Functionality
PTP supports the following functionality:
-
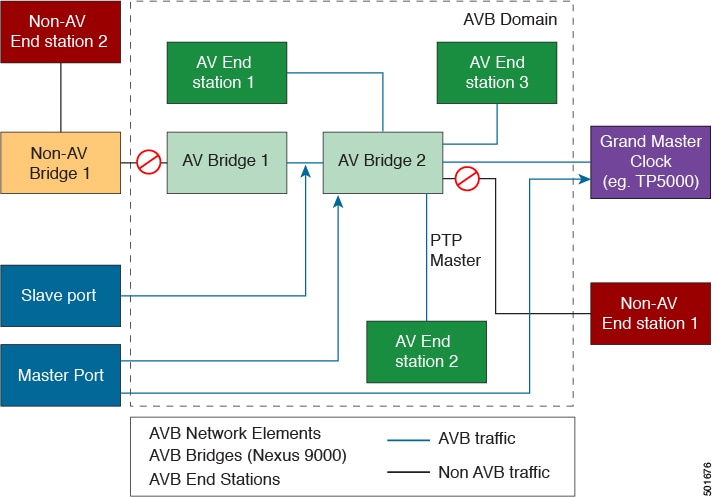
Multicast and unicast PTP transport—In the multicast transport mode, PTP uses multicast destination IP address 224.0.1.129 as per IEEE 1588 standards for communication between devices. For the source IP address, it uses the user configurable global IP address under the PTP domain. In the unicast transport mode, PTP uses configurable unicast source and destination IP addresses that can be configured under an interface. In both, the unicast and the multicast modes, PTP uses UDP ports, 319 for event messages and 320 for general messages communication between devices.
-
PTP multicast configuration is supported only under physical interface for L2 or L3.
-
PTP unicast configuration is supported only under physical interface for L2 or L3.
-
PTP is supported with virtual interfaces such as Port-channel, SVI, and tunnel only when configured on associated physical interfaces. When PTP unicast is configured on L2/L3 Port-Channel members, the unicast source IP configuration is derived from the PTP VLAN SVI primary IP or L3 Port-Channel primary IP respectively.
-
PTP encapsulation over UDP over IP—PTP uses UDP as the transport protocol over IP. In both, the unicast and multicast modes, PTP uses UDP ports 319 for event messages and 320 for general messages communication between devices. L2 encapsulation mode is not supported.
-
PTP profiles—PTP supports default (1588) , AES67, and SMPTE 2059-2 profiles. They all have different ranges of sync and delay request intervals. For information on the default profile, refer to IEEE 1588. For more information on AES67 and SMPTE 2059-2, refer to the respective specifications.
-
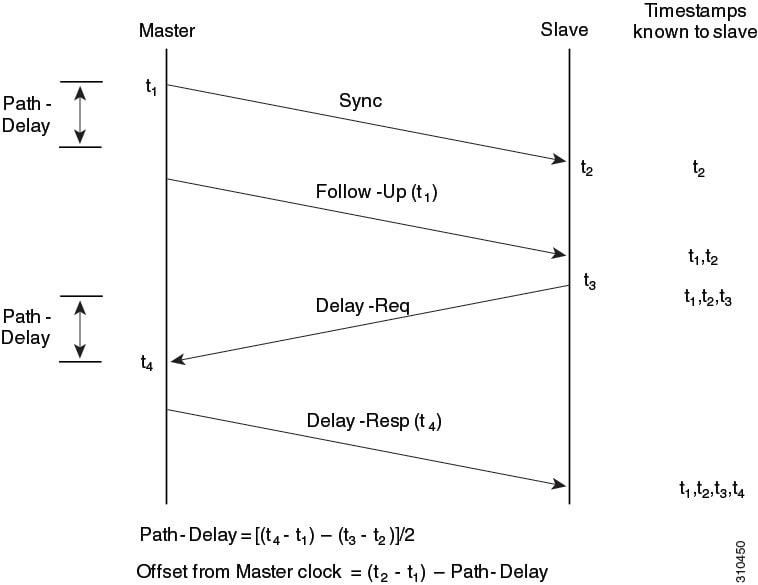
Path delay measurement—We support delay request and response mechanism to measure the delay between the master and slave devices. Peer delay request and response mechanism is not supported.
-
Message intervals—You can configure the interval at which the announce, sync, and delay request messages needs to be sent between devices.
-
Best master clock (BMC) selection—BMC algorithm is used to select master, slave, and passive states of the PTP enabled interfaces based on the Announce message received as per 1588 specification.
-
PTP Offload - This feature distributes the PTP functionality to the line cards and allows scaling of the number of PTP sessions that are supported on the system. This feature is available for Cisco Nexus 9500 platform switches with N9K-X97160YC-EX line card, 9700-FX, 9636C-R, 9636Q-R, 9624D-R2, and 9636C-RX line cards.
-
Dynamic Unicast - This feature allows BMCA to select roles dynamically as follows, rather than assigning static roles.
-
Use the ptp peer <ipv4>/<ipv6> command to configure Peer IPs.
-
Port remains in a Listening state until the Peer IP is reachable, when it transitions to Master state.
-
Announce packets are sent as soon as the peer is reachable.
-
Based on Announce packet (using BMCA), Role will be decided. Port state transitions accordingly.
-
-
PTP Time Distribution Hold - In a properly synchronized PTP network, when any PTP node goes down and comes up, the PTP clock is synchronized to its primary time source (GM). During this process, the local node has significant correction and it tries to correct its local clock. At that time, the node can send incorrect time to the downstream nodes and cause issues for all downstream nodes. The Time Distribution (TD) hold feature, introduced in Cisco NX-OS Release 10.5(1)F, resolves this issue by ensuring that the node is properly synchronized to its primary source and distributes time to the downstream nodes during boot up.
The TD hold feature holds the time distribution until a Boundary Clock (BC) node locks to the primary time source and settles down to the target correction value. The TD hold enabled node receives all PTP packets, does the normal state change, and synchronizes time, but it does not send any PTP packets out.

Note
If all nodes reboot at the same time (with a difference of few seconds), each node will be in active hold time, which sometimes results in no nodes having secondary port. This leads to the BMC taking a long time to find the best clock. Hence, the user needs to take this into account when enabling this feature.
-
High Availability - Stateful restarts are not supported for PTP. After a reboot or a supervisor switchover, the running configuration is applied. For more information on high availability, see the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS High Availability and Redundancy Guide.
-
Mixed Mode - PTP supports Mixed mode for delivering PTP messages, which is detected automatically by Cisco Nexus device, based on the type of delay_req message received from connected client and no configuration is required. In this mode when slave sends delay_req in unicast message, master also replies with unicast delay_resp message.
 Feedback
Feedback