MACsec, defined in
802.1AE, provides MAC-layer encryption over wired networks by using out-of-band
methods for encryption keying. The MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) Protocol provides
the required session keys and manages the required encryption keys. MKA and
MACsec are implemented after successful authentication using the 802.1x
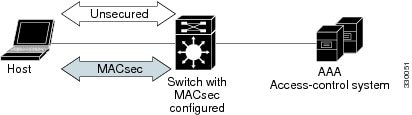
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) framework. Only host facing links
(links between network access devices and endpoint devices such as a PC or IP
phone) can be secured using MACsec.
A switch using MACsec
accepts either MACsec or non-MACsec frames, depending on the policy associated
with the client. MACsec frames are encrypted and protected with an integrity
check value (ICV). When the switch receives frames from the client, it decrypts
them and calculates the correct ICV by using session keys provided by MKA. The
switch compares that ICV to the ICV within the frame. If they are not
identical, the frame is dropped. The switch also encrypts and adds an ICV to
any frames sent over the secured port (the access point used to provide the
secure MAC service to a client) using the current session key.
The MKA Protocol
manages the encryption keys used by the underlying MACsec protocol. The basic
requirements of MKA are defined in 802.1x-REV. The MKA Protocol extends 802.1x
to allow peer discovery with confirmation of mutual authentication and sharing
of MACsec secret keys to protect data exchanged by the peers.
The EAP framework
implements MKA as a newly defined EAP-over-LAN (EAPOL) packet. EAP
authentication produces a master session key (MSK) shared by both partners in
the data exchange. Entering the EAP session ID generates a secure connectivity
association key name (CKN). Because the switch is the authenticator, it is also
the key server, generating a random 128-bit secure association key (SAK), which
it sends it to the client partner. The client is never a key server and can
only interact with a single MKA entity, the key server. After key derivation
and generation, the switch sends periodic transports to the partner at a
default interval of 2 seconds.
The packet body in an
EAPOL Protocol Data Unit (PDU) is referred to as a MACsec Key Agreement PDU
(MKPDU). MKA sessions and participants are deleted when the MKA lifetime (6
seconds) passes with no MKPDU received from a participant. For example, if a
client disconnects, the participant on the switch continues to operate MKA
until 6 seconds have elapsed after the last MKPDU is received from the client.

 Feedback
Feedback