Overview
Cisco Nexus Data Broker (NDB) is a solution that builds scalable packet broker network solutions, providing a software-defined approach for monitoring both out-of-band and inline network traffic using Cisco Nexus Dashboard Data Broker controller software and Cisco Nexus switches.
-
NDB enables packet monitoring for performance monitoring, intrusion detection, and compliance checking.
-
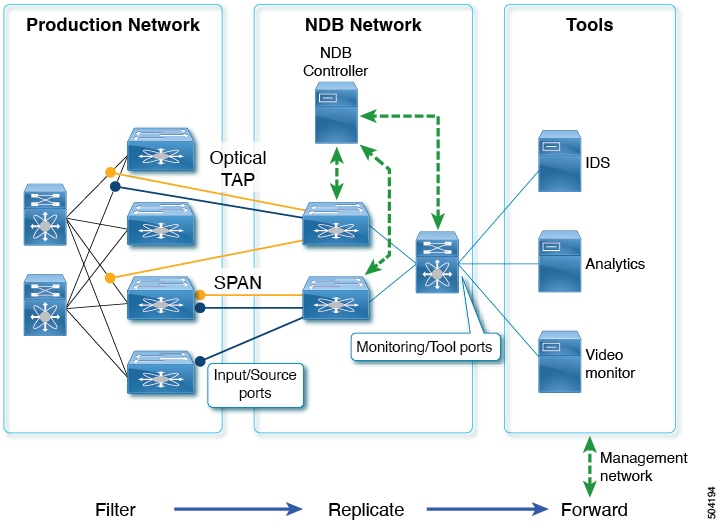
Header stripping is performed on NDB switches, allowing traffic to be filtered, replicated, and stripped of headers before being forwarded to monitoring tools.
-
Input/source ports are where header stripping occurs, and monitoring/tool ports connect directly to the tools.
Header Stripping and Feature Benefits
The reasons for removing the header are as follows:
-
Some monitoring tools do not understand an encapsulated packet.
-
Presence of an additional header skews the analytics data.
-
Addition of a header adds to the packet size, hampering the optimization of the amount of data that is sent to and processed by the tools.
The benefits of the packet header or label stripping feature of Cisco Nexus Data Broker switch are as follows:
-
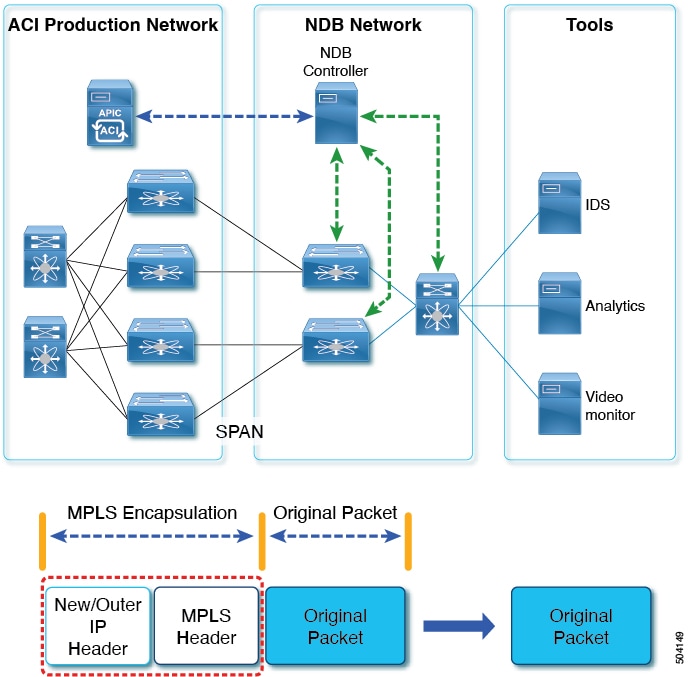
Enable Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) label stripping
-
Native support for VXLAN header stripping from copy traffic
-
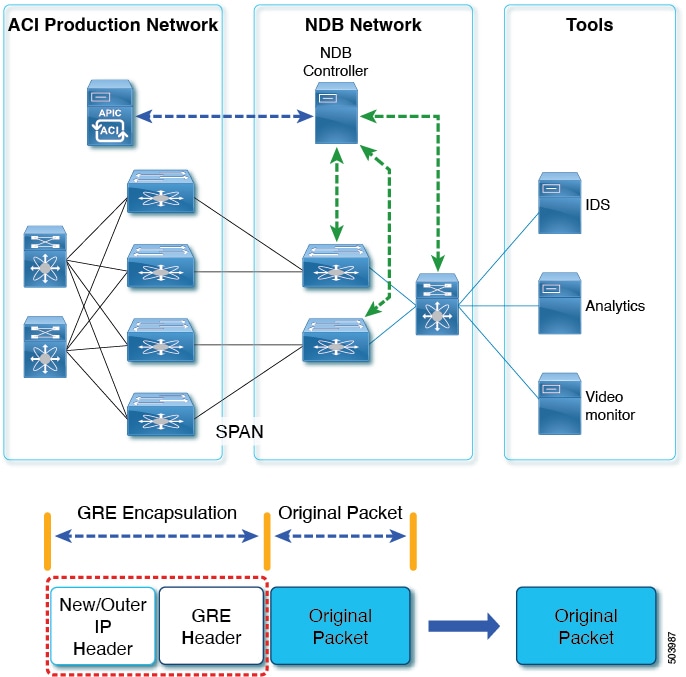
Support for Generic Route Encapsulation (GRE) header stripping
-
Q-in-Q VLAN header stripping at egress
NDB aligns the legacy VXLAN, IVXLAN, ERSPAN, GRE, and MPLS stripping functionality to the Overlay Forwarding Manager (OFM) based model. The OFM hosts the command line interface (CLI) for header stripping functionality.
This chapter contains the following sections:

 Feedback
Feedback