Cisco AI POD Infrastructure for Enterprises Guide Using UCS C885A Servers and Nexus 9364E-SG2 Switches
February 2026
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)—especially with the rapid rise of agentic AI, physical AI, generative AI, and HPC-scale training and inference—have become critical drivers of business innovation. Yet the infrastructure required to operationalize these workloads is fundamentally different from that required by traditional enterprise applications. Depending on the use case, AI infrastructure demands massive parallel GPU compute, ultra-low latency and high-bandwidth networking, specialized data pipelines, and security architectures capable of protecting an end-to-end AI supply chain.
To address these challenges, Cisco and NVIDIA have partnered to deliver the Cisco Secure AI Factory with NVIDIA, a fully validated, full-stack solution that integrates NVIDIA GPUs and software, Cisco® compute and networking, and security embedded at every layer—from silicon to systems to the distributed AI pipeline.
This architecture brings together NVIDIA’s accelerated computing stack with Cisco’s 800G-ready networking, global-scale observability, and zero-trust security to make AI clusters faster to deploy, easier to operate, and more cost-effective to scale across data centers and distributed edge environments.
Within this broader solution, Cisco AI PODs represent the modular building blocks for training, fine tuning and inference clusters. The NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architecture endorsement in this document applies specifically to Cisco AI POD Infrastructure for Enterprises with Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers and Cisco Nexus 9364E-SG2 switches, providing a reference architecture for building a robust, scalable, and operationally simple AI infrastructure that allows enterprises to confidently deploy and manage AI clusters with built-in security, performance, and lifecycle management.
Note: Cisco AI POD Infrastructure for Enterprises design with NVIDIA in this document is compliant with NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architecture and endorsed by NVIDIA for Infrastructure Configuration and Spectrum-X based on NVIDIA Enterprise RA for 2-8-9-400.
Audience
This document is intended for IT architects, data-center engineers, AI/ML infrastructure specialists, and anyone responsible for designing and deploying high-performance enterprise infrastructure for AI workloads.
Scope
The purpose of this reference architecture is to provide a prescriptive Cisco AI POD design based on the NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architecture using Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers and Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches. The architectural principles and components in the design ensure predictable performance, reliability, and scalability for demanding AI workloads. While the NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architecture for 2-8-9-400 offers a range of modular designs, this document details one specific architecture endorsed by NVIDIA.
Solution overview
This Reference Architecture (RA) provides a prescriptive blueprint for a scalable Cisco AI POD architecture, combining the following enterprise-grade, best-in-class components:
● Compute: Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers with high-density NVIDIA HGX H200 GPUs and Bluefield-3 network adapters, aligned with NVIDIA’s HGX-based 2-8-9-400 architecture. The servers are managed using Cisco Intersight®.
● Networking: Cisco Nexus 9000 Series 400/800GbE switches providing non-blocking, high-performance backend (east/west) and frontend (north/south) fabrics. Both fabrics are centrally managed by Cisco Nexus Dashboard, which delivers comprehensive operational simplicity through AI deployment templates based on best practices for automated rollout and streamlined lifecycle management.
● Storage: A flexible, high-performance storage architecture for AI datasets and models, supporting both traditional (NetApp, Pure Storage) and newer (VAST Data) NVIDIA-certified storage partners.
● Orchestration: this prescriptive architecture is centered on Red Hat OpenShift for robust, enterprise-grade workload orchestration.
This architecture is based on building blocks of Scalable Units (SUs) consisting of four servers with eight GPUs each, using a four-way rail-optimized design. This design delivers a nonblocking, lossless, and performant fabric for GPU-to-GPU communication, along with a scalable frontend fabric for management, orchestration, storage, and other services to support enterprise AI initiatives.
The key hardware components in the reference architecture are described below.
Compute: Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server
AI model training and fine-tuning often involve extensive matrix multiplications and parallel computations that require multiple high-performance GPUs, both within a node and across systems. The Cisco UCS C885A M8 is a high-performance, 8-GPU (NVIDIA SXM-based), 8RU rack server designed to provide the GPU density and high-speed interconnects required for training and fine-tuning complex deep-learning models.
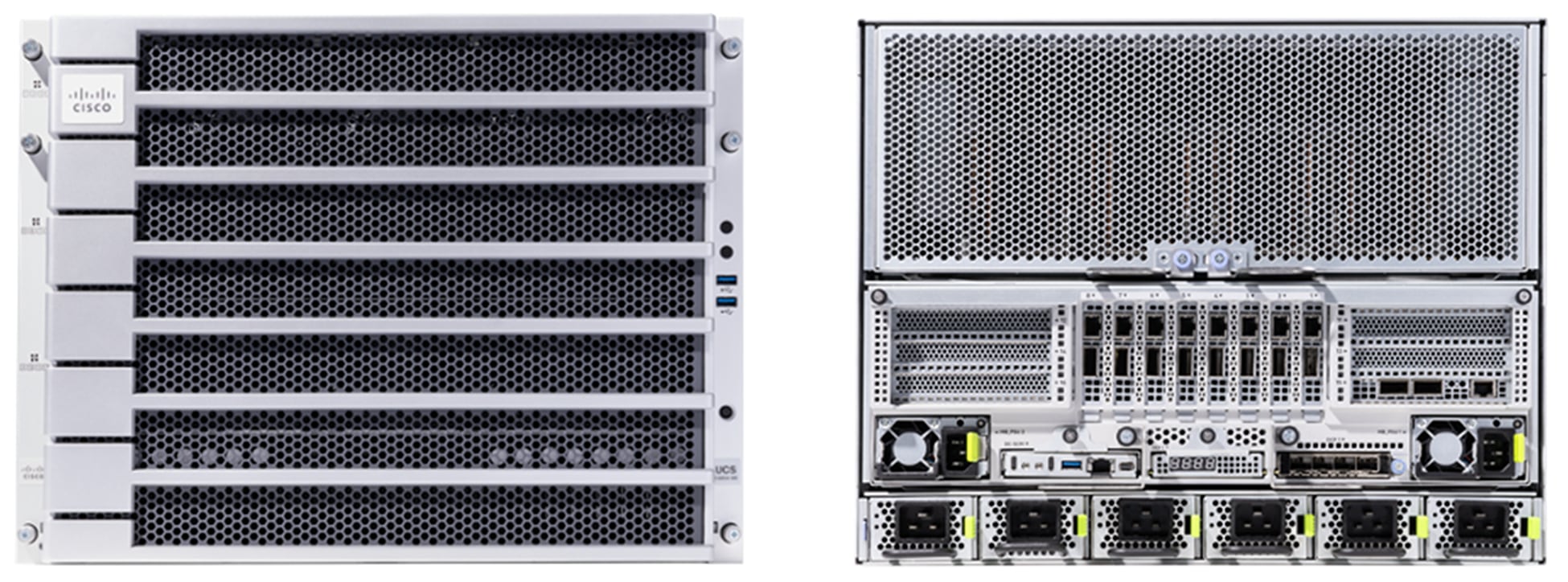

Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server (front and rear views) based on NVIDIA HGX architecture
The Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server is based on NVIDIA’s HGX architecture, specifically the HGX 2-8-9-400 design pattern when using 2 CPUs, 8 NVIDIA GPUs, 9 NVIDIA NICs, and 400Gbps of bandwidth for GPU-to-GPU communication. Each server contains 2x AMD EPYC CPUs, up to 3 TB of DDR DRAM, 30 TB of NVMe local storage, and hot-swappable fan trays and power supplies. The 8x NVIDIA HGX H200 (SXM-based) GPUs within the server are interconnected using high-speed NVLink interconnects, with external connectivity provided by NVIDIA BlueField-3 adapters. Detailed specifications are provided in the References section at the end of this document.
For backend connectivity, each UCS C885A server is equipped with eight PCIe Gen5 x16 HHHL adapters serving as east/west NICs for high-speed inter-node GPU-to-GPU communication across the fabric. While the UCS C885A supports multiple configuration options, this reference architecture utilizes the NVIDIA BlueField-3 B3140H SuperNIC with a single 400GbE port to deliver performance and critical capabilities such as GPUDirect RDMA.
Each UCS C885A server is also equipped with four PCIe Gen5 x16 FHHL slots to accommodate up to four frontend (north/south) NICs. While the platform supports various adapters, this reference architecture utilizes the NVIDIA BlueField-3 B3220 (2x200G) or B3240 (2x400G) for connectivity to the frontend fabric.
Network: Cisco Nexus switches with Nexus Dashboard (or Cisco fabric options)
The network fabric plays a crucial role in connecting dense GPU servers, ensuring the high-bandwidth, low-latency and lossless communication that is essential for distributed training and fine tuning. Cisco offers a range of high-performance switches suitable for leaf or spine roles within this architecture. These platforms provide the necessary port density, switching capacity, and advanced features to support demanding AI/ML workloads, including lossless Ethernet and remote direct memory access (RDMA) over Converged Ethernet (RoCE). All switches described below can be deployed and centrally managed using Cisco Nexus Dashboard in either a backend or frontend fabric.
Cisco Nexus 9364E-SG2 switch
The Cisco Nexus 9364E-SG2 switch is a high-density, 2RU 800GbE switch designed for next-generation data centers. Based on Cisco Silicon One® technology, these switches are built to support modern cloud architectures and address the growing demand for high-performance, power-efficient connectivity. These switches can be deployed as a high-density leaf or a compact spine switch in both backend and frontend fabrics, offering increased port count and switching capacity for ‘AI’ i.e. scalable AI deployments.
Cisco Nexus 9364E-SG2 switch
The Nexus 9364E-SG2 provides 64x 800GbE ports and comes in both QSFP-DD and OSFP form factors. These ports are flexible and can operate at lower port speeds and densities, including 400GbE, 200GbE, and 100GbE speeds.
The switch provides a high forwarding throughput of 51.2 Terabits per second (Tbps) to accommodate high aggregate bandwidth requirements. An on-die buffer of 256 MB provides resiliency against traffic microbursts and prevents packet loss, which is critical for AI/ ML workloads.
These switches are particularly well suited for AI/ML applications, providing the low latency, congestion-management mechanisms, and telemetry capabilities such applications require. They support features such as dynamic load balancing (DLB), priority flow control (PFC), and explicit congestion notification (ECN), along with lossless transport for RDMA over converged Ethernet (RoCE). Integrated with tools such as Cisco Nexus Dashboard, the Nexus 9364E-SG2 provides a robust platform for building high-performance AI/ML network fabrics, offering security, automation, visibility, analytics, and assurance.
Cisco Nexus 9332D-GX2B switch
The Cisco Nexus 9332D-GX2B is a 1RU fixed-configuration switch engineered for high-density (400GbE) deployments. Its typically deployed as a leaf switch in the frontend fabric, connecting multiple GPU servers to the enterprise network.
![]()
Cisco Nexus 9332D-GX2B switch
The Nexus 9332D-GX2B features 32x 400GbE QSFP-DD ports. Each 400GbE port can be configured to operate at various speeds, including 100GbE, 50GbE, 25GbE, and 10GbE, providing flexibility for different connectivity requirements. The switch provides a high forwarding throughput of 25.6 Terabits per second (Tbps) and 8.5 billion packets per second, ensuring efficient packet processing for latency-sensitive AI traffic. A 60-MB shared buffer helps manage traffic bursts and prevent packet loss, which is critical for maintaining lossless communication in AI/ML environments.
Cisco Nexus 9364D-GX2A switch
The Cisco Nexus 9364D-GX2A is a higher-density 2RU fixed-configuration switch, designed to support larger-scale 400GbE deployments. It can function as a high-density leaf or a compact spine switch in the frontend (or backend) fabric, offering increased port count and switching capacity for a scalable deployment.

Cisco Nexus 9364D-GX2A switch
The Nexus 9364D-GX2A features 64x 400GbE QSFP-DD ports. Similar to the Nexus 9332D-GX2B, these ports are flexible and can operate at 100GbE, 50GbE, 25GbE, and 10GbE speeds. The switch provides a high forwarding throughput of 51.2 Terabits per second (Tbps) and 17 billion packets per second, accommodating very high aggregate bandwidth requirements. A shared buffer of 120 MB provides resiliency against traffic microbursts and prevents packet loss, which is critical for AI/ ML workloads.
Management
To operationalize the Cisco AI POD infrastructure, specific management components are used in this reference architecture. A dedicated Cisco UCS management and services cluster is deployed to host the orchestration, control plane, and management components for Red Hat OpenShift, independent of the AI workload cluster running on the high-performance UCS GPU servers.
Cisco UCS Management Cluster
The management cluster can be hosted on either Cisco UCS C-Series rack servers or Cisco UCS X-Series Direct systems. Both options provide the necessary compute, memory, and local storage capacity. The number of management servers is determined by the High-Availability (HA) requirements of Red Hat OpenShift, which typically requires a minimum of three control plane nodes.
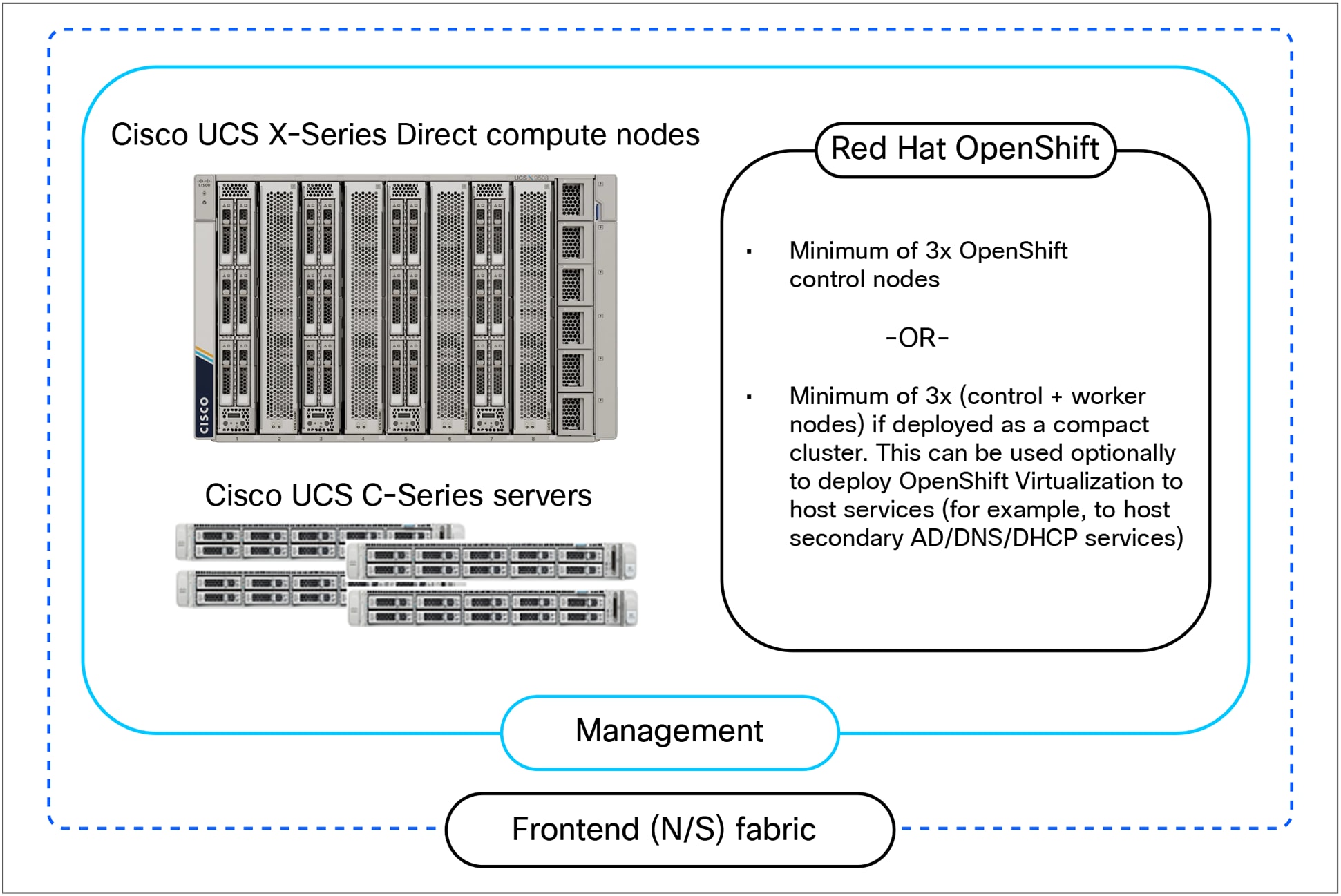
Cisco UCS management options
In this specific design, Cisco UCS X-Series Direct is used to host these management and services functions. Cisco UCS X-Direct provides a self-contained, modular system that integrates a Cisco UCS X9508 Chassis with two Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect 9108 100G modules capable of supporting up to 20 Cisco UCS servers and 8 x 100GbE uplinks for connecting to a frontend fabric in an AI deployment.
For more information on UCS X-Series Direct, see data sheet and at-a-glance.
Cisco Intersight
Cisco Intersight® is an IT operations platform that provides comprehensive infrastructure lifecycle management, delivered as a service from the cloud or as a private virtual appliance for on-premises deployments. It provides IT teams with a unified, real-time view of all Cisco UCS, converged, and hyperconverged infrastructure regardless of their location-across data centers, remote sites, branch offices, and edge environments-from a single dashboard. By utilizing a cloud-operating model, Intersight simplifies deployment, configuration, and maintenance, ensuring consistent compliance and security posture across the environment. Intersight also offers centralized automation and simplicity, driving operational efficiency for server lifecycle management. In this reference architecture,
Cisco Intersight provides unified SaaS-based management for all Cisco UCS infrastructure.
For more information, see the Cisco Intersight IT operations platform page.
Cisco Nexus Dashboard
Cisco Nexus Dashboard (ND) serves as the unified management and operations platform for deploying and managing the network fabrics in the AI POD architecture. It provides specific best-practice blueprints for deploying both the high-speed backend (east-west) and frontend (north-south) fabrics typically seen in AI/ML deployments. By taking a software-defined approach, Nexus Dashboard enables centralized, fabric-level deployments instead of manual switch-by-switch configuration, ensuring configuration consistency while minimizing errors. This “one fabric” approach simplifies overall management and provides a single API endpoint for automation. It also enhances operational ease with integrated monitoring, AI-driven traffic management, customizable dashboards, and multi-fabric lifecycle management. ND’s scale-out architecture and single API automation capabilities provide customers with a simplified, scalable, and intelligent platform for all enterprise data center fabric operations.
For more information, see the Nexus Dashboard page.
Cisco Nexus 93108TC-FX3 switch
The Cisco Nexus 93108TC-FX3 switch provides 48 100-Mbps or 1/10-Gbps 10GBASE-T ports and six 1/10/25/40/100-Gbps QSFP28 ports in 1RU form-factor. In this reference architecture, this switch serves as the out-of-band (OOB) management switch, connecting the management ports of all devices in the solution.
![]()
Cisco Nexus 93108TC-FX3 switch
For more information, see the Cisco Nexus 93108TC-FX3 Switch page.
This section outlines the design for the different subsystems in the reference architecture.
Dual fabric design
AI training and fine-tuning GPU clusters typically rely on two independent networks: a backend fabric for parallel processing and synchronization across GPU nodes, and a frontend fabric for ingesting training data, checkpointing, and connectivity to the rest of the enterprise. In hybrid deployments, the frontend network also handles inferencing traffic from users and applications.
In enterprise deployments, the frontend network can be a dedicated fabric or shared with an existing data-center network that meets the requirements. In contrast, the backend fabric is dedicated and isolated, with no direct connectivity to other parts of the enterprise or external networks.
Backend network fabric
The backend (east-west) fabric is critical for performant GPU-to-GPU communication and data exchange during collective operations, directly impacting the Job-Completion Times (JCTs) of training workloads. To minimize JCT, this fabric must provide high-bandwidth, low-latency, and lossless connectivity.
To meet these requirements, this design uses a two-tier, non-blocking spine-leaf (Clos) topology built using Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches and managed by Cisco Nexus Dashboard. This architecture provides low, predictable latency that is critical for GPU node-to-node communication while also providing the ability to scale out with ease and consistency as enterprise needs grow.
While this topology can support other routing architectures, this design uses an MP-BGP EVPN VXLAN fabric as it provides a flexible, scalable, and standards-based architecture that inherently supports the multitenancy that enterprises need.
The Ethernet virtual private network (EVPN) control plane provides the network overlays (virtualization) to support multitenancy across an IP underlay.
● Control Plane: Uses internet-scale Multi- Protocol Border Gateway Protocol (MP-BGP) to advertise both Layer 2 MAC addresses and Layer 3 IP information.
● Data Plane: Uses Virtual eXtensible LAN (VXLAN) to provide the IP/UDP-based data-plane encapsulation for the overlay networks.
A key benefit of this architecture is its native support for both Layer 2 extension and Layer 3 forwarding with flexible network segmentation. This allows enterprises to efficiently share the training fabric across multiple teams (multi-tenancy) while retaining the flexibility to use either Layer 2 or Layer 3 overlays for GPU-to- GPU communication.
Frontend network fabric
The frontend (north-south) fabric serves as a multi-purpose network in an AI deployment, providing key services to orchestrate and manage the GPU infrastructure and the workloads running on them. In a hybrid deployment, it also serves as the inferencing network that users utilize to access the ML models running on the GPU cluster. Since the backend fabric is typically isolated with no external connectivity, the frontend fabric serves as a gateway to the GPU cluster, providing connectivity for storage access, cluster management, and user (including inference) access.
The frontend fabric in this reference architecture also uses a two-tier, spine-leaf, Clos topology using Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches, mirroring the backend fabric design. A key advantage of this design is the use of Cisco Nexus Dashboard to provide unified management for both the backend and frontend fabrics. This unified management approach ensures operational consistency and simplicity, especially at scale.
However, unlike the dedicated, non-blocking (typically 400GbE) backend fabric, the frontend fabric is a shared (100GbE/200GbE) fabric. To ensure adequate performance, the NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architecture recommends providing a minimum of 12.5Gbps per GPU for storage traffic and 25Gbps per GPU for user traffic. As such, while the backend is strictly non-blocking, the frontend fabric is typically deployed with oversubscription between the leaf and spine layers. This design allows customers to customize the oversubscription ratio as needed to meet their specific bandwidth requirements; as needs increase, they can reduce this ratio simply by adding more links.
GPU-to-GPU connectivity across Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack servers
In this reference architecture, the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers connect to the backend (east-west) fabric for GPU-to-GPU communication using a 4-way rail-optimized topology, as shown in Figure 7. In this topology, the eight NVIDIA BlueField-3 backend NICs in each server connect to four upstream leaf switches. Specifically, each leaf switch connects to the same two GPU ranks across multiple nodes, forming a dedicated Rail-Group (RG) per leaf switch as shown.
The number of UCS C885A nodes that can be connected to a given leaf switch depends on the port density of the selected switch model. For example, using Nexus 9364E-SG2 leaf switches and factoring in non-blocking upstream connectivity to spine switches, a single switch of this model type can support up to 32 UCS C885A nodes in this design.
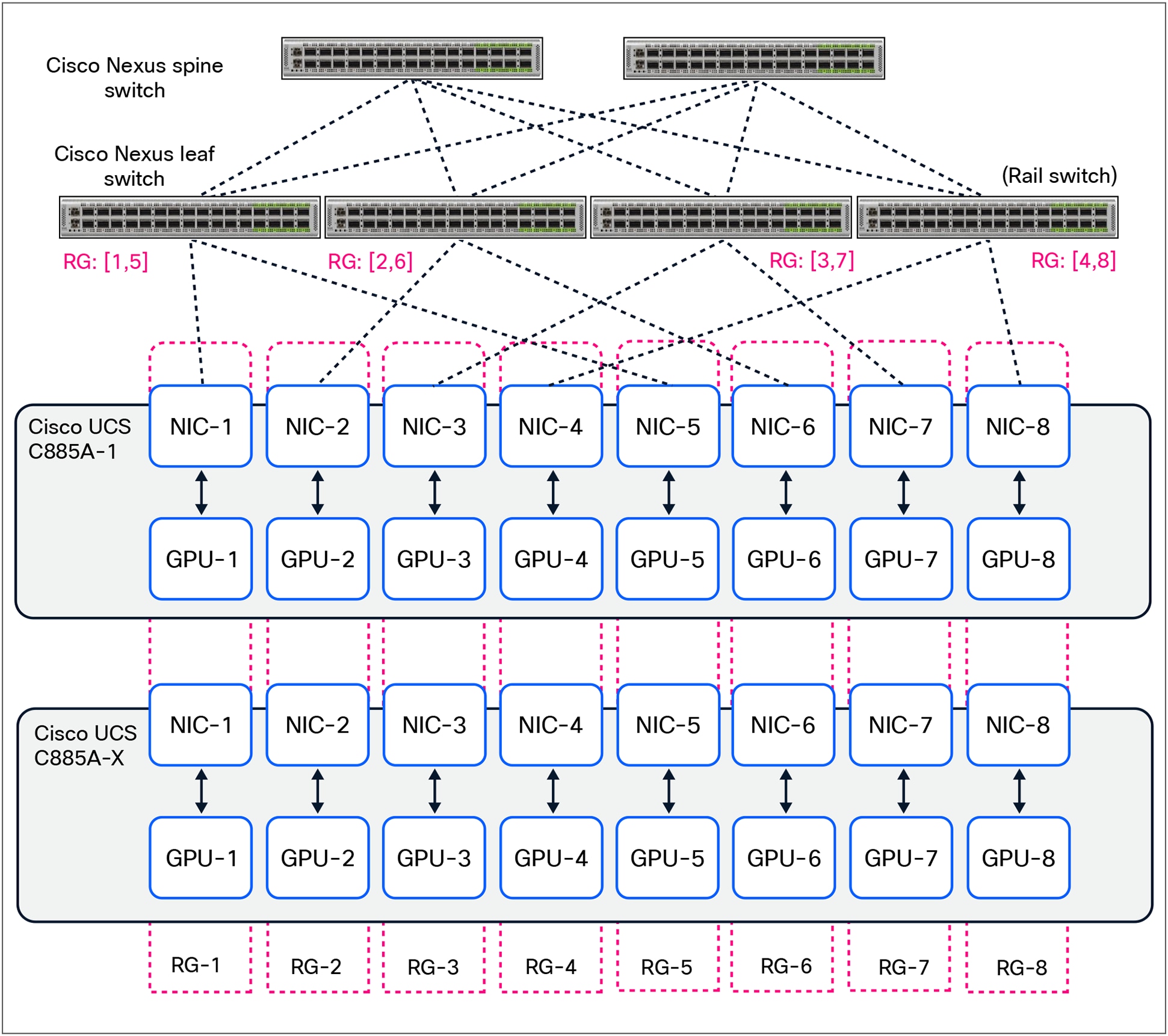
Rail-optimized (4-way) topology
GPU-to-GPU connectivity within Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack servers
The Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers utilize high-speed NVLink interconnects to facilitate ultra-low latency communication between GPUs within the same node. The detailed PCIe and NVLink connectivity within the servers is shown in Figure 8.
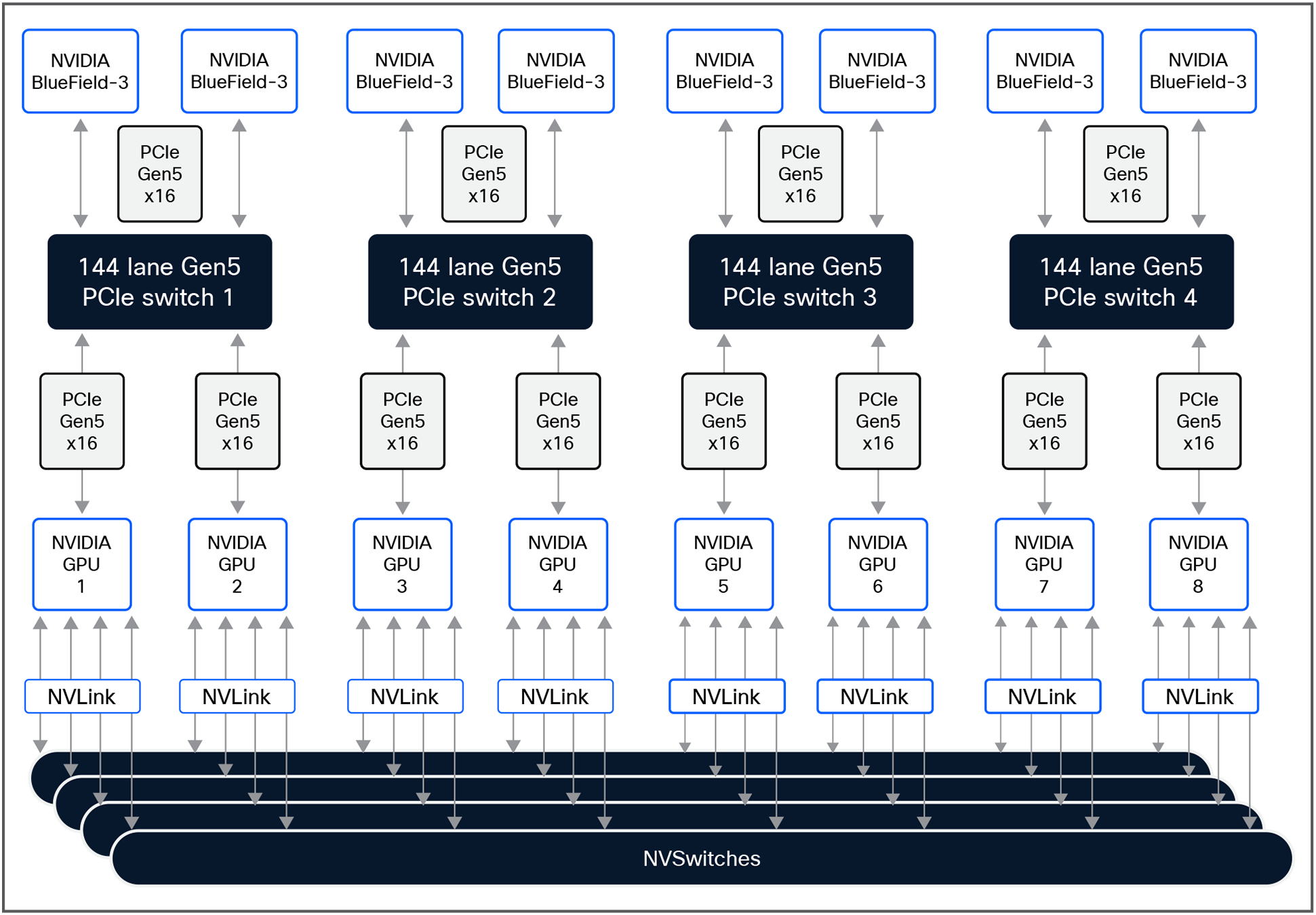
NVLink and PCIe connectivity within Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server
Cisco UCS GPU server to frontend fabric connectivity
The frontend fabric connects the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack servers to the management/ orchestration components, as well as to storage systems. In hybrid deployments, this network also handles user traffic for accessing inference models hosted on the Cisco UCS GPU servers.
This design uses 400GbE links between leaf and spine switches with oversubscription. Each server is equipped with up to two frontend NICs (typically 2x 200GbE) for connecting to the frontend fabric. To ensure high availability and bandwidth aggregation, these NIC ports are configured in an active/active port-channel. This configuration ensures the fabric meets the NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architecture requirement of providing a minimum of 12.5Gbps per GPU for storage traffic and 25Gbps per GPU for user traffic.
Since the frontend fabric is typically shared and carries mixed traffic types, Quality of Service (QoS) should be deployed to prioritize latency-sensitive inferencing requests or storage traffic as needed.
Solution topology – high-level
The high-level solution design for scaling to a 256-GPU cluster is shown in Figure 9.
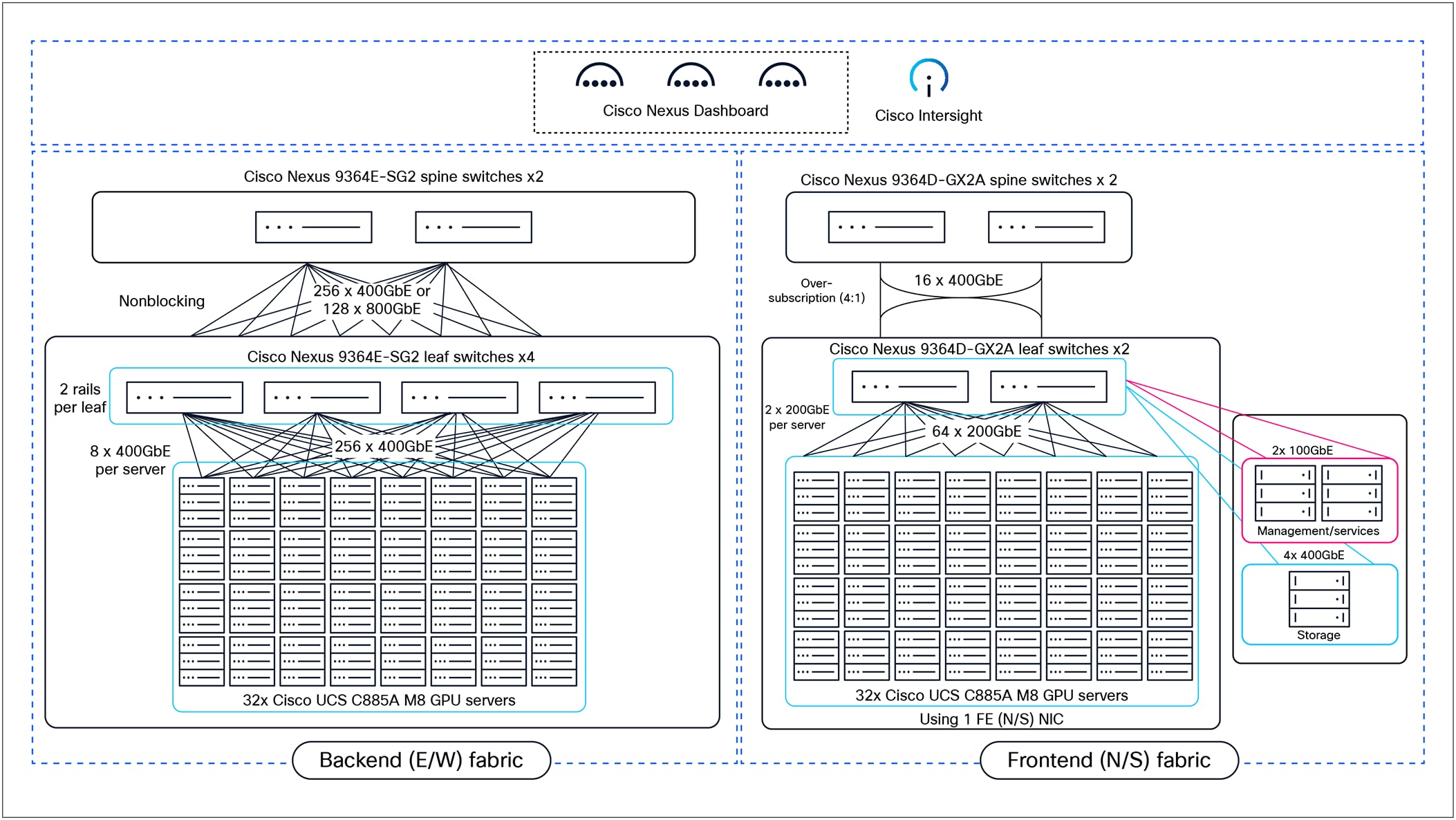
High-level solution topology – 256-GPU cluster
This section provides a proposed deployment topology and rack layouts that enterprises can use in their AI deployments.
Network topology
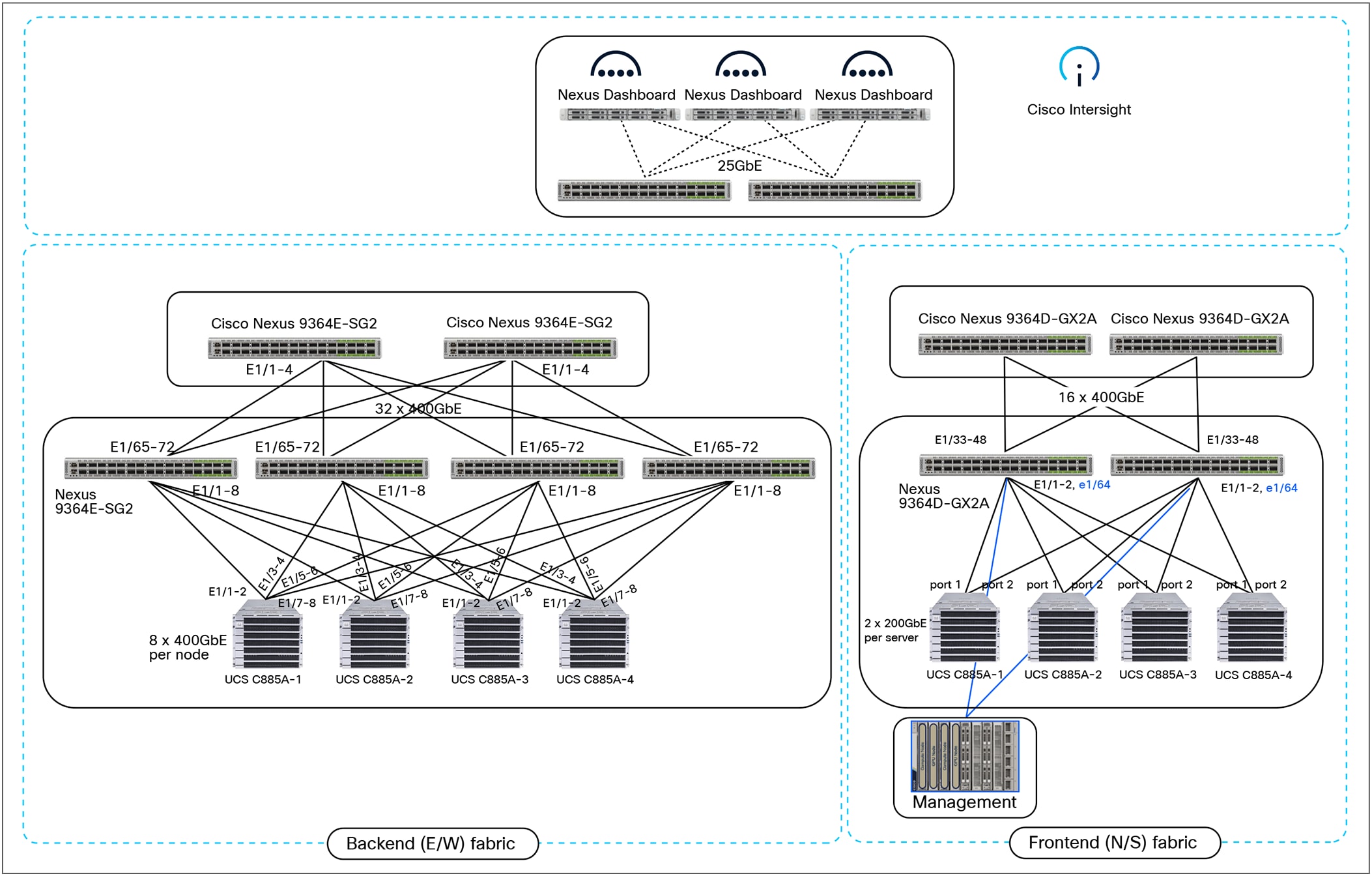
Example physical topology
Software stack and versions
Table 1. Software stack and versions
| Component |
Software/firmware |
Notes |
|||
| Backend fabric |
|||||
| Cisco N9364E-SG2 |
Cisco NX-OS 10.4(3) or higher |
Spine and leaf switches |
|||
| Frontend fabric |
|||||
| Cisco Nexus 9332D-GX2B |
Cisco NX-OS 10.4(3) or higher |
Spine and leaf switches |
|||
| Cisco Nexus 9364D-GX2A |
Cisco NX-OS 10.4(3) or higher |
Spine and leaf switches |
|||
| Cisco UCS compute |
|||||
| Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server |
- |
- |
|||
| NVIDIA H200 GPU Driver |
570.172.08 or later |
Minimum version |
|||
| NVIDIA CUDA Version |
12.8 |
Minimum version |
|||
| Management/services |
|||||
| Cisco Nexus Dashboard |
4.1(1) |
3-node physical cluster |
|||
| Cisco Intersight |
N/A |
SaaS platform |
|||
| Cisco UCS X-Series - management |
- |
- |
|||
| Cisco UCS X9508 Chassis (UCSX-9508) |
N/A |
- |
|||
| Cisco UCS X Direct 100G (UCSX-S9108-100G) |
4.3 (5.240162) |
- |
|||
| Cisco UCS X210c M7 Compute Nodes (UCSX-210C-M7) |
5.2 (2.240080) |
Minimum of 3 nodes as control nodes for OpenShift |
|||
| PCIe Mezzanine Card for UCS-X server (UCSX-V4-PCIME) |
N/A |
Optional: only necessary for GPUs on UCS-X |
|||
| Cisco UCS X440p PCIe Node |
N/A |
Optional: only necessary for GPUs on UCS-X |
|||
| Cisco VIC 15231 MLOM (UCSX-ML-V5D200G) |
5.3 (3.91) |
2x100G mLOM |
|||
| Operating system/workload orchestration |
|||||
| Red Hat OpenShift |
4.18 or higher |
Deployed using Assisted Installer from console. redhat.com |
|||
| Red Hat NFD Operator |
Default version |
Node Feature Discovery Operator (NFD) to identify and label GPU |
|||
| 6.0 or later |
- |
||||
| NVIDIA Data Center GPU Driver |
570.172.08 or later |
- |
|||
| NVIDIA GPU Operator |
25.3.4 or higher |
- |
|||
| NVIDIA Network Operator |
25.7.0 |
- |
|||
| NVIDIA DOCA-OFED Driver |
3.0.0 or later |
- |
|||
| NVIDIA NIM Operator |
2.0.2 or later |
- |
|||
Interoperability
The interoperability information for the different components in the reference architecture are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2. Interoperability
| Component |
Interoperability matrix and other relevant links |
| Cisco UCS Hardware Compatibility Matrix (HCL) |
|
| NVIDIA Licensing |
|
| NVIDIA Certification |
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/data-center/products/certified-systems/ |
| NVIDIA AI Enterprise Qualification and Certification |
|
| NVIDIA Driver Lifecycle, Release and CUDA Support |
https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/tesla/drivers/index.html#lifecycle |
Rack layout
The rack layout, shown in Figure 11, is based on the assumption that each rack can minimally support 2x Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers (12.4kW per system) = ~30kW of power per rack.

Rack layout
Bill of Materials (BOM)
The switches can be either QSFP or OSFP models, but the BOM shown assumes QSFP. Also, one (1) frontend NIC per system is assumed, though the design can support more.
Table 3. Bill of materials
| Type |
PID |
Description |
Quantity |
|
| GPU Server |
||||
| 1 |
Cisco UCS Server |
UCSC-885A-M8-H28 |
2xAMD EPYC 9575F 3.3 GHz (Max Boost 5 GHz) CPUs, 8x NVHGX H200 SXM GPUs, 24x96GB up to 6,000MT/s DIMMs, 2x960GB M.2 NVMe Boot Drive, 2x2.5” 1.92TB NVMe SSD Server Drivers, 8x NVIDIA BlueField-3 B3140H SuperNIC (1x400G) for E-W N/W, 2x NVIDIA BlueField-3 B3220 (2x200G) for N-S N/W, 1xIntel X710-T2L |
32 |
| 2 |
Transceivers |
QSFP-400G-DR4 |
400 QSFP112 Transceiver, 400GBASE-DR4, SMF MPO-12 APC, 500m |
256 |
| 3 |
Transceivers |
QSFP-200G-SR4-S |
200G QSFP112 transceiver, MMF, 50GBASE-SR, MPO-12, 100m, parallel |
64 |
| 4 |
License |
DC-MGT-SAAS |
Cisco Intersight SaaS |
32 |
| Backend Fabric Switches |
||||
| 5 |
Spine-Leaf Switches |
N9364E-SG2-Q |
Cisco Nexus 9300 64xx800G QSFP-DD Switch |
6 |
| 6 |
Transceivers |
QDD-8X100G-FR |
Dual Port 800Gbe Transceivers |
384 |
| 7 |
Cables |
CB-M12-M12-SMF |
MPO-12 to MPO-12 cables |
512 |
| 8 |
License |
NXOS-AD-XF3 |
Perpetual License for 800G Fixed Platforms |
6 |
| 9 |
License |
DCN-FGLB-XF3 |
Perpetual-Fine Grain Load balancing on 800GbE Switches |
6 |
| Frontend Fabric Switches |
||||
| 10 |
Spine-Leaf Switches |
N9K-C9364D-GX2A |
Nexus 9300 Series, 64p 400G Switch |
4 |
| 11 |
Transceivers |
QDD-400G-SR8-S |
400GbE Transceivers, MPO-16, MMF, 100m |
32 |
| 12 |
Transceivers |
QDD-400G-DR4-S |
400GbE Transceivers |
18 |
| 13 |
Cables |
M16 to M12-MMF |
MPO-16 to 2x MPO-12 MMF Breakout cables |
32 |
| 14 |
Cables |
CB-M12-M12-SMF |
MPO-12 to MPO-12 cables |
8 |
| Management |
||||
| 15 |
Fabric Management |
ND-CLUSTER-L4 |
Nexus Dashboard Cluster |
1 |
| 16 |
Mgmt./Control Server(s) |
UCSX-M8-MLB |
UCSX9508 Blade Server Chassis with 3 OpenShift Control nodes for HA |
1 |
| 17 |
Chassis |
UCSX-9508-D-U |
UCSX 9508 Blade Server Chassis |
1 |
| 18 |
Server |
UCSX-215C-M8 |
Server w/o CPU or memory |
3 |
| 19 |
CPU |
UCSX-CPU-A9375F |
AMD 9375F 3.8GHz 320W 32C/256MB Cache DDR5 6000MT/s |
3 |
| 20 |
Memory |
UCSX-MRX32G1RE5 |
UCSX-MRX32G1RE5 32GB DDR5-6400 RDUNN 1Rx4 (16Gb) 1 |
6 |
| 21 |
Boot Drivers |
UCSX-NVM2-960GB |
960GB M.2 Boot NVMe |
6 |
| 22 |
NIC |
UCSX-MLV5D200GV2D |
Cisco VIC 15230 2x100G mLOM X-Series w/Secure Boot |
3 |
| 23 |
Uplink |
UCSX-S9108-100G |
Cisco UCS X-Series Direct Fabric Interconnect |
2 |
| 24 |
Transceivers |
QSFP-100-FR-s |
Cisco 100GbE Tranceivers -LC, Duplex, SMF, 2km |
8 |
| 25 |
Cables |
CB-M12-4LC-SMFSM |
Cable, MPO12-4X Duplex LC, Breakout cable, SMF, 5M |
8 |
| 26 |
License |
DC-MGT-SAAS |
Cisco Intersight SaaS |
3 |
| 27 |
Switch |
N9K-C93108TC-FX3 |
Nexus 9300 with 48p 100M/1/10GT & 6p 40/100G QSFP28+ |
4 |
| 28 |
Cables |
CAT64 |
Copper cable for 10G |
64 |
| 29 |
Cables |
CAT5E |
Copper cable for 1G |
96 |
| Software |
||||
| 30 |
OS/K8s Licenses |
RH-OPP2B-P3S |
OpenShift Plat Plus (BM), Prem 3-Yr SnS Req (Up to 2 CPUs and 128 cores) |
32 |
| 31 |
NVIDIA AI Enterprise License |
NV-AIE-S-3Y |
NVIDIA AI Enterprise Essentials Subscription per GPU, 3 year |
256 |
| Support |
||||
| 32 |
DC Support Services |
CON-CXP-DCC-SAS |
Solution Attached Services for DC-Cloud and Compute |
1+ |
| 33 |
Solutions Plus Services |
MINT-COMPUTE |
DC Compute Mentored Installation - MINT |
1 |
| Racks |
||||
| 34 |
Rack |
Cisco R42612 |
Cisco R-Series 42" racks for UCS and Nexus |
18 |
Additional information on licensing for the different components in the Cisco AI POD stack are available here:
● Cisco Intersight licensing: https://intersight.com/help/saas/getting_started/licensing_requirements/lic_intro.
● Cisco Nexus NX-OS licensing options guide: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/licensing-options/cisco-nexus-licensing-options-guide.html.
● NVIDIA licensing: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/unified_computing/ucs/release/notes/nvidia_ordering-guide.html.
● Red Hat OpenShift licensing: https://www.redhat.com/en/resources/self-managed-openshift-subscription-guide.
To find the supported transceivers for any component in the Cisco AI POD stack, including interoperability between them, go to Cisco’s Transceiver Matrix Group site. Links provided below.
● Main site and relevant sub-sites for Cisco’s Transceiver Matrix Group:
● Transceiver data sheets
◦ Cisco QSFP-DD800 Transceiver Modules Data Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/interfaces-modules/transceiver-modules/qsfp-dd800-transceiver-modules-ds.html
While Cisco and NVIDIA support a broad range of AI infrastructure designs, this document outlines a prescriptive Cisco AI POD reference architecture using Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers and Cisco Nexus® 9364E-SG2 switches. This specific design is endorsed by NVIDIA for Infrastructure Configuration and Spectrum-X, based on the NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architecture for 2-8- 9-400. Using this architecture, organizations can build a scalable, high-performance AI infrastructure foundation to accelerate their AI initiatives while minimizing deployment complexity and risk.
For more information, see:
Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server
● Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server Data Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/servers-unified-computing/ucs-c-series-rack-servers/ucs-c885a-m8-ds.html.
● Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server Spec Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/products/collateral/servers-unified-computing/ucs-c-series-rack-servers/ucs-c885a-m8-rack-server-spec-sheet.pdf.
● Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server Installation and Service Guide: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/servers-unified-computing/ucs-c-series-rack-servers/products-installation-guides-list.html.
● Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server At-a-Glance: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/servers-unified-computing/ucs-c-series-rack-servers/ucs-c885a-m8-aag.html.
Cisco Nexus switches
● Cisco Nexus 9332D-GX2B and Nexus 9364D-GX2A Switch Data Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/site/us/en/products/collateral/networking/switches/nexus-9000-series-switches/nexus-9300-gx2-series-fixed-switches-data-sheet.html#tabs-35d568e0ff-item-4bd7dc8124-tab.
● Cisco Nexus 9364E-SG2 Switch Data Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/nexus-9000-series-switches/nexus-9364e-sg2-switch-ds.html.
● Cisco Nexus Dashboard 4.1: Data Center Management for the AI Era - Cisco Blogs: https://blogs.cisco.com/datacenter/announcing-the-new-nexus-dashboard-for-simplifying-data-center-operations-in-the-ai-era.
● Cisco Nexus Dashboard 4.1.1 Release notes: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/dcn/nd/4x/release-notes/cisco-nexus-dashboard-release-notes-411.html.
● Cisco Nexus Dashboard Data Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/data-center-analytics/nexus-dashboard/datasheet-c78-744371.html.
● Cisco Data Center Networking (DCN) Licensing Ordering Guide: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/data-center-analytics/nexus-dashboard/guide-c07-744361.html.
Cisco UCS management servers and software
● Cisco UCS X-Series Direct At-a-Glance: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/servers-unified-computing/ucs-x-series-modular-system/ucs-x-series-direct-aag.html.
● Cisco UCS X-Series Direct Data Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/servers-unified-computing/ucs-x-series-modular-system/ucs-x-series-direct-ds.html.
● Cisco Intersight Data Sheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/cloud-systems-management/intersight/intersight-ds.html.
● Intersight At-a-Glance: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/cloud-systems-management/intersight/at-a-glance-c45-739419.html.
NVIDIA Enterprise Reference Architectures
For more information on NVIDIA’s Enterprise RA designs, refer to the following documents. (Please note that links are not available to these documents; they require access to NVIDIA’s portal.)
● ERA-00003-001_v04 - NVIDIA HGX H100+H200+B200 8-GPU and NVIDIA Spectrum Platforms - 28th February 2025.
● ERA-00010-001_v01 - Network Deployment Guide NVIDIA SpectrumX Platforms - 4th July 2025.