-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Configuration Guide, Release 2.x
-
New and Changed Information
-
Index
-
Preface
- Part 1 - Getting Started
- Part 2 - Cisco MDS SAN-OS Installation and Switch Management
- Part 3 - Switch Configuration
-
Part 4 - Fabric Configuration
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
Creating Dynamic VSANs
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Configuring Zones
-
Distributing Device Alias Services
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Configuring FICON
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
- Part 5 - Security
- Part 6 - IP Services
- Part 7 - Intelligent Storage Services
- Part 8 - Network and Switch Monitoring
- Part 9 - Traffic Management
- Part 10 - Troubleshooting
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring SCSI Flow Services and Statistics
SCSI Flow Configuration Client
Configuring SCSI Flow Services
Enabling SCSI Flow Configuration Distribution
Configuring SCSI Flow Identifiers
Displaying SCSI Flow Services Information
Configuring SCSI Flow Services and Statistics
Storage Services Module (SSM) supports in SCSI flow services and SCSI flow statistics in Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.0(2b) and later.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Configuring SCSI Flow Services
•
Enabling SCSI Flow Statistics
•
Displaying SCSI Flow Services Information
About SCSI Flow Services
A SCSI initiator/target combination is a SCSI flow. SCSI flow services provide enhanced features for SCSI flows, such as write acceleration and flow monitoring for statistics gathering on an SSM.
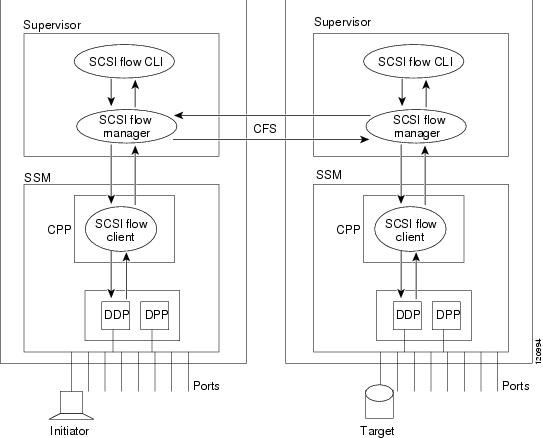
Functionally, the SCSI Flow Services functional architecture consists of the following components:
•
SCSI flow manager (SFM) on the supervisor
•
SCSI flow configuration CLI on the supervisor
•
SCSI flow configuration client on the Control Path Processor (CPP) of an SSM
•
SCSI flow feature set support on the Data Path Processor (DPP) of an SSM
Figure 38-1 shows an example of the SCSI Flow Services functional architecture.
Figure 38-1 SCSI Flow Services Functional Architecture
Note
The SCSI target and initiator must be connected to different SSMs on different switches.
Note
For statistics monitoring, the target device is not required to be connected to an SSM.
SCSI Flow Manager
The SCSI flow manager (SFM) resides on a supervisor module and handles the configuration of SCSI flows, validating them and relaying configuration information to the appropriate SSM. It also handles any dynamic changes to the status of the SCSI flow due to external events. The SFM registers events resulting from operations, such as port up or down, VSAN suspension, and zoning that affects the SCSI flow status, and updates the flow status and configuration accordingly.
The SFM on the initiator communicates to its peer on the target side using Cisco Fabric Services (CFS). Peer communication allows the initiator SFM to validate target parameters and program information on the target side.
SCSI Flow Configuration Client
A SCSI flow configuration client (SFCC) resides on the CPP of the SSM. It receives flow configuration requests from the SFM, programs the DPP corresponding to the initiator and target port interfaces, and responds to the SFM with the status of the configuration request.
SCSI Flow Data Path Support
The DPP on the SSM examines all the messages between the initiator and target and provides SCSI flow features such as Fibre Channel write acceleration and statistics monitoring.
Configuring SCSI Flow Services
A SCSI flow specification consists of the following attributes:
•
SCSI flow identifier
•
VSAN identifier
•
SCSI initiator port WWN
•
SCSI target port WWN
•
Flow feature set consisting of Fibre Channel write acceleration and statistics monitoring.
The SCSI flow specification is a distributed configuration because the SCSI initiator and the target might be physically connected to SSMs on two different switches located across the fabric. The configuration does not require information to identify either the switch name or the SSM slot location for either the initiator or the target. The manual SCSI flow configuration is performed only at the initiator side. This simplifies the configuration process. The initiator switch sends the configuration to the SFM on the target switch using CFS. No SCSI flow configuration is necessary on the target switch.
Enabling SCSI Flow Services
In Cisco MDS SAN-OS Releases 2.0(1b) through 2.1(1a), you can only enable SCSI flow services on the entire SSM. As of Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.1(2), you can enable SCSI flow services either on the entire SSM or on groups of four interfaces.
Enabling SCSI flow services on interfaces has the following restrictions:
•
The fewest number of interfaces which you can enable is four. You can specify fc1 through fc4 but not fc1 through fc2.
•
The first interface in the group must be 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, or 29. You can specify fc5 through fc8 but not fc7 through fc10.
•
The groups of four interfaces do not need to be consecutive. You can specify fc1 through fc8 and fc17 through fc20.
Note
Fibre Channel write acceleration can only be provisioned on the entire SSM, not a group of interfaces on the SSM.
To enable SCSI Flow Services, follow these steps:
Enabling SCSI Flow Configuration Distribution
To enable SCSI flow configuration distribution using CFS, follow these steps:
Configuring SCSI Flow Identifiers
A SCSI flow identifier is unique on a switch and is chosen by the user, like VSAN identifiers. To configure a SCSI flow identifier, follow these steps:
About SCSI Flow Statistics
The statistics that can be collected for SCSI flows include the following:
•
SCSI reads
–
Number of I/O s
–
Number of I/O blocks
–
Maximum I/O blocks
–
Minimum I/O response time
–
Maximum I/O response time
•
SCSI writes
–
Number of I/Os
–
Number of I/O blocks
–
Maximum I/O blocks
–
Minimum I/O response time
–
Maximum I/O response time
•
Other SCSI commands (not read or write)
–
Test unit ready
–
Report LUN
–
Inquiry
–
Read capacity
–
Mode sense
–
Request sense
•
Errors
–
Number of timeouts
–
Number of I/O failures
–
Number of various SCSI status events
–
Number of various SCSI sense key errors or events
To take advantage of this feature, only the initiator must be directly attached to an SSM.
Note
The SCSI flow statistics feature requires the Enterprise Package license installed only on the initiator switches.
Note
For SCSI flow statistics, the initiator must connect to an SSM on a Cisco MDS switch while the target can connect to any other switch in the fabric. The SCSI flow initiator and target cannot connect to the same switch.
Enabling SCSI Flow Statistics
To enable SCSI flow statistics monitoring, follow these steps:
Clearing SCSI Flow Statistics
Use the clear device-name statistics flow-id command to clear SCSI flow statistics (for debugging purposes):
switch# clear scsi-flow statistics flow-id 3Displaying SCSI Flow Services Information
Use the show scsi-flow command to display information about SCSI Flow Services (see Example 38-1 to Example 38-5).
Example 38-1 Displays Applications Provisioned on an SSM
switch# show ssm provisioningModule Ports Application Provisioning Status-----------------------------------------------------------4 1-32 scsi-flow successExample 38-2 Displays SCSI Flow Services Configuration for All SCSI Flow Identifiers
switch# show scsi-flowFlow Id: 3Initiator VSAN: 101Initiator WWN: 21:00:00:e0:8b:05:76:28Target VSAN: 102Target WWN: 21:00:00:20:37:38:7f:7dTarget LUN: ALL LUNsFlow Verification Status:-------------------------Initiator Verification Status: successTarget Verification Status: successInitiator Linecard Status: successTarget Linecard Status: successFeature Status:---------------Write-Acceleration enabledWrite-Acceleration Buffers: 1024Configuration Status: successStatistics enabledConfiguration Status: successFlow Id: 4Initiator VSAN: 101Initiator WWN: 21:00:00:e0:8b:05:76:28Target VSAN: 102Target WWN: 21:00:00:20:37:38:a7:89Target LUN: ALL LUNsFlow Verification Status:-------------------------Initiator Verification Status: successTarget Verification Status: successInitiator Linecard Status: successTarget Linecard Status: successFeature Status:---------------Write-Acceleration enabledWrite-Acceleration Buffers: 1024Configuration Status: successExample 38-3 Displays SCSI Flow Services Configuration for a Specific SCSI Flow Identifier
switch# show scsi-flow flow-id 3Flow Id: 3Initiator VSAN: 101Initiator WWN: 21:00:00:e0:8b:05:76:28Target VSAN: 102Target WWN: 21:00:00:20:37:38:7f:7dTarget LUN: ALL LUNsFlow Verification Status:-------------------------Initiator Verification Status: successTarget Verification Status: successInitiator Linecard Status: successTarget Linecard Status: successFeature Status:---------------Write-Acceleration enabledWrite-Acceleration Buffers: 1024Configuration Status: successStatistics enabledConfiguration Status: successExample 38-4 Displays SCSI Flow Services Statistics for All SCSI Flow Identifiers
switch# show scsi-flow statisticsStats for flow-id 4 LUN=0x0000------------------------------Read StatsI/O Total count=2I/O Timeout count=0I/O Total block count=4I/O Max block count=2I/O Min response time=5247 usecI/O Max response time=10160 usecI/O Active Count=0Write StatsI/O Total count=199935I/O Timeout count=0I/O Total block count=12795840I/O Max block count=64I/O Min response time=492 usecI/O Max response time=10056529 usecI/O Active Count=16Non Read-Write StatsTest Unit Ready=4Report LUN=38Inquiry=50Read Capacity=3Mode Sense=0Request Sense=0Total StatsRx Frame Count=3792063Rx Frame Byte Count=6549984752Tx Frame Count=3792063Tx Frame Byte Count=6549984752Error StatsSCSI Status Busy=0SCSI Status Reservation Conflict=0SCSI Status Task Set Full=0SCSI Status ACA Active=0Sense Key Not Ready=0Sense Key Medium Error=0Sense Key Hardware Error=0Sense Key Illegal Request=0Sense Key Unit Attention=28Sense Key Data Protect=0Sense Key Blank Check=0Sense Key Copy Aborted=0Sense Key Aborted Command=0Sense Key Volume Overflow=0Sense Key Miscompare=0Example 38-5 Displays SCSI Flow Services Statistics for a Specific SCSI Flow Identifier
switch# show scsi-flow statistics flow-id 4Stats for flow-id 4 LUN=0x0000------------------------------Read StatsI/O Total count=2I/O Timeout count=0I/O Total block count=4I/O Max block count=2I/O Min response time=5247 usecI/O Max response time=10160 usecI/O Active Count=0Write StatsI/O Total count=199935I/O Timeout count=0I/O Total block count=12795840I/O Max block count=64I/O Min response time=492 usecI/O Max response time=10056529 usecI/O Active Count=16Non Read-Write StatsTest Unit Ready=4Report LUN=38Inquiry=50Read Capacity=3Mode Sense=0Request Sense=0Total StatsRx Frame Count=3792063Rx Frame Byte Count=6549984752Tx Frame Count=3792063Tx Frame Byte Count=6549984752Error StatsSCSI Status Busy=0SCSI Status Reservation Conflict=0SCSI Status Task Set Full=0SCSI Status ACA Active=0Sense Key Not Ready=0Sense Key Medium Error=0Sense Key Hardware Error=0Sense Key Illegal Request=0Sense Key Unit Attention=28Sense Key Data Protect=0Sense Key Blank Check=0Sense Key Copy Aborted=0Sense Key Aborted Command=0Sense Key Volume Overflow=0Sense Key Miscompare=0Default Settings
Table 38-1 lists the default settings for Intelligent Storage Services parameters.
Table 38-1 Default Intelligent Storage Services Parameters
SCSI flow services
Disabled
SCSI flow services distribution
Enabled
SCSI flow statistics
Disabled

 Feedback
Feedback