Interfaces and Circuits
This section explains how the interfaces and circuits are represented in the network plot.
|
Graphic |
Description |
|---|---|

|
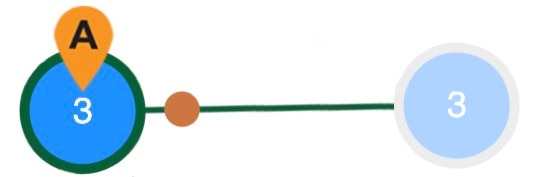
A solid line indicates a link between two devices. The color of the line varies depending on the outbound traffic utilization. For details on mapping between the color of the links and the traffic utilization, see Traffic utilization. When an interface or circuit is selected, the width of the link doubles ( When there are more than one link between two devices, a dotted line appears ( |

|
A red circle with a white X on a circuit indicates the circuit has failed. |
|
|
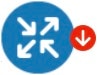
A red circle with a white down arrow on a circuit indicates the circuit is not operational because of one of the these reasons:
|

|
A gray circle with a white X on a circuit indicates the circuit is inactive. |

|
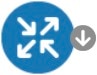
A gray circle with a white down arrow on a circuit indicates the circuit is not operational because of one of the following reasons:
|
 ).
).
 ).
).


















 ) indicates the rerouted demand over an LSP.
) indicates the rerouted demand over an LSP.

 ) shows the rerouted shorted IGP path of a demand during a failure.
) shows the rerouted shorted IGP path of a demand during a failure.

 ) shows the rerouted shorted latency path of a demand during a failure.
) shows the rerouted shorted latency path of a demand during a failure.

 ) shows the rerouted aggregated path of a demand during a failure.
) shows the rerouted aggregated path of a demand during a failure.




 ) indicates the rerouted shorted TE path of an LSP during a failure.
) indicates the rerouted shorted TE path of an LSP during a failure.

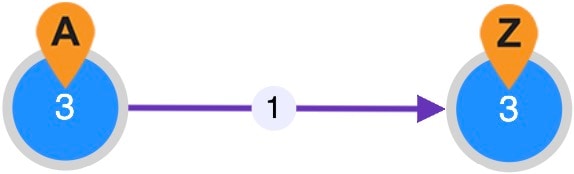
 ) indicates the rerouted primary path of an LSP during a failure.
) indicates the rerouted primary path of an LSP during a failure.
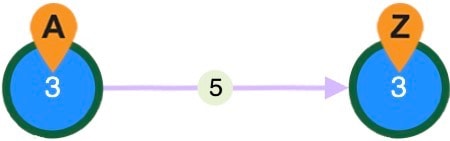
 ) shows the rerouted standby path of an LSP during a failure.
) shows the rerouted standby path of an LSP during a failure.
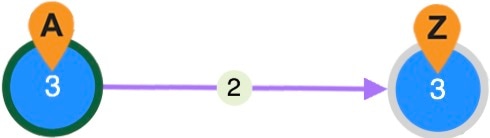
 ) shows the rerouted alternate path of an LSP during a failure.
) shows the rerouted alternate path of an LSP during a failure.






 Feedback
Feedback