- Preface
- Software Licensing
- The Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)
- Configuring Interfaces
- Switch Alarms
- Initial Switch Configuration (IP address assignments and DHCP autoconfiguration)
- How to Setup and Use the Cisco Configuration Engine
- How to Create and Manage Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
- Configuring PROFINET
- Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- MACsec
- Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode and SGACL Logging
- Configuring SGT Exchange Protocol over TCP (SXP) and Layer 3 Transport
- Configuring VLANs
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- How to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring the FlexLinks and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
- Configuring DHCP
- Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- How to Configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- One-to-one (1:1) Layer 2 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- How to Configure CDP
- Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring Quality of Service (QoS)
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IP multicast routing
- Configuring Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
- Configuring Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping
- Configuring HSRP and VRRP
- Configuring IPv6 access control lists (ACLs)
- Configuring Embedded Event Manager (EEM)
- IP Unicast Routing
- IPv6 Unicast Routing
- Unicast Routing Overview
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Dying-Gasp
- How to Configure Enhanced Object Tracking
- Configuring MODBUS TCP
- Configuring Ethernet CFM
- Working with the Flash File System
- How to Configure EtherChannels
- Troubleshooting
- How to use a Secure Digital (SD) flash memory module (SD card)
Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode and SGACL Logging
SGACL Monitor Mode and SGACL Logging are supported on IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 Series Switches in Cisco IOS Release 15.2(8)E and later.
Security group-based access control is a component of the Cisco TrustSec security architecture, which builds secure networks by establishing domains of trusted network devices. For comprehensive information about TrustSec, including TrustSec prerequisites, guidelines and limitations, and configuration procedures, see Cisco TrustSec Switch Configuration Guide. For information about Configuring SGT Exchange Protocol over TCP (SXP) and Layer 3 Transport, see Configuring SGT Exchange Protocol over TCP (SXP) and Layer 3 Transport.
Restrictions for Configuring SGACL Policies
The following restrictions apply to the Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 Series Switches when configuring SGACL policies:
■![]() Cisco TrustSec can be configured only on physical interfaces, not on logical interfaces.
Cisco TrustSec can be configured only on physical interfaces, not on logical interfaces.
■![]() When SXP is configured between a Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, or IE 5000 switch and another switch, SGACL policies are not enforced on Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, or IE 5000 series switches. SGACL policies are downloaded for the destination SGT, but policy statements are not applied to the traffic that is initiated from the source SGT.
When SXP is configured between a Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, or IE 5000 switch and another switch, SGACL policies are not enforced on Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, or IE 5000 series switches. SGACL policies are downloaded for the destination SGT, but policy statements are not applied to the traffic that is initiated from the source SGT.
IP device tracking must be enabled on both switches and these switches should have Layer2 adjacency configured between them so that a Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, or IE 5000 can tag packets with the corresponding SGT learned via the SXP protocol.
You can enable IP device tracking on Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, or IE 5000 series switches by using the ip device tracking maximum < number > command. Based on your topology, configure the number of IP clients using the number argument. We do not recommend configuring a high number of IP clients on ports/interfaces.
IP device tracking is enabled by default on all ports in Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E, and in Cisco IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 switches using this release image, SGACL policies are enforced.
■![]() CTS SGACLs cannot be enforced for punt (CPU bound) traffic due to hardware limitations.
CTS SGACLs cannot be enforced for punt (CPU bound) traffic due to hardware limitations.
The following restrictions apply to IPv6 SGACL enforcement:
■![]() SGACL enforcement is bypassed for IPv6 multicast traffic.
SGACL enforcement is bypassed for IPv6 multicast traffic.
■![]() SGACL enforcement is bypassed for IPv6 packets with Link-Local IPv6 source/destination addresses.
SGACL enforcement is bypassed for IPv6 packets with Link-Local IPv6 source/destination addresses.
SGACL Monitor Mode
During the pre-deployment phase of Cisco TrustSec, you can use monitor mode to test security policies without enforcing them to make sure that the policies function as intended. If the security policies do not function as intended, monitor mode identifies that and allows you to correct the policy before enabling security group access control list (SGACL) enforcement. Seeing the outcome of the policy actions before enforcing them lets you confirm that the subject policy meets the security requirements (access is denied to resources if users are not authorized).
The monitoring capability is provided at the SGT-DGT pair level. When you enable the SGACL monitoring mode feature, the deny action is implemented as an ACL permit on the line cards. This allows the SGACL counters and logging to display how connections are handled by the SGACL policy. Since all the monitored traffic is permitted, there is no disruption of service due to SGACLs while in the SGACL monitor mode.
The IPServices license is required to enable SGACL Monitor Mode.
Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode - CLI
To configure SGACL Monitor Mode through the CLI, follow these steps:
Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode - Radius (ISE)
To enable SGACL Monitor Mode using the Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) GUI, select Monitor as shown below:
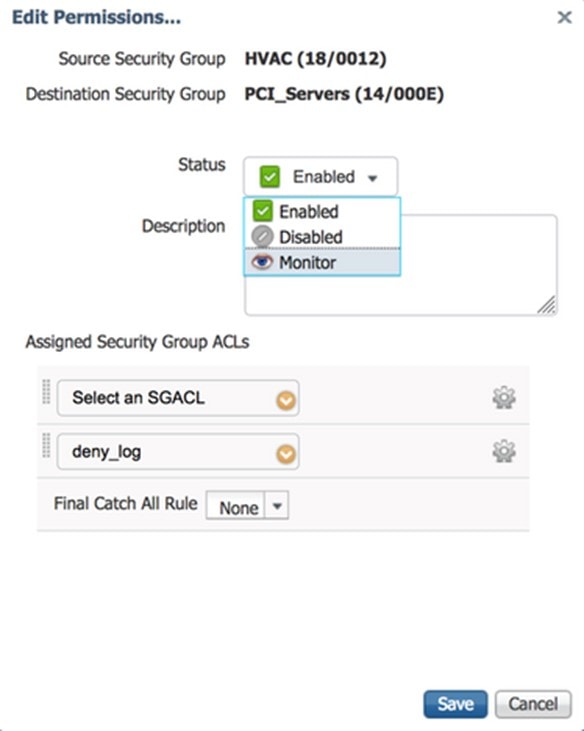
An eye icon indicates that Monitor mode is enabled.

The policy matrix change needs to be pushed to network devices by using the Deploy function at the top of the matrix. This utilizes RADIUS CoA to inform the devices that a change has been made.
After the update is downloaded to the switch, use the show cts role-based permissions command to verify the configuration. The policy permissions show the specific policy in Monitor Mode by appending the term “monitored”.
Verifying Configuration
The following examples are output from the show cts role-based permissions and show cts role-based counters commands, which you can use to display SGACL Monitor Mode status.
The HW-Monitor column of show cts role-based counters displays the count of enforcement events that are being monitored in hardware and not actually enforced.
SGACL Logging
The log option in cts applies to individual ACEs and causes packets that match the ACE to be logged. The first packet logged by the log keyword generates a syslog message.
SGACL Logging is only triggered when the Cisco ACE Application Control Engine has the logging keyword.
When logging is enabled in SGACL, the switch logs the following information:
■![]() The source security group tag (SGT) and destination SGT
The source security group tag (SGT) and destination SGT
■![]() The action performed on the packet
The action performed on the packet
To enable Cisco TrustSec role-based (security group) access control enforcement, use the cts role-based enforcement command in global configuration mode. To configure a logging interval for an SGACL, enter:
cts role-based enforcement [ logging-interval interval ]
The valid values for the interval argument are from 5 to 86400 seconds. The default is 300 seconds.
To enable logging, use the log keyword before the ACE definition in the SGACL configuration. For example, permit ip log.
The following is a sample log, displaying source and destination SGTs, ACE matches for deny action). The logging rate-limit command can be used to limit the rate of messages logged per second.
 Feedback
Feedback