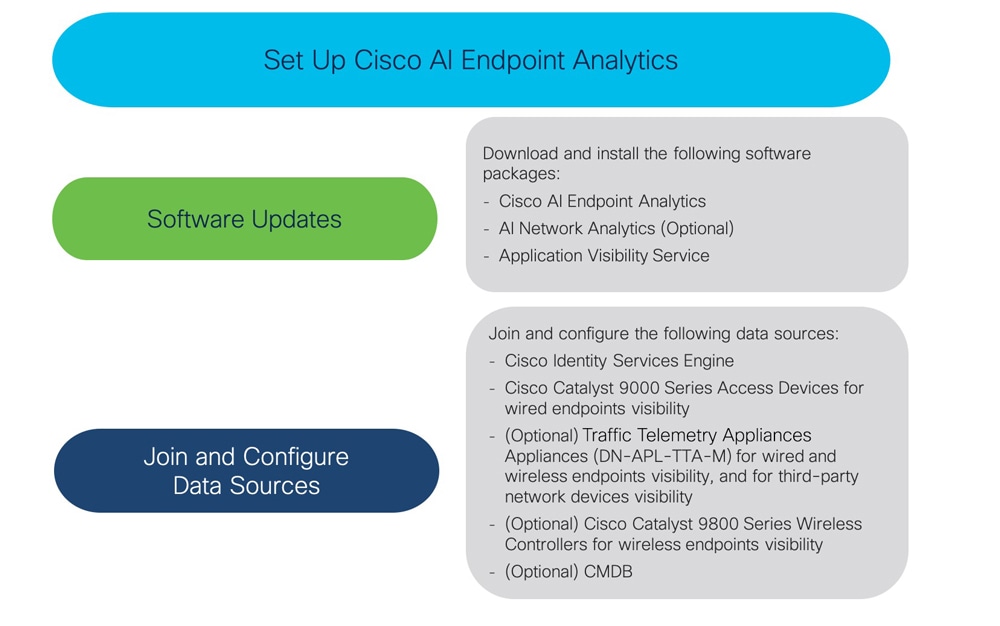
Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics overview
Visibility is the first step towards securing an endpoint. Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics is an endpoint visibility solution that helps you identify and profile endpoints and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics engine enables you to assign labels to endpoints, using the telemetry information received from the network from various sources.
The profiling labels that are available in Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics are endpoint type, hardware model, manufacturer, and operating system type. This is called multifactor classification.
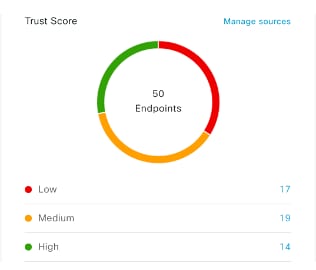
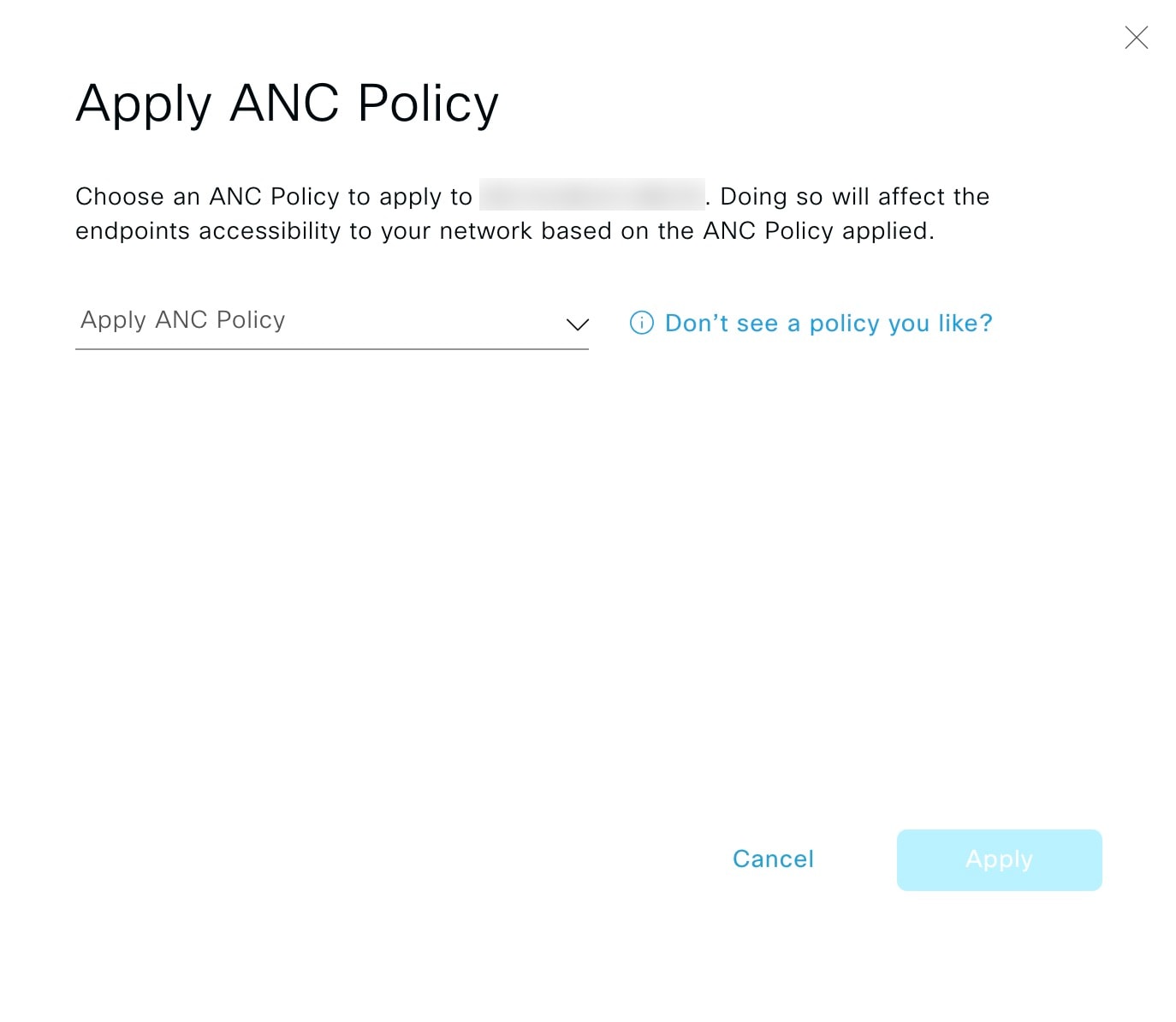
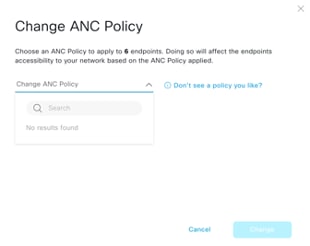
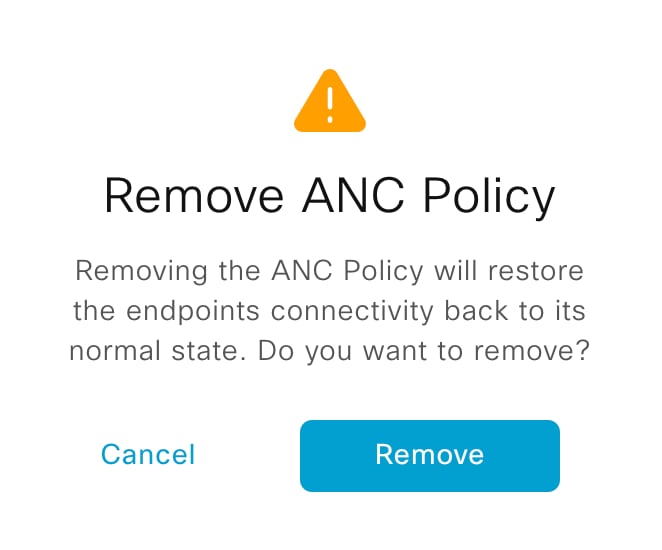
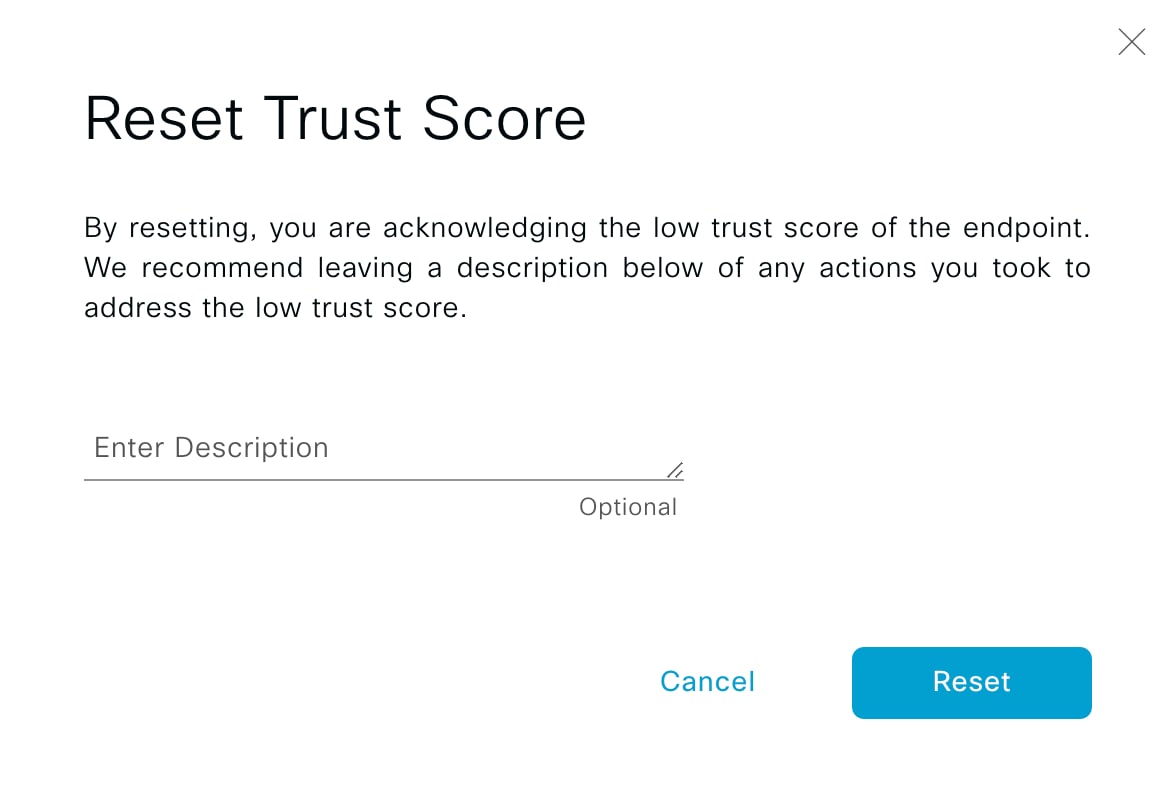
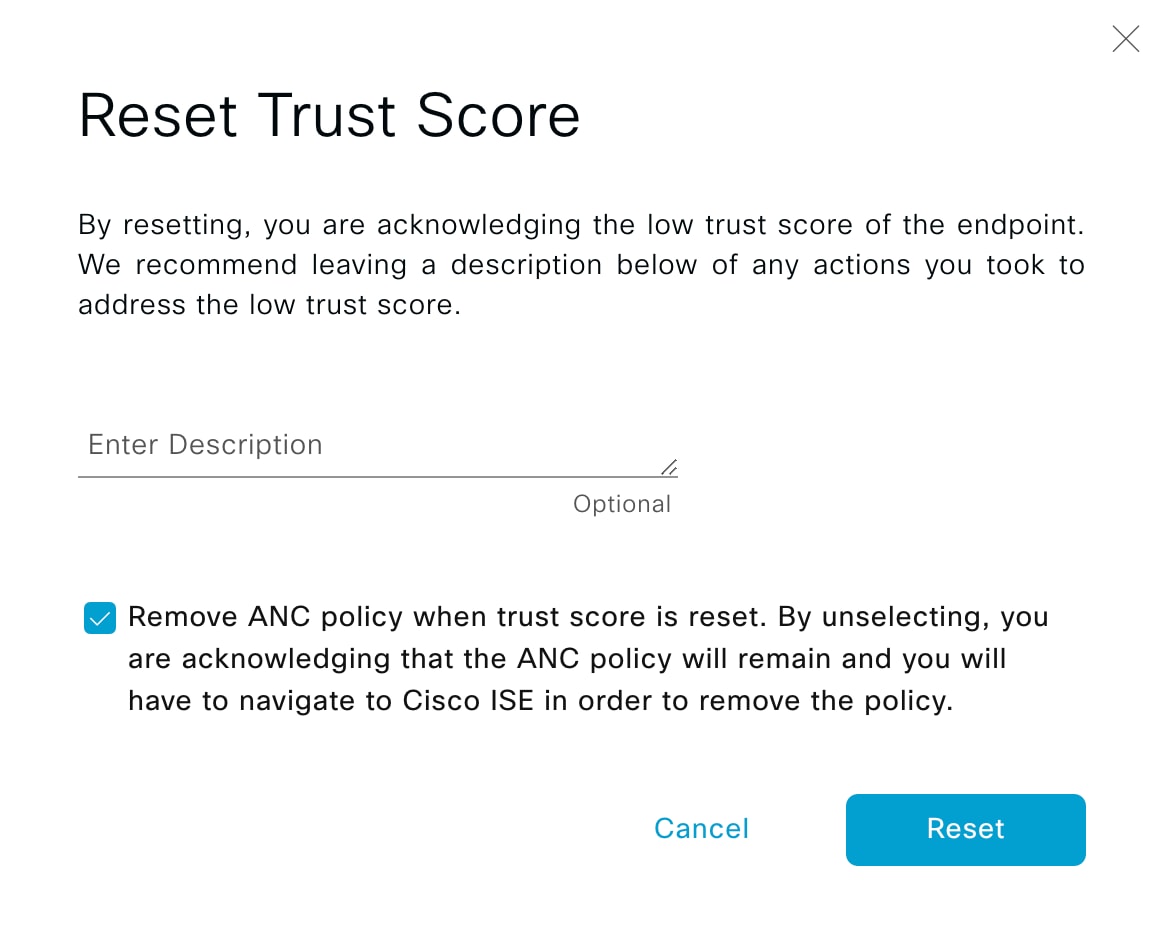
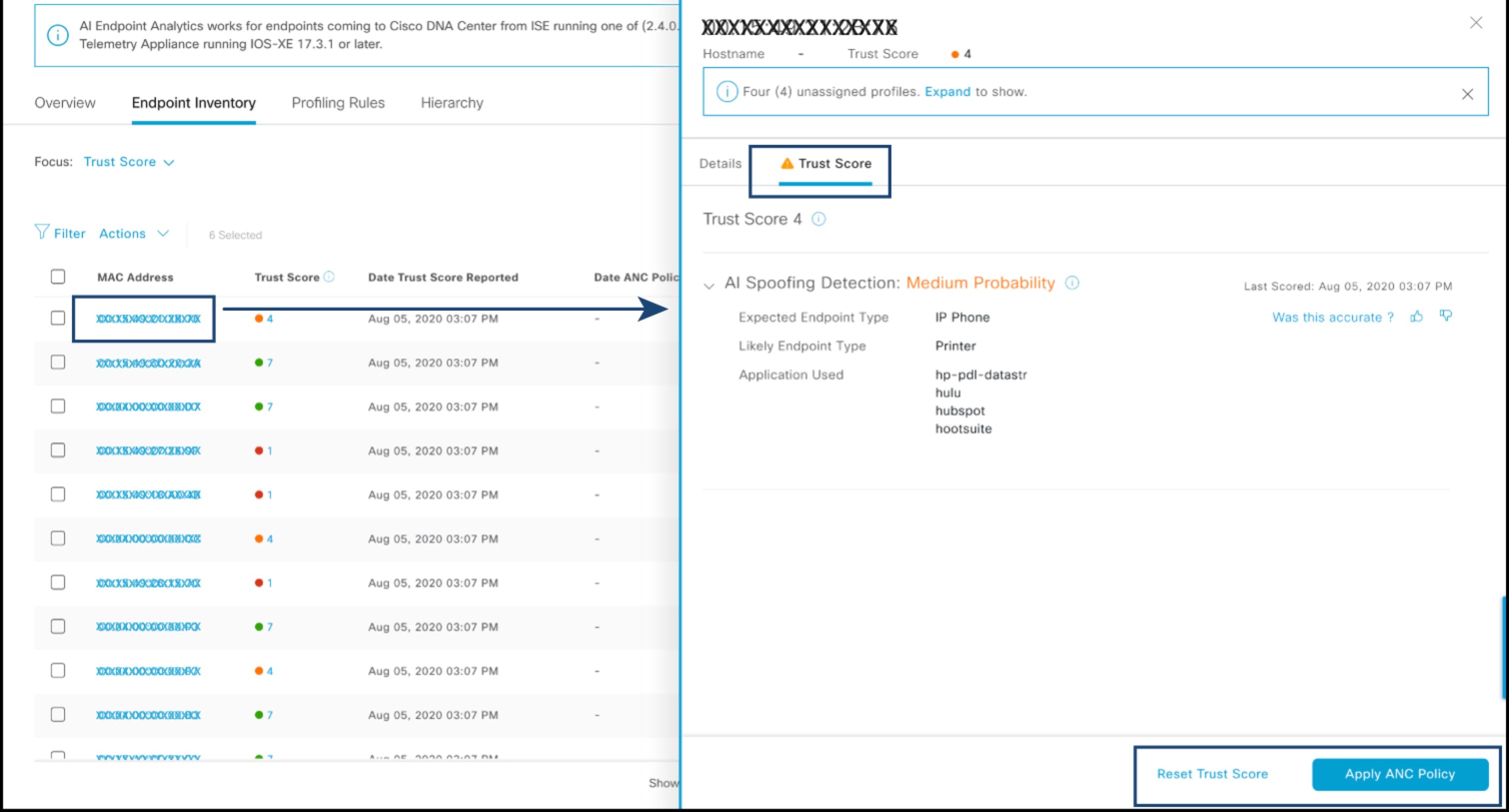
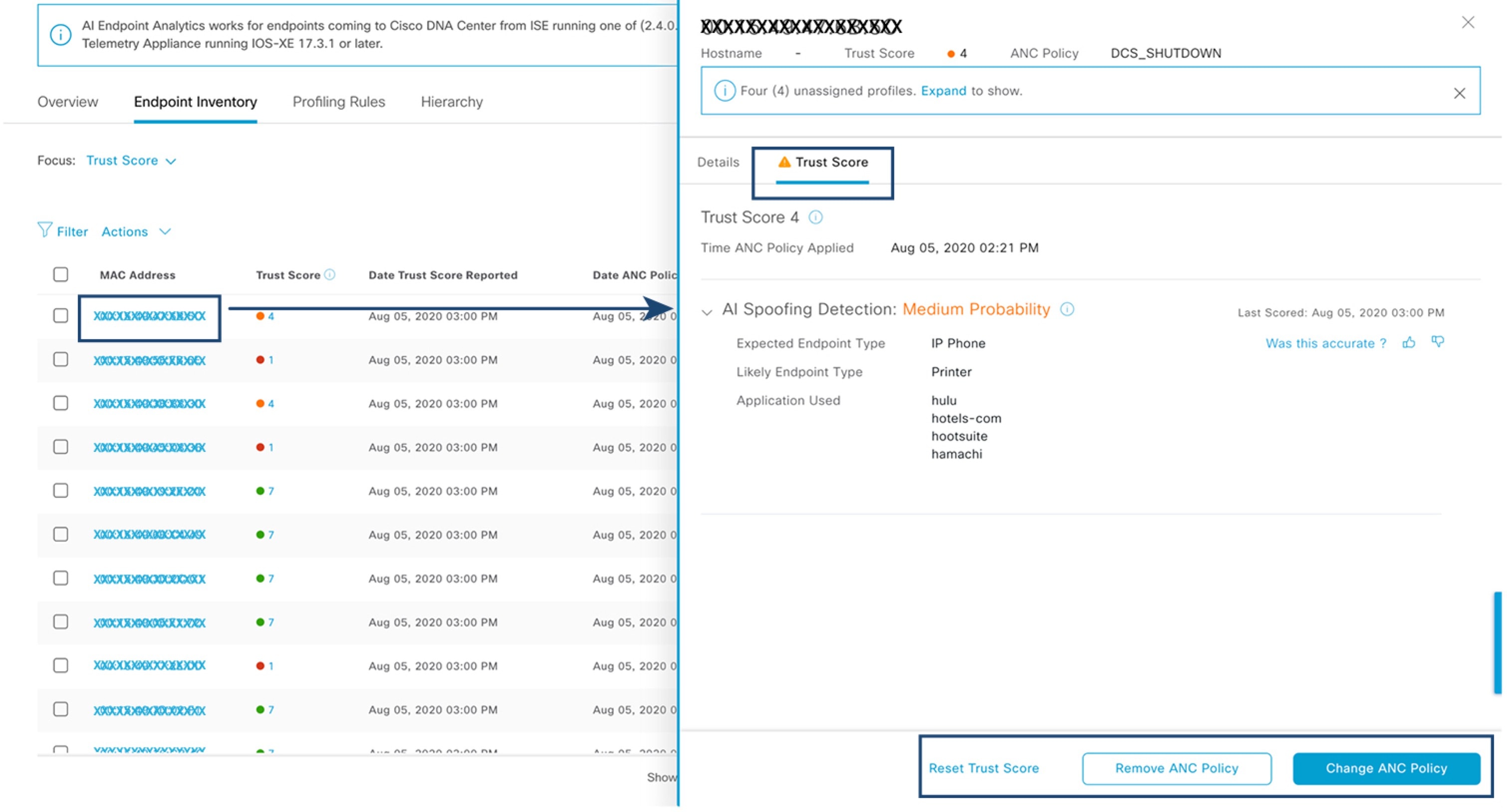
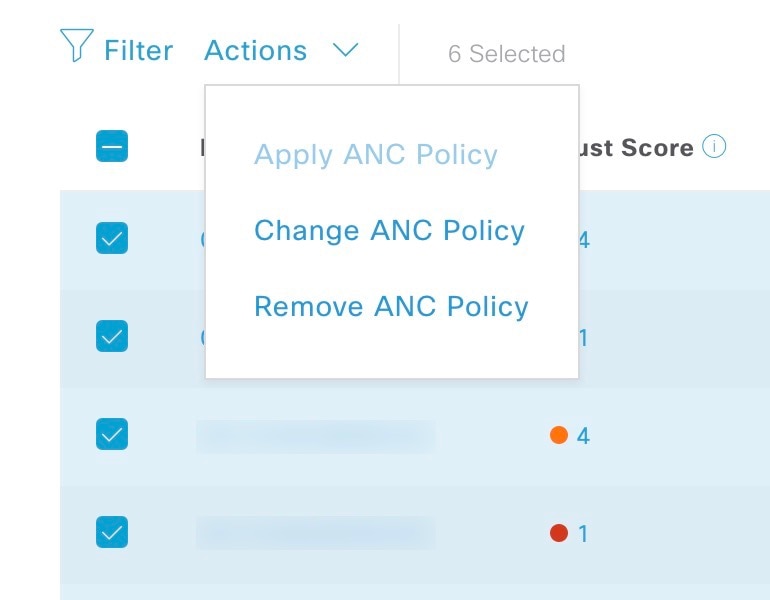
Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics provides nuanced visibility and enforcement in your network with features like Trust Scores that allow you to identify and act upon potentially risky endpoints and devices. You can also manage potential risks by applying ANC policies through Cisco ISE, from the Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics GUI. You can monitor and work around the issue of random and changing MAC addresses from endpoints in Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics and accurately identify endpoints through a unique attribute called the DUID instead of MAC addresses.
Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics helps you gather endpoint telemetry from different sources. The primary source is the Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR) mechanism. The NBAR mechanism is embedded in Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series switches (access devices) and performs deep packet inspection (DPI). Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics can also receive telemetry from Catalyst Center Traffic Telemetry Appliance.
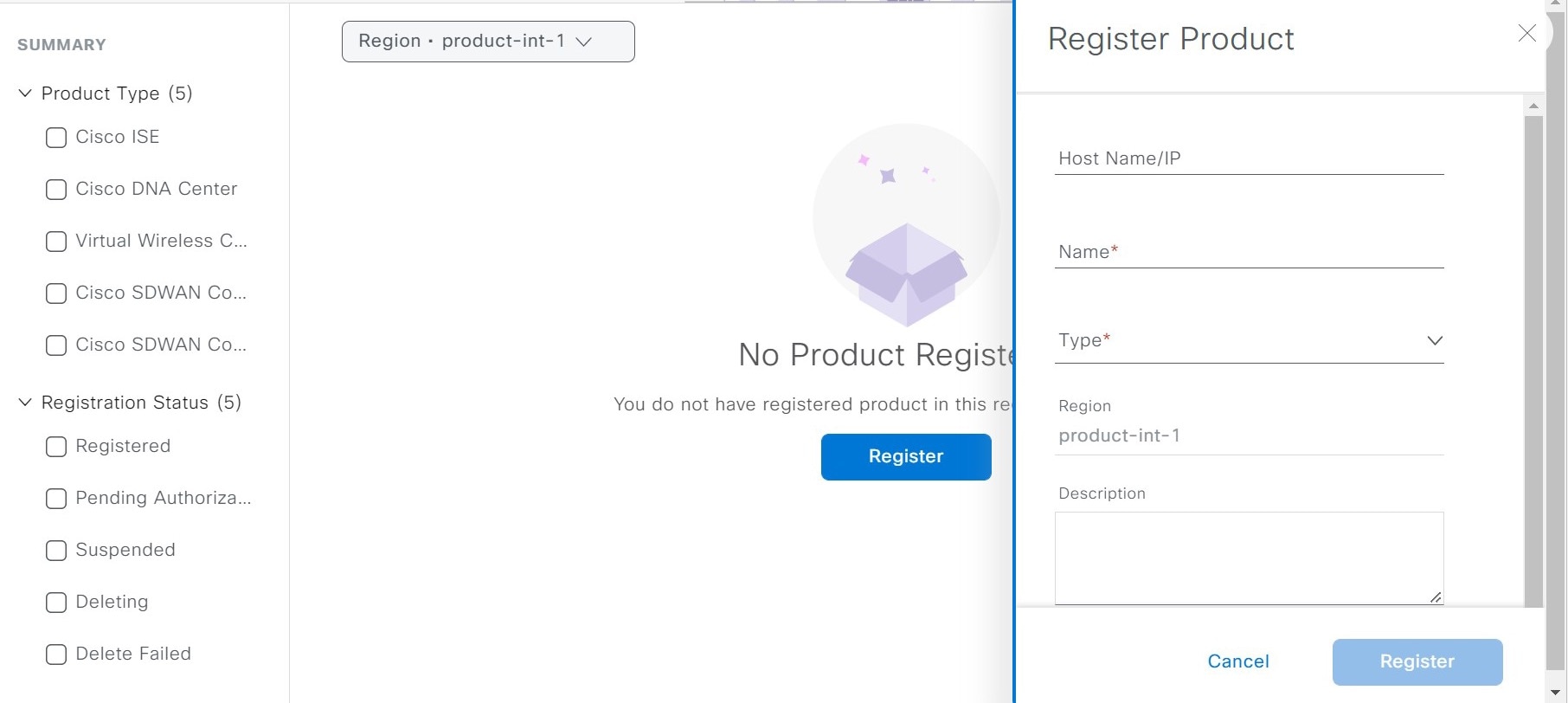
You can gather endpoint context information from various sources such as Cisco ISE, self-registration portals, and configuration management database (CMDB) software such as ServiceNow.
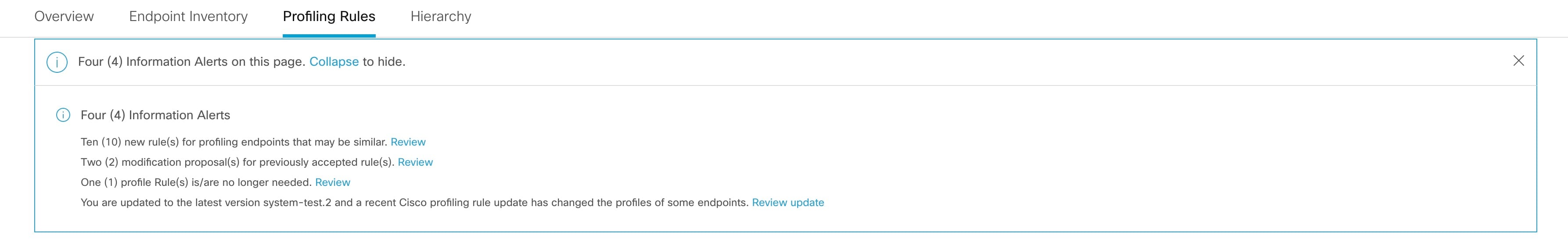
Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics allows data inflow from a wide range of network devices, expanding your ability to easily identify and profile endpoints with greater accuracy, and act upon any anomalies. You can aggregate varied endpoint information and use the data to profile endpoints in Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics. After endpoints are profiled, AI and machine learning algorithms can also be used to reduce the number of unknown endpoints by intuitively leveraging different methods.




 Feedback
Feedback