CFM on EVPN
An Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) is an Ethernet layer operation, administration, and management (OAM) protocol that
-
operates end-to-end per service instance
-
provides proactive connectivity monitoring and fault verification, and
-
enables fault isolation in large networks.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|
CFM on EVPN |
Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100]) (select variants only*) *This feature is now supported on the Cisco 8011-4G24Y4H-I routers. |
|
CFM on EVPN |
Release 24.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700 [ASIC: K100]) (select variants only*) * The CFM on EVPN functionality is now extended to the Cisco 8712-MOD-M routers. |
|
CFM on EVPN |
Release 24.3.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100])(select variants only*); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100])(select variants only*) * The CFM on EVPN functionality is now extended to:
|
|
CFM on EVPN |
Release 24.2.11 |
Introduced in this release on: Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: Q200, P100]) (select variants only*) You can now proactively monitor connectivity and verify faults and isolate them for EVPN services. This is because Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) is now available for EVPN and provides end-to-end service level OAM (Operations, Administration, and Maintenance) for EVPN services. * This feature is supported only on routers with Q200 and 88-LC1-36EH line cards. |
CFM on EVPN feature highlights and benefits
CFM on EVPN provides essential capabilities to monitor and maintain the health and connectivity of EVPN services. The key highlights and benefits include:
-
Fault detection and isolation—enables rapid detection of connectivity faults within EVPN domains, helping to isolate and pinpoint issues quickly to minimize service disruption.
-
Proactive monitoring—supports continuous monitoring of EVPN service health through periodic continuity checks, ensuring early identification of potential problems.
-
Service assurance—verifies the operational status of EVPN instances, CFM helps maintain high service availability and reliability.
-
Standardized protocols—uses IEEE 802.1ag and ITU-T Y.1731 standards, ensuring interoperability across multi-vendor environments.
-
Scalability—designed to scale with large EVPN deployments, supporting multiple maintenance domains and endpoints.
-
Simplified troubleshooting—provides detailed fault management tools such as loopback and linktrace messages, which assist network operators in diagnosing and resolving issues efficiently.
-
Integration with EVPN— is tightly integrated with EVPN control plane mechanisms, enabling seamless operation and management within EVPN architectures.
Supported offload types and timer values
Continuity Check Messages (CCMs) are heartbeat messages exchanged periodically among all Maintenance End Points (MEPs) within a service. Each MEP sends multicast CCMs and receives CCMs from all other MEPs, enabling peer discovery and connectivity verification. The offload type is determined by where CCMs are processed.
Currently, only the Non-offload type is supported, where CCMs are generated and processed by the CPU. For a CFM session on a bundle interface or similar, CCM timers must be set to one second or greater.
CCM timers define the intervals at which CCMs are sent and received. If CCMs are not received within the configured interval, the CFM MEP is considered down. The supported CCM timer values for the Non-offload type are:
-
1 second
-
10 seconds
-
1 minute
-
10 minutes
Restrictions for CFM on EVPN
To ensure accurate CFM operation on EVPN, observe these restrictions:
-
Loopback and linktrace results may show artifacts such as multiple or varying responses for the same instance.
-
Do not configure CFM on interfaces with untagged encapsulation for EVPN pseudowire, as this is unsupported by Cisco IOS XR software.
Supported services for CFM on EVPN
CFM on EVPN support these service types:
-
EVPN E-LAN—CFM plays a crucial role in EVPN E-LAN services by enabling service providers and enterprises to maintain high availability and ensure the reliability of their distributed Ethernet services.
-
EVPN E-Line—CFM facilitates monitoring and maintaining the health of point-to-point Ethernet services over packet-switched networks, which is essential for service providers managing EVPN E-Line services.
 Note |
CFM on EVPN is supported only on single-homed devices. |
CFM on EVPN E-LAN single-homing
CFM on EVPN E-LAN single-homing is a network monitoring feature that
-
operates on networks running E-LAN services with single-homed devices
-
monitors the health and performance of E-LAN services, and
-
provides high-speed Layer 2 services with enhanced resiliency.
How CFM on EVPN E-LAN single-homing works
Summary
The key components involved in the CFM on EVPN E-LAN single-homing process are:
-
Single-homed device: Connects to the EVPN E-LAN service and participates in connectivity monitoring.
-
CFM: Monitors and verifies connectivity within the EVPN E-LAN domain.
-
EVPN E-LAN domain: The network environment where devices communicate and connectivity is managed.
The CFM on EVPN E-LAN single-homing process enables continuous connectivity monitoring by the single-homed device within the EVPN E-LAN domain, and detects faults through continuity checks and alerts administrators to ensure network stability and simplify troubleshooting.
Workflow
These stages describe how CFM on EVPN E-LAN single-homing works.
- The single-homed device connects to the EVPN E-LAN service.
- CFM is enabled on the device to monitor connectivity within the EVPN E-LAN domain.
- CFM initiates continuity checks between the single-homed device and other devices in the EVPN E-LAN.
- CFM detects any connectivity faults and generates alarms or notifications.
- Network administrators use CFM results to troubleshoot and resolve connectivity issues.
Result
This process ensures continuous monitoring and fault detection in single-homed EVPN E-LAN environments, improving network stability and simplifying troubleshooting.
Configure CFM on EVPN E-LAN full mesh topology
Enable and verify CFM on EVPN E-LAN full mesh topology to monitor network continuity and detect faults.
Use this task to configure CFM continuity checks, MEP cross-checks, and interface settings on Cisco routers participating in an EVPN E-LAN full mesh topology.
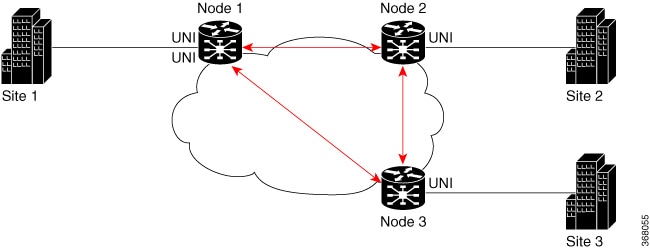
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Enable Ethernet CFM and configure the domain and service. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure MEP cross-checks. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Repeat steps 1 and 2 on nodes 2 and 3, adjusting MEP IDs accordingly. For node 2, configure MEP cross-check with respective mep-id values of node 1 and node 3 (1111 and 1113 respectively, in this example). For node 3, configure MEP cross-check with respective mep-id values of node 1 and node 2 (1111 and 1112 respectively, in this example). |
|
Step 4 |
Enable CFM on the interface. Example: |
|
Step 5 |
Repeat step 4 on nodes 2 and 3 with their respective MEP IDs. You must repeat the above configurations for node 2 and node 3, with the respective mep-id values (that is, 1112 for node 2 and 1113 for node 3, in this example). |
|
Step 6 |
Running configuration of CFM on EVPN E-LAN full mesh topology. Example: |
CFM is enabled on all nodes in the EVPN E-LAN full mesh topology, providing continuous connectivity monitoring and fault detection.
Configure CFM on EVPN E-LAN hub and spoke topology
Configure CFM on an EVPN E-LAN hub and spoke topology with SLA profiles to monitor connectivity between the hub and spoke nodes.
This task extends the full mesh CFM configuration by adding SLA operation profiles on the hub node to ensure continuous network service monitoring.
Before you begin
Complete the full mesh CFM configuration steps on all nodes.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Enable Ethernet CFM with the MEP domain, service, and MEP ID, and configure SLA profiles for spoke nodes’ MEP IDs. The CFM configuration for the hub and spoke topology remains the same as that of full mesh topology mentioned above, except for these additional steps for SLA profile configuration to be done under the interface. You must configure the SLA profile between the hub and the spokes to ensure continuous network services. In this example, 1112 and 1113 are the mep-id values of node 2 and node 3. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Running configuration of CFM on EVPN E-LAN hub and spoke topology. Example: |
SLA profiles are configured on the hub node, enabling continuous service-level monitoring between the hub and spoke nodes.
Configure CFM for different domain types and bridge domains
Configure Ethernet CFM continuity checks and MEP cross-checks for various domain levels, multiple MEPs, and multiple services across different EVPN bridge domains.
Use these examples to configure CFM in complex EVPN environments with multiple bridge domains, domain levels, and services.
Before you begin
Ensure you have the necessary domain, service, bridge group, and bridge domain information.
Procedure
|
Follow these steps for each of these scenarios. |
Scenario 1: Up MEPs with the same domain and level
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Enable Ethernet CFM continuity check. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure MEP cross-check. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Configure the bridge domain and assign interfaces to the bridge domain. Example: |
|
Step 4 |
Enable CFM on interfaces with respective MEP IDs. Example: |
|
Step 5 |
Running configuration of scenario 1. Example: |
Scenario 2: Multiple Up MEPs on AC interfaces in the same bridge domain
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Enable Ethernet CFM continuity check. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure MEP cross-check. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Enable Ethernet CFM continuity check for another domain level. Example: |
|
Step 4 |
Configure MEP cross-check. Example: |
|
Step 5 |
Configure the bridge domain and assign interfaces to the bridge domain. Example: |
|
Step 6 |
Enable CFM on interfaces with multiple MEPs for both domains. Example: |
|
Step 7 |
Running configuration of scenario 2. Example: |
Scenario 3: Multiple services for different EVPN bridge domains
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Enable Ethernet CFM continuity check. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure MEP cross-check. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Enable Ethernet CFM continuity check for another service. Example: |
|
Step 4 |
Configure MEP cross-check. Example: |
|
Step 5 |
Configure the bridge domain and assign interfaces to the bridge domain. Example: |
|
Step 6 |
Configure another bridge domain and assign interfaces to the bridge domain. Example: |
|
Step 7 |
Enable CFM on interfaces with corresponding domain, service, and MEP IDs. Example: |
|
Step 8 |
Running configuration of scenario 3. Example: |
Scenario 4: Different EVPN bridge domains on different domain levels
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Enable Ethernet CFM continuity check. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure MEP cross-check. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Enable Ethernet CFM continuity check for another domain and service. Example: |
|
Step 4 |
Configure MEP cross-check for antoher domain. Example: |
|
Step 5 |
Configure the bridge domain and assign interfaces to the bridge domain. Example: |
|
Step 6 |
Configure another bridge domain and assign interfaces to the bridge domain. Example: |
|
Step 7 |
Enable CFM on interfaces with corresponding domain, service, and MEP IDs. Example: |
|
Step 8 |
Running configuration of scenario 4. Example: |
CFM on EVPN E-Line single-homing
A CFM on EVPN E-Line single-homing is a network monitoring solution that
-
operates on networks using EVPN E-Line single-homed devices
-
monitors E-Line services providing high-speed Layer 2 connectivity, and
-
ensures high resiliency for the Layer 2 services.
CFM up MEP is supported only on single-homing Layer 2 main and subinterfaces.
How CFM on EVPN E-Line single-homing works
Summary
The key components involved in the CFM on EVPN E-Line single-homing process are:
-
Cisco routers (Nodes 1, 2, and 3): These routers form the network topology and are interconnected.
-
CFM: Provides fault detection and monitoring capabilities within the EVPN E-Line service.
-
EVPN E-Line service: A point-to-point Ethernet VPN service that supports single-homing configurations.
CFM on EVPN E-Line single-homing enables routers to exchange monitoring messages over a full mesh to detect faults and ensure continuous service integrity. This process supports rapid fault detection and high availability in single-homed EVPN E-Line deployments.
Workflow
These stages describe how CFM on EVPN E-Line single-homing works.
- Cisco routers (Nodes 1, 2, and 3) establish full mesh connectivity to support CFM operations within the EVPN E-Line topology.
- CFM messages are exchanged between the routers to monitor connectivity and detect faults.
- Faults detected by CFM trigger notifications and enable rapid troubleshooting within the EVPN E-Line single-homing environment.
- Routers maintain continuous monitoring to ensure service integrity and performance.
Result
This process enables robust fault management and monitoring for EVPN E-Line single-homing deployments, ensuring high availability and rapid fault detection in the network.
Configure CFM on EVPN E-Line single-homing
Enable and validate CFM to monitor service continuity and endpoint liveliness for EVPN E-Line service.
Use this task to configure CFM service continuity checks, Maintenance End Point (MEP) cross-checks, and enable CFM on interfaces for EVPN E-Line single-homing deployments.

Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Enable CFM continuity check. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure MEP cross-check to validate remote MEPs. Example:Repeat the above configurations for node 2 and node 3, with the respective mep-id values. For node 2, configure MEP cross-check with respective mep-id values of node 1 and node 3 (2001 and 3001 respectively, in this example). For node 3, configure MEP cross-check with respective mep-id values of node 1 and node 2 (4001 and 2001 respectively, in this example). |
|
Step 3 |
Enable CFM on the interface. Example:You must repeat the above configurations for node 2 and node 3, with the respective mep-id values. |
|
Step 4 |
Running configuration of CFM on EVPN E-Line. Example: |
|
Step 5 |
Use the show ethernet cfm services command to verify CFM on EVPN E-Line. Example: |
CFM is configured on EVPN E-Line, providing continuous service monitoring and fault detection through MEP cross-checks and continuity checks, ensuring network reliability and rapid troubleshooting.
 Feedback
Feedback