- Preface
- Software Licensing
- The Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)
- Configuring Interfaces
- Switch Alarms
- Initial Switch Configuration (IP address assignments and DHCP autoconfiguration)
- How to Setup and Use the Cisco Configuration Engine
- How to Create and Manage Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
- Configuring PROFINET
- Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- MACsec
- Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring SGACL Monitor Mode and SGACL Logging
- Configuring SGT Exchange Protocol over TCP (SXP) and Layer 3 Transport
- Configuring VLANs
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- How to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring the FlexLinks and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
- Configuring DHCP
- Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- How to Configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- One-to-one (1:1) Layer 2 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- How to Configure CDP
- Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring Quality of Service (QoS)
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IP multicast routing
- Configuring Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
- Configuring Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping
- Configuring HSRP and VRRP
- Configuring IPv6 access control lists (ACLs)
- Configuring Embedded Event Manager (EEM)
- IP Unicast Routing
- IPv6 Unicast Routing
- Unicast Routing Overview
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Dying-Gasp
- How to Configure Enhanced Object Tracking
- Configuring MODBUS TCP
- Configuring Ethernet CFM
- Working with the Flash File System
- How to Configure EtherChannels
- Troubleshooting
- How to use a Secure Digital (SD) flash memory module (SD card)
- Restrictions for Static IP Unicast Routing
- Information About Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- IP Routing
- How to Configure Static IP Unicast Routing
- Enabling IP Unicast Routing
- Assigning IP Addresses to SVIs
- Configuring Static Unicast Routes
- Monitoring and Maintaining the IP Network
- Additional References for Configuring IP Unicast Routing
Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
This chapter describes how to configure IP Version 4 (IPv4) static IP unicast routing on the switch. Static routing is supported only on switched virtual interfaces (SVIs) and not on physical interfaces. The switch does not support routing protocols.
Restrictions for Static IP Unicast Routing
Information About Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
Note: When configuring routing parameters on the switch and to allocate system resources to maximize the number of unicast routes allowed, use the sdm prefer lanbase-routing global configuration command to set the Switch Database Management (SDM) feature to the routing template.
IP Routing
In some network environments, VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks. In an IP network, each subnetwork is mapped to an individual VLAN. Configuring VLANs helps control the size of the broadcast domain and keeps local traffic local. However, network devices in different VLANs cannot communicate with one another without a Layer 3 device to route traffic between the VLANs, referred to as inter-VLAN routing. You configure one or more routers to route traffic to the appropriate destination VLAN.
Figure 85 shows a basic routing topology. Switch A is in VLAN 10, and Switch B is in VLAN 20. The router has an interface in each VLAN.
Figure 85 Routing Topology Example
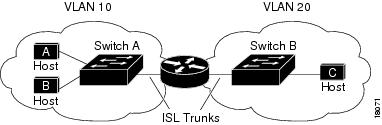
When Host A in VLAN 10 needs to communicate with Host B in VLAN 10, it sends a packet addressed to that host. Switch A forwards the packet directly to Host B, without sending it to the router.
When Host A sends a packet to Host C in VLAN 20, Switch A forwards the packet to the router, which receives the traffic on the VLAN 10 interface. The router uses the routing table to finds the correct outgoing interface, and forwards the packet on the VLAN 20 interface to Switch B. Switch B receives the packet and forwards it to Host C.
When static routing is enabled on Switch A and B, the router device is no longer needed to route packets.
Types of Routing
Routers and Layer 3 switches can route packets in these ways:
■![]() Using default routing to send traffic with a destination unknown to the router to a default outlet or destination
Using default routing to send traffic with a destination unknown to the router to a default outlet or destination
■![]() Using static routes to forward packets from predetermined ports through a single path into and out of a network
Using static routes to forward packets from predetermined ports through a single path into and out of a network
■![]() Dynamically calculating routes by using a routing protocol
Dynamically calculating routes by using a routing protocol
The switch supports static routes and default routes. It does not support routing protocols.
How to Configure Static IP Unicast Routing
Steps for Configuring Routing
In these procedures, the specified interface must be a switch virtual interface (SVI)—a VLAN interface created by using the interface vlan vlan_id global configuration command and by default a Layer 3 interface. All Layer 3 interfaces on which routing will occur must have IP addresses assigned to them. See Assigning IP Addresses to SVIs.
Note: The switch supports 16 static routes (including user-configured routes and the default route) and any directly connected routes and default routes for the management interface. The switch can have an IP address assigned to each SVI. Before enabling routing, enter the sdm prefer lanbase-routing global configuration command and reload the switch.
Procedures for configuring routing:
■![]() To support VLAN interfaces, create and configure VLANs on the switch, and assign VLAN membership to Layer 2 interfaces.
To support VLAN interfaces, create and configure VLANs on the switch, and assign VLAN membership to Layer 2 interfaces.
■![]() Configure Layer 3 interfaces (SVIs) and physical routed port (no switchport).
Configure Layer 3 interfaces (SVIs) and physical routed port (no switchport).
Enabling IP Unicast Routing
By default, the switch is in Layer 2 switching mode, and IP routing is disabled. To use the Layer 3 capabilities of the switch, enable IP routing.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Assigning IP Addresses to SVIs
To configure IP routing, you need to assign IP addresses to Layer 3 network interfaces. This enables communication with the hosts on those interfaces that use IP. IP routing is disabled by default, and no IP addresses are assigned to SVIs.
An IP address identifies a destination for IP packets. Some IP addresses are reserved for special uses and cannot be used for host, subnet, or network addresses. RFC 1166, “Internet Numbers,” contains the official description of these IP addresses.
An interface can have one primary IP address. A a subnet mask identifies the bits that denote the network number in an IP address.
This task explains how to assign an IP address and a network mask to an SVI
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Enters interface configuration mode, and specifies the Layer 3 VLAN to configure. |
||
Configuring Static Unicast Routes
Static unicast routes are user-defined routes that cause packets moving between a source and a destination to take a specified path. Static routes can be important if the router cannot build a route to a particular destination and are useful for specifying a gateway of last resort to which all unroutable packets are sent.
Use the no ip route prefix mask { address | interface } global configuration command to remove a static route. The switch retains static routes until you remove them.
When an interface goes down, all static routes through that interface are removed from the IP routing table. When the software can no longer find a valid next hop for the address specified as the forwarding router's address in a static route, the static route is also removed from the IP routing table.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Monitoring and Maintaining the IP Network
|
|
|
|---|---|
Displays the administrative and operational status of all interfaces or a specified interface. |
Additional References for Configuring IP Unicast Routing
The following sections provide references related to switch administration:
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 1 of 3: Addressing and Services, Release 15.0 |
|
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a platform under the Cisco Access Products menu: http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
 Feedback
Feedback