EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay
A BGP Labeled Unicast (BGP-LU) underlay is a network transport method that
-
enables configuration of end-to-end services between data centers
-
supports various EVPN E-LAN and E-Line services, and
-
provides load balancing at the transport, BGP-LU, and service levels.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|
EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay |
Release 25.2.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100, K100], 8010 [ASIC: A100]); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100]) You can now configure end-to-end services between data centers using the BGP Labeled Unicast (BGP-LU) underlay with segment routing. The feature supports EVPN E-LAN and E-Line services and enables load balancing across transport, BGP-LU, and service levels using segment routing. |
|
EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay |
Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100]) (select variants only*) *This feature is now supported on the Cisco 8011-4G24Y4H-I routers. |
|
EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay |
Release 24.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700) (select variants only*) * The EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay functionality is now extended to the Cisco 8712-MOD-M routers. |
|
EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay |
Release 24.3.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100])(select variants only*); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100])(select variants only*) * The EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay functionality is now extended to:
|
|
EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay |
Release 24.2.11 |
Introduced in this release on: Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100]) (select variants only*) * The EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay functionality is now extended to routers with the 88-LC1-36EH line cards. |
|
EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services over BGP-LU Underlay |
Release 7.11.1 |
You can configure end-to-end services between data centers using the BGP Labeled Unicast (BGP-LU) underlay. This feature allows you to configure various EVPN E-LAN and E-Line services, and enables load balancing at transport, BGP-LU, and service level. |
End-to-end EVPN services with BGP-LU underlay
The EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay feature enables configuration of end-to-end EVPN services between data centers. This feature supports equal-cost multipath (ECMP) load balancing at three levels: transport, BGP-LU, and service.
This feature supports these services:
-
EVPN aliasing over BGP-LU using IGP, including segment routing (SR) or non-SR protocols such as LDP or IGP.
-
E-Line services over BGP-LU using IGP.
By leveraging BGP with label switching, this underlay provides seamless connectivity and efficient traffic distribution across data center networks. It allows network administrators to build scalable and resilient inter-data center services with flexible load balancing capabilities.
How EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay works
Summary
The key components involved in the EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay process are:
-
Leaf nodes: Configure EVPN with bridging and inter-subnet routing; act as default gateways for local hosts.
-
Spine nodes: Route traffic between leaf nodes and serve as route reflectors (RR) for iBGP.
-
Provider edge (PE) device and Data Center Interconnect (DCI): Connect spine nodes across data centers.
-
IS-IS labeled IGP and iBGP: Provide internal routing and route reflection across leaf, spine, and DCI nodes.
-
BGP Labeled Unicast (BGP-LU): Establishes labeled routes tunneled through IS-IS Segment Routing (SR) paths between data centers.
EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay use leaf and spine nodes with IS-IS and iBGP routing to establish labeled tunnels across data centers. This setup ensures scalable, resilient bridging and routing with efficient load balancing across interconnected sites.
Workflow
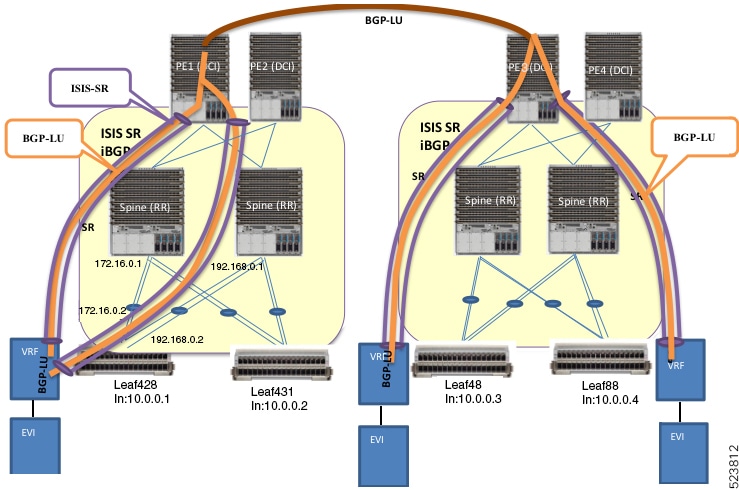
These are the stages of EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay.
- Configure EVPN with bridging and inter-subnet routing on leaf nodes.
- Connect hosts to leaf nodes, which route traffic across spine nodes.
- Connect spine nodes through PE devices and DCI for inter-data center connectivity.
- Enable IS-IS labeled IGP and iBGP across leaf, spine, and DCI nodes, with spine nodes acting as route reflectors.
- Configure IS-IS SR policy across leaf, spine, and DCI nodes.
- Establish BGP-LU sessions between data centers.
- Learn BGP-LU routes on leaf nodes and tunnel them through IS-IS SR labeled paths. For example, leaf node Leaf428 learns BGP-LU routes for remote loopback addresses 10.0.0.3 and 10.0.0.4.
Result
This process enables scalable and resilient EVPN bridging and E-Line services with efficient load balancing and routing across interconnected data centers.
Configure EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay with LDP
Configure EVPN Bridging and E-Line Services overging and E-Line Services over a BGP-LU underlay network using LDP.
This task applies to a network topology with P routers (P1, P2) and PE routers (PE1, PE2, PE3) connected across two BGP autonomous systems (AS 100 and AS 200). P1 connects to P2, and P1 connects to PE1 and PE2 in AS 100, while P2 connects to PE3 in AS 200.
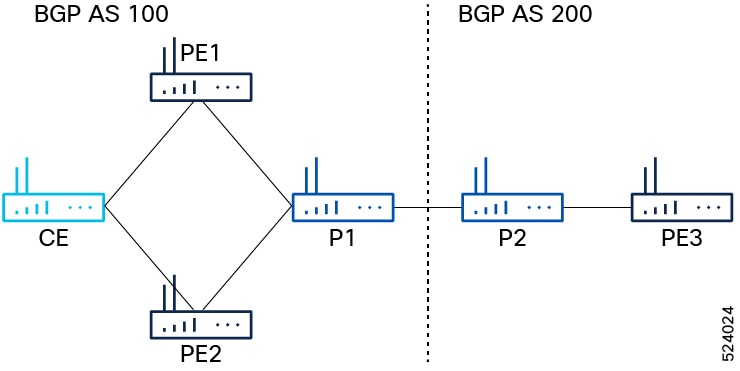
Before you begin
Ensure you have the network topology as described and access to configure IGP, MPLS, and BGP on all routers.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Configure IGP, MPLS, and BGP on PE1, PE2, and PE3. |
|
Step 2 |
Configure iBGP peer on P1 and PE2. |
|
Step 3 |
Configure P2 as route reflector. Example: |
|
Step 4 |
Configure route policy, IGP, MPLS, and BGP on P1 and P2. |
|
Step 5 |
Configure P1 and P2 as eBGP neighbor. |
|
Step 6 |
Configure PE1, PE2, and PE3 as iBGP neighbor. |
|
Step 7 |
For P1, the iBGP peers are PE1 and PE2, and the eBGP peer is P2. |
|
Step 8 |
Configure L2VPN and EVPN on PE1, PE2, and PE3. Example: |
|
Step 9 |
Use these show commands to verify that you have successfully configured EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay with LDP.
Example: |
Configure EVPN bridging and E-Line services over BGP-LU underlay with SR
Configure EVPN bridging and E-Line services over a BGP-LU underlay network using SR for efficient traffic engineering and simplified forwarding.
This task applies to networks where Segment Routing is enabled within the IGP domain using IS-IS, and BGP-LU is used to advertise loopback addresses with associated SR labels. The configuration involves PE and Route Reflector (RR) nodes participating in EVPN services over the SR-enabled underlay.
Before you begin
Ensure all participating nodes support IS-IS with Segment Routing and BGP-LU. Have loopback interfaces configured for router IDs and SR prefix SIDs assigned.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Configure IS-IS with SR on all participating nodes. Configure SR with IS-IS to enable SR within the IGP domain and assign prefix SIDs to the router loopback interface. Configure all the participating nodes, which include the PE or Route Reflector (RR) nodes in the underlay to run IS-IS and advertise their loopbacks with SIDs. The prefix SID varies for each node and instance. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure BGP on all nodes. Ensure that the bgp router-id is the loopback address used for peering and SR SID assignment. The router ID varies for each node. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Enable the BGP-LU address families and advertise the router loopback address with an associated label derived from the SR node SID. Configure all the participating nodes to advertise the router loopback address through BGP-LU. Example:The network and SID index vary for each node. The following is a sample configuration for IPv4 and IPv6 unicast address families. Example:Sample route-policy configuration. |
|
Step 4 |
Configure BGP neighbors and neighbor groups. Configure the BGP neighbors or neighbor groups to establish iBGP peering between all the participating nodes such as PEs and RRs, and enable the BGP-LU and EVPN address families. |

 Feedback
Feedback