- Preface
- Software Licensing
- The Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)
- Configuring Interfaces
- Switch Alarms
- Initial Switch Configuration (IP address assignments and DHCP autoconfiguration)
- How to Setup and Use the Cisco Configuration Engine
- How to Create and Manage Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
- Configuring PROFINET
- Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- MACsec
- Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode and SGACL Logging
- Configuring SGT Exchange Protocol over TCP (SXP) and Layer 3 Transport
- Configuring VLANs
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- How to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring the FlexLinks and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
- Configuring DHCP
- Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- How to Configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- One-to-one (1:1) Layer 2 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- How to Configure CDP
- Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring Quality of Service (QoS)
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IP multicast routing
- Configuring Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
- Configuring Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping
- Configuring HSRP and VRRP
- Configuring IPv6 access control lists (ACLs)
- Configuring Embedded Event Manager (EEM)
- IP Unicast Routing
- IPv6 Unicast Routing
- Unicast Routing Overview
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Dying-Gasp
- How to Configure Enhanced Object Tracking
- Configuring MODBUS TCP
- Configuring Ethernet CFM
- Working with the Flash File System
- How to Configure EtherChannels
- Troubleshooting
- How to use a Secure Digital (SD) flash memory module (SD card)
Configuring UDLD
Prerequisites for UDLD
■![]() When configuring the mode (normal or aggressive), make sure that the same mode is configured on both sides of the link.
When configuring the mode (normal or aggressive), make sure that the same mode is configured on both sides of the link.
Restrictions for UDLD
■![]() UDLD is not supported on ATM ports.
UDLD is not supported on ATM ports.
■![]() A UDLD-capable port cannot detect a unidirectional link if it is connected to a UDLD-incapable port of another switch.
A UDLD-capable port cannot detect a unidirectional link if it is connected to a UDLD-incapable port of another switch.
■![]() Loop guard works only on point-to-point links. We recommend that each end of the link has a directly connected device that is running STP.
Loop guard works only on point-to-point links. We recommend that each end of the link has a directly connected device that is running STP.
Information About UDLD
UDLD
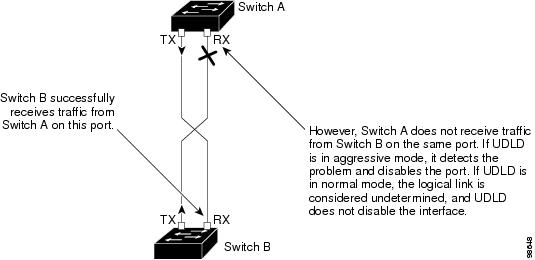
UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) is a Layer 2 protocol that enables devices connected through fiber-optic or twisted-pair Ethernet cables to monitor the physical configuration of the cables and detect when a unidirectional link exists. All connected devices must support UDLD for the protocol to successfully identify and disable unidirectional links. When UDLD detects a unidirectional link, it disables the affected port and alerts you. Unidirectional links can cause a variety of problems, including spanning-tree topology loops.
Modes of Operation
UDLD supports two modes of operation: normal (the default) and aggressive. In normal mode, UDLD can detect unidirectional links due to misconnected ports on fiber-optic connections. In aggressive mode, UDLD can also detect unidirectional links due to one-way traffic on fiber-optic and twisted-pair links and to misconnected ports on fiber-optic links.
In normal and aggressive modes, UDLD works with the Layer 1 mechanisms to learn the physical status of a link. At Layer 1, autonegotiation takes care of physical signaling and fault detection. UDLD performs tasks that autonegotiation cannot perform, such as detecting the identities of neighbors and shutting down misconnected ports. When you enable both autonegotiation and UDLD, the Layer 1 and Layer 2 detections work together to prevent physical and logical unidirectional connections and the malfunctioning of other protocols.
A unidirectional link occurs whenever traffic sent by a local device is received by its neighbor but traffic from the neighbor is not received by the local device.
In normal mode, UDLD detects a unidirectional link when fiber strands in a fiber-optic port are misconnected and the Layer 1 mechanisms do not detect this misconnection. If the ports are connected correctly but the traffic is one way, UDLD does not detect the unidirectional link because the Layer 1 mechanism, which is supposed to detect this condition, does not do so. In this case, the logical link is considered undetermined, and UDLD does not disable the port.
When UDLD is in normal mode, if one of the fiber strands in a pair is disconnected, as long as autonegotiation is active, the link does not stay up because the Layer 1 mechanisms detects a physical problem with the link. In this case, UDLD does not take any action and the logical link is considered undetermined.
In aggressive mode, UDLD detects a unidirectional link by using the previous detection methods. UDLD in aggressive mode can also detect a unidirectional link on a point-to-point link on which no failure between the two devices is allowed. It can also detect a unidirectional link when one of these problems exists:
■![]() On fiber-optic or twisted-pair links, one of the ports cannot send or receive traffic.
On fiber-optic or twisted-pair links, one of the ports cannot send or receive traffic.
■![]() On fiber-optic or twisted-pair links, one of the ports is down while the other is up.
On fiber-optic or twisted-pair links, one of the ports is down while the other is up.
■![]() One of the fiber strands in the cable is disconnected.
One of the fiber strands in the cable is disconnected.
In these cases, UDLD disables the affected port.
In a point-to-point link, UDLD hello packets can be considered as a heart beat whose presence guarantees the health of the link. Conversely, the loss of the heart beat means that the link must be shut down if it is not possible to reestablish a bidirectional link.
If both fiber strands in a cable are working normally from a Layer 1 perspective, UDLD in aggressive mode detects whether those fiber strands are connected correctly and whether traffic is flowing bidirectionally between the correct neighbors. This check cannot be performed by autonegotiation because autonegotiation operates at Layer 1.
Methods to Detect Unidirectional Links
UDLD operates by using two methods:
■![]() Neighbor database maintenance
Neighbor database maintenance
UDLD learns about other UDLD-capable neighbors by periodically sending a hello packet (also called an advertisement or probe) on every active port to keep each device informed about its neighbors.
When the switch receives a hello message, it caches the information until the age time (hold time or time-to-live) expires. If the switch receives a new hello message before an older cache entry ages, the switch replaces the older entry with the new one.
Whenever a port is disabled and UDLD is running, whenever UDLD is disabled on a port, or whenever the switch is reset, UDLD clears all existing cache entries for the ports affected by the configuration change. UDLD sends at least one message to inform the neighbors to flush the part of their caches affected by the status change. The message is intended to keep the caches synchronized.
■![]() Event-driven detection and echoing
Event-driven detection and echoing
UDLD relies on echoing as its detection mechanism. Whenever a UDLD device learns about a new neighbor or receives a resynchronization request from an out-of-sync neighbor, it restarts the detection window on its side of the connection and sends echo messages in reply. Because this behavior is the same on all UDLD neighbors, the sender of the echoes expects to receive an echo in reply.
If the detection window ends and no valid reply message is received, the link might shut down, depending on the UDLD mode. When UDLD is in normal mode, the link might be considered undetermined and might not be shut down. When UDLD is in aggressive mode, the link is considered unidirectional, and the port is disabled.
If UDLD in normal mode is in the advertisement or in the detection phase and all the neighbor cache entries are aged out, UDLD restarts the link-up sequence to resynchronize with any potentially out-of-sync neighbors.
If you enable aggressive mode when all the neighbors of a port have aged out either in the advertisement or in the detection phase, UDLD restarts the link-up sequence to resynchronize with any potentially out-of-sync neighbor. UDLD shuts down the port if, after the fast train of messages, the link state is still undetermined.
Figure 71 UDLD Detection of a Unidirectional Link
Default UDLD Settings
|
|
|
|---|---|
How to Configure UDLD
Enabling UDLD Globally
Follow these steps to enable UDLD in the aggressive or normal mode and to set the configurable message timer on all fiber-optic ports on the switch:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
udld { aggressive | enable | message time message-timer-interval } |
Specifies the UDLD mode of operation: ■ ■ An individual interface configuration overrides the setting of the udld enable global configuration command. For more information about aggressive and normal modes, see Modes of Operation. ■ Note: This command affects fiber-optic ports only. Use the udld interface configuration command to enable UDLD on other port types. For more information, see Enabling UDLD on an Interface. |
|
Enabling UDLD on an Interface
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Specifies the port to be enabled for UDLD, and enters interface configuration mode. |
||
| ■ ■ Note: Use the no udld port interface configuration command to disable UDLD on a specified fiber-optic port. For more information about aggressive and normal modes, see Modes of Operation. |
||
Setting and Resetting UDLD Parameters
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
(Optional) Enables the timer to automatically recover from the UDLD error-disabled state. |
||
(Optional) Specifies the time to recover from the UDLD error-disabled state. |
||
Maintaining and Monitoring UDLD
|
|
|
|---|---|
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to switch administration:
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a platform under the Cisco Access Products menu: http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
 Feedback
Feedback