Multicast Layer 2 EVPN Type 6 routes
A multicast Layer 2 EVPN Type-6 route is a BGP route type that:
-
enables selective multicast traffic forwarding over a VXLAN fabric,
-
advertises interest in specific multicast groups from VTEPs using SMET routes, and
-
optimizes bandwidth by only replicating multicast traffic to VTEPs with interested receivers.
In data center topologies, many hosts can be attached to a VLAN or subnet, possibly spanning multiple PODs. In VXLAN-based data centers, VXLAN Tunnel Endpoints (VTEPs) are devices connected to the fabric that create VXLAN tunnels to send Layer 2 traffic between VLAN segments.
Sources located on a VTEP can send IP multicast (S,G) traffic toward receivers by encapsulating packets in VXLAN on the source VTEP and flooding to all remote VTEPs. Receiving VTEPs decapsulate and forward to interested receivers. However, indiscriminate flooding wastes bandwidth if no receivers are interested.
-
Type 6 EVPN Selective Multicast (SMET) Routes provide a solution to efficiently send IP multicast traffic between sources and receivers over the VXLAN fabric.
-
Hosts attached to VTEPs express interest in multicast groups by sending membership reports on a VLAN; the VTEP snoops the IGMP reports and advertises a Type 6 EVPN SMET route to other remote VTEPs through BGP, enabling all VTEPs attached to the fabric to learn about receivers interested in specified multicast groups.
-
VTEPs (leaf nodes) will only send IP multicast (S,G) traffic originated from locally connected sources over the VXLAN fabric if there is at least one receiver on a remote VTEP that is interested in the traffic, thereby optimizing the use of the fabric by not sending multicast traffic if there are no interested receivers.
-
If ingress-replication is used in the underlay, the traffic can be further optimized by only sending multicast traffic to those VTEPs that have attached receivers.
 Note |
Cisco NX-OS does not currently support selective multicast delivery over a unicast underlay. |
RFC 9251 describes the procedures and NLRI formats for Type 6 EVPN SMET routes.
Functionality of Multicast Layer 2 EVPN Type-6 routes
Layer 2 EVPN Route Type-6 (SMET) routes for IPv4 (IGMP) routes have been supported in NX-OS as L2TRM**.
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 10.5(3)F, the Multicast Layer 2 EVPN Route Type-6 will support the following functionality:
-
IPv4 IGMP EVPN Type-6 SMET Routes using L2RIB instead of next-generation multicast VPN (NGMVPN).
-
IPv6 MLD Snooping EVPN Type-6 SMET Routes.
Generating IGMP EVPN routes using L2RIB
Starting from Cisco NX-OS Release 10.5(3)F, added the following capabilities to Type-6 EVPN SMET route functionality.
-
Multicast router or querier behind the EVPN domain, to support (*, *) route advertisement or receipt.
-
Multiversion (IGMPv2/v3/v2+v3) advertisement capability
These capabilities are in compliance with RFC 9251.
Generating MLD Snooping SMET route
Before Cisco NX-OS Release 10.5(3)F, SMET route generation was limited to IPv4 IGMP snooped entries. Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 10.5(3)F, Type-6 SMET route advertisement for MLD snooped routes is supported where L2RIB and BGP will handle IPv4 or IPv6 SMET routes from IGMP/MLD on the transmit side and receive side, filtering and forwarding routes appropriately. Multicast router and multiversion capability (MLDv1/v2/v1+v2) will be supported.
Topology of Multicast Layer 2 EVPN Type-6 routes (Reference)
EVPN Route Type-6 will support vPC, vPC Fabric peering and non-vPC topologies.
Sample topologies and associated control plane flow for these topologies are as mentioned below.
Layer 2 EVPN Network with vPC
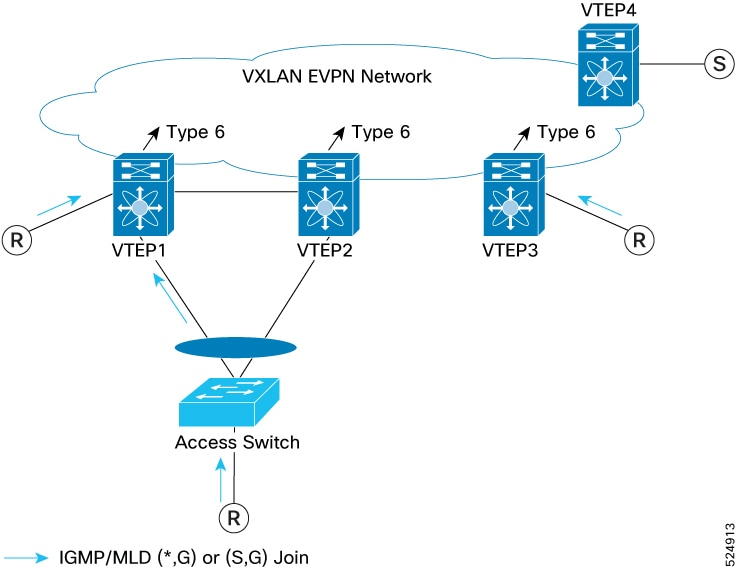
In this example topology, there are 4 VTEPs - a pair of vPC VTEPs (VTEP1 and VTEP2), and two standalone VTEPs (VTEP3 and VTEP4). Receivers (R) are attached to
-
an orphan port behind VTEP1,
-
access switch behind VPC complex VTEP1 and VTEP2, and
-
standalone switch VTEP3.
When these receivers send (*, G) and/or (S,G) IGMP / MLD membership reports that are received by the VTEP1, VTEP2 and VTEP3, each VTEP with attached receiver originates a Type-6 EVPN SMET route type, which is received by all VTEPs, including VTEP4 to which the source is attached.
When the source ‘S’ behind VTEP4 sends multicast (S,G) traffic, the traffic is encapsulated in VXLAN by VTEP4 and sent over the fabric toward receivers; receiving VTEPs VTEP1, VTEP2 and VTEP3 decapsulate the VXLAN packet and forward toward local networks, as shown in the attached figure Note that VTEP4 will only forward multicast traffic if it receives at least one EVPN Type-6 EVPN SMET route from other VTEPs in the fabric.
Layer 2 EVPN Network with vPC and External Querier
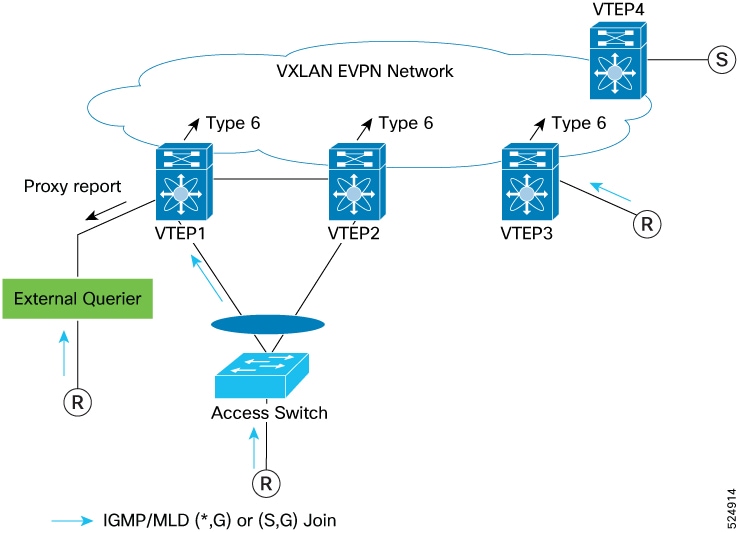
In this example topology, there is an external querier attached to the orphan port, and an election is done between the VTEP1 and External Querier to determine the Querier for the network. For the case where the external querier wins the election, VTEP1 views the external querier as attached to an ‘mrouter’ port; VTEP1 advertises a (*,*) route toward the EVPN network. Any multicast traffic received from source ‘S’ is forwarded toward the external querier. Furthermore, reports received from VTEP3 over SMET are sent as a proxy report toward the querier. There are variants of the ‘external querier’ topology, where the querier is attached to a standalone node, or attached to the vPC complex, and the case where the VTEP wins the Querier election. These variants are supported, though the specific IGMP / MLD report and traffic flows depend on the specific querier location or querier election winner.
Layer 2 EVPN Network with vPC and PIM Enabled Router
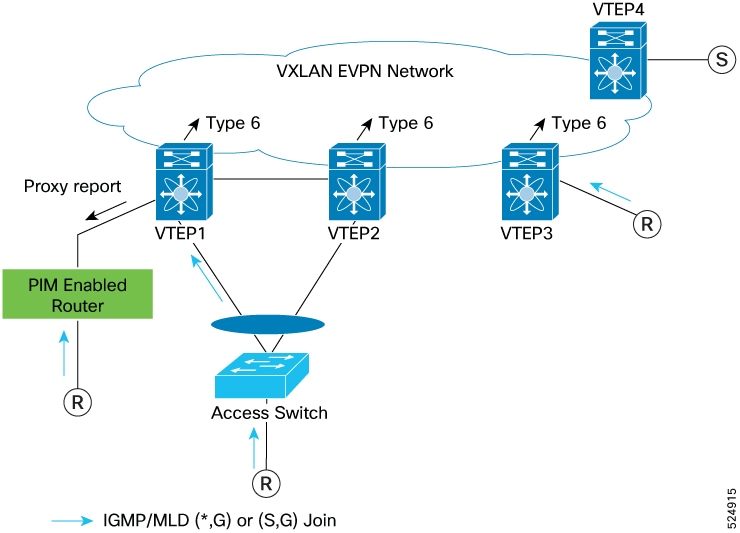
In this example topology, there is a PIM enabled router to the orphan port. In this case, vPC VTEP1 receives PIM hellos from the PIM enabled router, and views the orphan port as a mrouter port; VTEP1 will advertise a (*,*) route toward the EVPN network. Any multicast traffic received from source ‘S’ is forwarded toward the PIM enabled router. Furthermore, reports received from VTEP3 over SMET are sent as a proxy report toward the PIM enabled router. There are variants of the ‘PIM router’ topology, where the PIM enabled router is attached to a standalone node; however, the PIM enabled router attached to the vPC complex access switch is not supported.
 Note |
PIM enabled router attached to vPC complex access switch is not supported. |
 Feedback
Feedback