-
- Administration User Interface Reference
- Guest Access User Interface Reference
- Web Portals Customization Reference
- Policy User Interface Reference
- Operations User Interface Reference
- Network Access Flows
- Switch and Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Required to Support Cisco ISE Functions
- Supported Management Information Bases in Cisco ISE
- Admin Portal
- Setup Assistant
- Cisco ISE Licensing Impact on Setup Assistant
- Run the Setup Assistant
- Setup Assistant Overwrites Previous Configurations
- Identify Policy Requirements Page in Setup Assistant
- Configure Network Access Service Page in Setup Assistant
- Select Network Device Types Page in Setup Assistant
- Review and Confirm Your Choices Page in Setup Assistant
- Filter Data on Listing Pages
- Cisco ISE Internationalization and Localization
- Supported Languages
- End-User Web Portal Localization
- Support for UTF-8 Character Data Entry
- UTF-8 Credential Authentication
- UTF-8 Policies and Posture Assessment
- Cisco NAC and MAC Agent UTF-8 Support
- UTF-8 Support for Messages Sent to Supplicant
- Reports and Alerts UTF-8 Support
- UTF-8 Character Support in the Portals
- UTF-8 Support Outside the User Interface
- Support for Importing and Exporting UTF-8 Values
- UTF-8 Support on REST
- UTF-8 Support for Identity Stores Authorization Data
Navigate the Admin portal
- Admin Portal
- Setup Assistant
- Filter Data on Listing Pages
- Cisco ISE Internationalization and Localization
- MAC Address Normalization
- Admin Features Limited by Role-Based Access Control Policies
Admin Portal
The Admin portal is an administration console from which you can manage various identity services. The following figure shows the main elements of this portal.

Cisco ISE Dashboard
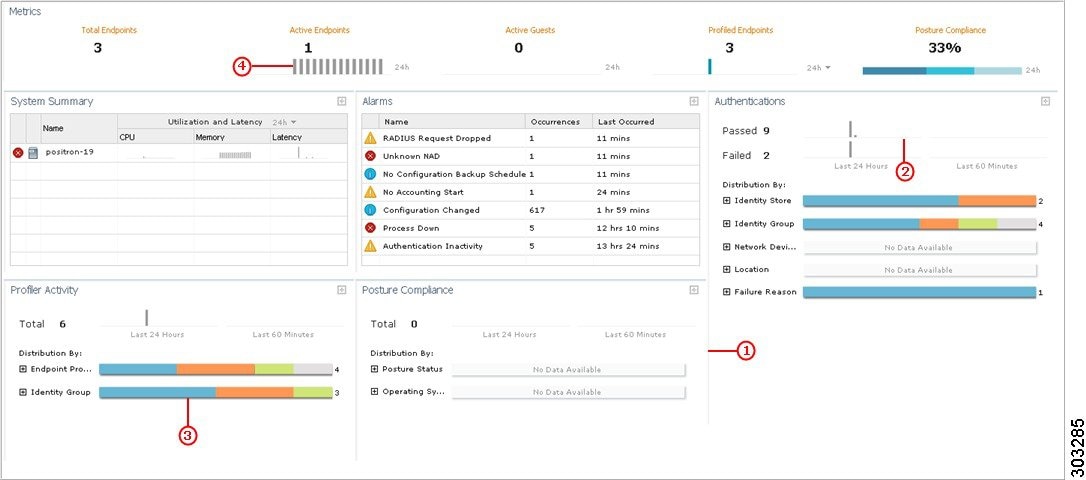
The Cisco ISE Dashboard displays live consolidated and correlated statistical data that is is essential for effective monitoring and troubleshooting. Dashboard elements show activity over 24 hours, unless otherwise noted. The following figure shows some of the information available on the Cisco ISE Dashboard.
Setup Assistant
The Setup Assistant guides you through a series of questions in a wizard-like interface retaining your responses and using them to configure Cisco ISE directly. It enables you to set up a basic working Cisco ISE configuration as a proof-of-concept for your network. Your answers to the questions impact these Cisco ISE features: authentication, authorization, profiling, posture, client provisioning, guest services, and support for personal devices.
- Cisco ISE Licensing Impact on Setup Assistant
- Run the Setup Assistant
- Setup Assistant Overwrites Previous Configurations
- Identify Policy Requirements Page in Setup Assistant
- Configure Network Access Service Page in Setup Assistant
- Select Network Device Types Page in Setup Assistant
- Review and Confirm Your Choices Page in Setup Assistant
Cisco ISE Licensing Impact on Setup Assistant
Setup Assistant functionality depends on the Cisco ISE license that you have applied to your configuration.
Run the Setup Assistant
When you start Cisco ISE for the first time, you are prompted to run the Setup Assistant. If you choose not to run it then, you can run it again later.
To perform this task, you must be a Super Admin. You can only run the Setup Assistant on the standalone or Primary Administration Node (PAN).
Setup Assistant Overwrites Previous Configurations
Each time you run the Setup Assistant, Cisco ISE overwrites previous settings, which can critically impact your configuration in the following ways:
-
All authentication, authorization, client provisioning, and posture policies are deleted and replaced, including any that you added without using the Setup Assistant.
-
Other settings, such as policy elements and web portal customizations, are overwritten with any newly specified values. If you do not enter anything for the optional settings, the Setup Assistant resets them to their default values.
Identify Policy Requirements Page in Setup Assistant
Wired or Wireless
You must indicate whether you want to support wired or wireless connections, or both. If you are using a Cisco ISE Wireless License, the wired option is unavailable.
These choices impact the policies that Cisco ISE creates, and also dictate other required responses. For example, if you choose wired, you can also indicate whether your network supports IP phones.
You must also indicate whether or not the wired connections are monitored or if network access must be enforced based on compliance:
-
Monitor generates non-compliance logs and reports, but does not require that users or devices comply with the defined policies.
In monitoring mode, posture and guest policies are ignored. If you support wired connections in monitoring mode, the Setup Assistant disables the guest and posture choices on the next page to prevent unauthorized computer and guest access.
If you support wired and wireless connections, you can enable the guest and posture features, but they will apply only to the wireless connections. The wireless connections always runs in enforcement mode.
Protected Subnets
You must indicate which subnets should are inaccessible by guests or noncompliant endpoints. This information is used when creating the downloadable ACLs.
Configure Network Access Service Page in Setup Assistant
User Authentication
Users belonging to these groups will be granted network access as employees and be allowed to create guest accounts using the Sponsor portal.
-
Internal users—If you choose to create an internal user, Cisco ISE creates a single user using the name you enter and assigns the user to the default Employee and ALL_ACCOUNTS user identity groups. You can verify this in the Administration > Identity Management > Identities > Users page after setup completes.
Because the Setup Assistant provides only the basic Cisco ISE configuration to demonstrate its functionality in your network, you cannot use it to import additional users into the internal user database. You can add additional internal users using the Admin portal after you complete the Setup Assistant.
-
Active Directory—If you choose to join the Active Directory domain, Cisco ISE adds the indicated AD domain and joins to it. After joining the domain, you must choose an Active Directory group. All users belonging to this group will be able to authenticate using Dot1x and create guests using the Sponsor portal. You can verify this from the Administration > Identity Management > External Identity Sources > Active Directory page after setup completes.
Posture Compliance
When you enable posture using the Setup Assistant, Cisco ISE checks for antispyware and antivirus definitions and installations on connected endpoints.
You must indicate whether you want to assess or assess and enforce posture compliance for employees and guests:
If you want to force Cisco ISE to redirect noncompliant endpoints to a remediation server before granting network access, enter the proxy server IP address.
If you enable posture compliance, Cisco ISE will:
-
Create the downloadable ACLs on the page. All DACLs created by the Setup Assistant include the prefix AutoGen, such as: AutoGen_DACL_PrePostureWired.
-
Create authorization profiles on the page. Authorization profiles created by the Setup Assistant include the prefix AutoGen, such as: AutoGen_profile_Byod_CWA.
-
Create authorization conditions on the and pages. Authorization conditions created by the Setup Assistant include the prefix AutoGen, such as: AutoGen_condition_Android_Devices or AutoGen_condition_GuestWired.
-
Create client provisioning policies on the page. Client provisioning policies created by the Setup Assistant include the prefix AutoGen, such as: AutoGen_Provisioning.
-
Create posture policies on the page. Posture policies created by the Setup Assistant include the prefix AutoGen, such as: AutoGen_Policy_Check_For_AS_Definition_Mac_Employee.
-
Create authorization policies on the page. Authorization policies created by the Setup Assistant include the prefix AutoGen, such as: AutoGen_policy_Registered_Wireless_Devices.
-
Create authentication policies on the page. Authorization policies created by the Setup Assistant include the prefix AutoGen, such as: AutoGen_AuthNPolicy_MAB.
Endpoint Profiling
Endpoint profiling discovers, identifies, and determines the capabilities of all attached endpoints on your network. If you enable endpoint profiling, Cisco ISE will:
Proxy Settings
Cisco ISE uses the proxy server to download Cisco-defined posture checks and client provisioning resources required for assessing posture of endpoints and allowing personal devices on the network. If you configure these proxy settings, Cisco ISE will update the settings on the page.
Guest User Support
To support guest users, you must create a sponsor user. Cisco ISE creates a single user using the name you enter and assigns the user to the default ALL_ACCOUNTS user identity group, which defines the user as a sponsor user. You can verify this from the page after setup completes.
If you add a simplified URL, Cisco ISE updates the Portal Name settings at the top of the page.
Support for Personal Devices
You can add a simplified URL for employees to use to access the My Devices portal, and Cisco ISE updates the Portal Namesettings at the top of the the page.
Web Portal Customizations
Select Network Device Types Page in Setup Assistant
Switches and Wireless Controllers
Cisco ISE adds the switches and wireless controllers to the page, updates the SNMP settings, and adds the RADIUS shared secret to the Authentication Settings option.
Depending on the choices you made previously, you must configure the switches and wireless controllers. Click the Wired or Wireless Network Diagram links to display sample network topologies that illustrate the required configuration details.
Review and Confirm Your Choices Page in Setup Assistant
Review Your Selection
Network Device Configuration
Configuration details for each configured switch and WLC display separately. Cisco ISE does not automatically update these configurations on the devices. If you want to completely replace the current device configuration, copy and paste the entire configuration. Alternatively, you can just copy the specific sections with the configuration changes you need. You can access the most current copy of the settings after exiting the Setup Assistant by choosing .
ISE Configuration
The ISE Configuration tab displays details about each setting, policy, profile, DACL, and network device added to Cisco ISE.
Filter Data on Listing Pages
Listing pages include tools that enable you to filter and customize the displayed information.
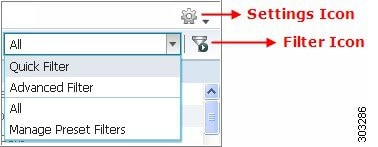
Data Filters in Listing Pages
You can customize and filter the information that displays in the listing pages using the settings and filter icons.
Customize the Displayed Field Attributes
You can customize the field attributes displayed in the listing pages. The available and default options vary based on the specific listing page.
Filter Data by Field Attributes Using the Quick Filter
The Quick Filter allows you to enter a value for any of the field attributes displayed in the listing page, refreshes the page, and lists only those records that match your filter criteria.
Filter Data by Conditions Using the Advanced Filter
The Advanced Filter allows you to filter information based on specified conditions, such as, First Name = Mike and User Group = Employee. You can specify more than one condition.
Create Custom Filters
You can create and save custom filters and modify the filter criteria in preset filters. Custom filters are not saved in the Cisco ISE database. You can only access them using the same computer and browser used to create them.
Cisco ISE Internationalization and Localization
Cisco ISE internationalization adapts the user interface for supported languages. Localization of the user interface incorporates locale-specific components and translated text.
In Cisco ISE, internalization and localization support focuses on support for non-English text in UTF-8 encoding to the end-user facing portals and on selective fields in the Admin portal.
Supported Languages
Cisco ISE, provides localization and internalization support for the following languages and browser locales:
End-User Web Portal Localization
The Guest, Sponsor, My Devices, and Client Provisioning portals are localized into all supported languages and locales. This includes text, labels, messages, field names, and button labels. If the client browser requests a locale that is not mapped to a template in Cisco ISE, the portals display content using the English template.
Using the Admin portal, you can modify the fields used for the Guest, Sponsor, and My Devices portals for each language individually, and you can add additional languages. Currently, you cannot customize these fields for the Client Provisioning portal.
You can further customize the Guest portal by uploading HTML pages to Cisco ISE. When you upload customized pages, you are responsible for the appropriate localization support for your deployment. Cisco ISE provides a localization support example with sample HTML pages, which you can use as a guide. Cisco ISE provides the ability to upload, store, and render custom internationalized HTML pages.
 Note | NAC and MAC agent installers and WebAgent pages are not localized. |
Support for UTF-8 Character Data Entry
Cisco ISE fields that are exposed to the end user (through the Cisco NAC agent, or supplicants, or through the Sponsor, Guest, My Devices, and Client Provisioning portals) support UTF-8 character sets for all languages. UTF-8 is a multibyte-character encoding for the unicode character set, which includes many different language character sets, such as Hebrew, Sanskrit, and Arabic.
Character values are stored in UTF-8 in the administration configuration database, and the UTF-8 characters display correctly in reports and user interface components.
- UTF-8 Credential Authentication
- UTF-8 Policies and Posture Assessment
- Cisco NAC and MAC Agent UTF-8 Support
- UTF-8 Support for Messages Sent to Supplicant
- Reports and Alerts UTF-8 Support
- UTF-8 Character Support in the Portals
- UTF-8 Support Outside the User Interface
- Support for Importing and Exporting UTF-8 Values
- UTF-8 Support on REST
- UTF-8 Support for Identity Stores Authorization Data
UTF-8 Credential Authentication
Network access authentication supports UTF-8 username and password credentials. This includes RADIUS, EAP, RADIUS proxy, RADIUS token, and web authentication from the Guest and Administrative portal login authentications. UTF-8 support for user name and password applies to authentication against the local identity store as well as external identity stores.
UTF-8 authentication depends on the client supplicant that is used for network login. Some Windows native supplicants do not support UTF-8 credentials. If you are experiencing difficulties with a Windows native supplicant, the following Windows hotfixes may be helpful:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;957218
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;957424

NoteRSA does not support UTF-8 users, hence UTF-8 authentication with RSA is not supported. Likewise, RSA servers, which are compatible with Cisco ISE 1.2, do not support UTF-8.
UTF-8 Policies and Posture Assessment
Policy rules in Cisco ISE that are conditioned on attribute values may include UTF-8 text. Rule evaluation supports UTF-8 attribute values. In addition, you can configure conditions with UTF-8 values through the Administrative portal.
Posture requirements can be modified as File, Application, and Service conditions based on a UTF-8 character set. This includes sending UTF-8 requirement values to the NAC agent. The NAC agent then assesses the endpoint accordingly, and reports UTF-8 values, when applicable.
Cisco NAC and MAC Agent UTF-8 Support
The Cisco NAC agent supports internationalization of text, messages, and any UTF-8 data that is exchanged with Cisco ISE. This includes requirement messages, requirement names, and file and process names that are used in conditions.
The following limitations apply:
Cisco NAC and MAC agent interfaces currently do not support localization.
WebAgent does not support UTF-8 based rules and requirements.
If an acceptable use policy (AUP) is configured, the policy pages are provided on the client side, based on the browser locale and the set of languages that are specified in the configuration. You are responsible for providing a localized AUP bundle or site URL.
UTF-8 Support for Messages Sent to Supplicant
RSA prompts and messages are forwarded to the supplicant using a RADIUS attribute REPLY-MESSAGE, or within EAP data. If the text contains UTF-8 data, it is displayed by the supplicant, based on the client’s local operating system language support. Some Windows-native supplicants do not support UTF-8 credentials.
Cisco ISE prompts and messages may not be in sync with the locale of the client operating system on which the supplicant is running. You must align the end-user supplicant locale with the languages that are supported by Cisco ISE.
Reports and Alerts UTF-8 Support
Monitoring and troubleshooting reports and alerts support UTF-8 values for relevant attributes, for Cisco ISE supported languages, in the following ways:
UTF-8 Character Support in the Portals
Many more character sets are supported in Cisco ISE fields (UTF-8) than are currently supported for localizations in portals and end-user messages. For example, Cisco ISE does not support right-to-left languages, such as Hebrew or Arabic, even though the character sets themselves are supported.
The following table lists the fields in the Admin and end-user portals that support UTF-8 characters for data entry and viewing, with the following limitations:
-
Cisco ISE does not support administrator passwords with UTF-8 characters.
-
Cisco ISE does not support UTF-8 characters in certificates.
UTF-8 Support Outside the User Interface
This section contains the areas outside the Cisco ISE user interface that provide UTF-8 support.
Debug Log and CLI-Related UTF-8 Support
Attribute values and posture condition details appear in some debug logs; therefore, all debug logs accept UTF-8 values. You can download debug logs containing raw UTF-8 data that can be viewed with a UTF-8 supported viewer.
ACS Migration UTF-8 Support
Cisco ISE, allows for the migration of ACS UTF-8 configuration objects and values. Migration of some UTF-8 objects may not be supported by Cisco ISE UTF-8 languages, which might render some of the UTF-8 data that is provided during migration as unreadable using Administrative portal or report methods. You must convert unreadable UTF-8 values (that are migrated from ACS) into ASCII text.
Support for Importing and Exporting UTF-8 Values
UTF-8 Support on REST
UTF-8 Support for Identity Stores Authorization Data
MAC Address Normalization
ISE supports normalization of MAC address entered by you in any of the following formats:
For the following ISE windows, you can provide full or partial MAC address:
-
Policy > Authorization
-
Policy > Policy Elements > Conditions > Authorization
-
Authentications > Filters (Endpoint and Identity columns)
-
Global Search
-
Operations > Reports > Reports Filters
-
Operations > Diagnostic Tools > General Tools > Endpoint Debug
For the following ISE windows, you should provide full MAC address (six octets separated by ‘:’ or ‘-’ or ‘.’):
-
Operations > Endpoint Protection Services Adaptive Network Control
-
Operations > Troubleshooting > Diagnostic Tools > General Tools > RADIUS Authentication Troubleshooting
-
Operations > Troubleshooting > Diagnostic Tools > General Tools > Posture Troubleshooting
-
Administration > Identities > Endpoints
-
Administration > System > Deployment
-
Administration > Logging > Collection Filter
REST APIs also support normalization of full MAC address.
Valid octet can contain only 0-9, a-f or A-F.
Admin Features Limited by Role-Based Access Control Policies
Cisco ISE provides role-based access control (RBAC) policies that ensure security by restricting administrative privileges. RBAC policies are associated with default admin groups to define roles and permissions. A standard set of permissions (for menu as well as data access) is paired with each of the predefined admin groups, and is thereby aligned with the associated role and job function.
Some features in the user interface require certain permissions for their use. If a feature is unavailable, or you are not allowed to perform a specific task, your admin group may not have the necessary permissions to perform the task that utilizes the feature.
Regardless of the level of access, any administrator account can modify or delete objects for which it has permission, on any page that it can access. Read-only functionality is unavailable for any administrative access.
 Feedback
Feedback