-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 3.4(1a)
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
- Getting Started
- Installation and Switch Management
- Switch Configuration
-
Fabric Configuration
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
SAN Device Virtualization
-
Creating Dynamic VSANs
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
Distributing Device Alias Services
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Configuring FICON
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
-
Security
-
Configuring FIPS
-
Configuring Users and Common Roles
-
Configuring SNMP
-
Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+
-
Configuring IPv4 Access Control Lists
-
Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
-
Configuring IPsec Network Security
-
Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring Fabric Binding
-
- IP Services
- Intelligent Storage Services
- Network and Switch Monitoring
- Traffic Management
- Troubleshooting
-
Launching Fabric Manager in Cisco SAN-OS Releases Prior to 3.2(1)
-
Cisco Fabric Manager Unsupported Feature List
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Configuration Limits for Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.1(x) and 3.2(x)
-
Table Of Contents
Port Security Configuration Guidelines
Configuring Port Security with Auto-Learning and CFS Distribution
Configuring Port Security with Auto-Learning without CFS
Configuring Port Security with Manual Database Configuration
Configuring Port Security Using Wizard
Forcing Port Security Activation
Copying an Active Database to the Config Database
Displaying Activated Port Security Settings
Displaying Port Security Statistics
Displaying Port Security Violations
Displaying Port Security Violations
Auto-Learning Device Authorization
Port Security Manual Configuration
Deleting Port Security Setting
Port Security Configuration Distribution
Activation and Auto-learning Configuration Distribution
Port Security Database Deletion
Port Security Database Cleanup
Configuring Port Security
All switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family provide port security features that reject intrusion attempts and report these intrusions to the administrator.
Note
Port security is only supported for Fibre Channel ports.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Port Security Configuration Guidelines
•
Port Security Manual Configuration
•
Port Security Configuration Distribution
•
Port Security Manual Configuration
•
Port Security Configuration Distribution
About Port Security
Typically, any Fibre Channel device in a SAN can attach to any SAN switch port and access SAN services based on zone membership. Port security features prevent unauthorized access to a switch port in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family in the following ways:
•
Login requests from unauthorized Fibre Channel devices (Nx ports) and switches (xE ports) are rejected.
•
All intrusion attempts are reported to the SAN administrator through system messages.
•
Configuration distribution uses the CFS infrastructure, and is limited to those switches that are CFS capable. Distribution is disabled by default.
•
Configuring the port security policy requires the ENTERPRISE_PKG license (see Chapter 10, "Obtaining and Installing Licenses").
This section includes the following topics:
Port Security Enforcement
To enforce port security, configure the devices and switch port interfaces through which each device or switch is connected, and activate the configuration.
•
Use the port world wide name (pWWN) or the node world wide name (nWWN) to specify the Nx port connection for each device.
•
Use the switch world wide name (sWWN) to specify the xE port connection for each switch.
Each Nx and xE port can be configured to restrict a single port or a range of ports.
Enforcement of port security policies are done on every activation and when the port tries to come up.
The port security feature uses two databases to accept and implement configuration changes.
•
Configuration database—All configuration changes are stored in the configuration database.
•
Active database—The database currently enforced by the fabric. The port security feature requires all devices connecting to a switch to be part of the port security active database. The software uses this active database to enforce authorization.
About Auto-Learning
You can instruct the switch to automatically learn (auto-learn) the port security configurations over a specified period. This feature allows any switch in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family to automatically learn about devices and switches that connect to it. Use this feature when you activate the port security feature for the first time as it saves tedious manual configuration for each port. You must configure auto-learning on a per-VSAN basis. If enabled, devices and switches that are allowed to connect to the switch are automatically learned, even if you have not configured any port access.
When auto-learning is enabled, learning happens only for the devices or interfaces that were not already logged into the switch. Learned entries on a port are cleaned up after you shut down that port if auto-learning is still enabled.
Learning does not override the existing configured port security policies. So, for example, if an interface is configured to allow a specific pWWN, then auto-learning will not add a new entry to allow any other pWWN on that interface. All other pWWNs will be blocked even in auto-learning mode.
No entries are learned for a port in the shutdown state.
When you activate the port security feature, auto-learning is also automatically enabled.
Note
If you enable auto-learning before activating port security, you cannot activate until auto-learning is disabled.
Port Security Activation
By default, the port security feature is not activated in any switch in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family.
By activating the port security feature, the following apply:
•
Auto-learning is also automatically enabled, which means:
–
From this point, auto-learning happens only for the devices or interfaces that were not logged into the switch.
–
You cannot activate the database until you disable auto-learning.
•
All the devices that are already logged in are learned and are added to the active database.
•
All entries in the configured database are copied to the active database.
After the database is activated, subsequent device login is subject to the activated port bound WWN pairs, excluding the auto-learned entries. You must disable auto-learning before the auto-learned entries become activated.
When you activate the port security feature, auto-learning is also automatically enabled. You can choose to activate the port security feature and disable auto-learning.
Tip
If a port is shut down because of a denied login attempt, and you subsequently configure the database to allow that login, the port does not come up automatically. You must explicitly issue a no shutdown CLI command to bring that port back online.
Port Security Configuration Guidelines
The steps to configure port security depend on which features you are using. Auto-learning works differently if you are using CFS distribution.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Configuring Port Security with Auto-Learning and CFS Distribution
•
Configuring Port Security with Auto-Learning without CFS
•
Configuring Port Security with Manual Database Configuration
Configuring Port Security with Auto-Learning and CFS Distribution
To configure port security, using auto-learning and CFS distribution, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enable port security. See the "Enabling Port Security" section.
Step 2
Enable CFS distribution. See the "Enabling Distribution" section.
Step 3
Activate port security on each VSAN. This turns on auto-learning by default. See the "Activating Port Security" section.
Step 4
Issue a CFS commit to copy this configuration to all switches in the fabric. See the "Committing the Changes" section. At this point, all switches are activated, and auto-learning.
Step 5
Wait until all switches and all hosts are automatically learned.
Step 6
Disable auto-learn on each VSAN. See the"Disabling Auto-learning" section.
Step 7
Issue a CFS commit to copy this configuration to all switches in the fabric. See the "Committing the Changes" section. At this point, the auto-learned entries from every switch are combined into a static active database that is distributed to all switches.
Step 8
Copy the active database to the configure database on each VSAN. See the "Port Security Database Copy" section.
Step 9
Issue a CFS commit to copy this configuration to all switches in the fabric. See the "Committing the Changes" section. This ensures that the configure database is the same on all switches in the fabric.
Step 10
Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration, using the fabric option. This saves the port security configure database to the startup configuration on all switches in the fabric.
Configuring Port Security with Auto-Learning without CFS
To configure port security using auto-learning without CFS, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enable port security. See the "Enabling Port Security" section.
Step 2
Activate port security on each VSAN. This turns on auto-learning by default. See the "Activating Port Security" section.
Step 3
Wait until all switches and all hosts are automatically learned.
Step 4
Disable auto-learn on each VSAN. See the "Disabling Auto-learning" section.
Step 5
Copy the active database to the configure database on each VSAN. See the "Port Security Database Copy" section.
Step 6
Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration This saves the port security configure database to the startup configuration.
Step 7
Repeat Step 1 through Step 6 for all switches in the fabric.
Configuring Port Security with Manual Database Configuration
To configure port security and manually configure the port security database, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enable port security. See the "Enabling Port Security" section.
Step 2
Manually configure all port security entries into the configure database on each VSAN. See the "Port Security Manual Configuration" section.
Step 3
Activate port security on each VSAN. This turns on auto-learning by default. See the "Activating Port Security" section.
Step 4
Disable auto-learn on each VSAN. See the "Disabling Auto-learning" section.
Step 5
Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration This saves the port security configure database to the startup configuration.
Step 6
Repeat Step 1 through Step 5 for all switches in the fabric.
Configuring Port Security Using Wizard
The Port Security Configuration wizard provides step-by-step procedures for setting up the Port Security Policy for a selected VSAN. The Port Security Configuration wizard also supports the central management through CFS,making it possible to complete the entire configuration at one place.
The wizard automatically conducts few essential operations. For example, if you want central management, the wizard conducts operations to check CFS capability, enable CFS, and issue CFS commit at the proper stages.
•
To manage security at a particular port, you do not need to run through the wizard to configure the port security policy from the VSAN wide, but you can directly edit accesses on the port itself. This operation can be done through the Port Binding dialog box. If the port's belonging switch has not enabled port security yet, the dialog box enables security first. If the port security is enabled, the dialog box will edit the policy database based on user operations.
Prerequisites
The prerequisites for configuring Port Security are as follows:
•
Port Security enabled on the switch.
•
Port Security Policy should be defined either manually by editing bound devices or switches or ports or by using autolearning.
•
Port Security Policy activated.
•
Activated and configured database synchronized through copy.
•
Activated database copied to be the startup configuration.
•
CFS should be enabled on all switches in the VSAN. A CFS master switch is selected to do all configurations. All changes will be distributed to the VSAN through the CFS commit command
To Configure Port Security follow these steps:
Step 1
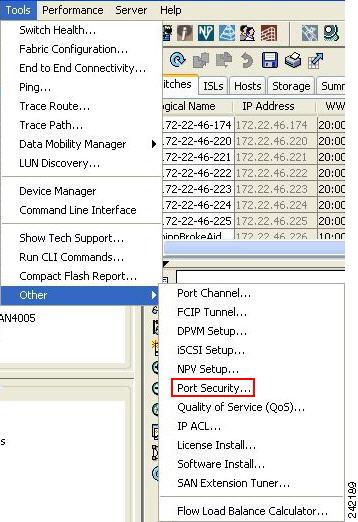
Select the Port Security Setup menu from the Fabric Manager tools menu, as shown in Figure 37-1.
Figure 37-1
Tools > Other> Port Security Menu
-OR-
Step 2
Click the Port Security
button on the toolbar.
Before launching the Port Security Setup Wizard, Fabric Manager checks the CFS capability of the switches in the VSAN.
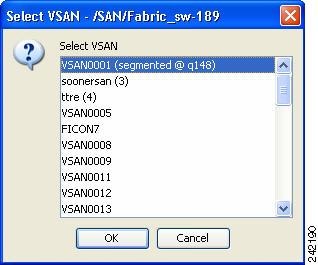
If VSAN context is not available, the wizard prompts to select VSAN as shown in Figure 37-2.
Figure 37-2 Select VSAN Window
Step 3
Select the VSAN from the list and click OK.
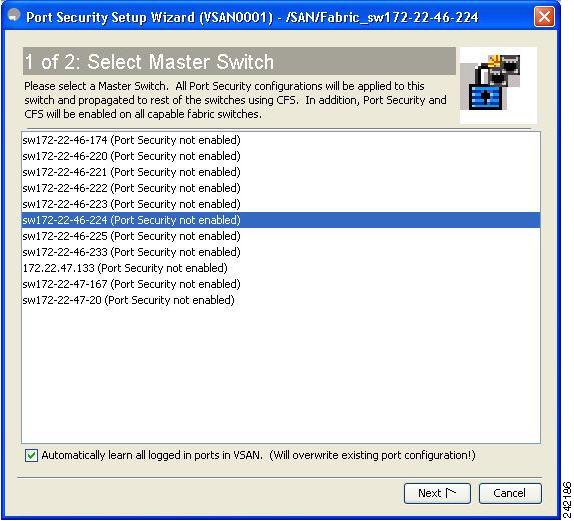
You see the first page of the Port Security Setup Wizard as shown in Figure 37-3.
Figure 37-3 Select Master Switch Page
Step 4
Do the following in the Select Master Switch page:
•
Select the required master switch.
•
Select Automatically learn all logged in ports in VSAN to Autolearn port configuration.
Step 5
Click Next to proceed.
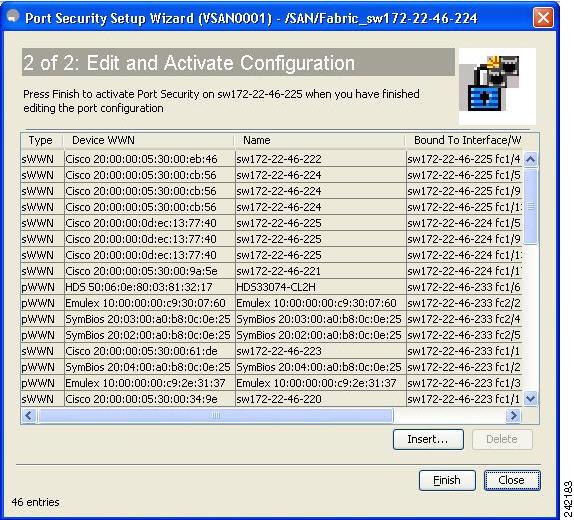
You see Edit and Activate Configuration as shown in Figure 37-4.
Figure 37-4
Edit and Activate Configuration Page
Step 6
Click Insert to create port binding.
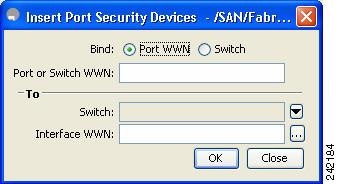
You see the Insert Port Security Devices dialog box as shown in Figure 37-5.
Figure 37-5
Insert Port Security Devices Dialog Box
Step 7
Two types of port binding can be created using the Insert Port Security Devices dialog box:
•
Port WWN-pWWN bound to an interface WWN.
•
Switch-Switch WWN bound to an interface. (Mainly useful for ISL binding.)
Step 8
Select the type of port binding by clicking the radion buttons and enter the supporting values.
Step 9
Click OK.
Step 10
Click Close to exit the Insert Port Security.... window.
Note
To delete an entry in the Edit and Activate Configuration page of the wizard, select the entry and click the Delete button.
Step 11
Click Finish to complete the Port Security Configuration for the selected switch.
Enabling Port Security
By default, the port security feature is disabled in all switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family.
To enable port security using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and then select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
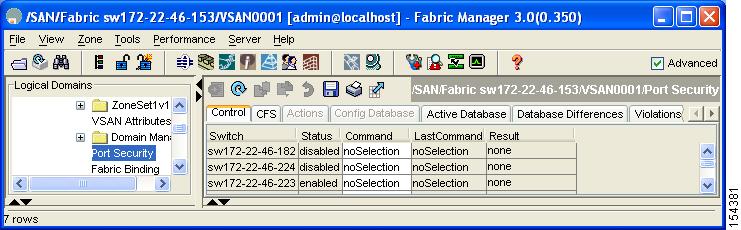
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane (see Figure 37-6).
To enable port security using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and then select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane (see Figure 37-6).
Figure 37-6 Port Security Configuration
Step 2
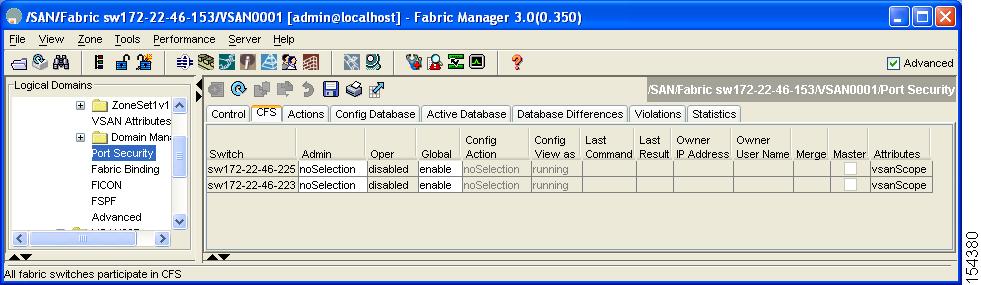
Click the CFS tab.
You see the information show in Figure 37-7.
Figure 37-7 Port Security CFS
Step 3
Enable CFS on all participating switches in the VSAN by clicking each entry in the Global column and selecting enable.
Step 4
Click Apply Changes to enable CFS distribution for the port security feature.
Step 5
Click the Control tab.
You see the port security enable state for all switches in the selected VSAN (see Figure 37-8).
Figure 37-8 Port Security Configuration
Step 6
Set the Command column to enable for each switch in the VSAN.
Step 7
Click the CFS tab and set the Command column to commit on all participating switches in the VSAN.
Step 8
Click Apply Changes to distribute the enabled port security to all switches in the VSAN.
Port Security Activation
This section includes the following topics:
•
Database Activation Rejection
•
Forcing Port Security Activation
•
Copying an Active Database to the Config Database
•
Displaying Activated Port Security Settings
•
Displaying Port Security Statistics
•
Displaying Port Security Violations
Activating Port Security
To activate port security using Fabric Manager, follow these steps: :
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Actions tab.
Step 3
Click in the Action column under Activation, next to the switch or VSAN on which you want to activate port security. You see a drop-down menu with the following options:
•
activate—Valid port security settings are activated.
•
activate (TurnLearningOff)—Valid port security settings are activated and auto-learn turned off.
•
forceActivate—Activation is forced.
•
forceActivate(TurnLearningOff)—Activation is forced and auto-learn is turned off.
•
deactivate—All currently active port security settings are deactivated.
•
NoSelection— No action is taken.
Step 4
Set the Action field you want for that switch.
Step 5
Uncheck the AutoLearn check box for each switch in the VSAN to disable auto-learning.
Step 6
Click the CFS tab and set the command column to commit on all participating switches in the VSAN.
Step 7
Click Apply Changes in Fabric Manager or Apply in Device Manager to save these changes.
Note
If required, you can disable auto-learning (see the "Disabling Auto-learning" section).
Database Activation Rejection
Database activation is rejected in the following cases:
•
Missing or conflicting entries exist in the configuration database but not in the active database.
•
The auto-learning feature was enabled before the activation. To reactivate a database in this state, disable auto-learning.
•
The exact security is not configured for each PortChannel member.
•
The configured database is empty but the active database is not.
If the database activation is rejected due to one or more conflicts listed in the previous section, you may decide to proceed by forcing the port security activation.
Forcing Port Security Activation
If the port security activation request is rejected, you can force the activation.
Note
An activation using the force option can log out existing devices if they violate the active database.
To forcefully activate the port security database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Actions tab.
Step 3
Click in the Action column under Activation, next to the switch or VSAN on which you want to activate port security and select the forceactivate option.
Step 4
Set the Action field you want for that switch.
Step 5
Click the CFS tab and set the command column to commit on all participating switches in the VSAN.
Step 6
Click Apply Changes in Fabric Manager or Apply in Device Manager to save these changes.
Database Reactivation
Tip
If auto-learning is enabled, and you cannot activate the database, you will not be allowed to proceed .
To reactivate the port security database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Disable auto-learning.
Step 2
Copy the active database to the configured database.
Tip
If the active database is empty, you cannot perform this step.
Step 3
Make the required changes to the configuration database.
Step 4
Activate the database.
Copying an Active Database to the Config Database
To copy the active database to the config database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Actions tab.
You see the switches for that VSAN.
Step 3
Check the CopyActive ToConfig check box next to the switch for which you want to copy the database.
The active database is copied to the config database when the security setting is activated.
Step 4
Uncheck the CopyActive ToConfig check box if you do not want the database copied when the security setting is activated.
Step 5
Click the CFS tab and set the command column to commit on all participating switches in the VSAN.
Step 6
Click Apply Changes to save these changes or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
Displaying Activated Port Security Settings
To display active port security settings using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Active Database tab.
You see the active port security settings for that VSAN.
Displaying Port Security Statistics
To display port security statistics using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Statistics tab.
You see the port security statistics for that VSAN.
Displaying Port Security Violations
Port violations are invalid login attempts (for example, login requests from unauthorized Fibre Channel devices). You can display a list of these attempts on a per-VSAN basis, using Fabric Manager.
To display port security violations, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Violations tab. You see the port security violations for that VSAN.
Displaying Port Security Violations
Port violations are invalid login attempts (for example, login requests from unauthorized Fibre Channel devices). You can display a list of these attempts on a per-VSAN basis, using Fabric Manager.
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Violations tab. You see the port security violations for that VSAN.
Auto-learning
This section contains the following topics:
•
Auto-Learning Device Authorization
About Enabling Auto-learning
The state of the auto-learning configuration depends on the state of the port security feature:
•
If the port security feature is not activated, auto-learning is disabled by default.
•
If the port security feature is activated, auto-learning is enabled by default (unless you explicitly disabled this option).
Tip
If auto-learning is enabled on a VSAN, you can only activate the database for that VSAN by using the force option.
Enabling Auto-learning
To enable auto-learning using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane (see Figure 37-9).
Figure 37-9 Port Security Configuration
Step 2
Click the Actions tab.
Step 3
Click in the Action column under Activation, next to the switch or VSAN on which you want to activate port security. You see a drop-down menu with the following options:
•
activate—Valid port security settings are activated.
•
activate (TurnLearningOff)—Valid port security settings are activated and auto-learn turned off.
•
forceActivate—Activation is forced.
•
forceActivate(TurnLearningOff)—Activation is forced and auto-learn is turned off.
•
deactivate—All currently active port security settings are deactivated.
•
NoSelection— No action is taken.
Step 4
Select one of the port security options for that switch.
Step 5
Check the AutoLearn check box for each switch in the VSAN to enable auto-learning.
Step 6
Click the Apply Changes icon to save these changes.
Disabling Auto-learning
To disable auto-learning using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane (see Figure 37-9).
Step 2
Click the Actions tab.
You see the switches for that VSAN.
Step 3
Uncheck the AutoLearn check box next to the switch if you want to disable auto-learning.
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to save these changes.
Auto-Learning Device Authorization
Table 37-1 summarizes the authorized connection conditions for device requests.
Authorization Scenarios
Assume that the port security feature is activated and the following conditions are specified in the active database:
•
A pWWN (P1) is allowed access through interface fc1/1 (F1).
•
A pWWN (P2) is allowed access through interface fc1/1 (F1).
•
A nWWN (N1) is allowed access through interface fc1/2 (F2).
•
Any WWN is allowed access through interface fc1/3 (F3).
•
A nWWN (N3) is allowed access through any interface.
•
A pWWN (P3) is allowed access through interface fc1/4 (F4).
•
A sWWN (S1) is allowed access through interface fc1/10-13 (F10 to F13).
•
A pWWN (P10) is allowed access through interface fc1/11 (F11).
Table 37-2 summarizes the port security authorization results for this active database. The conditions listed refer to the conditions from Table 37-1.
Port Security Manual Configuration
To configure port security on any switch in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family, follow these steps:
Step 1
Identify the WWN of the ports that need to be secured.
Step 2
Secure the fWWN to an authorized nWWN or pWWN.
Step 3
Activate the port security database.
Step 4
Verify your configuration.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Deleting Port Security Setting
About WWN Identification
If you decide to manually configure port security, be sure to adhere to the following guidelines:
•
Identify switch ports by the interface or by the fWWN.
•
Identify devices by the pWWN or by the nWWN.
•
If an Nx port is allowed to log in to SAN switch port Fx, then that Nx port can only log in through the specified Fx port..
•
If an Nx port's nWWN is bound to an Fx port WWN, then all pWWNs in the Nx port are implicitly paired with the Fx port.
•
TE port checking is done on each VSAN in the allowed VSAN list of the trunk port.
•
All PortChannel xE ports must be configured with the same set of WWNs in the same PortChannel.
•
E port security is implemented in the port VSAN of the E port. In this case the sWWN is used to secure authorization checks.
•
Once activated, the config database can be modified without any effect on the active database.
•
By saving the running configuration, you save the configuration database and activated entries in the active database. Learned entries in the active database are not saved.
Adding Authorized Port Pairs
After identifying the WWN pairs that need to be bound, add those pairs to the port security database.
Tip
Remote switch binding can be specified at the local switch. To specify the remote interfaces, you can use either the fWWN or sWWN-interface combination.
To add authorized port pairs for port security using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
Step 2
Click the Config Database tab.
Step 3
Click Create Row to add an authorized port pair.
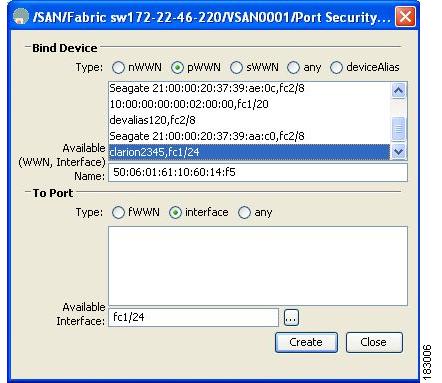
You see the Create Port Security dialog box shown in Figure 37-10.
Figure 37-10 Create Port Security Dialog Box
Step 4
Double-click the device from the available list for which you want to create the port security setting.
Step 5
Double-click the port from the available list to which you want to bind the device.
Step 6
Click Create to create the port security setting.
Step 7
Click the Apply Changes icon to save these changes.
Deleting Port Security Setting
To delete a port security setting from the configured database on a switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
Step 2
Click the Config Database tab.
You see the configured port security settings for that VSAN.
Step 3
Click the row you want to delete.
Step 4
Click Delete Row.
You see the confirmation dialog box.
Step 5
Click Yes to delete the row, or click No to close the confirmation dialog box without deleting the row.
Step 6
Click the Apply Changes icon to save these changes.
Port Security Configuration Distribution
The port security feature uses the Cisco Fabric Services (CFS) infrastructure to enable efficient database management, provide a single point of configuration for the entire fabric in the VSAN, and enforce the port security policies throughout the fabric (see Chapter 13, "Using the CFS Infrastructure").
This section includes the following topics:
•
Activation and Auto-learning Configuration Distribution
Enabling Distribution
All the configurations performed in distributed mode are stored in a pending (temporary) database. If you modify the configuration, you need to commit or discard the pending database changes to the configurations. The fabric remains locked during this period. Changes to the pending database are not reflected in the configurations until you commit the changes.
Note
Port Activation or deactivation and auto-learning enable or disable do not take effect until after a CFS commit if CFS distribution is enabled. Always follow any one of these operations with a CFS commit to ensure proper configuration. See the "Activation and Auto-learning Configuration Distribution" section.
Tip
In this case, we recommend that you perform a commit at the end of each operation: after After you activate port security and after you enable auto learning.
To enable distribution using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a VSAN and select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the port security configuration for that VSAN in the Information pane (see Figure 37-9).
Step 2
Click the Control tab.
You see the switches for that VSAN.
Step 3
Click the Command column and select enable or disable from the drop-down menu.
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to save the changes.
Locking The Fabric
The first action that modifies the existing configuration creates the pending database and locks the feature in the VSAN. Once you lock the fabric, the following situations apply:
•
No other user can make any configuration changes to this feature.
•
A copy of the configuration database becomes the pending database.
Committing the Changes
If you commit the changes made to the configurations, the configurations in the pending database are distributed to other switches. On a successful commit, the configuration change is applied throughout the fabric and the lock is released.
Activation and Auto-learning Configuration Distribution
Activation and auto-learning configurations in distributed mode are remembered merely as actions to be performed when you commit the changes in the pending database.
Learned entries are temporary and do not have any role in determining if a login is authorized or not. As such, learned entries do not participate in distribution. When you disable learning and commit the changes in the pending database, the learned entries become static entries in the active database and are distributed to all switches in the fabric. After the commit, the active database on all switches are identical and learning can be disabled.
If the pending database contains more than one activation and auto-learning configuration when you commit the changes, then the activation and auto-learning changes are consolidated and the behavior may change (see Table 37-3).
Table 37-3 Scenarios for Activation and Auto-learning Configurations in Distributed Mode
A and B exist in the configuration database, activation is not done and devices C,D are logged in.
1.
You activate the port security database and enable auto-learning.
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {A,B, C1 , D*}
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {null}
pending database = {A,B + activation to be enabled}
2.
A new entry E is added to the configuration database.
configuration database = {A,B, E}
active database = {A,B, C*, D*}
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {null}
pending database = {A,B, E + activation to be enabled}
3.
You issue a commit.
Not applicable
configuration database = {A,B, E}
active database = {A,B, E, C*, D*}
pending database = empty
A and B exist in the configuration database, activation is not done and devices C,D are logged in.
1.
You activate the port security database and enable auto-learning.
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {A,B, C*, D*}
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {null}
pending database = {A,B + activation to be enabled}
2.
You disable learning.
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {A,B, C, D}
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {null}
pending database = {A,B + activation to be enabled +
learning to be disabled}3.
You issue a commit.
Not applicable
configuration database = {A,B}
active database = {A,B} and devices C and D are logged out. This is equal to an activation with auto-learning disabled.
pending database = empty
1 The * (asterisk) indicates learned entries.
Tip
In this case, we recommend that you perform a commit at the end of each operation: after you activate port security and after you enable auto learning.
Database Merge Guidelines
A database merge refers to a union of the configuration database and static (unlearned) entries in the active database. See the CFS Merge Support, page 13-9 for detaileds concepts.
When merging the database between two fabrics, follow these guidelines:
•
Verify that the activation status and the auto-learning status is the same in both fabrics.
•
Verify that the combined number of configurations for each VSAN in both databases does not exceed 2K.
CautionIf you do not follow these two conditions, the merge will fail. The next distribution will forcefully synchronize the databases and the activation states in the fabric.
Database Interaction
This section includes the following topics:
•
Port Security Database Deletion
•
Port Security Database Cleanup
Database Scenarios
Figure 37-11 depicts various scenarios to depict the active database and the configuration database status based on port security configurations.
Figure 37-11 Port Security Database Scenarios
Port Security Database Copy
Tip
We recommend that you copy the active database to the config databaseafter disabling auto-learning. This action will ensure that the configuration database is in sync with the active database. If distribution is enabled, this command creates a temporary copy (and consequently a fabric lock) of the configuration database. If you lock the fabric, you need to commit the changes to the configuration databases in all the switches.
To copy the active database to the configuration database, using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a Fabric, expand a VSAN and then select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
Step 2
Select the Actions tab. You see all the configuration databases.
Step 3
Select the appropriate configuration database and check the Copy Active to Config checkbox.
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to save your changes.
To view the differences between the active database and the configuration database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a Fabric, expand a VSAN and then select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the Port Security information in the Information pane.
Step 2
Select the Database Differences tab. You see all the configuration databases.
Step 3
Select the appropriate configuration database. Select the Active or Config option to compare the differences between the selected database and the active or configuration database.
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to save your changes.
Port Security Database Deletion
Tip
If the distribution is enabled, the deletion creates a copy of the database. An explicit deletion is required to actually delete the database.
To delete a port security database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand a Fabric, expand a VSAN and then select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the Port Security information in the Information pane.
Step 2
Select the Config Database tab. You see all the configuration databases.
Step 3
Select the appropriate configuration database and click the Delete Row button.
Step 4
Click Yes if you want to delete the configuration database.
Port Security Database Cleanup
To clear all existing statistics from the port security database for a specified VSAN using Fabric Manager, follow the steps below:
Step 1
Expand a Fabric, expand a VSAN and then select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the Port Security information in the Information pane (see Figure 37-9).
Step 2
Select the Statistics tab.
You see all the configuration databases.
Step 3
Select the appropriate configuration database and check the Clear option.
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon o save your changes.
To clear any learned entries in the active database for a specified interface within a VSAN using Fabric Manager, follow the steps below:
Step 1
Expand a Fabric, expand a VSAN and then select Port Security in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the Port Security information in the Information pane.
Step 2
Select the Actions tab. You see all the configuration databases.
Step 3
Select the appropriate configuration database and check the AutoLearn option.
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to save your changes.
Note
You can clear the Statistics and the AutoLearn option only for switches that are local and do not acquire locks. Also, learned entries are only local to the switch and do not participate in distribution.
Default Settings
Table 37-6 lists the default settings for all port security features in any switch.
Auto-learn
Enabled if port security is enabled.
Port security
Disabled.
Distribution
Disabled.
Note
Enabling distribution enables it on all VSANs in the switch.

 Feedback
Feedback