- Overview of Prime Network GUI clients
- Setting Up the Prime Network Clients
- Setting Up Change and Configuration Management
- Setting Up Vision Client Maps
- Setting Up Native Reports
- Setting Up Fault Management and the Events Client Default Settings
- Viewing Devices, Links, and Services in Maps
- Drilling Down into an NE’s Physical and Logical Inventories and Changing Basic NE Properties
- Manage Device Configurations and Software Images
- How Prime Network Handles Incoming Events
- Managing Tickets with the Vision Client
- Viewing All Event Types in Prime Network
- Cisco Path Tracer
- Managing IP Address Pools
- Monitoring AAA Configurations
- Managing DWDM Networks
- Managing MPLS Networks
- Managing Carrier Ethernet Configurations
- Managing Ethernet Networks Using Operations, Administration, and Maintenance Tools
- Monitoring Carrier Grade NAT Configurations
- Monitoring Quality of Service
- Managing IP Service Level Agreement (IP SLA) Configurations
- Monitoring IP and MPLS Multicast Configurations
- Managing Session Border Controllers
- Monitoring BNG Configurations
- Managing Mobile Transport Over Pseudowire (MToP) Networks
- Managing Mobile Networks
- Managing Data Center Networks
- Monitoring Cable Technologies
- Monitoring ADSL2+ and VDSL2 Technologies
- Monitoring Quantum Virtualized Packet Core
- VSS Redundancy System
- Icon Reference
- Permissions Required to Perform Tasks Using the Prime Network Clients
- Correlation Examples
- Managing certificates
Managing IP Address Pools
An IP pool is a sequential range of IP addresses within a certain network. You can have multiple pool configurations. Each pool can have a priority and can be assigned to a group.
IP addresses can be assigned dynamically from a single pool or from a group of pools. The Least Recently Used (LRU) method is used to assign IP addresses. In each pool, the addresses are placed in a queue. At the time of assigning, the address at the head of the queue is assigned, and when released is placed at the end of the queue.
When a group of pools have the same priority, an algorithm is used to determine a probability for each pool based on the number of available addresses. A pool is selected based on the probability determined. This method allocates addresses evenly from the group of pools.
IP pool supports both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. With the IP Pool feature, Prime Network provides the flexibility of assigning IP addresses dynamically for services running on a network element. A service running on a network element can refer to an appropriate IP pool and an IP address gets assigned to the service from the IP pool.
These topics describe how to use the Vision client to view and manage IP pools. If you cannot perform an operation that is described in these topics, you may not have sufficient permissions; see Appendix B, “Permissions Required to Perform Tasks Using the Prime Network Clients” .
Viewing the IP Pool Properties
To view the IP pool properties for a device:
Step 1![]() In the Vision client, right-click the required device, and choose Inventory.
In the Vision client, right-click the required device, and choose Inventory.
Step 2![]() In the Inventory window, choose Logical Inventory > Context > IP Pools. A list of IP pools are displayed in the content pane.
In the Inventory window, choose Logical Inventory > Context > IP Pools. A list of IP pools are displayed in the content pane.
Table 14-1 describes the fields that are displayed in the content pane.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
Step 3![]() Right-click the IP pool name and choose Properties. The IP Pool Properties dialog box is displayed as shown in Figure 14-1.
Right-click the IP pool name and choose Properties. The IP Pool Properties dialog box is displayed as shown in Figure 14-1.
Figure 14-1 IP Pool Properties
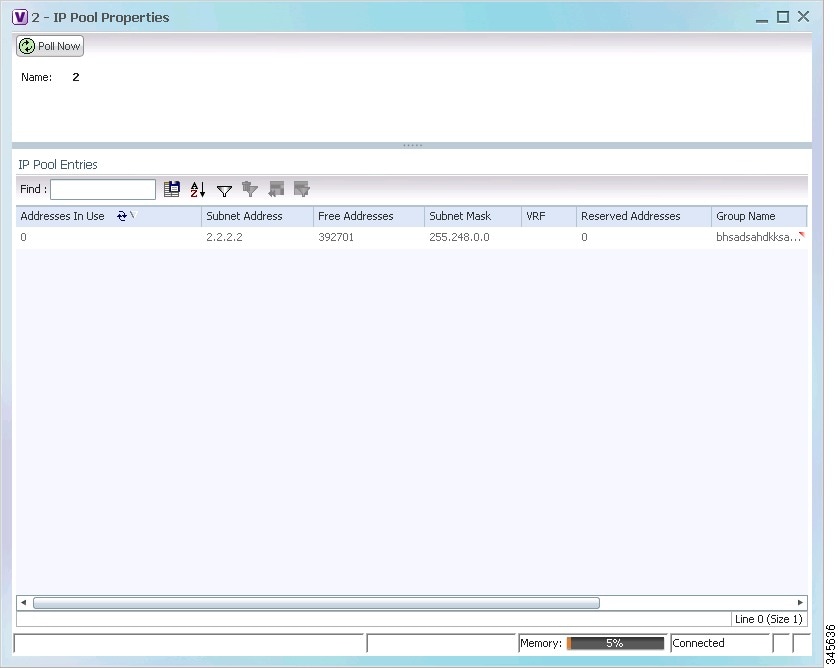
Table 14-2 describes the fields that are displayed in the IP Pool Properties dialog box.
Modifying and Deleting IP Pools
The following commands can be launched from the inventory by right-clicking on an IP pool name and choosing Commands > Configuration. Your permissions determine whether you can run these commands (see Appendix B, “Permissions Required to Perform Tasks Using the Prime Network Clients” ). To find out if a device supports these commands, see the Cisco Prime Network 5.2 Supported Cisco VNEs.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
 Feedback
Feedback