EVPN MPLS multihoming modes
EVPN MPLS multihoming modes are redundancy techniques in EVPN deployments that
-
connect a customer edge device to multiple provider edge devices
-
provide redundant connectivity for enhanced reliability, and
-
ensure uninterrupted traffic flow during network failures.
Modes of EVPN multihoming
These multihoming modes are supported:
-
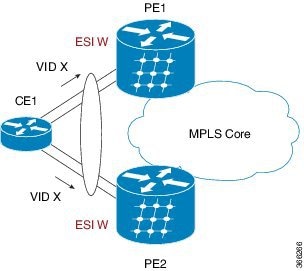
Single-active: Only one PE device in the group attached to the Ethernet segment forwards traffic to and from that segment. This mode prevents loops by allowing a single active forwarder.
-
All-active: All PEs connected to the Ethernet segment are permitted to forward traffic simultaneously. This mode enables load sharing and active-active redundancy.
-
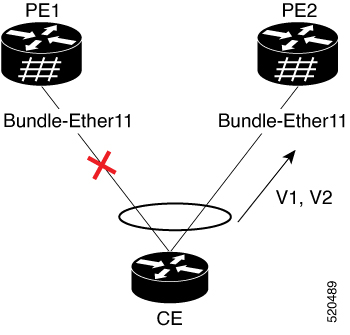
Port-active: Traffic is sent and received only by the PE that is in active mode on a specific port or interface. This mode supports single-active redundancy with load balancing at the port or interface level.
-
Single-flow-active: The PE that first advertises a host MAC address in a VLAN forwards traffic for that specific flow. This mode optimizes forwarding by directing each flow through a single active PE.
EVPN MPLS multihoming mode services
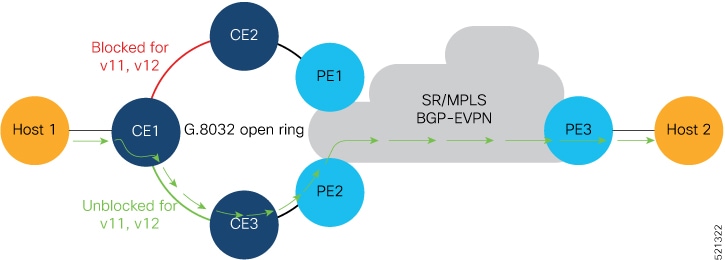
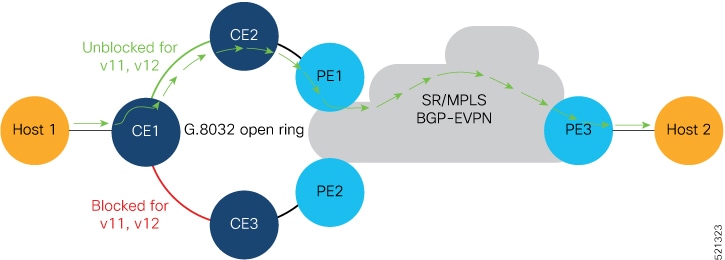
EVPN MPLS multihoming supports both E-LAN and E-LINE services.
This table compares the key features and use cases of EVPN E-LAN and E-LINE services.
|
Feature |
EVPN E-LAN |
EVPN E-Line |
|---|---|---|
|
Connectivity type |
Multipoint-to-Multipoint |
Point-to-Point |
|
Typical use cases |
Multi-site connectivity, interconnecting multiple locations |
Data center interconnects, connecting two sites |
|
MAC address learning |
Across all endpoints in the E-LAN |
Limited to two endpoints |
|
Supported modes |
|
|
While the configuration specifics differ between E-LAN and E-LINE services, their conceptual framework remains identical. Therefore, for conceptual understanding, the E-LAN documentation serves as the primary reference point for both services.

 Feedback
Feedback