- Preface
- Software Licensing
- The Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)
- Configuring Interfaces
- Switch Alarms
- Initial Switch Configuration (IP address assignments and DHCP autoconfiguration)
- How to Setup and Use the Cisco Configuration Engine
- How to Create and Manage Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
- Configuring PROFINET
- Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- MACsec
- Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode and SGACL Logging
- Configuring SGT Exchange Protocol over TCP (SXP) and Layer 3 Transport
- Configuring VLANs
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- How to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring the FlexLinks and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
- Configuring DHCP
- Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- How to Configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- One-to-one (1:1) Layer 2 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- How to Configure CDP
- Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring Quality of Service (QoS)
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IP multicast routing
- Configuring Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
- Configuring Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping
- Configuring HSRP and VRRP
- Configuring IPv6 access control lists (ACLs)
- Configuring Embedded Event Manager (EEM)
- IP Unicast Routing
- IPv6 Unicast Routing
- Unicast Routing Overview
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Dying-Gasp
- How to Configure Enhanced Object Tracking
- Configuring MODBUS TCP
- Configuring Ethernet CFM
- Working with the Flash File System
- How to Configure EtherChannels
- Troubleshooting
- How to use a Secure Digital (SD) flash memory module (SD card)
- Guidelines and Limitations
- PSK Based MKA Support for MACsec
- Prerequisites for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Restrictions for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Information About Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Configuring Certificate-based MACsec Encryption using Remote Authentication
- Verifying Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Configuration examples for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
MACsec
Media Access Control Security (MACsec) is the IEEE 802.1AE standard for authenticating and encrypting packets between two MACsec-capable devices.
For information about MACsec, including details about MACsec and MACsec Key Agreement (MKA), how to configure MKA and MACsec, and how to configure Cisco TrustSec MACsec, see Configuring MACsec Encryption.
This chapter includes the following information about MACsec specific to the IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 switches:
■![]() PSK Based MKA Support for MACsec
PSK Based MKA Support for MACsec
■![]() Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
Note: On the IE 4000, IE 4010, and the IE 5000, MACsec is included in the IP Services image only.
Guidelines and Limitations
MACsec on the IE5000 has the following guidelines and limitations:
■![]() Both models of IE 5000 downlinks are fully interoperable with IE 4000, IE 4010, Catalyst 9300/3850, and Catalyst IE 3x00 platforms.
Both models of IE 5000 downlinks are fully interoperable with IE 4000, IE 4010, Catalyst 9300/3850, and Catalyst IE 3x00 platforms.
■![]() On the IE-5000-16S12P, uplinks are fully functional when connected to another IE-5000-16S12P or a Catalyst 3850.
On the IE-5000-16S12P, uplinks are fully functional when connected to another IE-5000-16S12P or a Catalyst 3850.
■![]() On the IE-5000-12S12P-10G, uplinks when running at 10GE are fully functional when connected to another IE-5000-12S12P-10G running at 10GE or to a Catalyst 3850 running at 10GE.
On the IE-5000-12S12P-10G, uplinks when running at 10GE are fully functional when connected to another IE-5000-12S12P-10G running at 10GE or to a Catalyst 3850 running at 10GE.
■![]() When an IE 5000 uplink is connected to a Catalyst 9300, the IE 5000 must be the key server. CSCvs36043
When an IE 5000 uplink is connected to a Catalyst 9300, the IE 5000 must be the key server. CSCvs36043
■![]() IE-5000-12S12P-10G uplinks MACsec is not currently supported at GE speeds. CSCvs41335
IE-5000-12S12P-10G uplinks MACsec is not currently supported at GE speeds. CSCvs41335
■![]() IE-5000-16S12P uplinks connected to downlinks of the IE 5000 and IE 4000 is not currently supported. CSCvs44292
IE-5000-16S12P uplinks connected to downlinks of the IE 5000 and IE 4000 is not currently supported. CSCvs44292
Additional Guidelines and Limitations for IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 series switches
The default behavior of the IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 is to encrypt data traffic when the MACsec link is secured. However, if the remote peer does not secure the MACsec link, these switches send data unencrypted.
The Cisco IOS XE-based IE switches such as IE3x00 and Cisco Catalyst switches such as the 9300, 9200, and 9500 always secure the MACsec link regardless of the state of the MACsec session. When a MACsec link is configured, the traffic is sent encrypted. Any unencrypted traffic received on a MACsec-secured link is dropped.
When MACsec is enabled on a link, it accepts only encrypted data. This means all L2 protocol data frames, such as REP, PTP, ping, and control frames like CDP and LLDP, are blocked on the ingress side. The L2 protocol data frames are allowed only if the egress link also becomes MACsec enabled and a secure channel is established.
Implementing the MACsec Must-Secure feature aligns the default MACsec behavior of the 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 with that of the Cisco IOS-XE-based IE switches, including the IE3x00.
MACsec Must-Secure Feature Implementation
The MACsec Must-Secure feature implementation does not include a command option to set the mode to Should-Secure or Must-Secure. By default, the switch operated in Should-Secure mode in the 15.2(8)E5 release and previous releases. Starting with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(8)E6, the switch operates in Must-Secure mode by default.
The support for these modes is as follows:
■![]() The IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 supports Should-Secure mode in release 15.2(8)E5.
The IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 supports Should-Secure mode in release 15.2(8)E5.
■![]() The IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 supports Must-Secure mode in release 15.2(8)E6.
The IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 supports Must-Secure mode in release 15.2(8)E6.
Run the show macsec interface interface-id command to see whether the device is set to Should-Secure mode. If the show command output doesn’t display the "Access control" field, the device is in Should-Secure mode. For example:
switch# show macsec int gi1/1 | i Access
If the show command output displays “Access control: must secure," the device is in Must-Secure mode.
To change the mode from Must-Secure to Should-Secure, you need to downgrade the switch to 15.2(8)E5 release or earlier. Similarly, to change from Should-Secure to Must-Secure, you must upgrade the switch to the 15.2(8)E6 release or later.
Cipher Suite Support
IOS-based IE devices support the GCM-AES-128 Cipher Suite encryption algorithm but do not support the GCM-AES-256 Cipher Suite.
Ping Reachability
■![]() Ping works with default interface configurations (no configuration).
Ping works with default interface configurations (no configuration).
■![]() Ping does not work if macsec network-link is configured without Mutual Key Agreement (MKA).
Ping does not work if macsec network-link is configured without Mutual Key Agreement (MKA).
■![]() Ping works when MKA and macsec network-link are configured on both ends of the link.
Ping works when MKA and macsec network-link are configured on both ends of the link.
■![]() Ping does not work if you remove macsec network-link or MKA on one side of the interface.
Ping does not work if you remove macsec network-link or MKA on one side of the interface.
Using MACsec/MACsec Network-Link with MKA
■![]() Use the macsec network-link command only with MKA on switch interfaces. If you configure MACsec without MKA, then the MKA session will not be displayed.
Use the macsec network-link command only with MKA on switch interfaces. If you configure MACsec without MKA, then the MKA session will not be displayed.
■![]() You must configure macsec network-link to enable MACsec and secure the link between switches.
You must configure macsec network-link to enable MACsec and secure the link between switches.
Layer 2 Protocols with MACsec/CTS Manual
■![]() Layer 2 protocols such as PTP, PO, and REP were compatible with MACsec in release 15.2(8)E5 and earlier versions. From release 15.2(8)E6 onwards, Layer 2 protocols work only if the network links are secured and the keychain credentials are configured on the devices.
Layer 2 protocols such as PTP, PO, and REP were compatible with MACsec in release 15.2(8)E5 and earlier versions. From release 15.2(8)E6 onwards, Layer 2 protocols work only if the network links are secured and the keychain credentials are configured on the devices.
■![]() Layer 2 protocols work only if the network links are secured by MKA or SAP PMK and configured with the macsec network-link or the cts manual command.
Layer 2 protocols work only if the network links are secured by MKA or SAP PMK and configured with the macsec network-link or the cts manual command.
■![]() If a MACsec network link is configured only at one end of the link, MACsec traffic does not pass, and the protocol combination does not work.
If a MACsec network link is configured only at one end of the link, MACsec traffic does not pass, and the protocol combination does not work.
■![]() If a MACsec network link is configured at both ends, MACsec traffic is transmitted, and any integrated protocol functions, provided that MKA or SAP PMK is used to secure the network.
If a MACsec network link is configured at both ends, MACsec traffic is transmitted, and any integrated protocol functions, provided that MKA or SAP PMK is used to secure the network.
Observation on Key-Server Priority
The default key-server priority is set to 0. If not explicitly set, it defaults to 0.
For example, Device1 is configured as Key-server Priority 9 and Device2 is configured as Key-server Priority 10. The lower the priority value, the higher the preference for the switch to become the key server. In this example, the key server is displayed correctly as Device1 in the show mka session command output (“yes” is displayed for the key-server field). If Device1 is configured as key server priority 9 and Device2 has no priority configured, then the key server is not displayed correctly because Device2 without any priority (0 by default) is taken as the high key server priority.
MACSEC+ MKA Unidirectional/Bidirectional Traffic Throughput
MACSec on IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 has some overhead resulting in lesser throughput compared to unencrypted Layer2 frames. The overhead is around 28% for small frames (64 byte) and 2% for large frames (1472 byte).
Traffic drops of 28% are expected with a 100% maximum rate for 64 bytes frames. Therefore, if the maximum rate is 72%, a traffic loss is not seen. The following tables show the traffic frame rate loss.
MKA-PSK: CKN Behavior Change
To interoperate with Cisco switches running IOS XE, the CKN configuration must be zero-padded. From Cisco IOS XE Everest Release 16.6.1 onwards, for MKA-PSK sessions, instead of fixed 32 bytes, the Connectivity Association Key name (CKN) uses exactly the same string as the CKN, which is configured as the hex-string for the key.
For the above example, following is the output for the show mka session command:
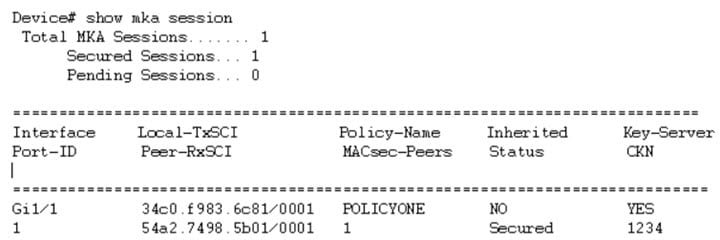
Note that the CKN key-string is exactly the same that has been configured for the key as hex-string.
For interoperability between two images, one having the CKN behavior change and one without the CKN behavior change, the hex-string for the key must be a 64-character hex-string padded with zeros to work on a device that has an image with the CKN behavior change. See the example below:
Configuration without CKN key-string behavior change:
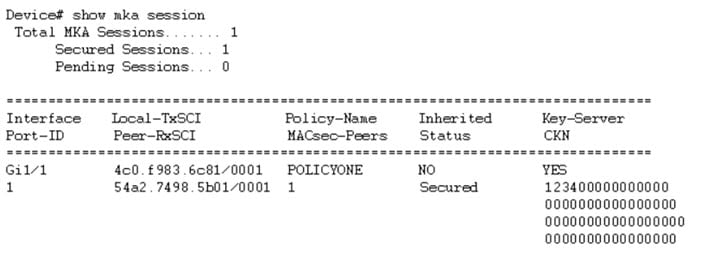
Configuration with CKN key-string behavior change:

PSK Based MKA Support for MACsec
This section provides information about configuring pre-shared key (PSK) based MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) MACsec encryption on the switch. This feature applies to Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7)E1a and later.
Information about PSK Based MKA
IE switches support Pairwise Master Key (PMK) Security Association Protocol (SAP) based support for MACsec to interconnect links between the switches. The PMK keys can be either derived statically from the switch configuration (manual mode) or derived from the RADIUS server during dot1X negotiation (dynamic mode). Manual mode does not support switch-to-host MACsec connections because SAP is a Cisco proprietary protocol.
IE switches have MKA support for MACSec on switch-to-host links. Here the keys are derived from the RADIUS server after dot1x authentication. However, manually configured PSK keys were not supported on IE switch platforms (running Cisco IOS) prior to Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7)E1a. Catalyst IE 3x00 platforms (running Cisco IOS XE) have PSK based MKA support for MACsec for statically derived keys from the switch configuration for switch-to-switch connections as well as dynamically derived keys from RADIUS server for switch-to-host links.
Catalyst IE 3x00 platforms do not have PMK SAP based support for MACsec. Therefore, for interoperability with the Catalyst IE 3x00 platforms, the PSK functionality is added to MACsec for Cisco IOS based IE switches.
Configuring PSK Based MKA
Follow the procedures in this section to configure PSK based MKA on IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 switches.
Configuring MKA
The MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) enables configuration and control of keying parameters. Perform the following task to configure MKA.
Example
You can use the show mka policy command to verify the configuration. Here's a sample output of the show command.
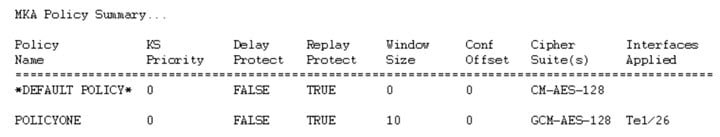
Configuring MACsec and MKA on Interfaces
Perform the following task to configure MACsec and MKA on an interface.
Configuring MKA Pre-shared Key
Perform the following task to configure MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) pre-shared key.
Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
This section provides information about Certificate-based MACsec Encryption. This feature applies to Cisco IOS Release 15.2(8)E and later.
Prerequisites for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
■![]() Certificate-based MACsec Encryption is supported on the IE4000, IE4010, and IE5000.
Certificate-based MACsec Encryption is supported on the IE4000, IE4010, and IE5000.
■![]() Ensure that you have a Certificate Authority (CA) server configured for your network.
Ensure that you have a Certificate Authority (CA) server configured for your network.
■![]() Ensure that you have configured Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) Release 2.0. Refer to the Cisco Identity Services Engine Administrator Guide, Release 2.3.
Ensure that you have configured Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) Release 2.0. Refer to the Cisco Identity Services Engine Administrator Guide, Release 2.3.
■![]() Ensure that both the participating devices, the CA server, and Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) are synchronized using Network Time Protocol (NTP). If time is not synchronized on all your devices, certificates will not be validated.
Ensure that both the participating devices, the CA server, and Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) are synchronized using Network Time Protocol (NTP). If time is not synchronized on all your devices, certificates will not be validated.
■![]() Ensure that 802.1x authentication and AAA are configured on your device.
Ensure that 802.1x authentication and AAA are configured on your device.
Restrictions for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
■![]() MKA is not supported on port-channels.
MKA is not supported on port-channels.
■![]() High Availability for MKA is not supported.
High Availability for MKA is not supported.
■![]() When you remove dot1x pae both from an interface, all configuration related to dot1x is removed from the interface.
When you remove dot1x pae both from an interface, all configuration related to dot1x is removed from the interface.
■![]() Certificate-based MACsec is supported only if the access-session host-mode is configured in multiple-host mode. The other configuration modes (multi-auth, multi-domain, or single-host) are not supported.
Certificate-based MACsec is supported only if the access-session host-mode is configured in multiple-host mode. The other configuration modes (multi-auth, multi-domain, or single-host) are not supported.
Information About Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
MKA MACsec is supported on switch-to-switch links. Using IEEE 802.1X Port-based Authentication with Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP-TLS), you can configure MKA MACsec between device ports. EAP-TLS allows mutual authentication and obtains an MSK (master session key) from which the connectivity association key (CAK) is derived for MKA protocol. Device certificates are carried, using EAP-TLS, for authentication to the AAA server.
Refer to Certificate-based MACsec Encryption For more information about Certificate-based MACsec Encryption, including how to configure Certificate-based MACsec Encryption using Remote Authentication.
Configuring Certificate-based MACsec Encryption using Remote Authentication
Follow these procedures to configure MACsec encryption using remote authentication:
■![]() Configure Certificate Enrollment Manually
Configure Certificate Enrollment Manually
■![]() Configure an Authentication Policy
Configure an Authentication Policy
Configuring Certificate Enrollment Manually
If network connection between the router and CA is not possible, perform the following task to set up manual certificate enrollment:
Enabling 802.1x Authentication and Configuring AAA
Configuring EAP-TLS Profile and 802.1x Credentials
Applying the 802.1x MKA MACsec Configuration on Interfaces
To apply MKA MACsec using EAP-TLS to interfaces, perform the following task:
Verifying Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
Use the following show commands to verify the configuration of certificate-based MACsec encryption. Sample output is shown below.
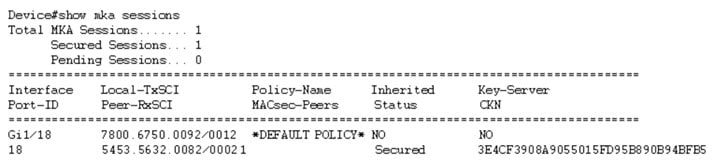
The show access-session interface interface-id details displays detailed information about the access session for the given interface.
Configuration examples for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
Example: Enrolling the Certificate
Configure Crypto PKI Trustpoint:
enrollment terminal
serial-number
fqdn MUSTS.mkadt.cisco.com
subject-name cn=MUSTS.mkadt.cisco.com,OU=CSG Security,O=Cisco Systems,L=Bengaluru,ST=KA,C=IN
subject-alt-name MUSTS.mkadt.cisco.com
revocation-check none
rsakeypair demo 2048
!
Manual Installation of Root CA certificate:
 Feedback
Feedback