BGP Link-State
BGP Link-State (BGP-LS) is a protocol extension that
-
distributes IGP link-state information via BGP
-
improves network topology visibility for applications like SR-PCE, and
-
uses a dedicated AFI/SAFI (RFC7752) to encode link-state attributes.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|
BGP Link-State |
Release 25.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
|
BGP Link-State |
Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on Cisco 8011-4G24Y4H-I routers. |
|
BGP Link-State |
Release 24.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100, K100])(select variants only); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100])(select variants only*) With BGP Link-State (BGP-LS), you can efficiently share IGP link-state information across your network, allowing applications such as Segment Routing Path Computation Element (SR-PCE) to gain greater topology awareness and optimize path computations using Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE). This feature uses Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI) to encode link-state data in the BGP-LS attribute as defined by RFC7752. *This feature is supported on:
|
BGP-LS extends BGP to carry Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) link-state information using a specific Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI). As defined in RFC7752, BGP-LS encodes each link-state object, such as a node, a link, or a prefix, in the BGP Network Layer Reachability Information (NLRI) format, while the properties of each object are conveyed using the BGP-LS path attribute. This approach enables controllers and applications to build a comprehensive topology view across multiple domains.
Example
A Segment Routing Path Computation Element (SR-PCE) can use BGP-LS data to discover node capabilities, learn mappings for SR segments, and compute optimal paths using Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE). This enables SR-PCE to steer traffic on paths different from the underlying IGP-based distributed best-path computation.
Deployment scenarios for BGP Link-State
This figure illustrates a typical BGP-LS deployment.
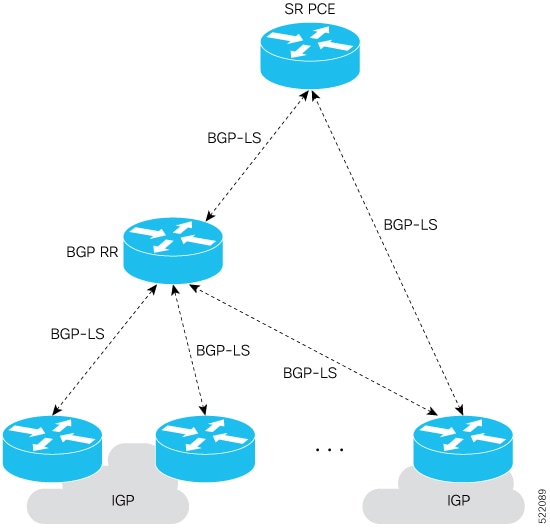
The deployment involves:
-
Configuring one or more BGP speakers (nodes) with BGP-LS in each IGP area.
-
Establishing an iBGP mesh between BGP speakers and route-reflectors.
-
Allowing route-reflectors to aggregate and share link-state information from all IGP areas and from eBGP peers in other autonomous systems (AS).
Usage guidelines and limitations for BGP Link-State
Functional limitations
IGPs do not use BGP-LS data from remote BGP peers, and BGP does not download the received BGP-LS information into other router components.
Instance-id usage
The identifier field in BGP Link-State, called the instance-id, specifies the IGP routing domain to which the NLRI is associated.
Some best practices for instance-id configuration are:
-
Assign a consistent instance-id value to all BGP-LS producers within a single IGP domain.
-
When only one protocol instance is present, configure the instance-id value to 0.
-
Use unique instance-id values for different routing protocol instances operating in separate IGP domains.
NLRIs with different instance-id values represent different IGP routing instances. If consistent instance-ids are not used, BGP-LS consumers may see duplicate objects or incorrect topology.
Configure BGP Link-State with a neighbor
Enable the exchange of BGP Link-State information with a BGP neighbor.
Use this task to distribute IGP link-state data (OSPF or IS-IS) to a BGP neighbor for use by controllers or applications such as SR-PCE.
Before you begin
-
Ensure you have access to the router CLI.
-
Confirm that the neighbor uses a private IP address.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Run the configure comamnd to enter configuration mode. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Specify the BGP AS number and enter BGP configuration mode. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Configure the neighbor using its IP address. Example: |
|
Step 4 |
Set the remote AS number for the neighbor and enter the link-state address family. Example: |
The router exchanges BGP Link-State data with the specified neighbor.
Configure a unique domain distinguisher (four-octet ASN)
Assign a unique identifier (domain distinguisher) for BGP Link-State using a four-octet ASN.
The domain distinguisher helps differentiate routing domains when distributing link-state information.
Follow these steps to configure the domain distinguisher.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In configuration mode, specify the BGP AS number and enter BGP configuration mode. Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Enter the link-state address family configuration mode. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Assign a unique domain distinguisher. Example:Possible range of domain-distinguisher: 1 to 4294967295 |
The router uses the specified four-octet ASN as the domain distinguisher for BGP-LS.
Distributing IGP link-state databases with BGP-LS
BGP Link-State (BGP-LS) enables the distribution of IGP link-state databases, including OSPF and IS-IS link-state data, across multiple, independent routing domains. This distribution allows controllers or applications to build end-to-end paths that span several domains.
To distribute OSPFv2 link-state data using BGP-LS:
-
Enter router configuration mode.
-
Configure the OSPF process.
-
Use the distribute link-state command with the appropriate instance-id.
Router# configure
Router(config)# router ospf 100
Router(config-ospf)# distribute link-state instance-id 32
 Feedback
Feedback