- Overview of Prime Network GUI clients
- Setting Up the Prime Network Clients
- Setting Up Change and Configuration Management
- Setting Up Vision Client Maps
- Setting Up Native Reports
- Setting Up Fault Management and the Events Client Default Settings
- Viewing Devices, Links, and Services in Maps
- Drilling Down into an NE’s Physical and Logical Inventories and Changing Basic NE Properties
- Manage Device Configurations and Software Images
- How Prime Network Handles Incoming Events
- Managing Tickets with the Vision Client
- Viewing All Event Types in Prime Network
- Cisco Path Tracer
- Managing IP Address Pools
- Monitoring AAA Configurations
- Managing DWDM Networks
- Managing MPLS Networks
- Managing Carrier Ethernet Configurations
- Managing Ethernet Networks Using Operations, Administration, and Maintenance Tools
- Monitoring Carrier Grade NAT Configurations
- Monitoring Quality of Service
- Managing IP Service Level Agreement (IP SLA) Configurations
- Monitoring IP and MPLS Multicast Configurations
- Managing Session Border Controllers
- Monitoring BNG Configurations
- Managing Mobile Transport Over Pseudowire (MToP) Networks
- Managing Mobile Networks
- Managing Data Center Networks
- Monitoring Cable Technologies
- Monitoring ADSL2+ and VDSL2 Technologies
- Monitoring Quantum Virtualized Packet Core
- VSS Redundancy System
- Icon Reference
- Permissions Required to Perform Tasks Using the Prime Network Clients
- Correlation Examples
- Managing certificates
Managing Session Border Controllers (SBCs)
This chapter identifies and describes the properties for Session Border Controllers (SBCs) that appear in the Vision client logical inventory. It also describes commands you can run to manage SBCs.
Session Border Controllers (SBCs) control and manage real-time multimedia traffic flows between IP network borders, handling signaling, and media. SBCs perform native IP interconnection functions required for real-time communications such as admission control, firewall traversal, accounting, signaling interworking, and quality-of-service (QoS) management. This includes:
- Protocol and media interworking
- Session routing
- Hosted Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall traversal
- Security and AAA
- Intra- and inter-VPN interconnections and optimization
- Media transcoding with an external media server
The Prime Network platform provides fault management, configuration, and performance monitoring for SBC services. Prime Network SBC commands allow you to configure SBC components.
An SBC consists of combined DBE and SBE functionality:
- Data Border Element (DBE)—Responsible for media-related functions.
- Signaling Border Element (SBE)—Responsible for call signaling-related functions.
In addition, the SBC can operate in the following deployment models:
- Distributed Model (DM)—Contains only the SBE or DBE, resulting in a distributed SBC.
- Unified Model (UM)—Contains both the SBE and DBE, thereby implementing the SBE and DBE as a single device.

Note![]() The existing Cisco SBC platforms support only DBE.
The existing Cisco SBC platforms support only DBE.
The following topics describe the SBC properties that are displayed in the Vision client logical inventory. If you cannot perform an operation that is described in these topics, you may not have sufficient permissions; see Permissions for Managing SBCs.
Viewing SBC Properties in Logical Inventory
To view SBC properties in the Vision client logical inventory, right-click the element configured for SBC, then choose Inventory > Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller.
The SBC properties are displayed as shown in Figure 24-1.
Figure 24-1 SBC Properties in Logical Inventory
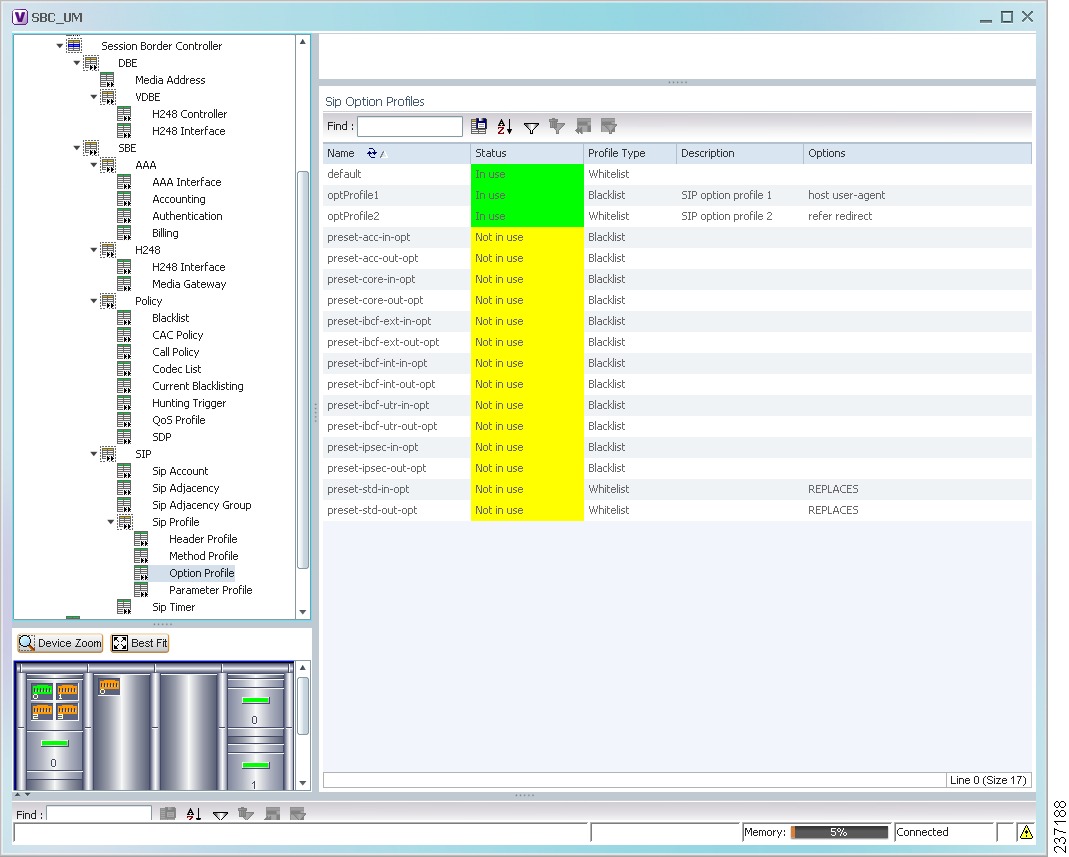
Table 24-1 describes the general SBC properties displayed in logical inventory.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Viewing SBC DBE Properties
The DBE controls media packet access to the network, provides differentiated services and QoS for different media streams, and prevents service theft.
To view SBC DBE properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > DBE.
Table 24-2 describes the DBE properties that appear in logical inventory.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Viewing Media Address Properties
A DBE uses a pool of sequential IPv4 media addresses as local media addresses.
To view SBC media address properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > DBE > Media Address.
Table 24-3 describes the SBC media address properties that are displayed in logical inventory.
Viewing VDBE H.248 Properties
To view VDBE H.248 properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > DBE > VDBE.
Table 24-4 describes the VDBE H.248 properties that are displayed in logical inventory.
Viewing SBC SBE Properties
The SBE controls the access of VoIP signaling messages to the network core and manipulates the contents of these messages. It does this by acting as a SIP B2BUA or H.323 gateway.
To view SBC SBE properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > SBE.
Table 24-5 describes the information displayed in logical inventory for an SBE.
Viewing AAA Properties
For devices that support local and remote billing, the SBC can send billing records to a AAA server using the RADIUS protocol.
To view AAA properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > SBE > AAA.
Table 24-6 describes the AAA properties that appear in logical inventory for the SBC SBE.
Viewing H.248 Properties
The H.248 interface is used for signaling between an SBE and a DBE in distributed mode and between an SBE and a transcoding media gateway. The SBE or SBC acts as an H.248 MGC, and the transcoding device acts as an H.248 media gateway. The connection between the MGC and the media gateway is an H.248 link.
To view H.248 properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > H248.
Table 24-7 describes the H.248 properties that appear in logical inventory for the SBC SBE.
Viewing Policy Properties
An SBC policy is a set of rules that define how the SBC treats different kinds of VoIP events. An SBC policy allows control of the VoIP signaling and media that pass through the SBC at an application level.
A policy set is a group of policies that can be active on the SBC at any one time. If a policy set is active, the SBC uses the rules defined within it to apply policy to events. Multiple policies can be set on a single SBC.
To view policy properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > Policy.
Table 24-8 describes the policy properties that appear in logical inventory for the SBC SBE.
Viewing SIP Properties
To view SIP properties, choose Logical Inventory > Session Border Controller > SIP.
Table 24-9 describes the SIP entries that appear in logical inventory for the SBC SBE.
Viewing SBC Statistics
The following SBC statistics commands can be launched from the inventory by right-clicking the appropriate node and choosing Commands > Configuration. Your permissions determine whether you can run these commands (see Permissions for Vision Client NE-Related Operations). To find out if a device supports these commands, see the Cisco Prime Network 5.2 Supported Cisco VNEs.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Based on the command selected, the device’s statistics are displayed. |
||
Configuring SBC Components
The following SBC component commands can be launched from the inventory by right-clicking the appropriate node and choosing Commands > Configuration. Your permissions determine whether you can run these commands (see Permissions for Vision Client NE-Related Operations). To find out if a device supports these commands, see the Cisco Prime Network 5.2 Supported Cisco VNEs.
 Feedback
Feedback