AI Performance: MLPerf Training on
Cisco UCS C885A M8 HGX Platform with NVIDIA GPUs White Paper
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
With generative AI poised to significantly boost global economic output, Cisco is helping to simplify the challenges of preparing organizations’ infrastructure for AI implementation. The exponential growth of AI is transforming data-center requirements, driving demand for scalable, accelerated computing infrastructure.
To this end, Cisco recently introduced the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server, a high-density GPU server designed for demanding AI workloads, offering powerful performance for model training, deep learning, and inference. Built on the NVIDIA HGX platform, it can scale out to deliver clusters of computing power that will bring your most ambitious AI projects to life. Each server includes NVIDIA Network Interface Cards (NICs) or SuperNICs to accelerate AI networking performance, as well as NVIDIA BlueField-3 Data Processing Units (DPUs) to accelerate GPU access to data and enable robust, zero-trust security. The new Cisco UCS C885A M8 is Cisco’s first entry into its dedicated AI server portfolio and its first eight-way accelerated computing system built on the NVIDIA HGX platform.
To help demonstrate the AI performance capacity of the new Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server, MLPerf benchmarking performance testing for Training 5.1 was conducted by Cisco, using NVIDIA H200 GPUs, as detailed later in this document.
Accelerated compute
A typical AI journey starts with training GenAI models with large amounts of data to build the model intelligence. For this important stage, the new Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server is a powerhouse designed to tackle the most demanding AI training tasks. With its high-density configuration of NVIDIA H200 Tensor Core GPUs, coupled with the efficiency of NVIDIA HGX architecture, the UCS C885A M8 provides the raw computational power necessary for handling massive data sets and complex algorithms. Moreover, its simplified deployment and streamlined management make it easier than ever for enterprise customers to embrace AI.

Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server
Scalable network fabric for AI connectivity
To train GenAI models, clusters of these powerful servers often work in unison, generating an immense flow of data that necessitates a network fabric capable of handling high bandwidth with minimal latency. This is where the newly released Cisco Nexus® 9364E-SG2 switch shines. Its high-density 800G aggregation ensures smooth data flow between servers, while advanced congestion management and large buffer sizes minimize packet drops— keeping latency low and training performance high. The Nexus 9364E-SG2 serves as a cornerstone for a highly scalable network infrastructure, allowing AI clusters to expand seamlessly as organizational needs grow.

Cisco Nexus 9364E-SG2 switch for AI connectivity
Purchasing simplicity
Once these powerful models are trained, you need infrastructure deployed for inferencing to provide actual value, often across a distributed landscape of data centers and edge locations. We have greatly simplified this process with new Cisco® AI PODs that accelerate deployment of the entire AI infrastructure stack itself. No matter where you fall on the spectrum of use cases mentioned at the beginning of this white paper, AI PODs are designed to offer a plug-and-play experience with NVIDIA accelerated computing. The pre-sized and pre-validated bundles of infrastructure eliminate the guesswork from deploying edge inferencing, large-scale clusters, and other AI inferencing solutions, with more use cases planned for release over the next few months.
Our goal is to enable customers to confidently deploy AI PODs with predictability around performance, scalability, cost, and outcomes, while shortening time to production-ready inferencing with a full stack of infrastructure, software, and AI toolsets. AI PODs include NVIDIA AI Enterprise, an end-to-end, cloud-native software platform that accelerates data science pipelines and streamlines AI development and deployment. Managed through Cisco Intersight®, AI PODs provide centralized control and automation, simplifying everything from configuration to day-to-day operations, with more use cases to come.
AI-cluster network design
An AI cluster typically has multiple networks—an inter-GPU backend network, a frontend network, a storage network, and an Out-of-Band (OOB) management network.
Figure 3 shows an overview of these networks. Users (in the corporate network in the figure) and applications (in the data-center network) reach the GPU nodes through the frontend network. The GPU nodes access the storage nodes through a storage network, which, in Figure 3, has been converged with the frontend network. A separate OOB management network provides access to the management and console ports on switches, the BMC ports on the servers, and the Power Distribution Units (PDUs). A dedicated inter-GPU backend network connects the GPUs in different nodes for transporting Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) traffic while running a distributed job.
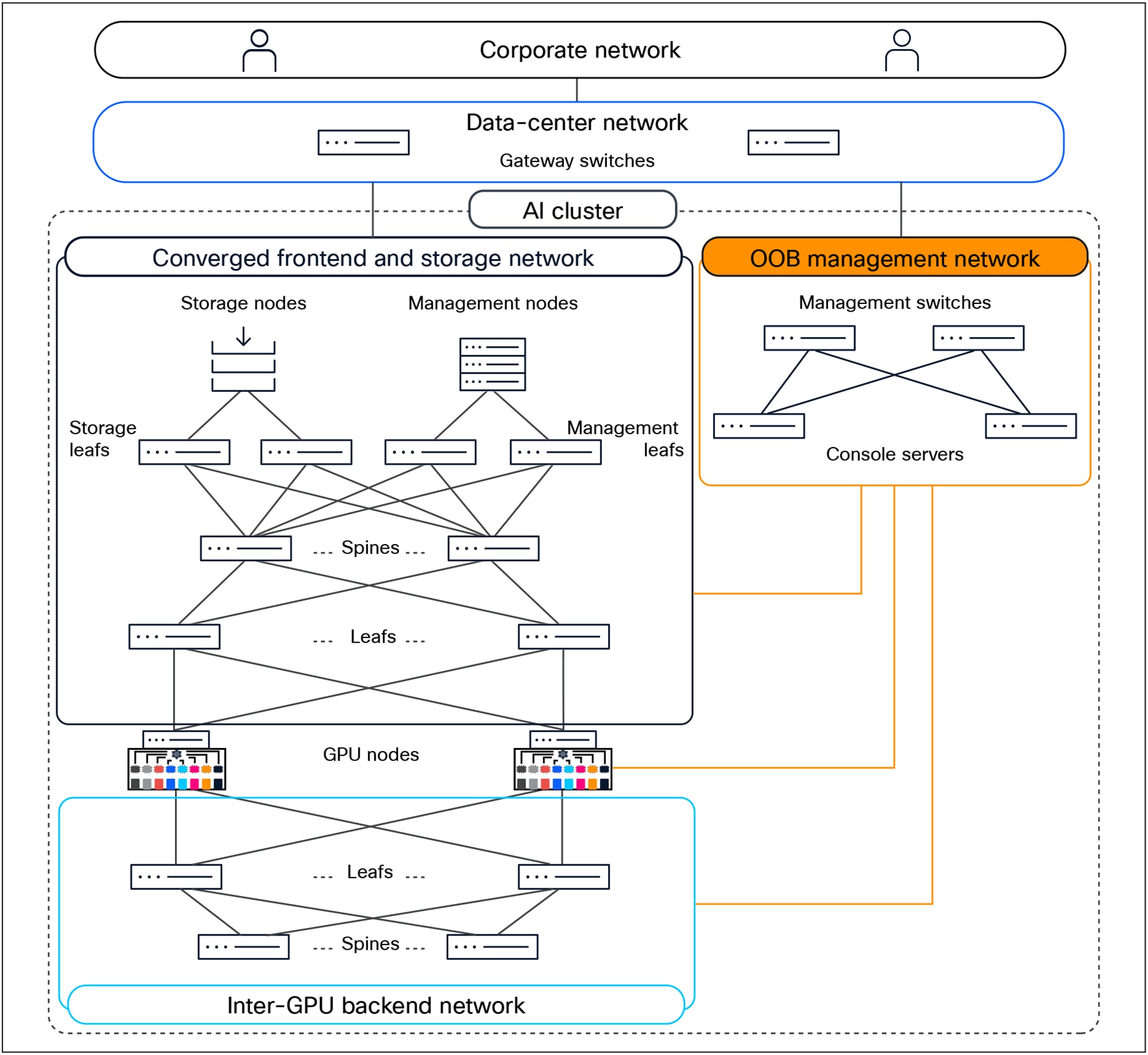
AI-cluster network design
Rail-optimized network design
GPUs in a scalable unit are interconnected using rail-optimized design to improve collective communication performance by allowing single-hop forwarding through the leaf switches, without the traffic going to the spine switches. In rail-optimized design, port 1 on all the GPU nodes connects to the first leaf switch, port 2 connects to the second leaf switch, and so on.
The acceleration of AI is fundamentally changing our world and creating new growth drivers for organizations, such as improving productivity and business efficiency while achieving sustainability goals. Scaling infrastructure for AI workloads is more important than ever to realize the benefits of these new AI initiatives. IT departments are being asked to step in and modernize their data-center infrastructure to accommodate these new demanding workloads.
AI projects go through different phases: training your model, fine tuning it, and then deploying the model to end users. Each phase has different infrastructure requirements. Training is the most compute-intensive phase, and Large Language Models (LLMs), deep learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and digital twins require significant accelerated compute.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/dcn/whitepapers/cisco-addressing-ai-ml-network-challenges.html
The acceleration of AI is fundamentally changing our world and creating new growth drivers for organizations, such as improving productivity and business efficiency while achieving sustainability goals. Scaling infrastructure for AI workloads is more important than ever to realize the benefits of these new AI initiatives. IT departments are being asked to step in and modernize their data-center infrastructure to accommodate these new demanding workloads.
AI projects go through different phases: training your model, fine tuning it, and then deploying the model to end users. Each phase has different infrastructure requirements. Training is the most compute-intensive phase, and Large Language Model (LLM), deep learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and digital twins require significantly accelerated compute.
AI-ready
Built on NVIDIA HGX architecture, and with eight high-performance GPUs, the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server delivers the accelerated compute power needed for the most demanding AI workloads.
Scalable
Scale your AI workloads across a cluster of Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Servers to address deep learning, large Language Model Training (LLM), model fine tuning, large model inferencing, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
Consistent management
Avoid silos of AI infrastructure by managing your AI servers with the same tool as your regular workloads.
For the MLPerf Training performance testing, performance was evaluated using 8x NVIDIA H200 GPUs on single-node and 16x NVIDIA H200 GPUs with two-node configurations on the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server. This is the standard configuration on the UCS C885A M8 server, and MLPerf Training benchmark results are collected for various datasets. This data will help in understanding the performance benefits of the UCS C885A M8 server for Training workloads. Performance data for selected datasets is highlighted in this white paper, along with a brief explanation of the performance on the C885A M8 rack server
● Built on the NVIDIA HGX platform, the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server offers a choice of 8 NVIDIA HGX H200 Tensor Core GPUs to deliver massive, accelerated computational performance in a single server, as well as one NVIDIA ConnectX-7 NIC or NVIDIA BlueField-3 SuperNIC per GPU to scale AI model training across a cluster of dense GPU servers.
● The server is managed by Cisco Intersight, which can help reduce your Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and increase your business agility.
Note: Initially, the local server management interface will handle configuration and management, while Cisco Intersight will provide inventory capabilities through an integrated Intersight Device Connector. Full management operations and configurations through Cisco Intersight will be introduced in future.
● The server is offered in fixed configurations that are optimized for intensive AI and HPC workloads.
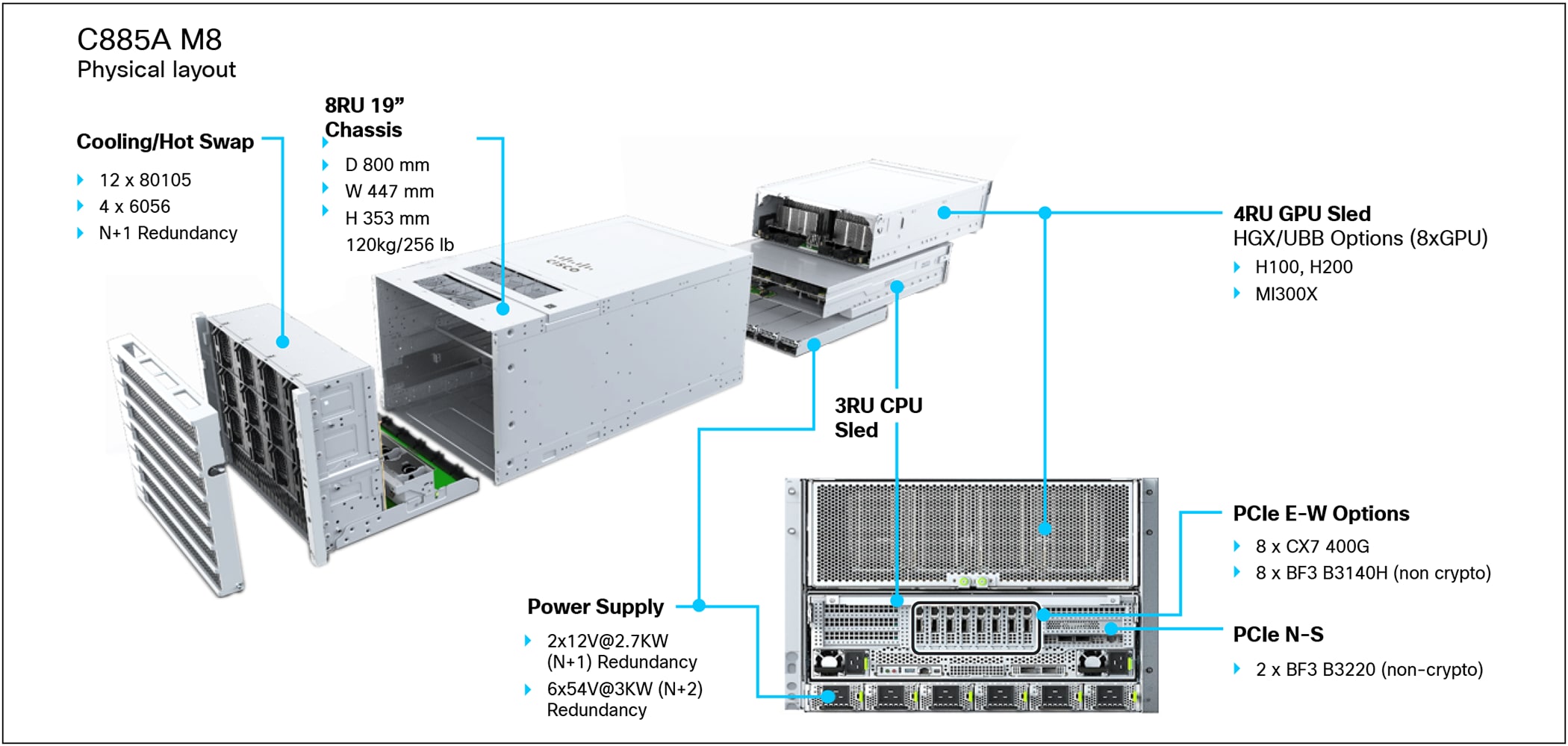
Detailed view of server
A specifications sheet for the UCA C885A M8 is available at: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/servers-unified-computing/ucs-c-series-rack-servers/ucs-c885a-m8-ds.html
MLPerf is a benchmark suite that evaluates the performance of machine-learning software, hardware, and services. The benchmarks are developed by MLCommons, a consortium of AI leaders from academia, research labs, and industry. The goal of MLPerf is to provide an objective yardstick for evaluating machine learning platforms and frameworks.
MLPerf has multiple benchmarks, including:
● MLPerf Training: measures the time it takes to train machine learning models to a target level of accuracy
● MLPerf Inference: Datacenter: measures how quickly a trained neural network can perform inference tasks on new data
The MLPerf Training benchmark suite measures how fast systems can train models to a target quality metric. Current and previous results can be reviewed through the results dashboard below.
The MLPerf Training Benchmark paper provides a detailed description of the motivation and guiding principles behind the MLPerf Training benchmark suite.
MLPerf Training: Test configuration
For the MLPerf Training performance testing covered in this document, the following Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server configuration was used:
● 8x NVIDIA H200 SXM GPUs on single-server node
● 16x NVIDIA H200 SXM GPUs on two-server nodes
MLPerf Training performance results
MLPerf Training benchmarks
The MLPerf Inference models listed in Table 1 were configured on the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server and tested for performance.
Table 1. MLPerf Training models
| Model |
Reference implementation model |
Description |
| retinanet 800x800 |
Single-stage object detection model optimized for detecting small objects in high-resolution images |
|
| llama2-70b |
Large language model with 70 billion parameters. It is designed for Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks and question answering. |
|
| rgat |
Graph-based neural network model that uses attention mechanisms to learn from relational data |
MLPerf Training 5.1 performance data
As part of the MLPerf Training 5.1 submission, Cisco has tested most of the datasets mentioned in Table 1 on the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server and submitted the results to MLCommons with NVIDIA H200 GPUs. The results are published on the MLCommons results page: https://mlcommons.org/benchmarks/inference-datacenter/
Cisco has also published performance data for MLPerf Training 5.1 with multi-node configurations. Two Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack servers were configured with 16x NVIDIA H200 GPUs. Performance data with two nodes is provided in Figures 5—7 below.
The below figure includes unverified MLPerf Training 5.1 results collected after the MLPerf submission deadline. For such data, there is a note added “Result not verified by MLCommons Association.”
Llama2_70b_lora
Llama2_70b_lora is a large language model from Meta, with 70 billion parameters. It is designed for various natural language processing tasks such as text generation, summarization, translation, and question answering.
Figure 5 shows the MLPerf 5.1 Training performance of the Llama2_70b_lora model tested on a Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server with 8x NVIDIA H200 GPUs.
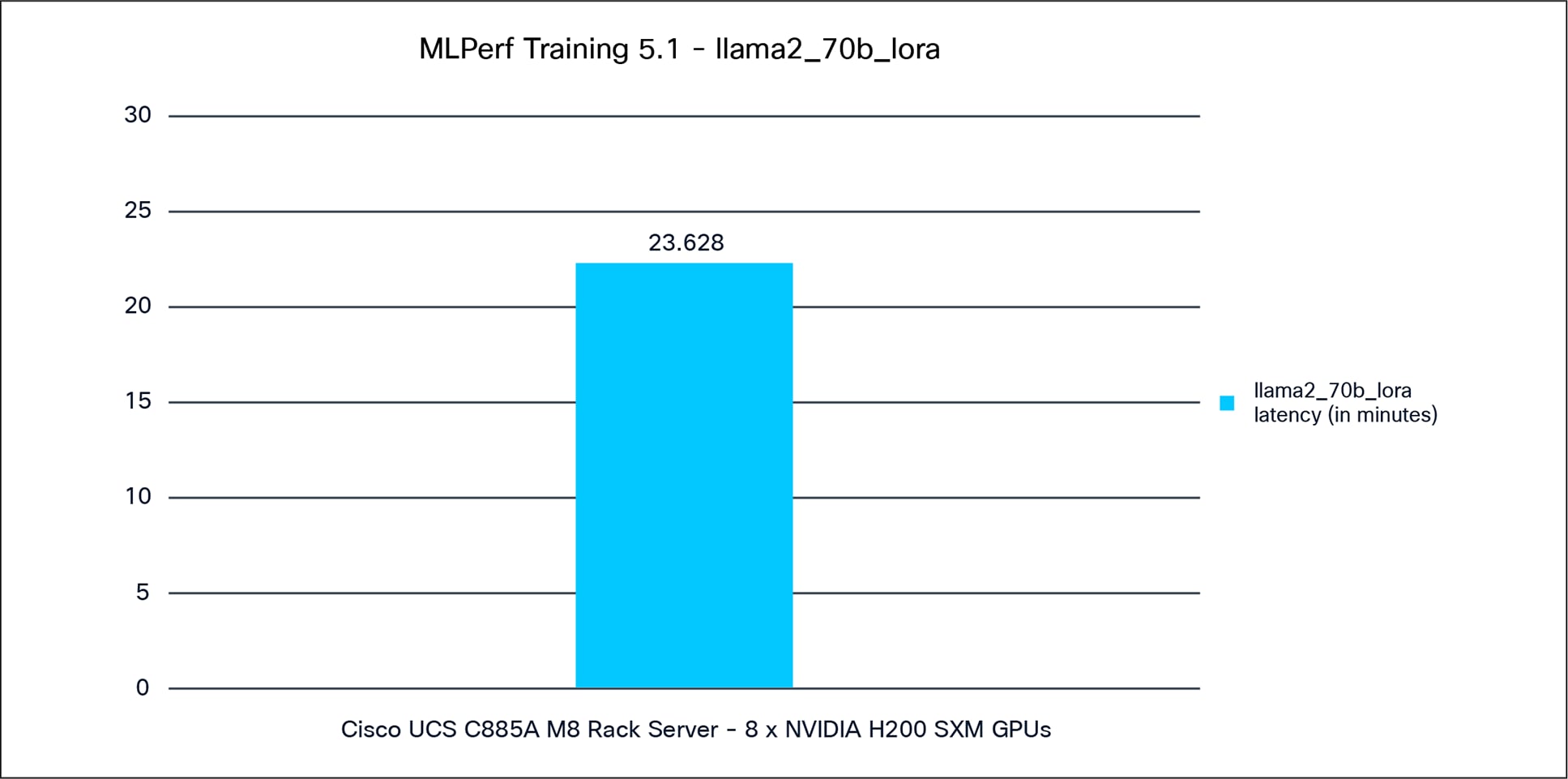
Llama2_70b_lora performance data on a Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server with 8 x NVIDIA H200 GPUs
Retinanet
Retinanet is a single-stage object-detection model known for its focus on addressing class imbalances using a novel focal-loss function. The “800x800” refers to the input image size, and the model is optimized for detecting small objects in high-resolution images.
Figure 6 shows the MLPerf Training 5.1 performance of the Retinanet model tested on Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server with 8x NVIDIA H200 GPUs.
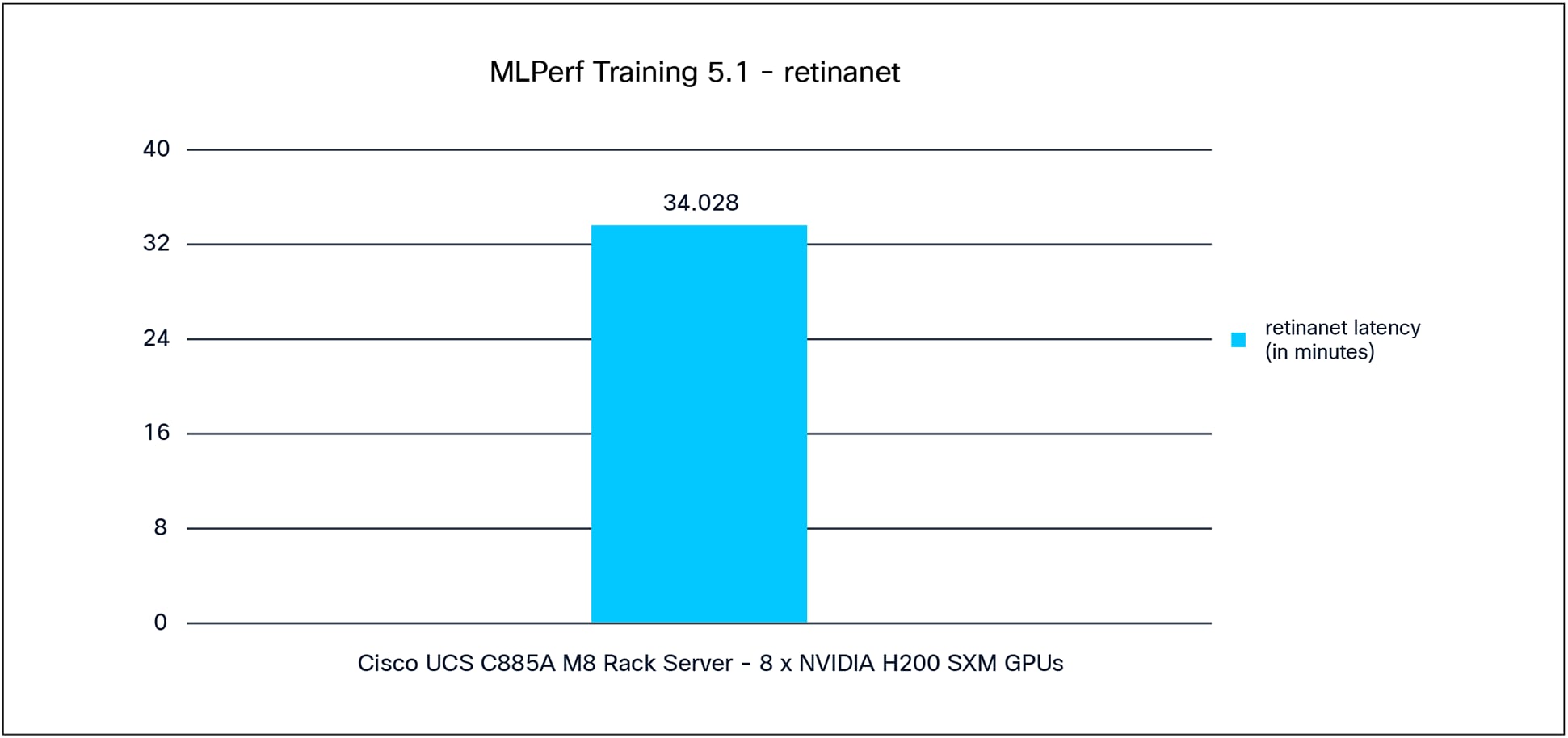
Retinanet performance data on a Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server with 8 x NVIDIA H200 GPUs.
RGAT
Relational Graph Attention Network (RGAT) is a graph-based neural-network model that uses attention mechanisms to learn from relational data. It is used for tasks such as graph classification, link prediction, and node classification, where the relationships between entities are key.
Figure 7 shows the MLPerf Training 5.1 performance of the RGAT model tested on a Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server with 8x NVIDIA H200 GPUs.
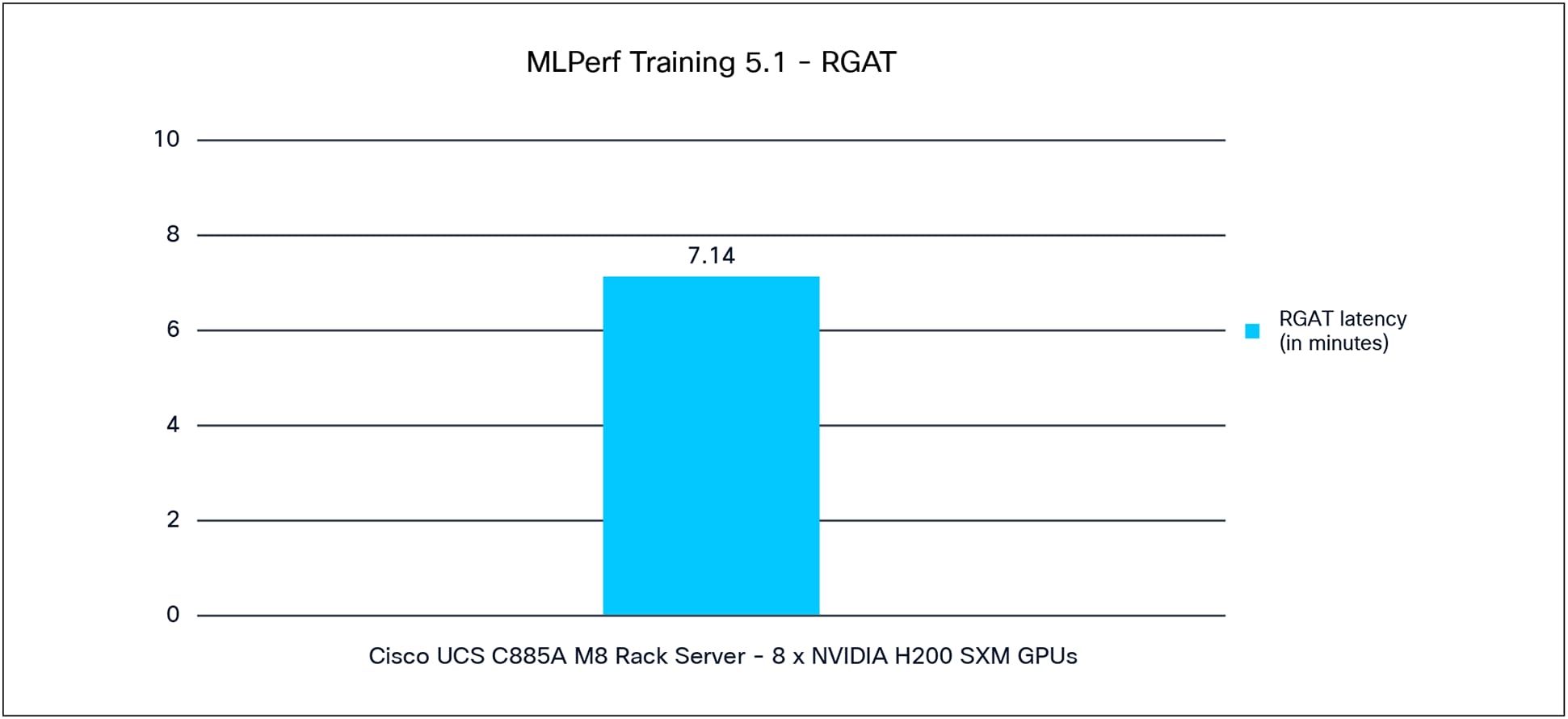
RGAT performance data on a Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server with 8 x NVIDIA H200 GPUs
Note: For RGAT performance data, the results have not been verified by MLCommons Association because the results were collected after the MLPerf submission deadline.
MLPerf Training 5.1 multi-node performance data
MLPerf Training multi-node testing evaluates how efficiently systems can train machine learning models across multiple interconnected computing nodes. This benchmarking suite, developed by MLCommons, aims to provide standardized metrics for comparing the performance of various hardware, software, and services in the context of distributed machine learning.
The benchmarks are continuously evolving to include new and emerging AI workloads, such as Generative AI (GenAI) and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). MLPerf results highlight the importance of dedicated low-latency interconnects between GPUs in multi-GPU systems for optimal distributed deep-learning training. Training models on multiple nodes introduces complexities, primarily due to communication overhead between nodes. To achieve efficient scaling, several technologies and optimizations are employed, such as RDMA (remote direct memory access), that are crucial for optimizing cross-node GPU-to-GPU communication and distributing training jobs efficiently. Distributed training frameworks and libraries such as NCCL (NVIDIA Collective Communications Library) are commonly used for distributed training and efficient communication across GPUs and nodes.
Llama2_70b_lora
Llama2_70b_lora is a large language model from Meta, with 70 billion parameters. It is designed for various natural language processing tasks such as text generation, summarization, translation, and question answering.
Figure 8 shows the single-node and multi-node configuration for MLPerf 5.1 Training performance of the Llama2_70b_lora model tested on a Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server with 8x and 16x NVIDIA H200 GPUs.
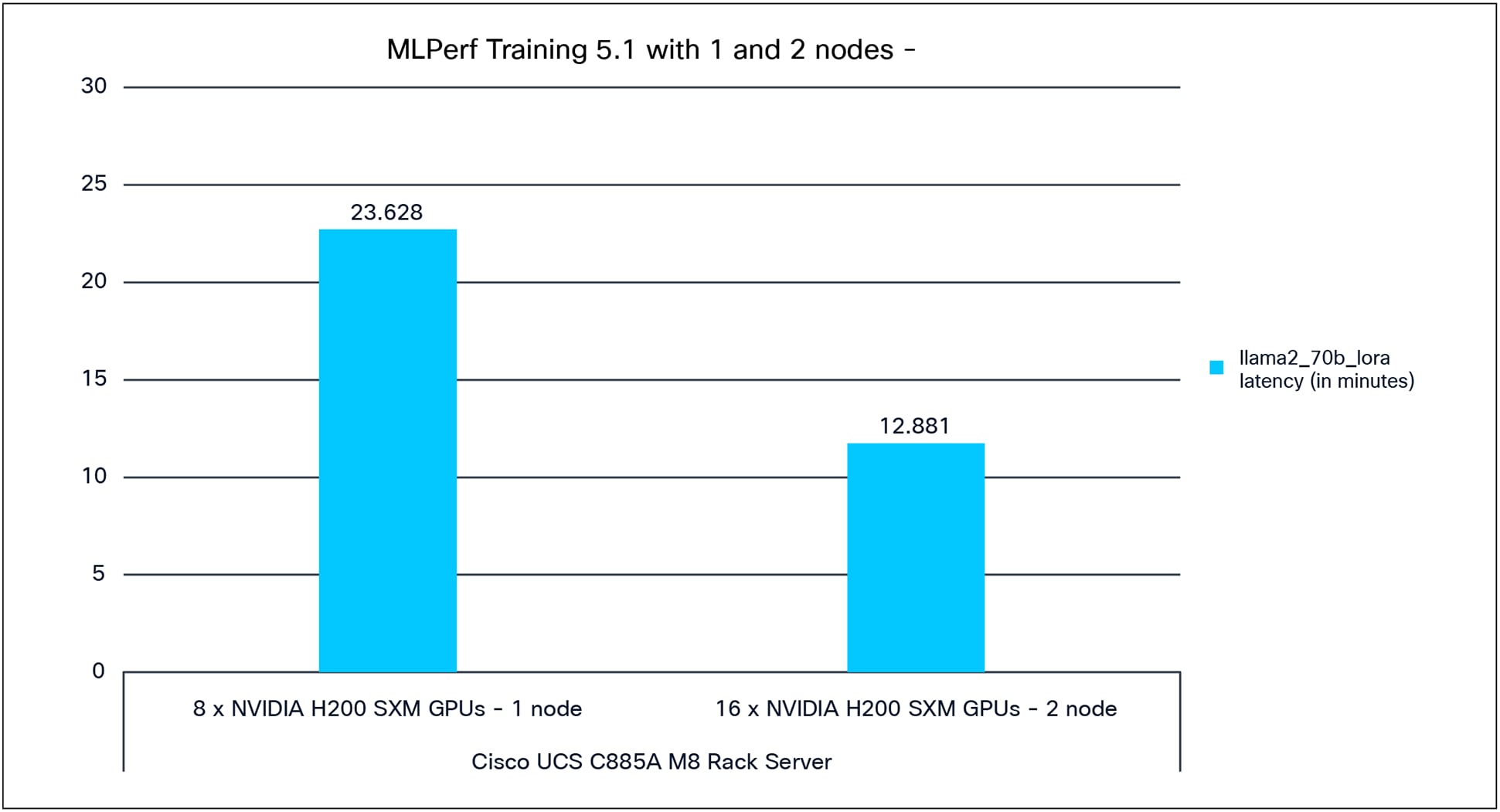
Multi node Llama2_70b_lora performance data on a Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack server with 8x and 16x NVIDIA H200 GPUs
Performance summary
Built on the NVIDIA HGX platform, the Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server delivers the accelerated compute needed to address the most demanding AI workloads. With its powerful performance and simplified deployment, it helps you achieve faster results from your AI initiatives.
Cisco successfully submitted MLPerf Training results in partnership with NVIDIA to enhance performance and efficiency, optimizing various inference workloads such as large language model (language), natural language processing (language), image classification (vision), object detection (vision), and graph classification (graph-based).
The results were exceptional AI performance across the Cisco UCS platforms for MLPerf Inference:
● The Cisco UCS C885A M8 platform with 8x NVIDIA H200 SXM GPUs emerged as the leader, with good performance for Retinanet and Llama2_70b_lora models for MLPerf Training v5.1 benchmark.
Table 2 lists the details of the server under test-environment conditions.
Table 2. Server properties
| Name |
Value |
| Product names |
Cisco UCS C885A M8 Rack Server |
| CPUs |
CPU: 2 x AMD EPYC 9575 64-core processor |
| Number of cores |
64 |
| Number of threads |
128 |
| Total memory |
2.3 TB |
| Memory DIMMs (16) |
96 GB x 24 DIMMs |
| Memory speed |
6400 MHz |
| Network adapter |
● 8x NVIDIA B3140H BlueField-3 E-series SuperNIC 400GbE/NDR
● 2x NVIDIA B3220 BlueField-3 P-Series 200GbE/NDR
|
| GPU controllers |
● NVIDIA HGX H200 8-GPU
|
| SFF NVMe SSDs |
● 16 x 1.9 TB 2.5-inch-high performance high endurance NVMe SSD
|
Note: For the server’s BIOS settings, the system default values were applied.
Table 3 lists the server BIOS settings applied for MLPerf testing.
Table 3. Server BIOS settings
| Name |
Value |
| SMT control |
Auto |
| NUMA nodes per socket |
NPS4 |
| IOMMU |
Enabled |
| Core performance boost |
Auto |
| Determinism enabled |
Power |
| APBDIS |
1 |
| Global C-state control |
Disabled |
| DF C-states |
Auto |
| Power profile selection |
High-performance mode |
Note: The rest of the BIOS settings are platform default values.
For additional information on the server, refer to: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/servers-unified-computing/ucs-c-series-rack-servers/ucs-c885a-m8-aag.html
Cisco AI-Ready Data Center Infrastructure: https://blogs.cisco.com/datacenter/power-your-genai-ambitions-with-new-cisco-ai-ready-data-center-infrastructure