! = Target Destination
* = Per hop Timeout
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC Ingress Ingr Action Relay Action
Hops Host Forwarded Egress Egr Action Previous Hop
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! 1 8843.e154.6f01 Gi0/2.1101 IngOk RlyHit:MEP
Not Forwarded 5657.a86c.fa92
Use the show ethernet cfm error configuration command to view Ethernet CFM configuration errors (if any). The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm error configuration command:
Router#show ethernet cfm error configuration -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- CFM Interface Type Id Level Error type -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Gi0/2 S,C 100,30 5 CFMLeak Gi0/2 S,C 100,30 1 CFMLeak
Troubleshooting Ethernet CFM Configuration
Table 1 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot issues pertaining to the Ethernet CFM configuration.
The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information about these commands.
 Caution | Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff. |
 Note | Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console command. |
|
debug Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
debug ethernet cfm all |
Enables all Ethernet CFM debug messages. |
|
debug ethernet cfm diagnostic |
Enables low-level diagnostic debugging of Ethernet CFM general events or packet-related events. |
|
debug ethernet cfm error |
Enables debugging of Ethernet CFM errors. |
|
debug ethernet cfm packets |
Enables debugging of Ethernet CFM message packets. |
|
debug ecfmpal all |
Enables debug messages for all Ethernet CFM platform events. |
|
debug ecfmpal api |
Displays debug messages for all Ethernet CFM platform API events. |
|
debug ecfmpal common |
Displays debug messages for all Ethernet CFM platform common events. |
|
debug ecfmpal ecfmpal |
Enables debugging of all Ethernet CFM platform events. |
|
debug ecfmpal epl |
Enables debugging of all Ethernet CFM platform endpoint list (EPL) events. |
|
debug ecfmpal isr |
Enables debugging of all Ethernet CFM platform interrupt service request (ISR) events. |
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
Y.1731 Performance Monitoring (PM) provides a standard Ethernet PM function that includes measurement of Ethernet frame delay, frame delay variation, frame loss, and frame throughput measurements specified by the ITU-T Y-1731 standard and interpreted by the Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) standards group.
 Note | This feature is supported only if you have purchased the advipservices licensing module. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html . |
- Frame Delay
- Restrictions for Configuring Two-Way Delay Measurement
- Configuring Two-Way Delay Measurement
- Configuration Examples for Two-Way Delay Measurement
- Verifying Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration
- Troubleshooting Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration
Frame Delay
Ethernet frame delay measurement is used to measure frame delay and frame delay variations. Ethernet frame delay is measured using the Delay Measurement Message (DMM) method.
Restrictions for Configuring Two-Way Delay Measurement
Follow the guidelines and restrictions listed here when you configure two-way delay measurement:
- Y.1731 PM measurement works only for a point-to-point network topology.
- The granularity of the clock for delay measurement is in seconds and nanoseconds.
- CFM Y.1731 packets work with a maximum of two VLAN tags. The expected behavior is not observed with more VLAN tags. Also, CFM Y.1731 packets do not work with untagged cases.
Configuring Two-Way Delay Measurement
The following steps show how to configure two-way delay measurement. Both single and double tagging methods are included in the steps listed below.
- ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain value vlan vlan-id mpid value cos value source mpid value
- ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain value vlan vlan-id inner-vlan inner vlan-id mpid value cos value source mpid value
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ip
sla
operation
number
4.
Do one of the following:
5.
aggregate
interval
seconds
6.
exit
7.
ip
sla
schedule
operation
number
life
value
forever
start-time
value
8.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Two-Way Delay Measurement
This example shows how to configure two-way delay measurement using single tagging:
router>enable router#configure terminal router(config)#ip sla 1101 router(config-ip-sla)#ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain customer vlan 100 mpid 3101 cos 1 router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#aggregate interval 30 router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#exit router(config)#ip sla schedule 1102 life forever start-time now router(config)#end
This example shows how to configure two-way delay measurement using double tagging:
router>enable router#configure terminal router(config)#ip sla 1101 router(config-ip-sla)#ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain customer vlan 100 inner-vlan 1101 mpid 3101 cos 1 source mpid 4101 router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#aggregate interval 30 router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#exit router(config)#ip sla schedule 1101 life forever start-time now router(config)#end
Verifying Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the performance-monitoring sessions:
- show run | sec ip sla
- show ip sla summary
- show ip sla statistics entry-number
- show ip sla configuration entry-number
- show ethernet cfm pm session summary
- show ethernet cfm pm session detail session-id
- show ethernet cfm pm session db session-id
The following are the sample outputs of the commands listed above:
Router#show run | sec ip sla
ip sla auto discovery
ip sla 1101
ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain customer vlan 100 inner-vlan 1101 mpid 3101 cos
1 source mpid 4101
ip sla schedule 1101 life forever start-time now
Router#show ip sla summary
IPSLAs Latest Operation Summary
Codes: * active, ^ inactive, ~ pending
ID Type Destination Stats Return Last
(ms) Code Run
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
*1101 y1731-delay Domain:customer V - OK 27 seconds ag
lan:100 CVlan:110 o
1 Mpid:3101
Router#show ip sla statistics
IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics
IPSLA operation id: 1101
Delay Statistics for Y1731 Operation 1101
Type of operation: Y1731 Delay Measurement
Latest operation start time: *10:43:12.930 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013
Latest operation return code: OK
Distribution Statistics:
Interval
Start time: *10:43:12.930 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013
Elapsed time: 15 seconds
Number of measurements initiated: 7
Number of measurements completed: 7
Flag: OK
Router#show ip sla configuration 1101
IP SLAs Infrastructure Engine-III
Entry number: 1101
Owner:
Tag:
Operation timeout (milliseconds): 5000
Ethernet Y1731 Delay Operation
Frame Type: DMM
Domain: customer
Vlan: 100
CVlan: 1101
Target Mpid: 3101
Source Mpid: 4101
CoS: 1
Max Delay: 5000
Request size (Padding portion): 64
Frame Interval: 1000
Clock: Not In Sync
Threshold (milliseconds): 5000
Schedule:
Operation frequency (seconds): 30 (not considered if randomly scheduled)
Next Scheduled Start Time: Start Time already passed
Group Scheduled : FALSE
Randomly Scheduled : FALSE
Life (seconds): Forever
Entry Ageout (seconds): never
Recurring (Starting Everyday): FALSE
Status of entry (SNMP RowStatus): Active
Statistics Parameters
Frame offset: 1
Distribution Delay Two-Way:
Number of Bins 10
Bin Boundaries: 5000,10000,15000,20000,25000,30000,35000,40000,45000,-1
Distribution Delay-Variation Two-Way:
Number of Bins 10
Bin Boundaries: 5000,10000,15000,20000,25000,30000,35000,40000,45000,-1
Aggregation Period: 30
History
Number of intervals: 2
Router#show ethernet cfm pm session summary
Number of Configured Session : 150
Number of Active Session: 2
Number of Inactive Session: 148
Router#
Router(config)#show ethernet cfm pm session detail 0
Session ID: 0
Sla Session ID: 1101
Level: 7
Service Type: S,C
Service Id: 100,1101
Direction: Down
Source Mac: 5352.a824.04fr
Destination Mac: 5067.a87c.fa92
Session Version: 0
Session Operation: Proactive
Session Status: Active
MPID: 4101
Tx active: yes
Rx active: yes
RP monitor Tx active: yes
RP monitor Rx active: yes
Timeout timer: stopped
Last clearing of counters: *00:00:00.000 UTC Mon Jan 1 1900
DMMs:
Transmitted: 117
DMRs:
Rcvd: 117
1DMs:
Transmitted: 0
Rcvd: 0
LMMs:
Transmitted: 0
LMRs:
Rcvd: 0
VSMs:
Transmitted: 0
VSRs:
Rcvd: 0
SLMs:
Transmitted: 0
SLRs:
Rcvd: 0
Test ID 0
Router1#
Router#show ethernet cfm pm session db 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TX Time FWD RX Time FWD
TX Time BWD RX Time BWD Frame Delay
Sec:nSec Sec:nSec Sec:nSec
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Session ID: 0
****************************************************************************
3591340722:930326034 3591340663:866791722
3591340663:866898528 3591340722:930707484 0:274644
****************************************************************************
3591340723:927640626 3591340664:864091056
3591340664:864182604 3591340723:927976302 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340724:927640626 3591340665:864091056
3591340665:864167346 3591340724:927961044 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340725:927671142 3591340666:864121572
3591340666:864213120 3591340725:928006818 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340726:927655884 3591340667:864106314
3591340667:864197862 3591340726:927991560 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340727:927732174 3591340668:864167346
3591340668:864533538 3591340727:928327236 0:228870
****************************************************************************
3591340728:927655884 3591340669:864121572
3591340669:864197862 3591340728:928006818 0:274644
****************************************************************************
3591340729:927671142 3591340670:864121572
3591340670:864197862 3591340729:927991560 0:244128
****************************************************************************
Troubleshooting Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration
Table 1 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot issues pertaining to the two-way delay measurement configuration.
The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information about these commands.
 Note | Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff. |
 Note | Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console command. |
|
debug Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
debug epmpal all |
Enables debugging of all Ethernet performance monitoring (PM) events. |
|
debug epmpal api |
Enables debugging of Ethernet PM API events. |
|
debug epmpal rx |
Enables debugging of Ethernet PM packet-receive events. |
|
debug epmpal tx |
Enables debugging of Ethernet PM packet-transmit events. |
 Feedback
Feedback