Ports
Sources
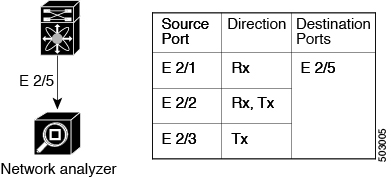
The interfaces from which traffic can be monitored are called SPAN sources. Sources designate the traffic to monitor and whether to copy ingress (Rx), egress (Tx), or both directions of traffic.
SPAN sources include the following:
-
Ethernet ports (but not subinterfaces)
-
The inband interface to the control plane CPU

Note
When you specify the supervisor inband interface as a SPAN source, the device monitors all packets that are sent by the Supervisor CPU.
-
VLANs
-
When you specify a VLAN as a SPAN source, all supported interfaces in the VLAN are SPAN sources.
-
VLANs can be SPAN sources only in the ingress direction.
-
-
Satellite ports and host interface port channels on the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender (FEX)
-
These interfaces are supported in Layer 2 access mode and Layer 2 trunk mode. They are not supported in Layer 3 mode, and Layer 3 subinterfaces are not supported.
-
Cisco Nexus 9300 and 9500 platform switches support FEX ports as SPAN sources in the ingress direction for all traffic and in the egress direction only for known Layer 2 unicast traffic flows through the switch and FEX. Routed traffic might not be seen on FEX HIF egress SPAN.
-
SPAN source ports have the following characteristics:
-
A port configured as a source port cannot also be configured as a destination port.
-
If you use the supervisor inband interface as a SPAN source, all packets generated by the supervisor hardware (egress) are monitored.

Note
Rx is from the perspective of the ASIC (traffic egresses from the supervisor over the inband and is received by the ASIC/SPAN).
 Note |
A single SPAN session can include mixed sources in any combination of the above. |
Destinations
SPAN destinations refer to the interfaces that monitor source ports. Destination ports receive the copied traffic from SPAN sources. SPAN destinations include the following:
-
Ethernet ports
-
Port channels
-
CPU as destination port
-
Uplink ports on Cisco Nexus 9300 Series switches
 Note |
FEX ports are not supported as SPAN destination ports. |
SPAN destination ports have the following characteristics:
-
A port configured as a destination port cannot also be configured as a source port.
-
The same destination interface cannot be used for multiple SPAN sessions.
-
Destination ports do not participate in any spanning tree instance. SPAN output includes bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) Spanning Tree Protocol hello packets.
 Feedback
Feedback