Overview
This topic explains the architecture for Cisco IoT FND that employs a distributed multi-site deployment using EnterpriseDB Standard Postgres with the Postgres Distributed (PGD) solution. This design ensures continuous operation by utilizing two active FND application servers across separate data centers, automated database failover via co-located PGD Proxies, and DNS-based traffic routing, providing enterprise-grade resilience and data protection.
This architecture is intended for deployments that require continuous operation and resilience against server, database, and data center failures, and it is illustrated in the HA architecture diagram provided in the specification.
Summary
This process describes how the HA and DR architecture for Cisco IoT FND with PostgreSQL operates to maintain service availability through distributed database replication, active application servers, and DNS‑based traffic redirection.
Workflow
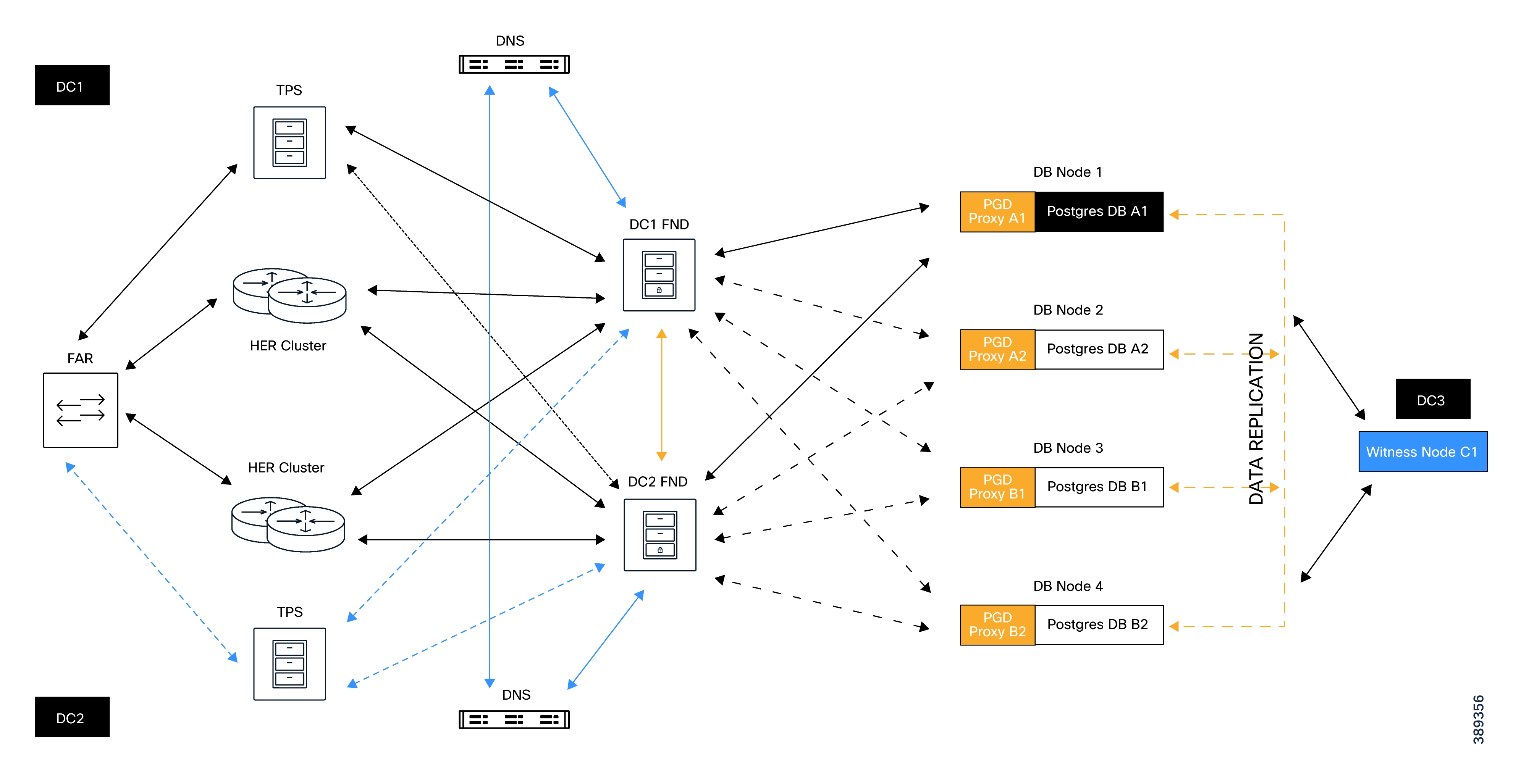
- Cisco IoT FND application servers and PostgreSQL database nodes are deployed across multiple data centers to eliminate single points of failure.
- EnterpriseDB PostgreSQL with Postgres Distributed replicates data across all database nodes, designating one node as the primary and the others as standby nodes.
- PGD Proxy instances act as the access layer between FND and PostgreSQL, dynamically routing all database connections to the current primary node.
- Two FND application servers run in active mode and connect to the database through the PGD proxies, ensuring uninterrupted application access during database failover.
- The FND application servers synchronize cache and configuration updates using secure REST‑based communication to maintain consistency across sites.
- Routers using a fully qualified domain name that is resolved by a global server load balancing DNS service.
- When a failure occurs at the database, application, or site level, the system automatically promotes healthy database nodes and redirects application traffic to the active site.
Result
The HA and DR architecture ensures continuous availability of Cisco IoT FND by automatically handling failures without manual intervention. This approach protects data integrity, minimizes service disruption, and supports reliable operation of large‑scale IoT deployments across multiple data centers.