- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Setting Up Devices and Using the GUI Clients
- Working with the Cisco Prime Network Vision Client
- Viewing and Managing NE Properties
- Device Configurations and Software Images
- Working with Prime Network Vision Maps
- Working with Links
- Labeling NEs Using Business Tags
- Working with the Prime Network Events
- Tracking Faults Using Prime Network Events
- Working with Tickets in Cisco Prime Network Vision
- Working with Reports
- Using Cisco PathTracer to Diagnose Problems
- Monitoring Carrier Ethernet Services
- Monitoring Carrier Grade NAT Properties
- Monitoring DWDM Properties
- Monitoring Ethernet Operations, Administration,and Maintenance Tool Properties
- Monitoring Y.1731 IPSLA Configuration
- IPv6 and IPv6 VPN over MPLS
- Monitoring MPLS Services
- Viewing IP and MPLS Multicast Configurations
- Monitoring MToP Services
- Viewing and Managing SBCs
- Monitoring AAA Configurations
- Monitoring IP Pools
- Monitoring BNG Configurations
- Monitoring Mobile Technologies
- Monitoring Data Center Configurations
- Icon and Button Reference
- Glossary
- Index
Monitoring Carrier Grade NAT Properties
Carrier Grade NAT is a large-scale Network Address Translation (NAT) that provides translation of millions of private IPv4 addresses to public IPv4 addresses. These translations support subscribers and content providers with a bandwidth throughput of at least 10 Gbps full-duplex.
Carrier Grade NAT addresses the IPv4 address completion problem. It employs Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT) to aggregate many private IPv4 addresses into fewer public IPv4 addresses. For example, a single public IPv4 address with a pool of 32,000 port numbers supports 320 individual private IP subscribers, assuming that each subscriber requires 100 ports. Carrier Grade NAT also offers a way to implement a graceful transition to IPv6 addresses.
Carrier Grade NAT attributes and instances are configured as a CRS-ADVSVC-PLIM card on Cisco CRS-1 routers. To route internal public addresses to external public addresses, a VPN Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instance is created. Interfaces are created for the VRF at the subscriber-side (private) and the Internet-side (public). The VRF enables static or dynamic routing of protocols on the interfaces.
Cisco Prime Network supports the following instances for Carrier Grade NAT:
•![]() Stateful Address Translation- NAT44 Stateful
Stateful Address Translation- NAT44 Stateful
•![]() Stateless Address Translation- NAT 64 Stateless (X-LAT)
Stateless Address Translation- NAT 64 Stateless (X-LAT)
•![]() IPv6 rapid deployment (6rd)
IPv6 rapid deployment (6rd)
Each Carrier Grade NAT instance has several attributes listed under them, such as preferred location, address pools, associated interfaces, and statistics. The attributes are grouped under related categories. The categories and attributes are listed below:

Note ![]() IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT44) is not supported for devices running Cisco IOS XR software version 4.0.
IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT44) is not supported for devices running Cisco IOS XR software version 4.0.
The following topics describe how to use Prime Network Vision to view Carrier Grade NAT properties:
•![]() User Roles Required to View Carrier Grade NAT Properties
User Roles Required to View Carrier Grade NAT Properties
•![]() Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Logical Inventory
Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Logical Inventory
•![]() Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Physical Inventory
Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Physical Inventory
User Roles Required to View Carrier Grade NAT Properties
This topic identifies the roles that are required to view Carrier Grade NAT properties in Prime Network Vision. Prime Network determines whether you are authorized to perform a task as follows:
•![]() For GUI-based tasks (tasks that do not affect elements), authorization is based on the default permission that is assigned to your user account.
For GUI-based tasks (tasks that do not affect elements), authorization is based on the default permission that is assigned to your user account.
•![]() For element-based tasks (tasks that do affect elements), authorization is based on the default permission that is assigned to your account. That is, whether the element is in one of your assigned scopes and whether you meet the minimum security level for that scope.
For element-based tasks (tasks that do affect elements), authorization is based on the default permission that is assigned to your account. That is, whether the element is in one of your assigned scopes and whether you meet the minimum security level for that scope.
For more information on user authorization, see the Cisco Prime Network 3.10 Administrator Guide.
The following tables identify the tasks that you can perform:
•![]() Table 14-1 identifies the tasks that you can perform if a selected element is not in one of your assigned scopes.
Table 14-1 identifies the tasks that you can perform if a selected element is not in one of your assigned scopes.
•![]() Table 14-2 identifies the tasks that you can perform if a selected element is in one of your assigned scopes.
Table 14-2 identifies the tasks that you can perform if a selected element is in one of your assigned scopes.
By default, users with the Administrator role have access to all managed elements. To change the Administrator user scope, see the topic on device scopes in the Cisco Prime Network 3.10 Administrator Guide.
Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Logical Inventory
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties in logical inventory:
Step 1 ![]() In Prime Network Vision, double-click the Cisco CRS device configured for Carrier Grade NAT.
In Prime Network Vision, double-click the Cisco CRS device configured for Carrier Grade NAT.
Step 2 ![]() In the inventory window, click Logical Inventory > Carrier Grade NAT.
In the inventory window, click Logical Inventory > Carrier Grade NAT.
The Carrier Grade NAT properties are displayed in logical inventory as shown in Figure 14-1.
Figure 14-1 Carrier Grade NAT in Logical Inventory
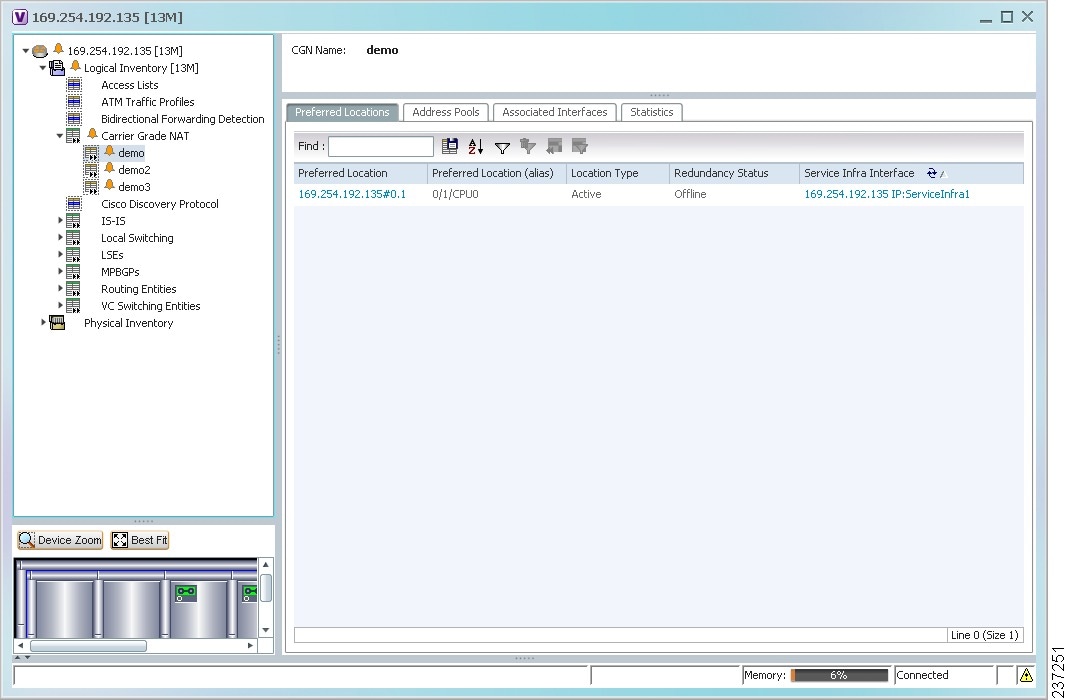
Table 14-3 describes the Carrier Grade NAT properties that are displayed.
|
|
|
|---|---|
CGN Name |
Name of the Carrier Grade NAT service. |
|
|
|
Preferred Location |
Hyperlinked entry to the card in physical inventory. |
Preferred Location (alias) |
Location of module in clear text. |
Location Type |
Configured type of location: Active or Standby. |
Redundancy Status |
Redundancy state: Online or Offline. If the field is empty, it means the data was not collected from the device. |
Service Infra Interface |
Hyperlinked entry to the routing entity in logical inventory. For more information about routing entities in logical inventory, see Viewing Routing Entities. |
|
|
|
Inside VRF |
Hyperlinked entry to the inside VRF in logical inventory. For more information about VRF properties in logical inventory, see Viewing VRF Properties. |
Address Family |
Type of IP address in this pool: IPv4 or IPv6. |
Outside VRF |
Hyperlinked entry to the outside VRF in logical inventory. For more information about VRF properties in logical inventory, see Viewing VRF Properties. |
Address Pool |
Range of IP addresses that can be used for the service instance. If an end address is not specified, the entire range of 255 addresses is used for the address pool. |
|
|
|
Interface |
Hyperlinked entry to the associated entry in logical inventory: • • |
|
|
|
Service Type Name |
Name of the Carrier Grade NAT service. |
Service Type |
Type of Carrier Grade NAT service: 6RD, XLAT, or NAT44. |
|
|
|
Statistics Name |
Name of the statistic. For statistic names and descriptions, see Table 14-4. |
Statistics Value |
Value of the statistic. |
You can also display pool utilization by right-clicking a VNE and choosing Commands > Show > Pool Utilization.
Viewing Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Physical Inventory
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties in physical inventory:
Step 1 ![]() In Prime Network Vision, double-click the Cisco CRS device configured for Carrier Grade NAT.
In Prime Network Vision, double-click the Cisco CRS device configured for Carrier Grade NAT.
Step 2 ![]() To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a specific interface, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > card > interface. See Table 3-11 for a description of the information displayed in the Subinterfaces table.
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a specific interface, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > card > interface. See Table 3-11 for a description of the information displayed in the Subinterfaces table.
Step 3 ![]() To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a Cisco CRS-CGSE-PLIM card, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > PLIM-card.
To view Carrier Grade NAT properties configured on a Cisco CRS-CGSE-PLIM card, click Physical Inventory > chassis > shelf > slot > PLIM-card.
Figure 14-2 shows an example of Carrier Grade NAT properties in physical inventory.
Figure 14-2 Carrier Grade NAT Properties in Physical Inventory
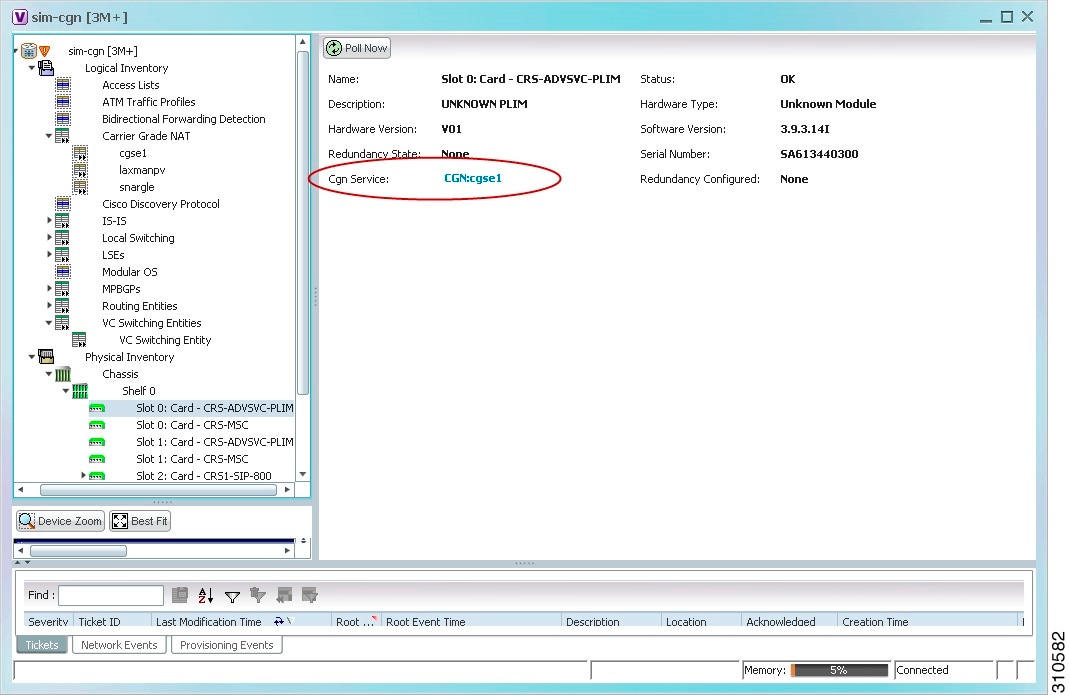
The field CGN Service is displayed, and the entry is hyperlinked to the associated Carrier Grade NAT service in logical inventory.
Configuring CG NAT Service
The following commands can be launched from the inventory by right-clicking the appropriate node and selecting Commands.
The table below lists the configuration commands and the supported network elements. Before executing any commands, you can preview them and view the results. If desired, you can also schedule the commands.
For details on the software versions Prime Network supports for thes supported network elements, see the Cisco Prime Network 3.10 Supported Cisco VNEs. To run the Carrier Grade NAT commands, the software on the network element must support the Carrier Grade NAT technology.

Note ![]() You might be prompted to enter your device access credentials while executing a command. Once you have entered them, these credentials will be used for every subsequent execution of a command in the same GUI client session. If you want to change the credentials, click Edit Credentials. The Edit Credentials button will not be available for SNMP commands or if the command is scheduled for a later time.
You might be prompted to enter your device access credentials while executing a command. Once you have entered them, these credentials will be used for every subsequent execution of a command in the same GUI client session. If you want to change the credentials, click Edit Credentials. The Edit Credentials button will not be available for SNMP commands or if the command is scheduled for a later time.
 Feedback
Feedback