- Preface
- Software Licensing
- The Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)
- Configuring Interfaces
- Switch Alarms
- Initial Switch Configuration (IP address assignments and DHCP autoconfiguration)
- How to Setup and Use the Cisco Configuration Engine
- How to Create and Manage Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
- Configuring PROFINET
- Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- MACsec
- Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode and SGACL Logging
- Configuring SGT Exchange Protocol over TCP (SXP) and Layer 3 Transport
- Configuring VLANs
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- How to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring the FlexLinks and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
- Configuring DHCP
- Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- How to Configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- One-to-one (1:1) Layer 2 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- How to Configure CDP
- Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring Quality of Service (QoS)
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IP multicast routing
- Configuring Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
- Configuring Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping
- Configuring HSRP and VRRP
- Configuring IPv6 access control lists (ACLs)
- Configuring Embedded Event Manager (EEM)
- IP Unicast Routing
- IPv6 Unicast Routing
- Unicast Routing Overview
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Dying-Gasp
- How to Configure Enhanced Object Tracking
- Configuring MODBUS TCP
- Configuring Ethernet CFM
- Working with the Flash File System
- How to Configure EtherChannels
- Troubleshooting
- How to use a Secure Digital (SD) flash memory module (SD card)
Cisco Industrial Ethernet 4000, 4010 and 5000 Switch Software Configuration Guide
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- September 16, 2016
Chapter: Configuring RMON
Configuring RMON
Prerequisites for RMON
■![]() You must configure SNMP on the switch to access RMON MIB objects.
You must configure SNMP on the switch to access RMON MIB objects.
■![]() We recommend that you use a generic RMON console application on the network management station (NMS) to take advantage of the RMON network management capabilities.
We recommend that you use a generic RMON console application on the network management station (NMS) to take advantage of the RMON network management capabilities.
Restrictions for RMON
Information About RMON
RMON
RMON is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard monitoring specification that allows various network agents and console systems to exchange network monitoring data. You can use the RMON feature with the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent in the switch to monitor all the traffic flowing among switches on all connected LAN segments as shown in Figure 72.
Figure 72 Remote Monitoring Example
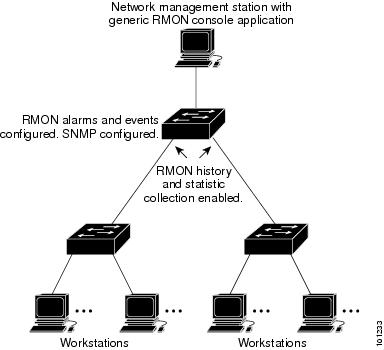
The switch supports these RMON groups (defined in RFC 1757):
■![]() Statistics (RMON group 1)—Collects Ethernet statistics on an interface.
Statistics (RMON group 1)—Collects Ethernet statistics on an interface.
■![]() History (RMON group 2)—Collects a history group of statistics on Ethernet ports for a specified polling interval.
History (RMON group 2)—Collects a history group of statistics on Ethernet ports for a specified polling interval.
■![]() Alarm (RMON group 3)—Monitors a specific management information base (MIB) object for a specified interval, triggers an alarm at a specified value (rising threshold), and resets the alarm at another value (falling threshold). Alarms can be used with events; the alarm triggers an event, which can generate a log entry or an SNMP trap.
Alarm (RMON group 3)—Monitors a specific management information base (MIB) object for a specified interval, triggers an alarm at a specified value (rising threshold), and resets the alarm at another value (falling threshold). Alarms can be used with events; the alarm triggers an event, which can generate a log entry or an SNMP trap.
■![]() Event (RMON group 9)—Specifies the action to take when an event is triggered by an alarm. The action can be to generate a log entry or an SNMP trap.
Event (RMON group 9)—Specifies the action to take when an event is triggered by an alarm. The action can be to generate a log entry or an SNMP trap.
Because switches supported by this software release use hardware counters for RMON data processing, the monitoring is more efficient, and little processing power is required.
Note: 64-bit counters are not supported for RMON alarms.
RMON is disabled by default; no alarms or events are configured.
How to Configure RMON
Configuring RMON Alarms and Events
You can configure your switch for RMON by using the command-line interface (CLI) or an SNMP-compatible network management station.
Collecting Group History Statistics on an Interface
You must first configure RMON alarms and events to display collection information.
Collecting Group Ethernet Statistics on an Interface
Monitoring and Maintaining RMON
|
|
|
|---|---|
Configuration Examples for RMON
Configuring an RMON Alarm Number: Example
The following example shows how to configure an RMON alarm number:
The alarm monitors the MIB variable ifEntry.20.1 once every 20 seconds until the alarm is disabled and checks the change in the variable’s rise or fall. If the ifEntry.20.1 value shows a MIB counter increase of 15 or more, such as from 100000 to 100015, the alarm is triggered. The alarm in turn triggers event number 1, which is configured with the rmon event command. Possible events can include a log entry or an SNMP trap. If the ifEntry.20.1 value changes by 0, the alarm is reset and can be triggered again.
Creating an RMON Event Number: Example
The following example creates RMON event number 1:
The event is defined as High ifOutErrors and generates a log entry when the event is triggered by the alarm. The user jjones owns the row that is created in the event table by this command. This example also generates an SNMP trap when the event is triggered.
Configuring RMON Statistics: Example
This example shows how to collect RMON statistics for the owner root :
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to switch administration:
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Cisco IOS basic commands |
|
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a platform under the Cisco Access Products menu: http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
 Feedback
Feedback