SRv6 microloop avoidance
A SRv6 microloop avoidance is a SRv6 feature that
-
detects if microloops are possible following a topology change
-
creates temporary loop-free SR-TE policy paths to the destination using a list of segments, and
-
replaces the temporary paths with regular forwarding paths after a Routing Information Base (RIB) update delay timer expires.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
SRv6 microloop avoidance |
Release 25.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700 [ASIC: K100], 8010 [ASIC: A100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
|
SRv6 microloop avoidance |
Release 7.3.1 |
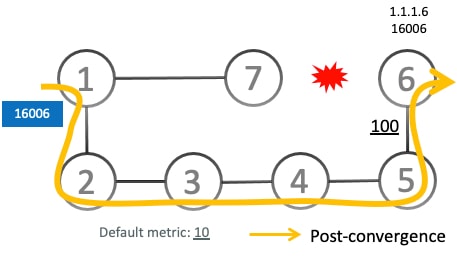
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: Q200]; Centralized Systems (8600 [ASIC:Q200]); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: Q200]) SRv6 microloop avoidance enhances network stability by preventing transient packet loops, also known as microloops, during network convergence after a topology change. The router temporarily reroutes traffic over a stable, loop-free path until all devices have updated their routes, reducing packet loss and jitter and improving user experience. |
Key concepts of SRv6 microloop avoidance
-
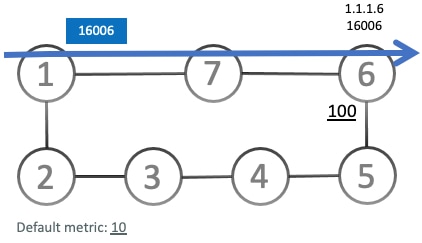
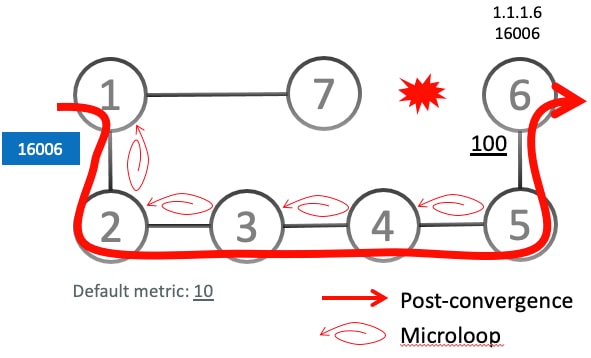
Microloops: Amicroloop is a brief packet loop that occurs in the network following a topology change (link down, link up, or metric change events), is caused by the non-simultaneous convergence of different nodes in the network, and results in packet loss, jitter, and out-of-order packets if traffic is looped between nodes.
-
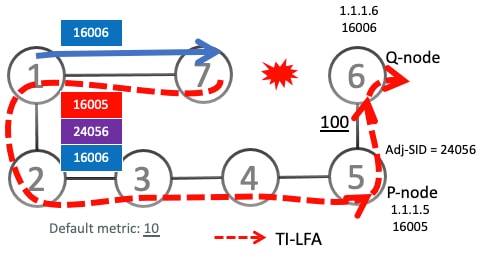
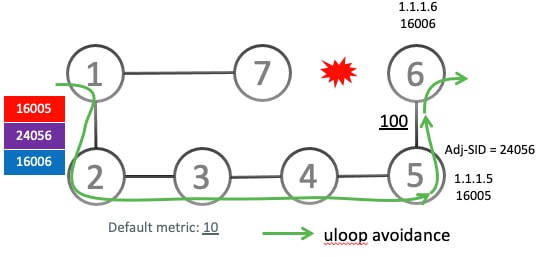
Temporary SR-TE Policy Paths: Loop-free paths to a destination, constructed using a list of segments, that are temporarily installed by the feature to avoid microloops.
-
RIB update delay timer: A configurable timer that dictates how long the temporary microloop avoidance policy is used before the network transitions to regular, natively converged forwarding paths.
-
Loop-free forwarding: The primary goal and outcome of the feature, ensuring that traffic continues to be forwarded without being caught in transient loops during network topology changes and convergence.
Benefits of SRv6 microloop avoidance
SRv6 microloop avoidance provides significant value by mitigating the detrimental effects of microloops, a long-standing challenge in IP networks. This feature offers substantial benefits for network stability, performance, and user experience within SRv6 deployments.
The feature provides these key benefits:
-
Addresses a fundamental network challenge: SRv6 microloop avoidance resolves the issue of transient packet loops that occur immediately after topology changes due to non-simultaneous router convergence.
-
Prevents service degradation: SRv6 microloop avoidance eliminates packet loss, jitter, and out-of-order packets caused by microloops, which directly impact application performance, especially for real-time services.
-
Ensures loop-free forwarding during convergence: The feature proactively detects potential microloops and temporarily steers traffic onto specially constructed, loop-free SRv6-TE policy paths, ensuring continuous and stable forwarding during network convergence.
-
Improves network stability and predictability: By preventing microloops, the network's behavior during topology changes becomes more predictable and stable, reducing transient issues and simplifying troubleshooting.
-
Enhances application performance: By preventing microloop-induced packet impairments, it directly contributes to a higher quality of service for all applications, particularly sensitive ones.
-
Leverages SRv6 capabilities: The solution seamlessly integrates into existing SRv6 deployments by using SRv6 Segment Identifiers (SIDs) to construct and enforce temporary microloop-avoidant paths.
-
Offers local behavior with global benefits: The feature operates as a local behavior, meaning that individual nodes can implement it to protect their own forwarding, contributing to overall network stability without requiring universal deployment.
 Feedback
Feedback