|
Run Commands
|
This link is available only for routers, wireless controllers, switches, and hubs.
Launch the Command Runner application to run diagnostic CLI commands and view the resulting command output on a device.
To launch Command Runner, you must have installed the Command Runner application. For more information, see the Cisco Catalyst Center Administrator Guide.
|
|
Manage APs
|
This link is available only for Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers on which the Per-Device Configuration feature is enabled.
For a wireless controller that is provisioned using Per-Device Configuration, click this link to manage the associated APs.
|
Note
|
If the wireless controller is provisioned using the intent-based wireless network configurations with site-based network profiles, you can only view
the list of associated APs using this link.
|
For more information, see Manage APs associated with a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
|
|
View 360
|
This link is available for all devices.
Displays the Device 360 window for that device.
To open this window, you must have installed the Assurance application.
|
|
Interfaces
|
This tab is available for all devices except APs.
Displays information about the device's ports, such as its Ethernet ports, in a topology or table view.
For more information about device interfaces, see Display information about a device interface.
|
|
Layer 2 Configuration
|
This tab is available only for Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series Switches and Cisco Catalyst IE switches running Cisco IOS-XE 17.3
or later. For a complete list of supported devices, see the Cisco Catalyst Center Compatibility Matrix.
|
Note
|
Classic IE switches are not supported.
|
Displays information about the layer 2 configuration of a device such as VLAN, Discovery Protocols, STP, VTP, and so on.
For more information, see View and edit layer 2 configuration of a device.
|
|
Security
|
This tab is available only for Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series Switches and Cisco Catalyst IE switches.
Displays the Cisco TrustSec details configured on the device.
For more information, see View and edit security configuration of a device.
|
|
Industrial Configuration
|
This tab is available only for Cisco Catalyst IE switches.
Displays configurations specific to IE switches such as, CIP and Profinet details, alarms, and port configurations.
For more information, see View and edit industrial configuration of a device.
|
|
Hardware & Software
|
This tab is available on all devices.
Displays the device's hardware and software details, such as its uptime, provision status, and Cisco ISE integration status,
with an operational summary.
|
|
Configuration
|
This tab is available only for APs, routers, and switches.
For routers, switches, and hubs, this tab displays detailed configuration information that is similar to what is displayed
in the output of the show running-config command. You can hide line numbers, search for a command line or piece of text, or export the CLI output.
For APs, this tab displays information about the AP configuration and radio configurations.
This feature is not supported for wireless controllers, so configuration data is not returned for this device type.
|
|
Power
|
This tab is available only for routers and switches.
Displays details about the device's power usage and supplies.
To specify or narrow down the data in the Power Supplies table, you can either:
-
Click Search Table, manually enter a value, and then press the Enter key. The narrowed search results are displayed with the value highlighted throughout the table.
-
Click the filter icon (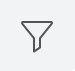 ) to display power supplies by any combination of values, such as values for the Name, Operational Status, and Serial Number fields. ) to display power supplies by any combination of values, such as values for the Name, Operational Status, and Serial Number fields.
|
|
Fans
|
This tab is available only for routers and switches.
Displays details about fans.
To specify or narrow down the data in the Fans table, you can either:
-
Click Search Table, manually enter a value, and then press the Enter key. The narrowed search results are displayed with the value highlighted throughout the table.
-
Click the filter icon ( ) to display fans by any combination of values for the Name and Operational Status fields. ) to display fans by any combination of values for the Name and Operational Status fields.
|
|
SFP Modules
|
This tab is available only for routers and switches.
Displays details such as the manufacturer and the ports that Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) modules are connected to.
To specify or narrow down the data in the SFP Modules table, you can either:
-
Click Search Table, manually enter a value, and then press the Enter key. The narrowed search results are displayed with the value highlighted throughout the table.
-
Click the filter icon ( ) to display SPF modules by any combination of values, such as values for the Name, Platform, and Serial Number fields. ) to display SPF modules by any combination of values, such as values for the Name, Platform, and Serial Number fields.
|
|
User Defined Fields
|
This tab is available for all devices.
Displays the user-defined fields that are associated with the device.
Click Manage User Defined Fields to display the Manage User Defined Fields
slide-in pane. You can do these tasks:
-
Click Create New Fields to create a new field.
-
Click Search Table, manually enter a value, and then press the Enter key. The narrowed search results are displayed with the value highlighted throughout the table.
-
Click the filter icon ( ) to display user-defined fields by any combination of values, such as values for the Name, Description, and Action fields. ) to display user-defined fields by any combination of values, such as values for the Name, Description, and Action fields.
To add a user-defined field to a device, you first must create a user-defined field in the Manage User Defined Fields
slide-in pane. For more information, see Create user-defined fields.
To display a user-defined field, you must assign it to a device and add a value to it. For more information, see Add user-defined fields to a device.
|
|
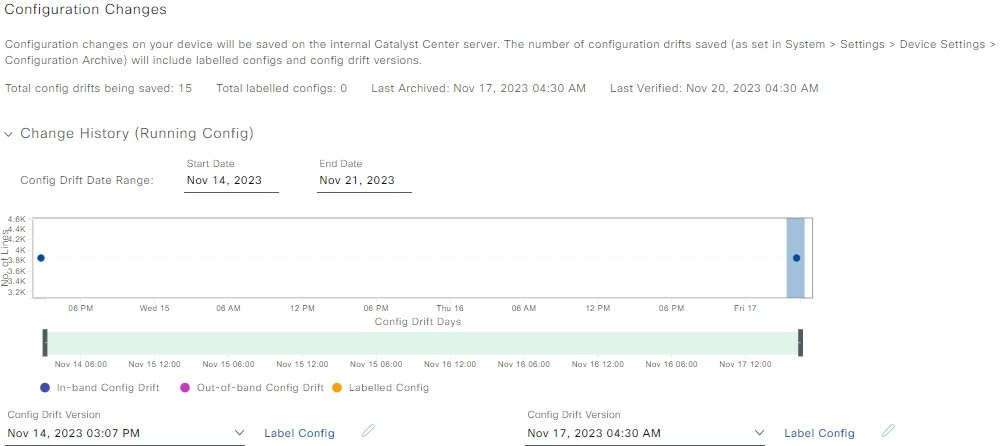
Config Drift
|
This tab is available for all devices.
Displays configuration changes on the device, including a change history, and compares two configuration versions. You can
do these tasks:
-
Label the configuration drift on the time line for future reference. For more information, see Label configuration drift.
-
Pick any two versions of the same device and compare their running configuration data.
|
|
REP Rings
|
This tab is available for Cisco Catalyst Industrial Ethernet 3100, 3200, 3300, 3400, 4000, 5000, and 9300 Series Switch. Cisco
Embedded Services 3300 Series Switches (ESS3300), S5200, and S5800.
Displays details about Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) rings, such as its name, ring size, first adjacent device, and so
on.
Click Create REP Ring and follow the workflow to create a REP ring.
For more information, see Delete a node from a REP ring or Delete a REP ring.
|
|
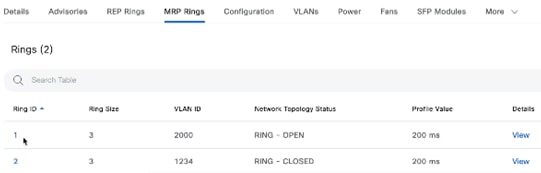
MRP Rings
|
This tab is available only for Cisco Industrial Ethernet (IE) 3000, 4000, 5000 Series Switches.
Displays details about Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) rings, such as ring ID, ring size, VLAN ID, network topology status,
profile value, and ring details.
To view the MRP ring details from view, click anywhere on the ring.
For more information, see MRP ring for nonfabric deployment and View MRP ring status for nonfabric deployment.
|
|
Wireless Info
|
This tab is available only for wireless controllers.
Displays details about managed sites, wireless, redundancy, health parameters, and more.
In the Wireless Summary tab, in the SSIDs table, you can search for a specific value by clicking Search Table, manually entering a value, and then pressing the Enter key. The narrowed search results are displayed with the value highlighted throughout the table.
|
|
CONFIGURATION
|
This area is available only for wireless controllers.
-
Mobility: This tab displays mobility details, such as the mobility group name, RF group name, and so on.
The Mobility Peers table is displayed if mobility peers are configured on the device. If mobility peers are not configured, see Configure mobility group.
You can filter the table to display specific mobility peers by any combination of values, such as values for MAC address, Device Name, and IP Address fields.
-
Per-Device Configuration: Available only for Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers on which this feature is enabled.
For the wireless controller, you can use Per-Device Configuration to manage individual features such as, WLAN configurations, RF configurations, and so on.
|
Note
|
If the wireless controller is provisioned using the intent-based configurations with site-based network profiles, you can only view the device configurations
in this area.
|
For more information, see Per-Device Configuration for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
|
|
Advisories
|
This tab is available for all devices.
Displays a device's advisory details in the Advisories table. You can do these tasks:
-
Click Manage All to display the Security Advisories window to manage your devices and advisories.
-
Click Filter to display advisories by any combination of values, such as values for the Advisory ID and Advisory Title fields. Then click Apply.
-
Click an advisory ID to display more information about that advisory.
-
In the Custom Match Pattern column, click Add match pattern to add or update a condition to match with devices in the CONDITIONS text box. Then you can save the match pattern and run a scan to check the number of devices that match with the match pattern.
|
|
Field Notices
|
Displays information about field notices for the device. See View Field Notices.
|
|
Potential Field Notices
|
Displays information about potential field notices for the device.
|
|
Summary
|
This tab is available for all devices.
Displays a device's compliance summary, such as when compliance last ran for the Startup vs Running configuration. You can
do these tasks:
-
Click Run Compliance Check to check the device for compliance.
-
Click View Preference for Acknowledged Violations to view the list of acknowledged violation attributes. You can unlist a violation to open it.
|

 Active
Active
 Expiring
Expiring
 Expired
Expired
 Not Provisioned
Not Provisioned
 ) for the device.
) for the device.
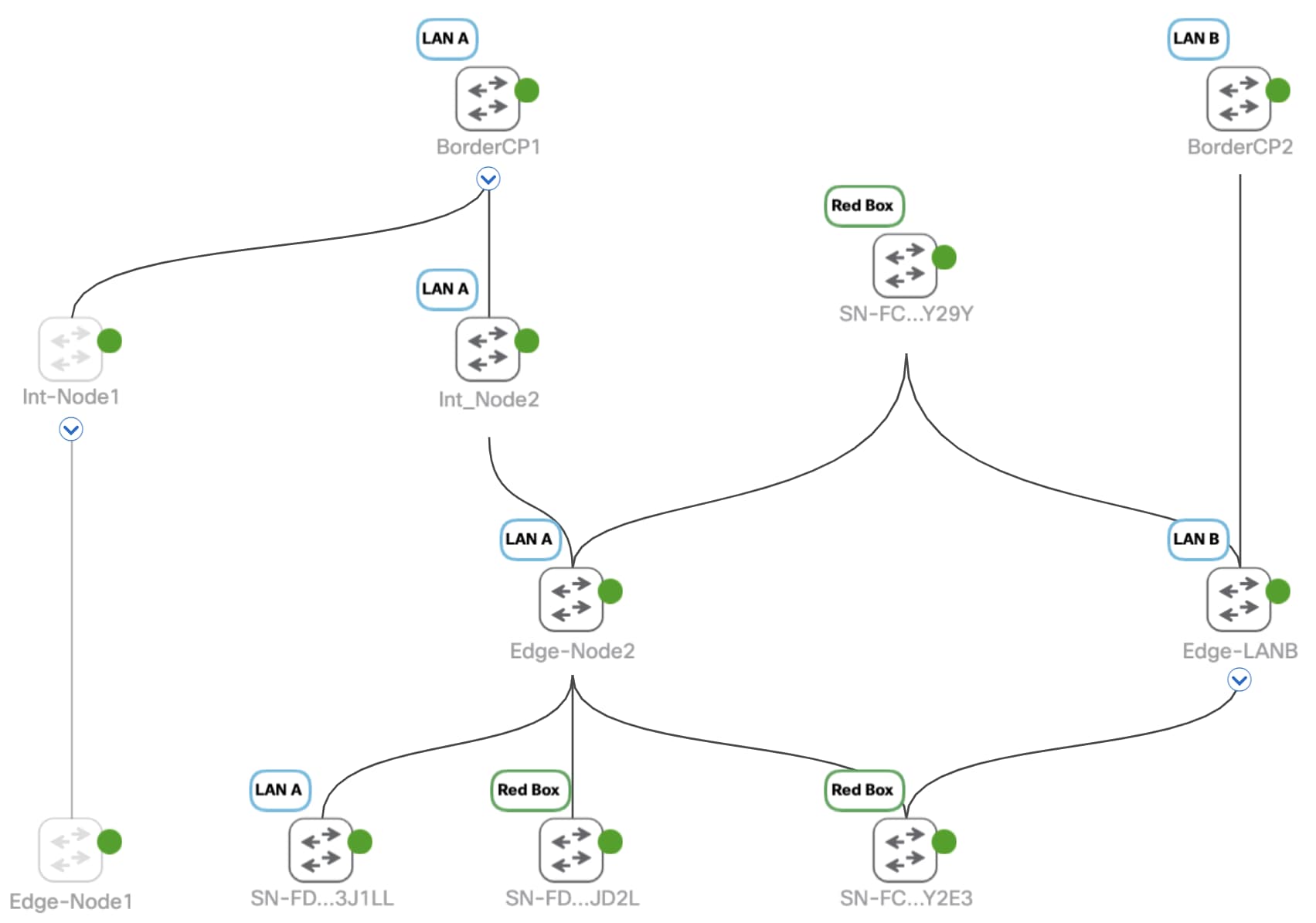
 ) to switch to the Topology map view.
) to switch to the Topology map view.
 ).
).

 ) button.
) button.
 ) button.
) button.
 icon
icon
 icon
icon
 Feedback
Feedback