- Preface
- Product Overview
- Graphical User Interface
- Device and Subdevice Manager
- Users Account Manager
- Configuration and Image Update Jobs Manager
- Groups
- Namespace Manager
- Query Manager
- Data Manager
- Directory Manager
- Parameters Manager
- Templates
- Security Manager
- Log Manager
- Service Manager
- Bulk Data Manager
- Email Manager
- Image Service
- Upgrade or Downgrade Cisco IOS Image
- Backup and Restore
- PIX Firewall Device Support
- ASA Firewall Device Support
- IMGW Device Module Development Kit
- Troubleshooting
- Software Licenses and Acknowledgements
- Index
Graphical User Interface
The Cisco Configuration Engine GUI is partially compliant with the Accessibility Design Requirements. This chapter provides general information about the GUI.
Logging In
Step 1![]() Launch your web browser.
Launch your web browser.
Step 2![]() Go to the Cisco Configuration Engine URL.
Go to the Cisco Configuration Engine URL.
For example: http://< ip_address >

Note If encryption is set during Setup (see “Encryption” section), use https://<ip_address>.
The login window appears (see Figure 2-1).
Figure 2-1 Logging Into the Configuration Engine
This is the value for the Configuration Engine login parameter that you entered during setup.
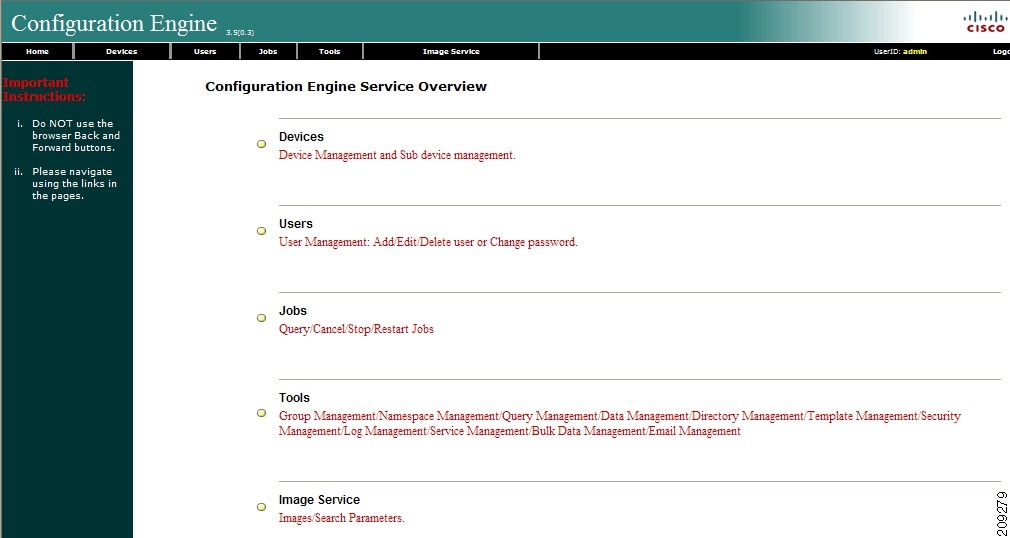
For an Administrator, the full-function Cisco Configuration Engine Home page appears (see Figure 2-2).
For an Operator, a limited-function Cisco Configuration Engine Home page appears without access to user-related tasks.
Figure 2-2 Administrator-level Home Page
Levels of Access
In Internal Directory mode, there are two categories of users who have access to device information:
An Administrator has full access to system administration tasks. An Operator has access to only limited set of tasks (see “Operator-Level Operations” section).
Feature Operations
The Cisco Configuration Engine GUI (see Figure 2-2) provides the following feature operations:
- Devices – Click this tab to conduct operations on Devices and Subdevices (see Chapter 3, “Device and Subdevice Manager”).
- Users – Click this tab to operate on user accounts (see Chapter 4, “User Account Manager”).
- Jobs – Click this tab to access background update tasks that have been assigned a Job IDs (see Chapter 5, “Configuration and Image Update Jobs Manager”).
- Tools – Click this tab to access the following features:
–![]() Group Manager (see Chapter 6, “Groups”)
Group Manager (see Chapter 6, “Groups”)
–![]() Namespace Manager (see Chapter 7, “Namespace Manager”)
Namespace Manager (see Chapter 7, “Namespace Manager”)
–![]() Query Manager (seeChapter 8, “Query Manager”)
Query Manager (seeChapter 8, “Query Manager”)
–![]() Data Manager (see Chapter 9, “Data Manager”)
Data Manager (see Chapter 9, “Data Manager”)
–![]() Directory Manager (see Chapter 10, “Directory Manager”)
Directory Manager (see Chapter 10, “Directory Manager”)
–![]() Parameter Manager (see Chapter 11, “Parameter Manager”)
Parameter Manager (see Chapter 11, “Parameter Manager”)
–![]() Template Manager (see Chapter 12, “Templates”)
Template Manager (see Chapter 12, “Templates”)
–![]() Security Manager (see Chapter 13, “Security Manager”)
Security Manager (see Chapter 13, “Security Manager”)
–![]() Log Manager (see Chapter 14, “Log Manager”)
Log Manager (see Chapter 14, “Log Manager”)
–![]() Service Manager (see Chapter 15, “Service Manager”)
Service Manager (see Chapter 15, “Service Manager”)
–![]() Bulk Data Manager (see Chapter 16, “Bulk Data Manager”)
Bulk Data Manager (see Chapter 16, “Bulk Data Manager”)
–![]() Email Manager (see Chapter 17, “Email Manager”)
Email Manager (see Chapter 17, “Email Manager”)
- Image Service – Click this tab to work with Images and Search Parameters (see Chapter 18, “Image Service”).
 Feedback
Feedback