Virtual Switch Interface Master MIB
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Virtual Switch Interface Master MIB
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Verifying that the SNMP Agent Has Been Enabled
Virtual Switch Interface Master MIB
The Virtual Switch Interface (VSI) protocol is a means for a network control application to control the operation of a switch. The VSI protocol is implemented between a VSI master, running on a router, and a VSI slave, running on the switch. The master communicates with a set of slaves across a control interface that connects the router to the switch. Each master/slave connection is referred to as a VSI session. The VSI protocol enables the router to control the switch.
The Virtual Switch Interface Master MIB allows you to enlist the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to monitor the status of the VSI protocol and the results of its operations.
This MIB is primarily oriented toward management of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) systems. As such, the MIB resides in routers that are also label switch controllers (LSCs). These are routers that are VSI capable, and whose network control application is MPLS.
VSI Masters and Slaves
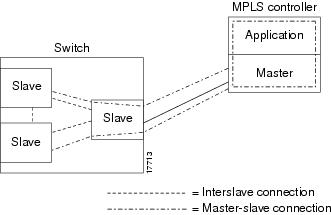
A controller application uses a VSI master to control one or more VSI slaves. For the BPX, the controller application and master VSI reside in an external 7200 or 7500 series router and the VSI slaves are resident in BXM cards on the BPX node (Figure 1).
The controller sets up the following types of connections:
Control virtual connections (VCs)
•
Master to Slave
•
Slave to Slave
User Connection
•
User connection (that is, cross-connect)
Figure 1 VSI Controller and Slave VSIs
This document includes the following major sections:
•
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Feature Overview
The VSI Master MIB supports the following VSI components:
•
VSI controllers—Each controller represents an instance of the VSI Master control protocol. A controller communicates with a slave across a control interface. The controller, which runs the VSI protocol, supports a network control application. The application can perform the following functions with the help of the VSI:
–
Discover configuration information that exists on the switch.
–
Monitor the status of the VSI sessions
–
Monitor the status of and collect statistics from interfaces and virtual circuits on the switch
–
Control the virtual circuit cross-connect table inside an switch
•
VSI sessions—Each VSI controller manages a set of VSI slaves, through a set of VSI sessions. VSI slaves reside on the controlled switch. The VSI controller uses the VSI protocol to discover the characteristics of the VSI slaves. The table generated by the network control application includes an entry for each VSI slave.
•
Logical interfaces—Logical interfaces represent external interfaces that are available for connections. When you pair two external interfaces (represented by two logical interfaces), they provide physical paths through the switch. These physical paths support cross-connects.
•
Cross-connects—Cross-connects are virtual links across two interfaces. The participating interfaces that support these links are listed in the MIB's vsiLogicalIfTable entries.
Benefits
The VSI Master MIB provides a standardized vehicle for monitoring the operation of the VSI protocol within an LSC. It also displays the results of the operations of the protocol. Specifically, the VSI Master MIB allows you to monitor
•
Connections between the LSC and the switch it controls
•
The status of the interfaces in the switch
•
Virtual circuits (VCs) that are maintained across the interfaces
The following is a partial list of the supported MIB objects
Controllers
•
Controller identifier
•
Number of cross-connects maintained in the switch
•
Protocol version
•
Controller interface index
•
Slave interface identifiers
•
Controller IP address
Sessions
•
Virtual path identifier (VPI) for session connections
•
Virtual circuit identifier (VCI) for the sessions
•
Switch identifier
•
Switch name
•
Session state
•
Protocol session monitoring
Interfaces
•
Interface name
•
Operational state
•
Administrative state
•
Operational statistics
•
Cross-connect usage
•
Cross-connect availability
•
Cross-connect capacity
•
Interface capabilities
•
VC ranges
•
Interface index
•
IP address
Cross-Connects:
•
Interface associations
•
State
•
Identifiers
•
VPI/VCI identifiers for supporting interfaces
Restrictions
The VSI Master MIB is for MPLS controllers only.
Related Documents
See the following documents for more information:
•
Virtual Switch Interface Master MIB
http://www.cisco.com/public/mibs/v2/CISCO-VSIMASTER-MIB.my
•
MPLS Label Switch Controller Enhancements
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121newft/121t/121t3/index.htm
Supported Platforms
This feature is supported on the following platforms:
•
Cisco 7200 series
•
Cisco 7500 series
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature.
MIBs
Virtual Switch Interface Master MIB
http://www.cisco.com/public/mibs/v2/CISCO-VSIMASTER-MIB.my
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see the Cisco MIB web site on Cisco Connection Online (CCO) at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature.
Prerequisites
Memory requirements:
•
The VSI Master MIB requires 75K of space.
•
The runtime dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) is approximately 5K times the number of logical/slave interfaces that the VSI controller manages.
Configuration Tasks
See the following sections for configuration tasks for the VSI Master MIB feature. Each task in the list indicates if the task is optional or required.
•
Enabling the SNMP Agent (Required)
•
Verifying that the SNMP Agent Has Been Enabled (Optional)
Enabling the SNMP Agent
The SNMP agent for the VSI Master MIB is disabled by default. To enable the SNMP agent, perform the following steps:
Verifying that the SNMP Agent Has Been Enabled
To verify that the SNMP agent has been enabled, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Access the router through a Telnet session:
prompt# telnet 10.10.10.1Step 2
Enter the privileged mode:
router# enableStep 3
Display the running configuration and look for SNMP information:
router# show running-configuration......snmp-server community public ROIf you see any "snmp-server" statements, SNMP has been enabled on the router.
Configuration Examples
In the following example, the SNMP agent is enabled:
snmp-server communityIn the following example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2C are enabled. The configuration permits any SNMP manager to access all objects with read-only permissions using the community string public.
snmp-server community publicIn the following example, read-only access is granted for all objects to members of access list 4 that specify the comaccess community string. No other SNMP managers have access to any objects.
snmp-server community comaccess ro 4Command Reference
The following commands are introduced or modified in the feature or features documented in this module. For information about these commands, see the Cisco IOS Network Management Command Reference at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/netmgmt/command/reference/br_book.html. For information about all Cisco IOS commands, go to the Command Lookup Tool at http://tools.cisco.com/Support/CLILookup or to the Cisco IOS Master Commands List.
•
snmp-server community
Glossary
inform request—A message sent by an SNMP agent to a network management station, console, or terminal to indicate that a significant event occurred. SNMP inform requests are more reliable than traps because an inform request sends an SNMP response protocol data unit (PDU). If the manager does not receive an inform request, it does not send a response. If the sender never receives a response, the inform request can be sent again. Thus, inform requests are more likely to reach their intended destination.
Management Information Base—See MIB.
MIB—Management Information Base. A database of network management information that is used and maintained by a network management protocol such as SNMP. The value of a MIB object can be changed or retrieved through the use of SNMP commands, usually through a network management system. MIB objects are organized in a tree structure that includes public (standard) and private (proprietary) branches.
Simple Network Management Protocol—See SNMP.
SNMP—Simple Network Management Protocol. A management protocol used almost exclusively in TCP/IP networks. SNMP provides a means to monitor and control network devices, and to manage configurations, statistics collection, performance, and security.
trap—A message sent by an SNMP agent to a network management station, console, or terminal to indicate that a significant event occurred. Traps are less reliable than inform requests, because the receiver does not send an acknowledgment when it receives a trap. The sender cannot determine if the trap was received.
VSI Master—A VSI master process implementing the master side of the VSI protocol in a VSI controller. Sometimes the whole VSI controller might be referred to as a "VSI Master," but this is not strictly correct.
1.
A device that controls a VSI switch, for example, a VSI Label Switch Controller
2.
A process implementing the master side of the VSI protocol
VSI Slave—A VSI slave is either of the following:
1.
A switch (in the "Single Slave model") or a port card (in the "Multiple Slave Model") that implements the VSI
2.
A process implementing the slave side of the VSI protocol

Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
This Document Applies to These Products
- Collaboration Endpoints - Retired Products
- Conferencing - Retired Products
- Contact Center - Retired Products
- Optical Networking - Retired Products
- Routers - Retired Products
- Security - Retired Products
- Servers - Unified Computing (UCS) Retired Products
- Storage Networking Retired Products
- Switches - Retired Products
- Video - Retired Products
- Wireless - Retired Products
 Feedback
Feedback