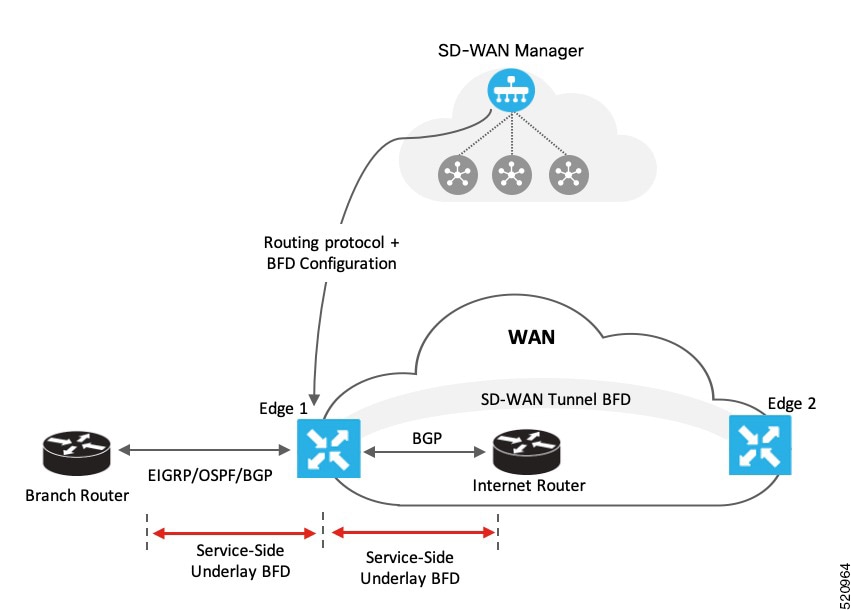
Overview
Explains how Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) enables rapid detection of link, device, and path failures in enterprise networks, helping ensure faster recovery and high availability for critical applications.
A Bi-directional Forwarding Detection (BFD) is a network protocol that
-
detects failures rapidly between forwarding engines,
-
operates with low overhead, and
-
enables faster reconvergence of business-critical applications.
BFD provides a single, standardized method to detect link, device, or protocol failures across any layer and media.
BFD in enterprise networks
In enterprise networks, organizations increasingly run business-critical applications on a shared IP infrastructure. They design these networks with high redundancy to protect data and ensure reliability. However, redundancy works effectively only when network devices detect failures and switch to alternate paths quickly.
Traditional protocols often take more than a second to identify failures, which delays recovery for time-sensitive applications. BFD solves this problem by detecting failures rapidly and triggering faster recovery, allowing networks to maintain consistent performance and uptime.