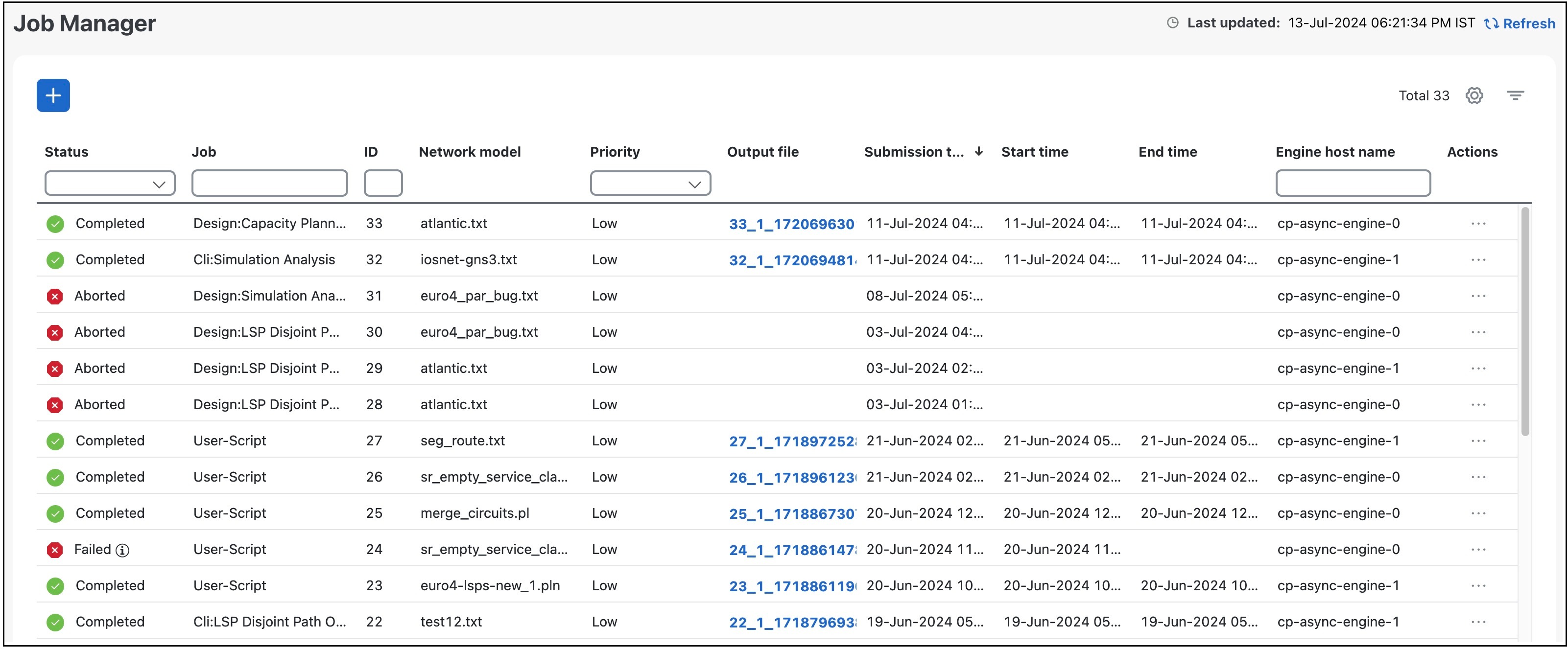
Job Manager
In Cisco Crosswork Planning, you can schedule tools and initializers to run as background jobs, also known as asynchronous jobs. These jobs execute in the background on the design engine instances configured during deployment. The Job Manager page provides details of these jobs.
With background jobs, you can
-
set a priority before it is submitted
-
schedule to run at a required time, or
-
cancel before it moves to the Running state
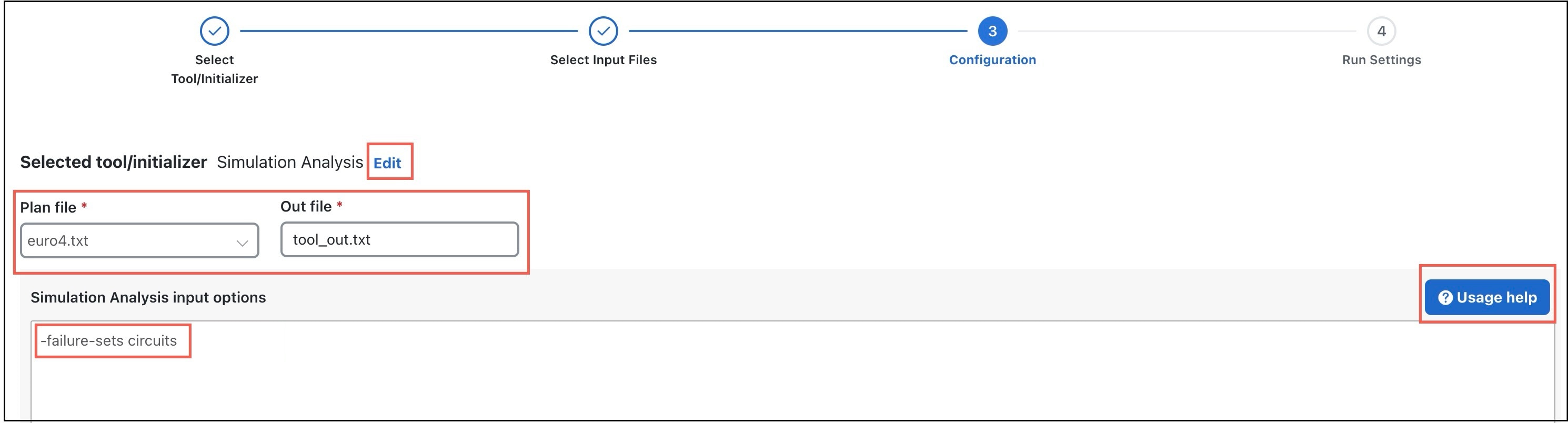
The Job Manager page also provides options to execute jobs using CLI and custom scripts. For details, see Run tools or initializers using CLI and Run external scripts.
User role permissions for Job Manager
In the Job Manager page
-
any user can view the jobs submitted by any other user
-
any user can view the results of the jobs submitted by any other user
-
any user can cancel (abort) the jobs submitted only by themselves, and
-
only admin users can cancel (abort) the jobs submitted by any user.
 Feedback
Feedback